Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Endo - Pulp Diseases
Загружено:
Yassin SalahИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Endo - Pulp Diseases
Загружено:
Yassin SalahАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
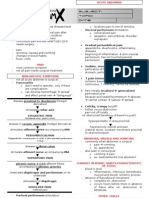
Reversable pulpitis - hyperemia Irreversible pulpitis Pulpal necrosis
D Acute pulpitis ( painful ) Chronic pulpitis (painless) Pulp undergo necrosis ass a sequel of
e acute or chronic pulpitis , as the
Occurs when the amount of irritation intensifies Chronic ulcerative pulpitis Chronic hyperplastic pulpitis ( pulp
f inflammation progress tissue
causing great increase in the interpulpal polyp)
pressure beyond the threshold limits of the Chronic inflammation of cariously Chronic inflammation of cariously continue to disintegrate until entire
sensory nerves causing variables degrees of exposed pulp characterized by exposed pulp characterized by ana pulp is necrotic .
pain. formation of abcess at the point over growth of granulomatous
of exposure leading to ulceration. tissue into the carious cavity
forming a polyp.
E - Incipient caries This response may arise at the end of acute phase or may develop from
t - Cervical erosion onset in case where the irritant is of low grade.
i - Occlusal attrition
o Usually seen secondry to acute
- Deep periodontal curettage pulpitis
l
o - Filling without insulation
g - Leaking restoration
y - Exposed dentinal tubules
It’s a reversible inflammation , if Acute Irreversible , starts initial then moderate
cause eliminated , inflammation & lastly advanced
reverse pulp will return to normal
S Nature of pain: Nature of pain: Nature of pain: Nature of pain: Nature of pain:
i - Type of pain : Sharp transient - Type of pain : Initially :mild shooting - Pain : usually abscent as no - Pain : usually polyp not - Pain:very mild & mostly
g pain By time: sharp shooting ( ↑by lying down) accumulation of fluids occur painful , it bleeds easily on abscent
n iside pulp & intra-pulpal probing ( open apex)
s - Stimulus: initially : cold (last 4 few min’s) pressure does not rise
& - Stimulus : cold (↓ immediately By time: spontaneous without stimulus - Stimulus: heat sometimes
after removal of stimulus)
s - Course of pain :transient - Course of pain : initially : intermittent
y By time: continues
m
p - Vitality testing : normal - Vitality testing : normal
t - Vitality testing : respond at - Vitality testing : pulp responds - Vitality testing : negative
o higher stimulation
m - Palpitation & percussion : -ve - Palpitation & percussion test : -ve
s - Palpitation & percussion : -ve - Palpitation & percussion : -ve
- Palpitation & percussion : -ve
- Stimulus : initially : cold
Followed by a stage : cold & hot - Visual examination reveals - This form seen in young
Advanced stage : heat causes sever the presence of long patients where this polyp
pain( relieved 4 few sec.’s by cold standing carious cavity appears as pinkish red globule
application ‘’Hot tooth ‘’) of tissue protruding from the
- Pain referred → neighboring teeth , pulp chamber.
opposing dentition & temporal area & ear
- Distribution of pain: always diffuse , cannot
localize correctly offended tooth .
- Pain control : initially : by analgesics
Advanced stage : nothing can stop pain
h Local vasodilatation & ↑ in ↑ pulpal pressure , tissue damage & bacterial
i permeability of blood vessels can toxins lead to formation of micro-abcesses at A zone of necrosis is seen at the The polyp is a complex of new
s cause slight ↑ in local pulpal the site of the carious exposure. The neutrophils surface of the pulp followed by a capillaries, proliferating fibroblasts
t pressure. Infiltration for few are the primary cells present. Surrounding the zone of leukocytic infiltration. & inflammatory cells.
o numbers of inflammatory cells . if abcess , a dense infiltration of lymphocytes, Beyond this zone, a zone of
irritation of pulp continues or ↑ , plasma cells & macrophages is seen. proliferating fibroblasts is seen.
case changesto irreversible pulpitis
& eventually necrosis.
R
a Normal No radiographic changes except No changes seen, except in some No changes seen, except in some No changes seen, except some cases
d Advanced stage :some widening in the cases there can be some widening cases there can be some widening there can be some widening in the
i periodontal membrane space in the periodontal membrane in the periodontal membrane periodontal membrane space.
o space. space.
g
r
a
p
h
i
c
Вам также может понравиться
- Endo AcuteДокумент1 страницаEndo AcutebouglaglastellaОценок пока нет
- Endodontic Diagnosis: DR - Suchetaprabhu Third Year Mds 2 8 / 0 6 / 1 8Документ77 страницEndodontic Diagnosis: DR - Suchetaprabhu Third Year Mds 2 8 / 0 6 / 1 8Tuan NguyenОценок пока нет
- MassДокумент8 страницMassYara YousefОценок пока нет
- Curs 10-Pulp Pathology II-1Документ32 страницыCurs 10-Pulp Pathology II-1Bianca BurcăОценок пока нет
- Soft Tissue SwellingДокумент34 страницыSoft Tissue Swellingsp25hgmc9jОценок пока нет
- Opath Lab. Pulp Periapical Diseases CompleteДокумент3 страницыOpath Lab. Pulp Periapical Diseases CompleteJaira LaguidaoОценок пока нет
- Abscess Dr. Nasrin Sultana JuyenaДокумент4 страницыAbscess Dr. Nasrin Sultana JuyenaShakil MahmodОценок пока нет
- Pain NCP BillrothДокумент2 страницыPain NCP BillrotharjayОценок пока нет
- Reso Urce Name Operative Dentistry: Treatment PlanningДокумент49 страницReso Urce Name Operative Dentistry: Treatment PlanningHamza AdeelОценок пока нет
- Dizziness HXДокумент4 страницыDizziness HXbadmanОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Pain in BiliodigestiДокумент19 страницPathophysiology of Pain in Biliodigestiprabowoaji12Оценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Pain in Biliary DisordersДокумент19 страницPathophysiology of Pain in Biliary Disordersprabowoaji12Оценок пока нет
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (NCP)Документ4 страницыDeep Vein Thrombosis (NCP)24 PAULINO ALDRIN MUJAR0% (1)
- Summary of Orlpt MTДокумент7 страницSummary of Orlpt MTGlea Marie EscanlarОценок пока нет
- Nerve Nerve Nerve Nerve Entrapment Entrapment Syndromes (Nes) Syndromes (Nes)Документ52 страницыNerve Nerve Nerve Nerve Entrapment Entrapment Syndromes (Nes) Syndromes (Nes)teshaleОценок пока нет
- Endodontic Emergency (Dr. Imran)Документ2 страницыEndodontic Emergency (Dr. Imran)aelessyaОценок пока нет
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5Документ1 страницаTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 5JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYОценок пока нет
- Hernia Case ProformaДокумент2 страницыHernia Case ProformaTanmay SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Varicose Case ProformaДокумент2 страницыVaricose Case ProformaSneha Naulakha100% (1)
- PALPATION of Swelling D Hussain NazeeshaДокумент17 страницPALPATION of Swelling D Hussain NazeeshaHUSSAIN NAZEESHAОценок пока нет
- Pain Definitions and Taxonomy of PainДокумент40 страницPain Definitions and Taxonomy of PainmorfisstefОценок пока нет
- Oral Pathology NotesДокумент2 страницыOral Pathology NotesMohamedОценок пока нет
- BLS - First Aid 2Документ5 страницBLS - First Aid 2jerry spiritОценок пока нет
- Diseases of The PulpДокумент1 страницаDiseases of The PulpFidz LiankoОценок пока нет
- Cyriax ConceptДокумент26 страницCyriax ConceptMeenakshiputraeashwarprasad MacherlaОценок пока нет
- Cap 49 Guyton 259710 Downloable 1847976Документ7 страницCap 49 Guyton 259710 Downloable 1847976Keidy P Quen AedoОценок пока нет
- Inflammation 2Документ4 страницыInflammation 2honovezaann.a.campita.ctucvmОценок пока нет
- Presentation 2Документ15 страницPresentation 2KaviyaОценок пока нет
- Pulpal and Periapical PathologyДокумент101 страницаPulpal and Periapical Pathologyammara100% (1)
- Sorting Out Endodontic Symptoms: ©JK Mitchell, DDS, Med April 2012Документ2 страницыSorting Out Endodontic Symptoms: ©JK Mitchell, DDS, Med April 2012sao_tren_troi100% (1)
- Acute Scrotal Pain in Adults and Adolescents - Approach To The Patient - DynaMedДокумент66 страницAcute Scrotal Pain in Adults and Adolescents - Approach To The Patient - DynaMedSebastian ChavesОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5 - Pulp and Periapical IДокумент116 страницLecture 5 - Pulp and Periapical IAlex ChangОценок пока нет
- NCP Ectopic PregnancyДокумент2 страницыNCP Ectopic PregnancykatrinajhorelletillesОценок пока нет
- Inv Asion P Hase: (Depression Phase)Документ1 страницаInv Asion P Hase: (Depression Phase)Kamille PinoОценок пока нет
- Tinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12Документ1 страницаTinywow Communicable-Diseases 48897647 12JULIUS CEZAR QUINAYОценок пока нет
- Concept Map On AppendicitisДокумент6 страницConcept Map On Appendicitisitalisayan_rondario80% (5)
- Acute AbdomenДокумент4 страницыAcute Abdomensarguss14Оценок пока нет
- Pulp DiseasesДокумент10 страницPulp DiseasesAdham AshrafОценок пока нет
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: (Depression Phase)Документ1 страницаInv A Sion Pha Se: (Depression Phase)rossvieОценок пока нет
- Abdominal Pain ExplainedДокумент4 страницыAbdominal Pain ExplainedNazmun LailahОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of Acute Abdominal PainДокумент4 страницыEvaluation of Acute Abdominal PainEdison Tan SantamariaОценок пока нет
- 27.neck SwellingsДокумент4 страницы27.neck SwellingsDurga VoraОценок пока нет
- PREOP3 1 DocxДокумент1 страницаPREOP3 1 DocxCamille Joy BaliliОценок пока нет
- Gynecological and Urogynecological Assessment ChecklistДокумент4 страницыGynecological and Urogynecological Assessment Checklistanne laureОценок пока нет
- Assessment of Peripheral VasculatureДокумент5 страницAssessment of Peripheral VasculatureCraigyyОценок пока нет
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: Rabies PatophysiologyДокумент1 страницаInv A Sion Pha Se: Rabies PatophysiologyRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanОценок пока нет
- Ulcer Case by S.P.KamthankarДокумент14 страницUlcer Case by S.P.KamthankarJaweria SyedОценок пока нет
- Dr. Praveen K. YadavДокумент32 страницыDr. Praveen K. YadavRaj RajОценок пока нет
- Communicable DiseasesДокумент14 страницCommunicable DiseasesKristine ManioОценок пока нет
- Inv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiДокумент1 страницаInv A Sion Pha Se: Bill Julius Samuel G. Alferez BSN IiiRudelsa Agcolicol LangamanОценок пока нет
- Comparison of Rheumatoid and OsteoarthritisДокумент4 страницыComparison of Rheumatoid and OsteoarthritisWaseem Khan AfridiОценок пока нет
- Head Nursing TemplateДокумент9 страницHead Nursing TemplateBianca MaeОценок пока нет
- ORTHOPAEDICS MANUAL PaulДокумент62 страницыORTHOPAEDICS MANUAL PaulRОценок пока нет
- Cme: Septic Arthritis: by Syafi'ie Syukri Bin Mohammed FaridzДокумент23 страницыCme: Septic Arthritis: by Syafi'ie Syukri Bin Mohammed FaridzGraldoОценок пока нет
- PREOP3Документ1 страницаPREOP3Void LessОценок пока нет
- Abdominal PainДокумент6 страницAbdominal PainHynne Jhea EchavezОценок пока нет
- Lumps and SwellingsДокумент3 страницыLumps and SwellingsEarn ChiОценок пока нет
- Spine PDFДокумент7 страницSpine PDFDRAHMEDFAHMYORTHOCLINIC100% (1)
- DeQuervain Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОт EverandDeQuervain Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsОценок пока нет
- Winter - The Coldest Season - Live ScienceДокумент11 страницWinter - The Coldest Season - Live ScienceYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Analysis of 3D Soft Tissue Changes After 1-And 2-Jaw Orthognathic Surgery in Mandibular Prognathism PatientsДокумент11 страницAnalysis of 3D Soft Tissue Changes After 1-And 2-Jaw Orthognathic Surgery in Mandibular Prognathism PatientsYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Park 2012Документ6 страницPark 2012Yassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Cevidanes 2005Документ8 страницCevidanes 2005Yassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Topic 4 20 MinДокумент1 страницаTopic 4 20 MinYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Prediction of Soft Tissue Deformations After CMF Surgery With Incremental Kernel Ridge Regression Pan2016Документ9 страницPrediction of Soft Tissue Deformations After CMF Surgery With Incremental Kernel Ridge Regression Pan2016Yassin SalahОценок пока нет
- NT Catalogue 2019Документ368 страницNT Catalogue 2019Yassin SalahОценок пока нет
- One Year Postoperative Hard and Soft Tissue Volumetric Changes After A Bsso Mandibular AdvancementДокумент9 страницOne Year Postoperative Hard and Soft Tissue Volumetric Changes After A Bsso Mandibular AdvancementYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Original ContributionДокумент11 страницOriginal ContributionYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Bodipack +: Interpretation of ResultsДокумент1 страницаBodipack +: Interpretation of ResultsYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- IPS E-Max CAD-IPS E-Max Press - Adhesive 1mm CrownДокумент1 страницаIPS E-Max CAD-IPS E-Max Press - Adhesive 1mm CrownYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Applications of 3D Imaging in Orthodontics: Part 1Документ10 страницApplications of 3D Imaging in Orthodontics: Part 1Yassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Prosthetic Options in Implant Dentistry: Bibin BhaskaranДокумент50 страницProsthetic Options in Implant Dentistry: Bibin BhaskaranYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Straumann Screw Retained Hybrid RestorationsДокумент36 страницStraumann Screw Retained Hybrid RestorationsHugoMoralesTecnicoDentalОценок пока нет
- IPS E-Max CAD For CEREC SpeedFire (Dentsply Sirona)Документ2 страницыIPS E-Max CAD For CEREC SpeedFire (Dentsply Sirona)Yassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Yassin Salah Mohammed YassinДокумент3 страницыYassin Salah Mohammed YassinYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Ms PresentДокумент3 страницыMs PresentYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- MCQ Review For Saudi Licensing Exam (SLE)Документ0 страницMCQ Review For Saudi Licensing Exam (SLE)Rakesh Kumar83% (6)
- CHAP 21 - Immediate Loading of Dental Implants PDFДокумент15 страницCHAP 21 - Immediate Loading of Dental Implants PDFYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Digital ImДокумент6 страницDigital ImYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- A Review of The Properties of Some Denture Base PolymersДокумент15 страницA Review of The Properties of Some Denture Base PolymersYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Pu1473410272 PDFДокумент1 страницаPu1473410272 PDFYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- 1st Lec2ndedДокумент9 страниц1st Lec2ndedYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- ImplantsДокумент284 страницыImplantsYassin Salah100% (1)
- Digital ImДокумент6 страницDigital ImYassin SalahОценок пока нет
- Full Blood Count Apr04, DR Eva RaikДокумент7 страницFull Blood Count Apr04, DR Eva RaikDanielcc LeeОценок пока нет
- Typing LessonsДокумент7 страницTyping LessonsPalash RakshitОценок пока нет
- Eyelashes Divert Airflow To Protect The EyeДокумент12 страницEyelashes Divert Airflow To Protect The EyeVincent John BorceloОценок пока нет
- All The Quotes ... Great Quotes..Документ32 страницыAll The Quotes ... Great Quotes..Muhammad Nizam YusofОценок пока нет
- Listeria MonocytogenesДокумент28 страницListeria Monocytogenestummalapalli venkateswara rao100% (1)
- Oecd 402Документ7 страницOecd 402Sandro SotomayorОценок пока нет
- Pure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFДокумент2 страницыPure Bio CH 2 Textbook Answers PDFno one100% (3)
- Memotain: A CAD/CAM Nickel-Titanium Lingual Retainer: Clinician'S CornerДокумент4 страницыMemotain: A CAD/CAM Nickel-Titanium Lingual Retainer: Clinician'S Cornerangianny_cdОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1-4 Spelling, Vocabulary and ComprehensionДокумент16 страницLesson 1-4 Spelling, Vocabulary and ComprehensionVera Hristofor - OjogОценок пока нет
- Data Interpretation & Numerical Ability: Sample Questions IIMKДокумент4 страницыData Interpretation & Numerical Ability: Sample Questions IIMKKarthuu RaajОценок пока нет
- CONSERVANCYДокумент1 страницаCONSERVANCYNamib Family Medical CentreОценок пока нет
- Fs 2 DLP Different Characteristics of VertebratesДокумент4 страницыFs 2 DLP Different Characteristics of VertebratesTerrence Mateo100% (1)
- I Think You Think I Love YouДокумент14 страницI Think You Think I Love YouBeatrice Nicolas33% (3)
- Umberto BERNABUCCIДокумент9 страницUmberto BERNABUCCIbermudez_eduard8792Оценок пока нет
- Grade 9 CardioДокумент16 страницGrade 9 CardioJamoi Ray VedastoОценок пока нет
- Parasitology TableДокумент9 страницParasitology TablehumanupgradeОценок пока нет
- ThreePointer's Guide To Histology Steeple Chase For 022 ClassДокумент54 страницыThreePointer's Guide To Histology Steeple Chase For 022 ClassNnaemeka Neboh100% (1)
- Wa0106.Документ6 страницWa0106.Priscila FreitasОценок пока нет
- Tantra - Sexual Martial Arts and SexerciseДокумент51 страницаTantra - Sexual Martial Arts and SexerciseElias Avendano Saca75% (4)
- Tanuki: The Badger' As Figure in Japanese: LiteratureДокумент24 страницыTanuki: The Badger' As Figure in Japanese: LiteratureNicole BednarzОценок пока нет
- Sexual and Asexual Reproduction: Types and Benefits ComparedДокумент34 страницыSexual and Asexual Reproduction: Types and Benefits ComparedArima Kousei50% (4)
- A Busy Mom's Guide To Daily Meal Preparation: I Just Wanted To Expound That What I Usually Do IsДокумент8 страницA Busy Mom's Guide To Daily Meal Preparation: I Just Wanted To Expound That What I Usually Do IsCarina TanОценок пока нет
- 74 Cue Card AnsДокумент167 страниц74 Cue Card Ansduaa fatimaОценок пока нет
- Snakes: Cold-Blooded Creatures that Require SunshineДокумент14 страницSnakes: Cold-Blooded Creatures that Require SunshineAvril TicaОценок пока нет
- Inugami-san to Nekoyama-san Manga & Anime AdaptationДокумент5 страницInugami-san to Nekoyama-san Manga & Anime AdaptationElineth GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Communicating Spirit: The White Wind Birth ChartДокумент35 страницCommunicating Spirit: The White Wind Birth ChartYannis KaratsОценок пока нет
- Can You Guess The Title of These ExtractsДокумент2 страницыCan You Guess The Title of These ExtractsHafis ZamОценок пока нет
- Rabies Control Program by DohДокумент11 страницRabies Control Program by DohSabrina Porquiado Magañan SNОценок пока нет
- Homeopathy Provings of Boa ConstrictorДокумент18 страницHomeopathy Provings of Boa Constrictoraruen79Оценок пока нет
- NappingДокумент1 страницаNappingKingson_786Оценок пока нет