Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
4
Загружено:
shaimenneАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
4
Загружено:
shaimenneАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Table 2.
2 Summary of Brick Wallet Test (Thapa, 2011)
Average
compressive Average
Experimental Specific Young's Shear
strength shear
Material setup and weight modulus modulus
(MPa) strength
type (kN/m3) (MPa) (MPa)
(MPa)
N/mm2
Mud Compression
17.5 34.5 - 1.09 -
mortar test on cubes
Brick Compression
13.5 - - 9.18 -
unit test on cubes
Compressive
19 - - 0.56 -
Mud test
masonry Combined
19 632 253 - 0.14
brick loading test
wall Diagonal
panel compression 19 336 172 - 0.14
test
2.4 Literature on experimental study on complete masonry buildings
Sathiparan (2016) investigated roof diaphragm effect on unreinforced masonry structure
under dynamic loading. Three one-quarter scale one–storey adobe masonry house models
with different roof conditions had been tested by subjecting them to sine sweep sinusoidal
loading signals (with varying frequency in the range of 2 to 35 Hz and an increasing input
amplitude ranging from 0.05g to 0.8g). The number of cycles was kept constant over the
runs. The key findings of the experiment were to understand roof diaphragm played
important role in failure mode of masonry structures. The incremental loading sequence
did not have any effect on finding on which acceleration level model failed but it helped
to demonstrate damage propagation. The models were loaded in the weak direction, in-
plane for walls with openings and out of plane for side walls.
Magenes, Penna, Senaldi, Rota and Galasco, A. (2015) performed a full scale
unreinforced two storey stone masonry building shaking table test in its original
configuration. The 1979 Montenegro earthquake was taken as input to be applied by the
shaking table and incremental dynamic testing was conducted. The unreinforced building
specimen with very flexible floors underwent the collapse mechanism. After the local
failure, connection between orthogonal walls were improved by installation of perimeter
8
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Axial force, gusset plate details, bolt specs for braced connectionДокумент1 страницаAxial force, gusset plate details, bolt specs for braced connectionshaimenneОценок пока нет
- Mulberry Hotel Building Construction Site: Soil Investigation Works ForДокумент11 страницMulberry Hotel Building Construction Site: Soil Investigation Works ForshaimenneОценок пока нет
- ST-02-DUCTILE DETAIL-02-Model PDFДокумент1 страницаST-02-DUCTILE DETAIL-02-Model PDFshaimenneОценок пока нет
- Grid 2-2 foundation stability and Grid 4-lvl3 strip footing checksДокумент7 страницGrid 2-2 foundation stability and Grid 4-lvl3 strip footing checksshaimenneОценок пока нет
- Nepal Education Dept checklist for design of new school facilitiesДокумент5 страницNepal Education Dept checklist for design of new school facilitiesshaimenneОценок пока нет
- ST-02-DUCTILE DETAIL-02-Model PDFДокумент1 страницаST-02-DUCTILE DETAIL-02-Model PDFshaimenneОценок пока нет
- 2222 PDFДокумент1 страница2222 PDFshaimenneОценок пока нет
- D M t t g Δ d eg st di tn FДокумент6 страницD M t t g Δ d eg st di tn FshaimenneОценок пока нет
- Tested and Derived Component Capacities: 1. Shear WallsДокумент15 страницTested and Derived Component Capacities: 1. Shear WallsshaimenneОценок пока нет
- DCell Architects, Engineers & Planners in NepalДокумент1 страницаDCell Architects, Engineers & Planners in NepalshaimenneОценок пока нет
- Building Type: Min 10 M Table DataДокумент2 страницыBuilding Type: Min 10 M Table DatashaimenneОценок пока нет
- Lumped mass modal analysis RC buildingДокумент17 страницLumped mass modal analysis RC buildingshaimenneОценок пока нет
- ST-14-BEAM DETAIL-2 - 14-Model PDFДокумент1 страницаST-14-BEAM DETAIL-2 - 14-Model PDFshaimenneОценок пока нет
- Bar, Refer The Working DWG Files Previously Sent For 880.5 Slab Detail)Документ2 страницыBar, Refer The Working DWG Files Previously Sent For 880.5 Slab Detail)shaimenneОценок пока нет
- ST-11-COLUMN DETAIL - 11-Model PDFДокумент1 страницаST-11-COLUMN DETAIL - 11-Model PDFshaimenneОценок пока нет
- ST-13-BEAM DETAIL-1 - 13-Model PDFДокумент1 страницаST-13-BEAM DETAIL-1 - 13-Model PDFshaimenneОценок пока нет
- ST-12-880.5 LVL BEAM PLAN AND TIE BEAM PLAN - 12-Model PDFДокумент1 страницаST-12-880.5 LVL BEAM PLAN AND TIE BEAM PLAN - 12-Model PDFshaimenneОценок пока нет
- ST-10-RCC WALL AND COLUMN LAYOUT - 10-Model PDFДокумент1 страницаST-10-RCC WALL AND COLUMN LAYOUT - 10-Model PDFshaimenneОценок пока нет
- Rebar Lapping Details: Typical Beam Profile Curtailment DetailsДокумент1 страницаRebar Lapping Details: Typical Beam Profile Curtailment DetailsshaimenneОценок пока нет
- 12Документ1 страница12shaimenneОценок пока нет
- SelfloveДокумент2 страницыSelfloveshaimenneОценок пока нет
- 4Документ1 страница4shaimenneОценок пока нет
- Pataleban distillery structural analysisДокумент16 страницPataleban distillery structural analysisshaimenneОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 MethodologyДокумент1 страницаChapter 3 MethodologyshaimenneОценок пока нет
- PoemДокумент2 страницыPoemshaimenneОценок пока нет
- ETABS Model-Blockwhole24 - 02 - 2020: Level 877Документ6 страницETABS Model-Blockwhole24 - 02 - 2020: Level 877shaimenneОценок пока нет
- EstimateДокумент24 страницыEstimateshaimenneОценок пока нет
- 6 May Janaki Mat SubmitДокумент1 890 страниц6 May Janaki Mat SubmitshaimenneОценок пока нет
- ETABS model analysis and design checks for building levelsДокумент7 страницETABS model analysis and design checks for building levelsshaimenneОценок пока нет
- ETABS model analysis and design checks for building levelsДокумент7 страницETABS model analysis and design checks for building levelsshaimenneОценок пока нет
- Class: 6 Subject: Chemistry Chapter: Matter Home Work (1) : Tania MondalДокумент2 страницыClass: 6 Subject: Chemistry Chapter: Matter Home Work (1) : Tania MondalSayantan Chakraborty100% (1)
- MOS Endsem Paper 2022 Sem 1Документ4 страницыMOS Endsem Paper 2022 Sem 1Xyz XyzОценок пока нет
- MMK1213 15Документ6 страницMMK1213 15S LubnaОценок пока нет
- Definition of Boyle's Law: What Is An Ideal Gas?Документ4 страницыDefinition of Boyle's Law: What Is An Ideal Gas?حسين كاظم ياسينОценок пока нет
- PRINCIPLES OF SEDIMENTATIONДокумент7 страницPRINCIPLES OF SEDIMENTATIONAhmad SalihОценок пока нет
- CLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFДокумент57 страницCLB 10703 - Physical Chemistry (Chapter 1) PDFSarah RashidОценок пока нет
- Pascal Principle LabДокумент4 страницыPascal Principle LabjunedrkaziОценок пока нет
- A i r e- M a x A s ia P t e L t d VAV Flow Calibration and Recommended AirflowДокумент1 страницаA i r e- M a x A s ia P t e L t d VAV Flow Calibration and Recommended AirflowKingsley LimОценок пока нет
- ITG43r - 07 Report On Structural Design andДокумент66 страницITG43r - 07 Report On Structural Design andHarun AlrasyidОценок пока нет
- Hokpunna, Compact Fourth OrderДокумент144 страницыHokpunna, Compact Fourth OrderDanielle WatsonОценок пока нет
- NPTEL Steel Structures Design MCQ AssignmentДокумент8 страницNPTEL Steel Structures Design MCQ AssignmentgowricivilОценок пока нет
- Otc18895 Flow Induced Pulsations in RisersДокумент5 страницOtc18895 Flow Induced Pulsations in Risershamadani100% (1)
- CE8301 SOM Unit 1Документ86 страницCE8301 SOM Unit 1durai muruganОценок пока нет
- Thermal properties of ammonium nitrateДокумент4 страницыThermal properties of ammonium nitratesj_scribdОценок пока нет
- Runner of Francis Turbine:) Cot Cot (Документ5 страницRunner of Francis Turbine:) Cot Cot (Arun Kumar SinghОценок пока нет
- Enzo Traverso The Origins of Nazi Violence - Min CompressedДокумент104 страницыEnzo Traverso The Origins of Nazi Violence - Min CompressedLifeisgoodenjoyОценок пока нет
- THD3602 Major Test 1 2023Документ3 страницыTHD3602 Major Test 1 2023LeighОценок пока нет
- CE140-0P (Fluid Mechanics) Problem Set # 2 Name: - Student No.Документ1 страницаCE140-0P (Fluid Mechanics) Problem Set # 2 Name: - Student No.AydinAkhtarpourОценок пока нет
- 8.64 Viscometers-Industrial: C. H. Kim B. G. Lipták J. E. JamisonДокумент21 страница8.64 Viscometers-Industrial: C. H. Kim B. G. Lipták J. E. Jamisonrahul12000Оценок пока нет
- Gas Processors Suppliers Association GPSA Eng (Bookos - Org) - 701-821!1!60!1!20Документ20 страницGas Processors Suppliers Association GPSA Eng (Bookos - Org) - 701-821!1!60!1!20Karen Vl100% (1)
- Simulation of Viscoelastic Materials in AbaqusДокумент5 страницSimulation of Viscoelastic Materials in AbaqusRahulprabhakaran VannostranОценок пока нет
- Internal FlowДокумент39 страницInternal FlowBahaa RaghebОценок пока нет
- Propiedades Físicas, Hidrocarburos (GPSA)Документ8 страницPropiedades Físicas, Hidrocarburos (GPSA)David EscobarОценок пока нет
- A10VSO32Документ72 страницыA10VSO32王涛Оценок пока нет
- 3.3.6.3.1 Notations and SymbolsДокумент4 страницы3.3.6.3.1 Notations and SymbolsSean WasilОценок пока нет
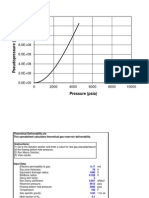
- Theoretical DeliverabilityДокумент197 страницTheoretical Deliverabilitymath62210Оценок пока нет
- Outlines: Theory Calculation Conclusion ReferencesДокумент31 страницаOutlines: Theory Calculation Conclusion ReferencesYè Paing Oo100% (3)
- Teh 908a PDFДокумент30 страницTeh 908a PDFAnonymous 73gEYyEtLОценок пока нет
- HydraulicsДокумент14 страницHydraulicsscrbdgharaviОценок пока нет
- Surface Tension: SynopsisДокумент3 страницыSurface Tension: SynopsisWillSmithОценок пока нет