Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
National pediatric evaluation
Загружено:
Maya SusantiИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
National pediatric evaluation
Загружено:
Maya SusantiАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
NATIONAL KNOWLEDGE BASED EVALUATION
OF INDONESIAN PEDIATRIC RESIDENT
July, 11, 2018-07-10
MNJ2018
For each of the following multiple choice questions,
select the one, most appropriate answer
1. A 7 year-old boy was sent to the hospital because he complained of recurrent cold. Now, he is still taking
allergy and cold medications from a doctor before. His father suffered from asthma and her mother often got
itchy skin. They want to know whether their child has an allergy. To support the diagnosis of allergy and to
determine the type of allergen, what is the most appropriate examination?
A. Atopy Patch Test C. Specific IgE
B. Intra Dermal Test D. Skin Prick Test E. Total IgE
2. A 4 month old, boys with chief complain pruritus in the body since 2 weeks ago. From family history, his
mother suffer from asthma, and father suffer from asthma. He still got exclusive breastfeeding until now.
From family history, the baby could classified as high risk of atopic with risk factor to get allergy disease for:
A.0-5% B. 5-15% C.20-40% D.40-60% E. 60-80%
3. Select the most appropriate diagnosis from the list of options of the following descriptions of rash with the
illness for which they are the most typical exanthem: A 12 year old boy develops petechiae and papules,
some of which become purpuric over his buttocks and legs, associated with painful swollen knees. There is
microscopic haematuria on testing. The platelet count is normal.
A. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome D. Meningococcal infection
B. Infectious mononucleosis E. Systemic onset juvenile chronic arthritis
C. Henoch – Schonlein purpura
4. Select the most appropriate diagnosis from the list of options that would best explain the following case: An
11 year old with a previous history of chronic glomerulonephritis presents with bruising and epistaxis. A full
blood count confirms a pancytopenia.
A. Haemolytic uraemic syndrome D. Renal vein thrombosis
B. Henoch Schonlein purpura E. Systemic lupus erythematosus
C. Renal tubular acidosis
5. Select the most appropriate diagnosis from the list of options of the following descriptions of rash with the
illness for which they are the most typical exanthem: A salmon-coloured, reticulate macular rash develops
mainly over the extensor surfaces of the limbs in a 5 year old boy with swinging temperature; hot, swollen,
painful knees and left elbow and palpable spleen. The ESR is 95. The blood count, C-reactive protein and
chest X-ray are normal.
A. Staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome D. Meningococcal infection
B. Infectious mononucleosis E. Systemic onset juvenile chronic arthritis
C. Henoch – Schonlein purpura
6. A 15 years old boy came to you with nose congestion and watery runny nose all year round since he was 11
years-old. You also found dark circle surrounding his eyes . Based on what you know, how would you
presume the cause of all year round rhinitis ?
A. Reptil pet C. Grass pollen
B. House dust mite D. Tree Pollen E. Flower Pollen
7. A premature baby girl was born 28 weeks of gestation and hospitalized in NICU. Currently she cannot
coordinate sucking and swallowing well. When the preterm infant have normal coordination of sucking and
swallowing?
A. 28 weeks B. 30 weeks C. 32 weeks D. 34 weeks E. 36 weeks
Ujian MCQ Nasional Tanggal 11 Juli 2018 |1
8. A 6-year old girl came with a complaint often looked blank since last 6 months. When stunned, the child does
not respond to any calls / questions. After the attack the child return to normal activities. Physical and
neurological examination sere normal. On EEG shows a picture of generalized slow spike-wave 2-3 spd.
What is the diagnosis of this patient?
A. Juvenile absence epilepsy D. Temporal lobe epilepsy
B. Idiopathic generalized epilepsy E. Childhood absence epilepsy
C. Day-dreaming
9. A 6 months child came to the emergency department with generalized seizures, tonic-clonic, for 20 minutes,
post-ictal child looks whimpering and lethargy. There was fever, cough, runny nose for 5 days, and the
history of immunization was not clear. Physical examinations showed bulding of fontanella, strabismus,
hemiparesis dexstra, meningeal stimuli sign (-).
What examination is needed to make a diagnosis:
A CT-scan of the head C. lumbar puncture
B. ultrasound of head D. procalcitonin E. complete blood
10. A 10-year-old girl suddenly not be able to stand and walk, the child was not able to control the micturition
and defecation. One week before there was a paralysis of the child and she has a high fever for 3 days with
cough and colds that are cured without treatment.
What is the diagnosis in this child?
A. Guillain-Barre Syndrome C. Transverse myelitis
B. Poliomyelitis D. Meningitis E. Multiple sclerosis
11. A 12 years boy came with complaints of difficulty breathing since 2 hours before admission, accompanied by
paralysis of the limbs. Two days before admission there was lower limb weakness, in the next day the child
could not lift his both hands.
What is the management to the patient?
A. Methyl-prednisolone IV 30 mg / kg / day for 3 days
B. Immunoglobulin 0.4 g / kg / day, for 3 days
C. Plasmapheresis for 2 cycles
D. Immunoglobulins 0.4 g / kg / day, for 5 days
E. Methyl prednisolone IV 1-2 mg / kg / day for 5 days
12. A 34 week newborn was performed initial step of resuscitation because of not breath at birth.
What is the indication of positive pressure ventilation?
A. Weak muscle tone or heart rate <100 beat/minute
B. Weak muscle tone or no breathing effort
C. Heart rate <100 beat/minute or respiratory distress
D. Heart rate <100 beat/minute or apnea
E. Has respiratory effort with chest retraction
13.After positive pressure ventilation, the baby breath spontaneously with chest retraction and other signs of
respiratory distress, and heart rate 120 beat/minute. What should doctors do next?
A. Continue positive pressure ventilation (PPV) D. Send to neonatal ward
B. Continuous positive airway pressure E. Free flow oxygen
C. PPV and chest compression
14.A preterm infant was born at 31 week gestational of age. What is the appropriate term for the infant?
A. Extremely preterm C. Moderate preterm
B. Very preterm D. Late preterm E. Mild Preterm
15.A 30 week infant was born in tertiary hospital. Now the baby’s age is 12 hour. Doctor decides to start
parenteral feeding. What is the contain of parenteral nutrition?
A. Protein 1 g/kg/day, lipid 0,5 g/kg/day, calcium
B. Protein 1 g/kg/day, lipid 0,5 g/kg/day, phosphate
C. Protein 1,5 g/kg/day, lipid 0,5 g/kg/day, magnesium
D. Protein 1,5 g/kg/day, lipid 1 g/kg/day, potassium
E. Protein 1,5 g/kg/day, lipid 1 g/kg/day, iron
16.A 33 week infant, now the infant’s age is 20 day. To monitor the growth of the baby, what chart should doctor
use that to be continued by WHO 2006 chart.
A. Fenton 2013 chart until 12 months after birth.
B. Fenton 2013 chart until 6 months after birth.
C. Fenton 2013 chart until 1 month after birth.
D. Fenton 2013 chart until 37 week gestational age.
E. Fenton 2013 chart until 40 week gestational age.
Ujian MCQ Nasional Tanggal 11 Juli 2018 |2
17.A 28 week infant was hospitalized for 20 days. Full enteral feeding was achieved with in 2 week. What is the
target of calories for this infant?
A. 115-120 kcal/kg/day D. 100-<105 kcal/kg/day
B. 110-<115 kcal/kg/day E. 95-<100 kcal/kg/day
C. 105-<110 kcal/kg/day
18.You are evaluating a 10-month-old infant for recurrent fracture following relatively minor trauma. You note
deep blue sclera and bowing of the lower extremities. X-ray examination reveals generalized osteopenia.
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Achondroplasia D. Osteo arthritis.
B. Spondyloepiphysial Dysplasia E. Rickets
C. Osteogenesis imperfecta
19.An 8-year-old boy was brought for his preschool checkup by his grandmother, who concerned about his
growth. According to his grandmother he was not growing appropriately in this last 2 years.
Which of the following best approximates the annual height increment of this boy?
A. 1-2 cm B. 3-4 cm C. 5-7 cm D. 8-10 cm E. 12-14 cm
20.An adolescent with type 1 diabetes presents in your clinic for follow-up visit. You note that his serum glucose
is elevated and his glycosylated hemoglobin (Hemoglobin A1c) level is 15.7 % (Normal < 7%).
This finding suggests poor metabolic control of his diabetes over at least which of the following time
periods?
A. 1 week B. 1 month C. 3 months D. 5 months E. 6 months
21.A 12-year-old girl is at the 3th percentile for height. She is an otherwise healthy child. The bone age is greater
than two standard deviations below the chronologic age, but in concordance with her height age. Of the
following, the MOST likely cause of this patient's short stature is:
A. Constitutional growth delay D. Hypothyroidism
B. Familial short stature E. Emotional deprivation
C. Growth hormone deficiency
22.An 8 year old is accidentally hit in the abdomen by a baseball bat. After several minutes of discomfort, he
seems to be fine. Over the ensueing 24 hours, however, he develops a fever, abdominal pain radiating to the
back and persistent vomiting. On examination, the child appears quite uncomfortable. The abdomen is tender,
with decreased bowel sounds throughout, but especialy painfull in the midepigastric region with guarding.
What is the diagnosis?
A. Appendicitis C. Chron disease E. Choledocal cyst
B. Pancreatitis D. Gallstones
23.A 10 year old boy comes with complaint of altered conciousness. About 2 weeks earlier he appeared to be
jaundice which preceded with other signs such as fever and abdominal pain. After few days of hospitalization
patient becomes more toxic, on examination the liver size is small, hepatic enzymes levels decrease with elevated
direct and indirect serum bilirubin levels. What is the correct diagnosis?
A. Autoimmune Hepatitis C. Hepatitis A
B. Fulminant Hepatic Failure D. Hepatitis B E. Hepatitis C
24.Fulminant hepatic failure may lead to encephalopathy, cerebral edema and brain death within several days.
Which mode of support might best prevent the progression from grade II to grade III + hepatic encephalopathy ?
A. Fluid restriction D. Continuous hemofiltration and plasma exchange
B. Furosemide transfusion E. Hemodialysis
C. Porcine hepatocyte column filtration
25.A previously healthy 6 months old child develops paroxysmal colicky abdominal pain. The infant has
occasional vomiting. Over the next 12 hours the infant passes stool containing blood and mucus and becomes
progressively lethargic. After fluid resuscitation, the most appropriate next step in management is :
A. Colonoscopy C. Meckel scan
B. Stool culture D. Air- contras enema E. Empiric antibiotic therapy
26.An 18-hour-old infant has bilious stained emesis following 3 initial feedings. The prenatal and delivery history
are unremarkable. On physical exam, the infant is quiet. The occasional peristaltic waves are noted and the
abdomen is not distended. Which of the following findings is MOST likely on further radiologic evaluation of
this infant?
A. GE reflux C. A “double bubble” sign
B. Pyloric hypertrophy D. Malrotation E. A choledochal duct cyst
Ujian MCQ Nasional Tanggal 11 Juli 2018 |3
27. 11 – month old boy, on screening laboratory testing of Hemoglobin 7.8g/dL, HCt 24%, Leucocyte count
10.000 /mm3. Thrombocyte 276.000/mm3. MCV 62 fl, normaly differential count, blood smear microcytic
hypochromic, Ferritin 1700.
Which of the following is the most appropiate recommendation:
A. blood transfusion D. Intravasculair iron dextran
B. oral ferrous sulfate E. An iron- fortified porridge
C. Intramusculair iron dextran
28. 7 years old boy presented to Emergency room with history of fever, pallor and nose bleeding, 4 weeks
duration. On examination: febrile, pale, petechie, subconjuctival bleeding, hepatosplenomegaly. Laboratory
finding : Complate Blood Count: Hb 5 gr/dl : WBC 50,000/uL. Platelet 15,000/uL; Lymphocyte count 78%; The
most likely clinical diagnosis is:
A. Acute Lymphoblastic leukemia D. Nasopharyngeal tumor
B. Limphoma Malignan Non Hodgkins E. Neuroblastoma stage IV
C. Anemia aplastic
29.Five years following successful treatment for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), the parents report that the
patient, who is now 8 year old, is experiencing serious difficulties with school performance. Areas of particular
concern relate to reading, language and mathematics. What component of ALL therapy would a possible cause
of cognitive dysfunction?
A. IT Methotrexate C. Cranial radiation
B. IT Cytarabin D. High dose Cyclophosphamide E. High dose IV Methotrexate
30.Four year old boy known case of hemophilia A coming to Emergency Room with first time right side knee
joint swelling in order to control bleeding at the joint, , it is necessary to raise the serum level of factor VIII to
about:
A. 1-2% of normal
B. 5-10% of normal
C. 10-25% of normal
D. 25-50% of normal
E. 75-100% of normal
31.The most urgent complication in a patient with Non – Hodgkin’s Lymphoma that needs to evaluated at
diagnosis and followed closely is :
A. An Elevated WBC > 50.000 D. A large of mediastinal mass
B. Elevated urine production E. Complaints of left flank pain
C. A uric Acid level of 6.0
32.Prognostic indicators at diagnosis in Patient with Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) in childhood include
age, biologicproperties of the leukemic blasts bone marrow and pheripheral blood.
A. Gender C. Prolonged fever
B. Down Syndrom D. Initial White blood count E. Hepatosplenomegli
33.15 years-old boy presented with 4 days ago history of bleeding gums, subconjuctival bleeding and petechie.
Complate Blood Count: Hb 6.5 g/dL, Leucocyte count 86.000 /mm3; Platelet 24.000/mm3; blast 30%. Uric Acid
7.2 mg/L, hyperphospatemia.
Which of the following is the most likely:
A. Leukostasis D. Superior vena cava syndrome
B. Tumor Lysis Syndrome E. Disseminated Intravasculair Coagulation
C. Septicemia
34.A boy 1 year old came with his mother to Primary Health Care . His complain were fever, poor apetite, runny
nose and sore throat within five days after exposure with his brother who suffered from Hand Foot and Mouth
Disease ( HFMD) .The typical rash of Hand Foot and Mouth Disease is :
A. Papulo vesicles throughout the body
B. Macular erythema arising centripetal
C. Petichie arising on the test Rumple Leed
D. Macular papules around the mouth, hands and feet
E. Macular papules accompanied by strawberry tongue
35.You are evaluating a 10-month-old girl who has had a temperature to 38.9°C for 2 days. Her parents deny
other symptoms except a slight increase in fussiness. Her immunizations are up to date. Findings on physical
examination are normal, and she appears well. Which of the following tests is most helpful in establishing a
diagnosis in this child?
A. Blood culture C. Complete blood count
B. Chest radiograph D. C-reactive protein E. Urine culture
Ujian MCQ Nasional Tanggal 11 Juli 2018 |4
36.A 10-year-old girl came to the hospital with the main complaint of gum bleeding 1 day before admission. She
had suffered high grade fever for 6 days, and headache, retro-orbital and muscle pain. T: 90/65 mmHg, pulse rate
96 x/min, respiratory rate 24 x/minute, temp 36.5.0C. The liver was not palpable,. The extremities were warm,
Tourniquet test was Positive. Laboratory examination revealed: hemoglobin 11.5 g/dl, hematocrite 34.6%,
leukocyte 2,700/mm3, and platelet 45,000/mm3. The most likely diagnosis in this patient would be
A. Dengue fever D. Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever grade III
B. Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever grade I E. Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever grade II
C. Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever grade IV
37.A 5-year-old boy has been febrile for 2 days. He does not want to drink and vomited this morning. There have
been no cough, rhinorhea nor diarrhea. On examination, he is sleepy but arousable and has temperature of
39,60C. His posterior oropharynx is markedly erythematous with enlarged, simmetrical and cryptic tonsils that are
laden with exudate. Shoddy cervical lymphadenopathy is noted. He moves his neck vigorously in an effort to
thwart your examination. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A. Coxsackie pharyngitis
B. Streptococcal tonsillitis
C. Parapharyngeal abces
D. Lymphadenitis
E. Retropharyngeal abces
38.A 14-years-old boy presents with extreme fatigue. Testing shows fever, generalized lymphadenopathy,
atypical lymphocytes, and a positive heterophile antibody test. Epstein-Barr virus is suspected. Which of the
following diagnosis is most likely?
A. Croup C. Mononucleosis
B. Epiglottitis D. Bronchiolitis E. Pertussis
39.Amir, 2 year old boy came with his mother with the main complaint of high grade fever for 4 days. Mother
also complaint of some red rashes appear in his face since yesterday that spread to his neck and chest. The mother
said that his neighbour was suffered with the same complaint, and now hospitalized due to dyspnea. What is the
most likely diagnosis of Amir?
A. Rubella C. Measles
B. Scarlet fever D. Varicella E. Exanthema subitum
40.A 5 years old boy came to health center with day 3 of fever, acute onset, high fever and not doing wellHe also
complain of pain on retro orbital, leg and also head ache. This boy looked ill, with temperature 38.6, BP 100/65,
pulse 125/min and petechiae on his right hand. What is the probable diagnosis of this case?
A. Dengue viral infection C. Typhoid fever
B. Dengue fever D. Undiferentiated fever E. Dengue haemorrhagic fever
41.The results of the examination of anthropometry plotting a boy age 10 months on the WHO 2006 chart
Weight for Lenght <-2 SD, the interpretation is
A. a malnutrition. C. severely stunted
B. Wasted D. stunted E. severely wasted
42.A 19 –month old baby was admitted to an emergency room with febrile seizures. Fever appeared since last
night, accompanied by cough and cold. Seizure lasted 1 minute. After seizure he was crying, conscious, and there
had history of febrile seizures when she was 13 month old. Physical examination revealed no abnormalities.
Laboratory results showed leukopenia. A week before the fever, he received measles vaccine. Based on that case,
what is the classification of the “adverse events following immunization”?
A. vaccine product-related reaction D. immunization anxiety-related reaction
B. vaccine quality defect-related reaction E. coincidental event
C. immunization error-related reaction
43A 2- year-old boys is developing normally, which of the following receptive language milestones is consistent
with her developmental age ?
A. Point to part of picture D. Follow two step command
B. Name body part with function E. Knows function of certain objects
C. Knows right and left on self
44. How long should you correct for gestational age when evaluating preterm infants?
A. 6 months. C. 24 months.
B. 12 months. D. Until kindergarten. E. Until entry to high school.
Ujian MCQ Nasional Tanggal 11 Juli 2018 |5
45. A three year old child growing consistently between the 1 SD and the 2 SD on the WHO BMI-for- Age
growth chart would be categorized as:
A. Within normal range. C. Risk of overweight
B. Underweight D. Overweight E Risk of Obese
46.A mother wants to start giving complementary food to her baby. She is confused what solid food should be
given to her baby for the first moment. What the appropriate suggestion should be given?
A. Fortified cereal C. Pure banana
B. Fortified rice D. Fortified wheat-base-cereal E. Fortified-rice-base-cereal
47.A child with idiopathic obesity is diagnosed to have a pathological cause for the obesity.
Which of the following clinical feature is likely to be present?
A. Height velocity of 4 cm/year or more D. Advanced bone age
B. Shorter than age matched peers E. Early growth spurt
C. Increased linier growth
48.A obese boy, 11 year old, brought to the clinic. His mother worried about his health. Which one of the
statement bellow is correct as the most frequent obesity comorbidity?
A. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome C. Hypertension
B. Non Alcoholic steatohepatitis D. Hyperlipidemia E. Cardiomyopaty
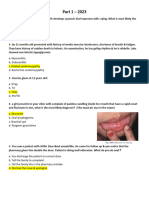
49.A 3-year-old girl came up with palpebra edema, glazed eyes and a round face. Physical examination showed
hepatomegaly and thin reddish hair that easily removed. There are pinkish patches on her skin that widespread all
over her body.
What is the diagnosis?
A. Marasmus D. Mild Protein-Energy Malnutrition
B. Kwashiorkor E. Moderate Protein-Energy Malnutrition
C. Marasmus-Kwashiorkor
50.Two years old boy brought to outpatient clinic because skin problem. From physical examination she has
generalized edema, irritable, reddish hair and easily removed, and prominent pinkish patches on his skin. What
is the name of skin lesion?
A. Baggy pants C. Ulcerated exudative lesions
B. Hypopigmentation D. Crazy pavement dermatosis E. Acute dermatitis
51.A 12 years old male present to ED with wheezing and increased work of breathing for the fifth time in the past
year. On examination, his respiratory rate 30 breaths/minute and oxygen saturation is 98% in room air. He is
talking in complete sentences and there is expiratory wheezing with prolonged expiratory phase. What is the
first treatment he should receive?
A. Nebulized β-agonists D. Intravenous steroid
B. Nebulized β-agonists+ anticholinergic E. Intravenous aminophylline
C. Subcutanes epinephrine
52.A 10 years old girl present to ED with wheezing and increased work of breathing for the fifth time on the last
six months. She has been using inhaled fenoterol inhaler per week to control wheezing. In addition to
fenoterol inhaler, what is the best additional medicine she should receive?
A. Fluticasone inhaler C. Procaterol inhaler
B. Salmeterol inhaler D. Theophyllin slow released E. Formoterol inhaler
53.You are seeing a 14 old girl in the Emergency room with an acute asthma attack. She looks very
uncomfortable, she has diffuse wheezing throughout all lung fields and is requiring 50% oxygen by face mask to
maintain oxygen saturations above 90%. A nurse reports that when the patient blows in her peak flow meter it
reads in the normal range. What should you do next?
A. send the patient home D. get another peak flow
B. repeat the peak flow several more times E. Get the Lung function test
C. ignore the results and treat for severe asthma
54.A 2 months old girl came to Emergency Room with chief complain worsening respiratory distress since 2 days
ago. 3 days prior to admission she had fever, cough and decreased appetite. Her physical examination showed
febrile infants, tachypnea with chest indrawing and rales in both lung.
What is the diagnosis of this case?
A. Bronchiolitis C. Bronchitis
B. Bronchopneumonia D. Asthma E. Tuberculosis
Ujian MCQ Nasional Tanggal 11 Juli 2018 |6
55.A 2 months old girl came to Emergency Room with chief complain worsening respiratory distress since 2 days
ago. 3 days prior to admission she had fever, cough and decreased appetite. Her physical examination showed
febrile infants, tachypnea with chest indrawing and rales in both lung. Chest X ray showed infiltrates with
pneumatocele. What is the possible etiology of the disease?
A. Streptococcus pneumoniae D. Klebsiella pneumoniae
B. Haemophilus Influenzae E. Chlamidya pneumoniae
C. Staphylococcus aureus
56.A 2 year old boy presents to the ER with 4 day history of vomiting, diarrhea and fever. The patient is lethargic
and has cracked lips, sunken fontanelle and skin turgor back slowly. Laboratory result : Na : 120 mEq/L, K : 4
mEq/L, Cl : 100 mEq/L, KGD : 45 mg/dL.
What are the priorities of management for this patient?
A. Bolus D 10 % 5 cc/kgBW D. Give HES 10 % 10 cc/KgBW
B. Bolus D 10% 2 cc/KgBW E. Give HES 6 % 20 cc/KgBW
C. Give RL 10 cc/KgBW
57.An 8 year-old girl with Steven Johnsons syndrome is being treated for septic shock in the ED. She has already
received 80 ml/kg isotonic saline, has been intubated and dopamine was intiated when her shock failed to
improve at 60 ml/kg. Her cardiopulmonary assement at this juncture reveals that her HR = 160 x/min, her
peripheries are warm, flushed, pulses are bounding and Capillary refil time is flash < 1 sec, BP = 80/50. Urine
output is less than 1 ml/kg/hr.
What vasoactive medication should be intiated first ?
A. Epinephrine C. Dobutamine
B. Dopamine D. Norepinephrine E. Milrinone
58.A group of toxic compounds that effect muscarinic is bronchoconstriction and increased bronchial secretions
while nicotine effects which cause irregular movement, muscle contraction, and weakness in the muscles of the
volunteers are:
A. Organophosphate C. Strichnine
B. Organochlorines D. Paraquat E. Cyanide
59.A 12 year old child comes to the ED pulseless. ECG reveals a wide complex tachycardia. Initial management
should be:
A. Immediate defibrillation D. Bolus Epinephrine
B. Immediate synchronized cardioversion E. Bolus Atropine
C. Give Adenosine
60.A 12-years old girl admitted to your clinic to have general check up in order to continue her study. On
physical examination: alert, blood pressure 100/60 mmHg, body temperature 36.60C. On laboratory examination
Hb 11.6 g/dL, WBC 9600/mm3, serum ureum 24 mg/dL, serum creatinine 0.7 mg/dL. Urinalysis: brown, protein
(-), WBC: 2-4/hpf, RBC 0-1/hpf. Urinary culture: Staphylococcus epidermidis 105 /cfu.
What is our management?
A. No antibiotics C. Intravenous antibiotics
B. Oral antibiotics D. Probiotics E. Antiinflammatory drugs
61.A 9-years old boy admitted to pediatric emergency with complaint of disability of urinary voiding. Before the
complaint, he ate jengkol bean. There was no swelling history. His breath was well. On physical examination he
was alert with blood pressure of 110/70 mmHg, pulse 110x/minutes, temperature 36.9 0C. On suprapubic area
there was a palpable mass. On laboratory examination: Serum ureum 80 mg/dL, Serum creatinine 1.1 mg/dL,
Sodium: 140 mEq/L, Potassium 5 mEq/L, Cl 105 mEq/L Blood gas analysis: pH 7,31, HCO3 16, Our working
diagnosis is:
A. Prerenal Acute kidney injury D. Chronic kidney disease stage I
B. Renal Acute kidney injury E.
C. Postrenal Acute kidney injury
62. A 10-years old boy admitted to outpatient clinic because of pale and fatigue. On physical examination he was
alert, blood pressure 140/90 mmHg, his nutritional state was weight for age < -3 SD, height for age < -3 SD.
Urinalysis revealed: Protein (+2), RBC: 2-4/hpf, WBC: 2-4/hpf. Serum ureum 400 mg/dL, serum creatinine
15mg/dL, Hb: 8.0 g/dL, Platelete count: 300,000/mm3 Renal ultrasound: hyperechoic small size on bilateral
kidney. What is the mostly possible diagnostic for this patient?
A. Acute kidney injury D. Hemolytic uremic syndrome
B. Acute on chronic kidney disease E. Interstitial nephritis
C. Chronic kidney disease
Ujian MCQ Nasional Tanggal 11 Juli 2018 |7
63. A 7 years old boy admitted to outpatient clinic with swelling for the first time on whole his body. Diuresis
1.2 mL/kgBW/hour. On physical examination he was alert with vital signs were within normal limit.
Urinalysis revealed protein (4+). Serum ureum: 20 mg/dL. Serum creatinine: 0.6 mg/dL. The most common
etiology for this disease is:
A. Genetic mutation D. Henoch-Schonlein Nephritis
B. Congenital origin E. Idiopathic
C. Systemic Lupus Erithematosus
64.A 7-years old boy admitted to pediatric emergency unit with chief complaint of dark cola coloured urine.
There was history of impetigo about three weeks ago. On physical examination: alert, blood pressure 170/110
mmHg, swelling on eyelids, on urine examination: RBC 20/hpf, WBC 0-1/hpf, protein (+1)
Laboratory examination we will suggest:
A. C-reactive protein (CRP) D. Anticardiolipin antibody (ACA)
B. Antistreptolysin O titer (ASOT) E. Antinuclear antibody (ANA)
C. Deoxyribonuclease B (DNAse B)
65.Drugs that be used in management congenital heart disease for definitive treatment is:
A. Digoxin in ventricular septal defect D. Ibuprofen in patent duct arteriosus
B. Furosemide in atrial septal defect E. Captopril in pulmonary hypertension
C. Spironolactone in rheumatic heart disease
66.Male, 15 years old was brought with chief complain of shortness of breath since 3 days ago. On auscultation
found pansystolic murmur grade 3/6 at 5th intercostal space midclavicular line radiate to left lateral and louder
when patient lying to the left.
The most probable diagnosis is:
A Acute rheumatic fever D. Dilated cardiomiopathy
B Chronic rheumatic heart disease E. Restrictive cardiomiopathy
C Congenital heart disease
67. A baby, 8 months come with chief complaint of fever 7 days ago. On physical examination found she is
irritable, eye hyperemia, rash on the skin, enlargement of limph node on the neck size 1.5 mm, erythema on
hand and foot.
The most probable diagnosis is:
A. Measles C. Rubella
B. Scarlet fever D. Kawasaki disease E. Acute rheumatic fever
68. A female, 12 years old come with chief complaint of palpitation. On auscultation found wide and fixed split
2nd heart sound, and ejection systolic murmur heard on the 2nd intercostal space left parasternal line. ECG
shows right ventricular hypertrophic. Chest X-rays show CTR 0.8, and apex upward.
The most probable diagnosis is:
A. Pulmonary stenosis C. Atrial septal defect
B. Tetralogy of Fallot D. Aortic stenosis E. Persistent foramen oval
69. A baby, 8 months old, body weight 6 kg, come with chief complaint irritable, there is feeding problem. She is
alert, heart rate 250 times per minute, murmur not clear. ECG showed heart rate 250 times per minute,
narrowed QRS complex, no P wave.
The management is:
A. Cardioversion C. Digoxin
B. Adenosine D. Verapamil E. Amiodarone
70. A girl, 8 month old, she has colic and bloody diarrhea since 2 weeks ago. From skin prick test showed
positive result of cow’s milk allergen. She still had breastmilk and she also had cow’s milk. She got
complimentary food since 6 month old.
What information that could be given to patient?
A. Consumed goat’s milk
B. Consumed partial hydrolized milk
C. Cow’s milk changed with extensive hydrolized
D. Elimination diet for mother is not recommended
E. Food should be eliminated from egg and seafood
******* Selamat Bekerja *******
Ujian MCQ Nasional Tanggal 11 Juli 2018 |8
Вам также может понравиться
- MCQ Ke-5 2009Документ10 страницMCQ Ke-5 2009WirawanSiregarОценок пока нет
- Soal MCQ Nasional 9 Januari 2019Документ15 страницSoal MCQ Nasional 9 Januari 2019Primadiati Nickyta SariОценок пока нет
- National knowledge-based pediatric evaluationДокумент16 страницNational knowledge-based pediatric evaluationDwi HerawatiОценок пока нет
- Soal Ika MCQ NasionalДокумент27 страницSoal Ika MCQ NasionalElly LutfiasariОценок пока нет
- (PAED) End-Posting Examination Questions (R3G1)Документ16 страниц(PAED) End-Posting Examination Questions (R3G1)loxОценок пока нет
- MCQ Oktober 02 2019Документ15 страницMCQ Oktober 02 2019Yosepha Jo100% (1)
- Bawasig Pediatric ExamДокумент20 страницBawasig Pediatric Examخلدون سليمОценок пока нет
- Blueprints QA Pediatrics For Step 3 1Документ59 страницBlueprints QA Pediatrics For Step 3 1Moataz Trabeh100% (1)
- MCQ Maret 2021Документ16 страницMCQ Maret 2021promkes poloОценок пока нет
- اذكرونا بدعوة Pediatric Theory Final ExamДокумент23 страницыاذكرونا بدعوة Pediatric Theory Final ExamSarwar Sarkawt100% (1)
- Pediatrics Problem Solving QsДокумент32 страницыPediatrics Problem Solving QsabozinaОценок пока нет
- MSQ Base 6 Year PDFДокумент71 страницаMSQ Base 6 Year PDFAtul KumarОценок пока нет
- Paediatrics and Child Health Practice Exam Questions and AnsweДокумент16 страницPaediatrics and Child Health Practice Exam Questions and AnsweGirmaОценок пока нет
- Peds Smle QsДокумент56 страницPeds Smle QsMarwa Tariq Ahmed Abdulla Ahmed Al MurbatiОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics MCQ of The Day-November, 2008Документ13 страницPediatrics MCQ of The Day-November, 2008Mohammad Salem100% (1)
- MCQ Nas Inggris 12 12 2013 Kirim PDFДокумент16 страницMCQ Nas Inggris 12 12 2013 Kirim PDFRoni ArmandaОценок пока нет
- Pediatric 5th year 2017-محلولДокумент27 страницPediatric 5th year 2017-محلولmotasem alsharifОценок пока нет
- B33 - Paeds PDFДокумент5 страницB33 - Paeds PDFEthan KhooОценок пока нет
- Pedes McqsДокумент16 страницPedes McqsSyeda Aroosa Abbas Naqvi100% (1)
- 4 5839111053702598026Документ7 страниц4 5839111053702598026خلدون سليمОценок пока нет
- Transposition of The Great ArteriesДокумент23 страницыTransposition of The Great Arterieswaseem mohammedОценок пока нет
- Paeds MCQs Part 1Документ34 страницыPaeds MCQs Part 1SsОценок пока нет
- Soal MCQ 3 Nov 2014Документ17 страницSoal MCQ 3 Nov 2014Funnie AdeliaОценок пока нет
- Pediatric Case Scenarios and QuestionsДокумент101 страницаPediatric Case Scenarios and QuestionsOwaisОценок пока нет
- Development and Vaccines PDFДокумент52 страницыDevelopment and Vaccines PDFDr-Jahanzaib GondalОценок пока нет
- Bonus Paeds MCQs With ExplanationsДокумент17 страницBonus Paeds MCQs With ExplanationsSsОценок пока нет
- K1 (Anamnesis & Pemeriksaan Fisis)Документ42 страницыK1 (Anamnesis & Pemeriksaan Fisis)Esther Meyline XhypaОценок пока нет
- MCQ Tropmed 25 Maret 2010 PublishДокумент27 страницMCQ Tropmed 25 Maret 2010 PublishDapot Sianipar100% (1)
- Clinico-Pathologic Conference 2015Документ43 страницыClinico-Pathologic Conference 2015Ezekiel ArtetaОценок пока нет
- First Part Exam - Feb 2020Документ16 страницFirst Part Exam - Feb 2020hassan mohamedОценок пока нет
- Part 1-2023 (1st Version)Документ19 страницPart 1-2023 (1st Version)Waleed SofiОценок пока нет
- MCQ 14 Juli 2021 + Pembahasan FINALДокумент50 страницMCQ 14 Juli 2021 + Pembahasan FINALAnonymous pJxkvPQgОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics One Liner For TestДокумент2 страницыPediatrics One Liner For TestArvindhanОценок пока нет
- Paediatric Question BankДокумент27 страницPaediatric Question BankBashiru SelemaniОценок пока нет
- Ped A Internship 1517300917 PDF 2Документ13 страницPed A Internship 1517300917 PDF 2dariasuslowaОценок пока нет
- FC Paed (SA) Part II Past Papers - 2013 1st Semester 8-4-2014Документ5 страницFC Paed (SA) Part II Past Papers - 2013 1st Semester 8-4-2014matentenОценок пока нет
- Khalid Alfaki PedДокумент21 страницаKhalid Alfaki PedAli HusseinОценок пока нет
- Soal MCQ Pediatric 2014 Bag 1Документ3 страницыSoal MCQ Pediatric 2014 Bag 1Lena PurbalinggihОценок пока нет
- 2006Документ60 страниц2006Anatoliy ShchurovskiyОценок пока нет
- Pediatric 6th Year 2016Документ30 страницPediatric 6th Year 2016motasem alsharifОценок пока нет
- Non Non-Surgical Selection August 2021Документ19 страницNon Non-Surgical Selection August 2021Majd HosamОценок пока нет
- Lembar Jawaban MCQ Nas 19 Okt 2017Документ1 страницаLembar Jawaban MCQ Nas 19 Okt 2017WirawanSiregarОценок пока нет
- 5th Year 112 PediatricsДокумент12 страниц5th Year 112 PediatricsAmjad A. AmirОценок пока нет
- Mock Exam 5 23 21Документ4 страницыMock Exam 5 23 21Anne Lorraine BringasОценок пока нет
- Super Final 220-Zoonotic Infectious Diseases Exam Questions 8 SOLVED by ANKIT AKELAДокумент37 страницSuper Final 220-Zoonotic Infectious Diseases Exam Questions 8 SOLVED by ANKIT AKELAYara AlmouallemОценок пока нет
- Mid Term Examination Papaer PEDSДокумент15 страницMid Term Examination Papaer PEDSHaslinОценок пока нет
- Diagnosing Ectopic PregnancyДокумент5 страницDiagnosing Ectopic PregnancyDrPreeti Thakur ChouhanОценок пока нет
- Imle A 03 03 2015Документ82 страницыImle A 03 03 2015Moataz TrabehОценок пока нет
- MCQ4FULLДокумент139 страницMCQ4FULLBruta Brutal100% (2)
- PEDIATRICSДокумент51 страницаPEDIATRICSJoanne BlancoОценок пока нет
- SAQs PaediatricsДокумент43 страницыSAQs Paediatricss336336anl100% (1)
- Name: - Date: - Date of Rotation: - Score: - Pediatrics Shifting ExamДокумент5 страницName: - Date: - Date of Rotation: - Score: - Pediatrics Shifting ExamKristine Seredrica100% (1)
- NeomcqДокумент32 страницыNeomcqSyeda Aroosa Abbas NaqviОценок пока нет
- Clinicopathological Conference 2Документ23 страницыClinicopathological Conference 2Rem AlfelorОценок пока нет
- Pediatrics BookДокумент53 страницыPediatrics BookMobin Ur Rehman Khan100% (1)
- All Pediatrics 2Документ200 страницAll Pediatrics 2niemand daОценок пока нет
- Medical Council's Pre-Registration Exam HandbookДокумент47 страницMedical Council's Pre-Registration Exam HandbookBilal ShoaibОценок пока нет
- MCQ April 27th, 2020Документ10 страницMCQ April 27th, 2020Yosepha JoОценок пока нет
- Paeds MCQs For ReviewДокумент14 страницPaeds MCQs For Reviewsapiens HomoОценок пока нет
- Cutaneous Manifestations of Juvenile Onset Lupus Erythematosus: A Clinical StudyДокумент5 страницCutaneous Manifestations of Juvenile Onset Lupus Erythematosus: A Clinical StudyMaya SusantiОценок пока нет
- Harry 2018Документ11 страницHarry 2018Feby Arin BindaОценок пока нет
- Vasculitis in Juvenile-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Eve M. D. Smith, Hanna Lythgoe and Christian M. HedrichДокумент9 страницVasculitis in Juvenile-Onset Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Eve M. D. Smith, Hanna Lythgoe and Christian M. HedrichMaya SusantiОценок пока нет
- Jurnal KardiologiДокумент33 страницыJurnal KardiologiMaya SusantiОценок пока нет
- Belajar EKGДокумент12 страницBelajar EKGMaya SusantiОценок пока нет
- HEMATOLOGIДокумент4 страницыHEMATOLOGIMaya SusantiОценок пока нет
- Neonatal Sepsis: Ekawaty Lutfia Haksari Perinatology, Department of Child Health Gadjah Mada UniversityДокумент28 страницNeonatal Sepsis: Ekawaty Lutfia Haksari Perinatology, Department of Child Health Gadjah Mada Universityireneaurelia100% (1)
- Pakar ImunisasiДокумент38 страницPakar ImunisasiMifaul AzmiОценок пока нет
- HEMATOLOGIДокумент4 страницыHEMATOLOGIMaya SusantiОценок пока нет
- ID Hubungan Pemberian Imunisasi Dasar Denga PDFДокумент8 страницID Hubungan Pemberian Imunisasi Dasar Denga PDFVendrha 0895Оценок пока нет
- Organogenesis GlomerulusДокумент9 страницOrganogenesis GlomerulusMaya SusantiОценок пока нет
- PGD03 Pemantauan Hemodinamik QДокумент3 страницыPGD03 Pemantauan Hemodinamik QMaya SusantiОценок пока нет
- Presentation Illustrating The 2017 Classification of Seizure TypesДокумент54 страницыPresentation Illustrating The 2017 Classification of Seizure TypesMohamad Syaikhul IslamОценок пока нет
- Lap 2017Документ6 страницLap 2017Maya SusantiОценок пока нет
- Managing Acute Kidney Injury: An Overview of Current Treatment ApproachesДокумент26 страницManaging Acute Kidney Injury: An Overview of Current Treatment ApproachesMaya SusantiОценок пока нет
- TG226 IGRT Commissioning PDFДокумент15 страницTG226 IGRT Commissioning PDFmarkОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Nursing NCLEX Practice Quiz 2 (30 Items) : About Privacy Disclaimer ContactДокумент26 страницFundamentals of Nursing NCLEX Practice Quiz 2 (30 Items) : About Privacy Disclaimer ContactAkia Cayasan BayaОценок пока нет
- Contoh Jurnal Case ControlДокумент7 страницContoh Jurnal Case Controlkrisnantara7Оценок пока нет
- TM S Fusion Device Trabecular Metal Technology Cervical Solutions Surgical Technique GuideДокумент24 страницыTM S Fusion Device Trabecular Metal Technology Cervical Solutions Surgical Technique GuideTiến Khổng MinhОценок пока нет
- SNB QuestionsДокумент7 страницSNB Questionshardie himerОценок пока нет
- Bacterial Flora in Digestive Disease Focus On Rifaximin C. Scarpignato Et. Al. Karger 2008 WWДокумент156 страницBacterial Flora in Digestive Disease Focus On Rifaximin C. Scarpignato Et. Al. Karger 2008 WWFantasyoflove VallyОценок пока нет
- Cucurmin and Fennel For Parasite Infection, Cancer, Lugols EnemasДокумент4 страницыCucurmin and Fennel For Parasite Infection, Cancer, Lugols Enemaspaulxe100% (1)
- Job Responsibilities of Medical Officer and Other StaffДокумент18 страницJob Responsibilities of Medical Officer and Other StaffAlpit Gandhi100% (4)
- Biomarker Discovery in Cardio-Oncology.Документ8 страницBiomarker Discovery in Cardio-Oncology.Ștefan SpînuОценок пока нет
- Brosur BIOCARE HAV IgM Rapid Test Device OKДокумент1 страницаBrosur BIOCARE HAV IgM Rapid Test Device OKAlfarizi Julistyo S.Оценок пока нет
- Text Atlas of Wound Management (2012)Документ232 страницыText Atlas of Wound Management (2012)Alex Messi83% (12)
- Methodical Instructions: For The Practical Classes in Pharmacology TopicДокумент3 страницыMethodical Instructions: For The Practical Classes in Pharmacology TopicSahil SainiОценок пока нет
- Kelly Wright hw499 Unit 4 AssignmentДокумент9 страницKelly Wright hw499 Unit 4 Assignmentapi-526258935Оценок пока нет
- Prudent Religare Employee Benefit ManualДокумент24 страницыPrudent Religare Employee Benefit ManualSheikh AtifОценок пока нет
- 4 5771463918631256090Документ516 страниц4 5771463918631256090abdulОценок пока нет
- Health Promotion "Exclusive Breast Milk"Документ3 страницыHealth Promotion "Exclusive Breast Milk"Linda SaputriОценок пока нет
- GPP Conference Yields Strategies and Declaration for SE AsiaДокумент83 страницыGPP Conference Yields Strategies and Declaration for SE AsiaMaria Wisnu DonowatiОценок пока нет
- Nursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionДокумент2 страницыNursing Crib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Spontaneous AbortionJustin PasaronОценок пока нет
- Hiponatremia Predicts Length of Hospital Stay in ADHF PatientsДокумент4 страницыHiponatremia Predicts Length of Hospital Stay in ADHF PatientsMayang Sri WulandОценок пока нет
- Code Stroke AlgorithmДокумент1 страницаCode Stroke AlgorithmZharifah Fauziyyah NafisahОценок пока нет
- Disturbances of CirculationДокумент10 страницDisturbances of CirculationSuhan HasanОценок пока нет
- Project in MAPEHДокумент14 страницProject in MAPEHRamel Yen CerantesОценок пока нет
- Naming, Labeling, and Packaging of Pharmaceuticals: Special FeaturesДокумент9 страницNaming, Labeling, and Packaging of Pharmaceuticals: Special FeaturesjovanaОценок пока нет
- An Interprofessional Web Based Teaching Module To.9Документ4 страницыAn Interprofessional Web Based Teaching Module To.9Em Wahyu ArОценок пока нет
- Atcn 2022Документ10 страницAtcn 2022Al RadyaОценок пока нет
- Fendo 13 967102Документ9 страницFendo 13 967102Vilma Gladis Rios HilarioОценок пока нет
- TeratologyДокумент36 страницTeratologySafera RezaОценок пока нет
- Picot Presntation 2Документ18 страницPicot Presntation 2api-650274498Оценок пока нет
- Evaluating Lawyer-Client Communication with International Research ProjectДокумент29 страницEvaluating Lawyer-Client Communication with International Research ProjectabctandonОценок пока нет
- Skizo JurnalДокумент7 страницSkizo JurnalCikgu ZahranОценок пока нет