Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
07 12 17
Загружено:
Amit NampalliwarОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
07 12 17
Загружено:
Amit NampalliwarАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
MODE OF ACTION OF “TRIPHALA GUGGULU” IN MANAGEMENT OF MEDA
SANCHAYA JANYA YAKRIT YIKAR W.S.R. TO NON ALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER
DISEASE (NAFLD)
ABSTRACT
Avyayama, Divaswapna and excessive intake of Medasvi Dravya are the causative factors of
Medavaha Srotodushti. Excessive intake of these Ahar Vihara leads to Jatharagni Mandata and
decrease the Medodhatwagni, which leads to Medavriddhi. Excessive Meda deposits in the
various parts and organs of body including Yakrit, causes fatty liver, which in lack of treatment
can cause serious conditions. Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) can occur at all ages
including childhood, though the highest prevalence is described in those between 35– 45 years of
age. With some limitations, both population and hospital-based studies from the West report that
around 10–24% of general population, and 57–74% of obese individual may have Non Alcoholic
Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). The corresponding rates for Non Alcoholic Steato Hepatitis
(NASH) are 3–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Keywords:- Meda, Medodhatwagni, Yakrita, NAFLD, NASH
INTRODUCTION
Fatty Liver has become one of the major global health concerns worldwide. It is the most
common cause of liver-related morbidity and mortality in under-developed and developing
countries. Because of its potential to cause life threatening complications it has been kept on the
top of agenda in public health administrations. Here we have considered about Fatty Liver
Disease because of its prevalence, tendency to cause cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Meda is an important Dhatu of body, which in its natural state, maintains Snigdhata and
provides Bala to body. But when the quantity of Meda increases from normal, it causes various
structural and functional abnormalities inside body. According to Acharya Charakai Avyayama,
Divaswapna, excessive intake of Medasvi Dravya and Varuni Madya are the causative factors of
Medavaha Srotodushti. Excessive intake of these Ahar Vihara leads to Jatharagni Mandata and
decrease the Medodhatwagni, which leads to Medavriddhi so that Excessive Meda deposits in
the various parts and organs of body including Yakrita, which impairs the proper function of this
organ. The excessive fat deposit inside liver causes fatty liver, which in lack of treatment can
cause serious conditions.
The prevalence of fatty liver disease in India is found to be as high as 24%, which is
similar to that reported in some of the Western countries, where it correlates with the prevalence
of obesity. NAFLD can occur at all ages including childhood, though the highest prevalence is
described in those between 35– 45 years of age. With some limitations, both population and
hospital-based studies from the West report that around 10–24% of general population, and 57–
74% of obese individuals may have NAFLD. The corresponding rates for NASH are 3–4% and
15–20%, respectivelyii. Commented [WU1]: All references should be in Numerical
Aims & Objectives:
The main aim of the article is to study the mode of action of Triphala Guggulu in Medasanchaya
in liver (NAFLD).
Material & Methods: Commented [WU2]: Please write- Drug administration, Dose
Duration and time
Important manuscripts of Avurveda such as Charak Samhita, Sushrut Samhita, Dravya Guna,
Bhaisaija Ratnavali along with Rasa Shastra, literature like Ras Ratna Samuchya and Ayurvedic
formulary of India are the sources of various preparation of Ayurvedic medicines. Beside this, we
also search out different formulations containing ingredients of Triphala Guggulu in Ayurvedic
classics as well as different search engines like Pubmed, Google Scholars etc, and other
pharmacological journals to find out the probable mode of action in relation to NAFLD.
Ayurvedic Properties:
Triphala Guggulu is mentioned in Sharangdhar Samhita, Madhya Khandaiii, with its special
indication in Shooth, Arsh and Bhagandar chikitsa. In Triphala Guggulu, Haritaki 1 part,
Vibhitaki 1 part, Aamalaki 1 part, Pippali 1 part and Shudh Guggulu 5 part, to be taken with
Luke warm water as Anupana.
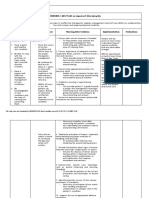
Rasapanchaka of Triphala Guggulu
Drug Rasa Guna Veerya Vipaka Karma
Haritaki Kashaya Pradana Laghu, Ruksha Ushna Madhur Tridoshaghana
Panchrasa (Kaphavatashamaka)
Vibhitaki Kashaya Laghu, Ruksha Ushna Madhur Tridoshaghana
(Kaphavatashamaka)
Aamalaki Amla Pradana Panchrasa Guru, Ruksha, Sheeta Sheeta Madhur Tridoshaghana
Pippali Katu Laghu, Snigdha, Anushna Madhur Kaphavatashamaka
Tikshna Sheeta
Guggulu Katu, Tikta Laghu, Ruksha Ushna Katu Tridoshaghana
Tikshna, Vishada,
Suksham, Sara
a) On the basis of Rasa
Katu, Tikta and Kashaya Rasa are present in maximum drugs. Katu Rasa has Deepana; Sneha-
Kleda- Sweda- Abhishyandinashaka; Kapha Shamaka and Srotoshodaka properties. Katu Rasa is
formed by Vayu and Agni Mahabhutaiv having qualities opposite to Kapha (Prithvi and Jala),
thus helps in reducing excessive Meda deposition in NAFLD. Tikta rasa has also got Deepana,
Lekhana, Kleda-Meda-Vasa-Sweada Shoshana and Pachana propertiesv. Tikta Rasa is a
combination of Vayu and Akasha Mahabhutavi. Substances that are made up of Vayu Mahabhuta
cause Rukshta and Laghuta in the body whereas Akasha Mahabhuta causes Laghuta in the body
thereby reducing excessive Meda Dhatuvii. These two Mahabhuta have qualities opposite to
Kapha. Tikta Rasa also shows Chedana and Shodhana propertiesviii. Kashaya Rasa is mainly
formed by conjugation of Vayu and Prithvi Mahabhuta. Vayu is Ruksha in quality and dries up
the excessive Sneha present in the body while Prithvi by virtue of Kathina and Sthira Guna
which are opposite to Drava and Sara Guna reduces the Shaithilta. Kashaya Rasa has Shoshana,
Kledanashak and Sleshamaprashaman propertiesix. So it clarifies the Srotorodha and scraps
excess Medodhatu from Liver and dries up excessive Meda.
b) On the basis of Guna:
Maximum contents possess Laghu, Ruksha properties. Laghu Guna increases the Agni
and decreases Kapha. It produces Laghuta in the body. Ruksha Guna may pacify vitiated Kapha
and Kleda due to its Shoshana Karmax. Laghu Guna also pacifies the Snigdha and Pichchila
properties of vitiated Kapha by the virtue of its Langhana and Lekhana Karmaxi. To cure
Srotodushti caused by Abhishyandi, property of Ama Shoshana Karma is required.
So, Triphala Guggulu is one of the ideal combination for the management of NAFLD;
having maximum ingredients possessing Katu, Tikta and Kshaya Rasa; Laghu, Ruksha Guna;
Ushna Virya; Katu-Vipaka ;VataKaphashamaka; Lekhaniya Medohara, Ama Pachana,
Dhatushoshana property which normalize the state of Agni and Srotas. Thus regulated Agni
checked the excessive accumulation of Medodhatu in Liver.
c) On the basis of Virya:
Contents of drug are mainly having Ushna Virya and rests are Sheeta Virya, but the most of
Sheeta Virya drugs are Mridu. Ushna Virya suppresses the action of Sheeta Virya drugs and due
to Agni Mahabhuta Pradanta, it possesses Vata and Kaphahara propertyxii.
d) On the basis of Vipaka:
Drugs having Katu Vipaka acts by their Kapha Shamaka property while drugs with Madhura
Vipaka acts as Rasayana e.g. Amalaki, Haritaki etc.
DISCUSSION
The disease NAFLD originates due to consumption of Kapha Vriddhikara Aahara Vihara and
Anya Nidana. These factors derange Jatharagni causing Ama Aanarasa which results in
Medodhatu Agnimandya. This condition leads to excessive accumulation of Medo Dhatu in
Liver causing the disease NAFLD. In Ayurveda, the action of drugs is executed in the body
through its pharmaco dynamics properties like Rasa, Guna, Veerya, Vipaka along with these
Prabhava is the specific property inherited by the drug which cannot be explained and the
principle of treatment in Ayurveda is based on Samprapti Vighatana which is achieved by
relieving Dosha Dushya Sammurchana. In the pathology of Meda Sanchaya Janya Yakrit Yikar,
Kapha is main Dosha and Meda is main Dushya, while Agnimandya takes place at
Medodhatvagni level. So, drug having Kapha and Medanashaka property and efficacy to correct
the function of Medodhatvagnimandya is effective to control Meda Sanchaya Janya Yakrit Yikar
(NAFLD).
So, Triphala Guggulu is one of the ideal combination for the management of
NAFLD; having maximum ingredients possessing Katu, Tikta and Kshaya Rasa; Laghu, Ruksha
Guna; Ushna Virya; Katu-Vipaka; VataKaphashamaka; Lekhaniya Medohara, Ama Pachana,
Dhatushoshana property which normalize the state of Agni and Srotas. Thus regulated Agni
checked the excessive accumulation of Medodhatu in Liver and management of NAFLD. By
virtue of its Rasapanchaka, contents of drug are very well indicated in Kapha predominant
pathologiesxiii. Due to this property, it breaks the Samprapti of disease.
CONCLUSION
On the basis of above observations it is concluded that Triphala Guggulu is effective in the
treatment of Meda Sanchaya in liver w.s.r to non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Commented [WU3]: Please write clinical data for efficacy,
statistical analysis
i
Agnivesha, Charak samhita, edited by pandit kaashinath pandey and gorakhnaath chaturvedi, , Chaukhambha
Publication, Varanasi, India, viman sthan -6/16
ii
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Caldwell SH. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: summary of an AASLD single topic
conference. Hepatology. 2003;37:1202–19.
iii
Sharangdhar Samhita, Madhya Khanda - 7/82-83.
iv
Agnivesha, Charak samhita, edited by pandit kaashinath pandey and gorakhnaath chaturvedi, , Chaukhambha
Publication, Varanasi, India, , Sutra sthan – 26/40
v
Sushrut,Sushrut Samhita, Twelvth edition, (2001), edited by Ambikadutta Shastri, Chaukhambha Publication,
Varanasi, India, Sutra sthan – 42/16
vi
Agnivesha, Charak samhita, edited by pandit kaashinath pandey and gorakhnaath chaturvedi, , Chaukhambha
Publication, Varanasi, India, , Sutra sthan – 26/40
vii
Sushrut,Sushrut Samhita, Twelvth edition, (2001), edited by Ambikadutta Shastri, Chaukhambha Publication,
Varanasi, India, Sutra sthan – 42/16
viii
Sushrut,Sushrut Samhita, Twelvth edition, (2001), edited by Ambikadutta Shastri, Chaukhambha Publication,
Varanasi, India, Sutra sthan – 42/17
ix
Agnivesha, Charak samhita, edited by pandit kaashinath pandey and gorakhnaath chaturvedi, , Chaukhambha
Publication, Varanasi, India, Sutra Sthan – 26/43
x
Ashtang Hridya, Ravi Dutt Tripathi, Reprint year 2016, Chaukhambha Bharati Academy, Varanasi, Sutra Sthana,
pg. 14
xi
Ashtang Hridya, Ravi Dutt Tripathi, Reprint year 2016, Chaukhambha Bharati Academy, Varanasi, Sutra Sthana,
pg. 14
xii
Sushrut,Sushrut Samhita, Twelvth edition, (2001), edited by Ambikadutta Shastri, Chaukhambha Publication,
Varanasi, India, Sutra sthan – 41/15
xiii
Agnivesha, Charak samhita, edited by pandit kaashinath pandey and gorakhnaath chaturvedi, , Chaukhambha
Publication, Varanasi, India, , Sutra sthan – 21/23
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Vaccine Research StatusДокумент112 страницVaccine Research StatusJunko Tsukuda100% (1)
- Researchers and by Clinicians For Use With Their PatientsДокумент3 страницыResearchers and by Clinicians For Use With Their PatientsAnton Henry MiagaОценок пока нет
- EmekaДокумент17 страницEmekamutiyasОценок пока нет
- Cardiac Case Study NDДокумент11 страницCardiac Case Study NDapi-313165458Оценок пока нет
- Chorea Continuum 2019Документ35 страницChorea Continuum 2019nicolasОценок пока нет
- 4 - Tracheostomy Care and SuctioningДокумент4 страницы4 - Tracheostomy Care and SuctioningABEGAIL BALLORANОценок пока нет
- Preoperative Assessment ChecklistДокумент27 страницPreoperative Assessment ChecklistHairina MazlanОценок пока нет
- Greater Political ParticipationДокумент12 страницGreater Political ParticipationBe-COOL State Of MindОценок пока нет
- Differences Between T.solium and T.saginata: Taeniasis or CysticercosisДокумент3 страницыDifferences Between T.solium and T.saginata: Taeniasis or CysticercosisVenkatapradeepОценок пока нет
- Journal TetanusДокумент10 страницJournal TetanusWinariieeyy NayyОценок пока нет
- Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Volume 2 - Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Therapeutic Applications in Disease and Injury - Volume 2Документ409 страницStem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Volume 2 - Stem Cells and Cancer Stem Cells, Therapeutic Applications in Disease and Injury - Volume 2ArtanОценок пока нет
- Use of Local and Axial Pattern Flaps For Reconstruction of The Hard and Soft Palate PDFДокумент9 страницUse of Local and Axial Pattern Flaps For Reconstruction of The Hard and Soft Palate PDFJose Luis Granados SolerОценок пока нет
- CLINICAL CHEMISTRY 2 Tumor MarkersДокумент3 страницыCLINICAL CHEMISTRY 2 Tumor MarkersSuzzaine EniazzusОценок пока нет
- Ch.12 Getting the measure of hormones講義Документ7 страницCh.12 Getting the measure of hormones講義邱小瀧Оценок пока нет
- Overweight, Hypertension and Heart Disease ClassificationsДокумент4 страницыOverweight, Hypertension and Heart Disease Classificationsjagadish chandra prasadОценок пока нет
- Asama PosterДокумент1 страницаAsama Postershuvojit moulikОценок пока нет
- Back Pain Differential DiagnosisДокумент9 страницBack Pain Differential DiagnosisSachin KpОценок пока нет
- Risk Prediction Model for Heart Failure in DiabetesДокумент20 страницRisk Prediction Model for Heart Failure in DiabetesjamesboendОценок пока нет
- What Are The Different Types of Stress?Документ2 страницыWhat Are The Different Types of Stress?Полина КосьминаОценок пока нет
- Instructions For Use: Home Sperm Test For Male FertilityДокумент2 страницыInstructions For Use: Home Sperm Test For Male FertilityRAVAN ZJОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Orientation To PharmacologyДокумент4 страницыChapter 1 - Orientation To Pharmacologydlneisha61Оценок пока нет
- Jadwal Emsb FebДокумент2 страницыJadwal Emsb FebArdianto SucintaОценок пока нет
- Prostrolane Intra Articular en INGLESДокумент6 страницProstrolane Intra Articular en INGLESjuanОценок пока нет
- NURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin IntegrityДокумент3 страницыNURSING CARE PLAN On Impaired Skin IntegrityAngelika VeluzОценок пока нет
- Annex A. ChecklistДокумент2 страницыAnnex A. ChecklistroseannurakОценок пока нет
- The Privacy Isuues of AppleДокумент7 страницThe Privacy Isuues of Applephysicser15Оценок пока нет
- Act 1. PhobiasДокумент2 страницыAct 1. PhobiasRoxanne CastilloОценок пока нет
- Nurs FPX 4050 Assessment 4 Final Care Coordination PlanДокумент6 страницNurs FPX 4050 Assessment 4 Final Care Coordination PlanEmma WatsonОценок пока нет
- Chapter 27 - Anxiety-Related, Obsessive-Compulsive, Trauma and Stressor-Related, Somatic, and Dissociative DisordersДокумент10 страницChapter 27 - Anxiety-Related, Obsessive-Compulsive, Trauma and Stressor-Related, Somatic, and Dissociative DisordersKTОценок пока нет
- 1 SMДокумент6 страниц1 SMmaryano 0015Оценок пока нет