Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Bag Filter Calculation
Загружено:
desgnhpОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Bag Filter Calculation
Загружено:
desgnhpАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
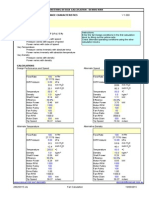
PULSE JET BAG FILTER DESIGN
Flow gas rate
Temperture
Concentration of the dust in gases
Average diameter of the particle in dust
Tye of dust to be handled
Calculation of filtering area
Total filtering area required as per Calculation
Volume occupied by filter
Consumption of Compressure Air
Surface occupied by the filter
Assumptions of bag size
Diameter of the bags to be fixed
Length of the bags
No of bags required
DISTRIBUTION
Number of Rows in the Bag house
Number of Columns in the Bag house
Formulas used in designing
The filtering surface (SF) given in m2 is estimated using the following expression:
SF m 2 0.26 F c0.18 350 0.5
Where:
F = gas flow at 25 °C given in m3/min
c = concentration of dust given in g/m3
φ = average diameter of the particle, in μm
For example, con F=700 m3/min , c = 40 g/m3, φ = 50 μm :
SF m 2 0.26 700 (40) 0.18 350 (50) 0.5 403m 2
3
Volume occupied by the filter (m ) = 0.33 · SF; 133 m3 for the example
Consumption of compressed air (Nm3/h) = 0.215 · SF; 87 Nm3/h for the example
2
Surface occupied by the filter (m ) = 0.047 · SF; 19 m2 for the example
In case the values of “c” and “φ” are unkown, an appropriate expression is:
SF m 2 0.014 Q, Q must be given in Nm 3 / h
PULSE JET BAG FILTER DESIGN
110000 m3/hr
120 degree C
e dust in gases 50 gm/m3
f the particle in dust 100 µm
Cement
required as per Calculation 842.5 m2
278.0 m3
mpressure Air 181.1 Nm3/hr
39.6 m2
gs to be fixed 0.15 m
3.5 m
505 nos
the Bag house 10 nos
s in the Bag house 51 nos
ssion:
= 0.33 · SF; 133 m3 for the example
= 0.215 · SF; 87 Nm3/h for the example
SF; 19 m2 for the example
:
Вам также может понравиться
- Bag Filter CalculationДокумент3 страницыBag Filter Calculationbeemasundar100% (1)
- PULSE JET BAG FILTER DESIGNДокумент2 страницыPULSE JET BAG FILTER DESIGNbasavaraju535Оценок пока нет
- Bag Filter CalculationДокумент4 страницыBag Filter CalculationJag Khadse100% (1)
- Bag Filter CalculationДокумент2 страницыBag Filter Calculationjenifferrayen71% (7)
- Rotary Airlock Valve PDFДокумент15 страницRotary Airlock Valve PDFPIY777Оценок пока нет
- Airslide Calculation Form Project: Department: Equipment NoДокумент3 страницыAirslide Calculation Form Project: Department: Equipment NoManoj Thakur0% (1)
- Rotary ValveДокумент2 страницыRotary Valvechem_taОценок пока нет
- Airslide CalculationДокумент1 страницаAirslide Calculationsunil_supeda33% (3)
- Belt Selection CalculationДокумент29 страницBelt Selection CalculationElwathig BakhietОценок пока нет
- Bucket Elevator Capacity Formulas REVISEDДокумент1 страницаBucket Elevator Capacity Formulas REVISEDbrpnaidu2157Оценок пока нет
- Id Fan Size CalcДокумент1 страницаId Fan Size CalculhatolkargmailcomОценок пока нет
- JETFLEX Kiln Burner: Installation, Operation and Maintenance InstructionsДокумент42 страницыJETFLEX Kiln Burner: Installation, Operation and Maintenance InstructionsJCSОценок пока нет
- Wetscrubber VenturiДокумент10 страницWetscrubber Venturiakifah100% (1)
- Design Guide For Air Slide Conveyor PDFДокумент4 страницыDesign Guide For Air Slide Conveyor PDFHasan Barzegar Avval100% (4)
- Bag Filter Selector: Filter Type: C (For This Type of Filter Contact Area Genovese)Документ8 страницBag Filter Selector: Filter Type: C (For This Type of Filter Contact Area Genovese)Ashish GulabaniОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 D1 CEMA Bucket Elevator HP and CalculationsДокумент4 страницыChapter 13 D1 CEMA Bucket Elevator HP and Calculationshafidh naufaldiОценок пока нет
- Screw Conveyor Excel CalculationДокумент8 страницScrew Conveyor Excel CalculationRaji Suri33% (9)
- Kiln Pre Heater Fan Power CalculationДокумент4 страницыKiln Pre Heater Fan Power CalculationVijay Bhan67% (3)
- Raw grinding mill capacity calculationДокумент6 страницRaw grinding mill capacity calculationBùi Hắc HảiОценок пока нет
- Bag Filter Calculation PDFДокумент4 страницыBag Filter Calculation PDFArun Gupta71% (7)
- Cement Ball-Mill-Heat-BalanceДокумент3 страницыCement Ball-Mill-Heat-Balanceanurag soni100% (1)
- Cement MillДокумент19 страницCement MillBùi Hắc HảiОценок пока нет
- Bag Filter Himenviro - O&m - Cement MillДокумент51 страницаBag Filter Himenviro - O&m - Cement Millsambhu0% (1)
- Air Slide Conveyor Design RequirementsДокумент1 страницаAir Slide Conveyor Design RequirementsayaskantkОценок пока нет
- Bag Filters Types, Working Principles & Daily Maintenance - INFINITY FOR CEMENT EQUIPMENT PDFДокумент14 страницBag Filters Types, Working Principles & Daily Maintenance - INFINITY FOR CEMENT EQUIPMENT PDFRICARDOALEXBORGES100% (2)
- Example 1 For Gearbox SelectionДокумент11 страницExample 1 For Gearbox SelectionNakkolop100% (1)
- TWO WAY DIVERTER - Technical-SpecificationДокумент94 страницыTWO WAY DIVERTER - Technical-Specificationmanoj983@gmail.comОценок пока нет
- How To Select A Rotary AirlockДокумент1 страницаHow To Select A Rotary Airlockshreemug100% (1)
- Screw Conveyor DesignДокумент14 страницScrew Conveyor DesignIrwan SattuОценок пока нет
- Vertical Mill CalculationsДокумент12 страницVertical Mill CalculationsAbhijeet Jhankal100% (1)
- Bag Filter Design CalculationsДокумент2 страницыBag Filter Design CalculationsSnehendu Biswas69% (13)
- Ventilation Blower Sizing Calculation for Tank StorageДокумент1 страницаVentilation Blower Sizing Calculation for Tank Storagevijayamalraj67% (3)
- Fan CalcДокумент1 страницаFan CalcGregory Nick Toledo VelizОценок пока нет
- Heat & Mass Equation For CementДокумент99 страницHeat & Mass Equation For Cementamit100% (1)
- Thermal design of water cooled ductДокумент8 страницThermal design of water cooled ductpavan100% (1)
- Conveyor Design Summary ReportДокумент1 страницаConveyor Design Summary ReportAlejandro Castro0% (1)
- SOP - Kiln Stopping ProcedureДокумент2 страницыSOP - Kiln Stopping ProcedureJCS100% (1)
- Blower CalculationДокумент7 страницBlower CalculationOA AooОценок пока нет
- Air in Standard and Normal ConditionДокумент2 страницыAir in Standard and Normal ConditionJoko DewotoОценок пока нет
- Typical Cement Mill Bag Filter Capital Cost CamparisonДокумент1 страницаTypical Cement Mill Bag Filter Capital Cost CamparisonKenny RuizОценок пока нет
- Calculate Bucket Elevator CapacityДокумент2 страницыCalculate Bucket Elevator CapacityBùi Hắc HảiОценок пока нет
- An Introduction to Fabric FiltersДокумент51 страницаAn Introduction to Fabric FiltersKaffelОценок пока нет
- System Characteristic Curve Shows Ventilation System Pressure LossДокумент5 страницSystem Characteristic Curve Shows Ventilation System Pressure LossMichael LagundinoОценок пока нет
- Material Residence Time in KilnДокумент2 страницыMaterial Residence Time in KilnVijay Bhan100% (2)
- Low NOx Rotary Kiln Burner TechnologyДокумент6 страницLow NOx Rotary Kiln Burner TechnologyKristínaОценок пока нет
- Pulse Jet Bag Filter Design: SF = 0 - 26⋅F⋅c + 350⋅φДокумент2 страницыPulse Jet Bag Filter Design: SF = 0 - 26⋅F⋅c + 350⋅φbasavaraju535Оценок пока нет
- Differential Pressure Across VenturiДокумент3 страницыDifferential Pressure Across VenturiAamirMalikОценок пока нет
- PULSE JET BAG FILTER DESIGNДокумент3 страницыPULSE JET BAG FILTER DESIGNNITIN P SHAHОценок пока нет
- Dust CollectionДокумент2 страницыDust CollectionRavindra DarjiОценок пока нет
- Bag Filter CalculationДокумент3 страницыBag Filter CalculationJag KhadseОценок пока нет
- FMR 1250Документ7 страницFMR 1250Shine Water ExpertsОценок пока нет
- Slug Catcher SizingДокумент6 страницSlug Catcher SizingrezaОценок пока нет
- Smoke - Ventilation CalculationsДокумент8 страницSmoke - Ventilation CalculationsdasmechОценок пока нет
- Fire Water & Foam Demand CalculationДокумент1 страницаFire Water & Foam Demand CalculationMohsin Shaikh100% (1)
- High Pressure Knock Out Drum (ALF)Документ12 страницHigh Pressure Knock Out Drum (ALF)Eng AlfОценок пока нет
- Degasser Tower CalculationДокумент1 страницаDegasser Tower Calculationbalaji krishnan100% (1)
- Fire Water DemandДокумент7 страницFire Water DemandamolbagadeОценок пока нет
- SAFF reactor design and specificationsДокумент4 страницыSAFF reactor design and specificationsRakesh Verma100% (2)
- Genset Ventilation System DesignДокумент3 страницыGenset Ventilation System Designabuya3kubmОценок пока нет
- Bag House Filter DesignДокумент5 страницBag House Filter DesignShermal FernandoОценок пока нет
- Crane Maintenance Check ListДокумент3 страницыCrane Maintenance Check ListdesgnhpОценок пока нет
- Monthly Maintenance ScheduleДокумент2 страницыMonthly Maintenance ScheduledesgnhpОценок пока нет
- 6620 Crane Manual 700 20013Документ108 страниц6620 Crane Manual 700 20013desgnhpОценок пока нет
- Firk-Lift Maintenance Check ListДокумент3 страницыFirk-Lift Maintenance Check ListdesgnhpОценок пока нет
- Maintenance History Card - For Each MachineДокумент2 страницыMaintenance History Card - For Each MachinedesgnhpОценок пока нет
- Nozzle Schedule: - : General DataДокумент1 страницаNozzle Schedule: - : General DatadesgnhpОценок пока нет
- 3 SMPLДокумент1 страница3 SMPLdesgnhpОценок пока нет
- 144Документ73 страницы144desgnhpОценок пока нет
- Vinati Organics' PAP project to drive 95% revenue growthДокумент21 страницаVinati Organics' PAP project to drive 95% revenue growthsujay85Оценок пока нет
- Welding DataДокумент8 страницWelding DatadesgnhpОценок пока нет
- Database Chapter 11 MCQs and True/FalseДокумент2 страницыDatabase Chapter 11 MCQs and True/FalseGauravОценок пока нет
- Mba Assignment SampleДокумент5 страницMba Assignment Sampleabdallah abdОценок пока нет
- Railway RRB Group D Book PDFДокумент368 страницRailway RRB Group D Book PDFAshish mishraОценок пока нет
- Sta A4187876 21425Документ2 страницыSta A4187876 21425doud98Оценок пока нет
- Leases 2Документ3 страницыLeases 2John Patrick Lazaro Andres100% (1)
- Laundry & Home Care: Key Financials 1Документ1 страницаLaundry & Home Care: Key Financials 1Catrinoiu PetreОценок пока нет
- Calc Fields Networking and Sharing: Welcome ToДокумент42 страницыCalc Fields Networking and Sharing: Welcome Toprashant adhikariОценок пока нет
- Chaman Lal Setia Exports Ltd fundamentals remain intactДокумент18 страницChaman Lal Setia Exports Ltd fundamentals remain intactbharat005Оценок пока нет
- Welding MapДокумент5 страницWelding MapDjuangОценок пока нет
- Inflatable Packers enДокумент51 страницаInflatable Packers enDavid LuhetoОценок пока нет
- GS Ep Cor 356Документ7 страницGS Ep Cor 356SangaranОценок пока нет
- Material Properties L2 Slides and NotesДокумент41 страницаMaterial Properties L2 Slides and NotesjohnОценок пока нет
- Aptio ™ Text Setup Environment (TSE) User ManualДокумент42 страницыAptio ™ Text Setup Environment (TSE) User Manualdhirender karkiОценок пока нет
- Module 5Документ10 страницModule 5kero keropiОценок пока нет
- Competency-Based Learning GuideДокумент10 страницCompetency-Based Learning GuideOliver BC Sanchez100% (2)
- Unit 5 - FitДокумент4 страницыUnit 5 - FitAustin RebbyОценок пока нет
- ARMOR Winter-Spring 2018 EditionДокумент84 страницыARMOR Winter-Spring 2018 Editionmai100Оценок пока нет
- BRD TemplateДокумент4 страницыBRD TemplateTrang Nguyen0% (1)
- COVID-19's Impact on Business PresentationsДокумент2 страницыCOVID-19's Impact on Business PresentationsRetmo NandoОценок пока нет
- Rencana Pembelajaran Semester Sistem Navigasi ElektronikДокумент16 страницRencana Pembelajaran Semester Sistem Navigasi ElektronikLastri AniОценок пока нет
- C79 Service Kit and Parts List GuideДокумент32 страницыC79 Service Kit and Parts List Guiderobert100% (2)
- Civil Aeronautics BoardДокумент2 страницыCivil Aeronautics BoardJayson AlvaОценок пока нет
- Bernardo Corporation Statement of Financial Position As of Year 2019 AssetsДокумент3 страницыBernardo Corporation Statement of Financial Position As of Year 2019 AssetsJean Marie DelgadoОценок пока нет
- Asian Construction Dispute Denied ReviewДокумент2 страницыAsian Construction Dispute Denied ReviewJay jogs100% (2)
- The Human Resource Department of GIK InstituteДокумент1 страницаThe Human Resource Department of GIK InstitutexandercageОценок пока нет
- Prestressing ProductsДокумент40 страницPrestressing ProductsSakshi Sana100% (1)
- Chapter 7 - Cash BudgetДокумент23 страницыChapter 7 - Cash BudgetMostafa KaghaОценок пока нет
- Usa Easa 145Документ31 страницаUsa Easa 145Surya VenkatОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Succession-1Документ8 страницIntroduction To Succession-1amun dinОценок пока нет
- Oop Assignment # 2 Submitted By: Hashir Khan Roll #: 22f-7465 Date: 3-3-2023Документ14 страницOop Assignment # 2 Submitted By: Hashir Khan Roll #: 22f-7465 Date: 3-3-2023Hashir KhanОценок пока нет
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessОт EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidОт EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1395)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsОт EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (94)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesОт EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2193)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingОт EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismОт EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (500)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldОт EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterОт EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (409)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)От EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (155)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceОт EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (23)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishОт EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (18)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayОт EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (125)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowОт EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (48)
- Infinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseОт EverandInfinite Powers: How Calculus Reveals the Secrets of the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (126)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationОт EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (158)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceОт EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Chasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombОт EverandChasing Heisenberg: The Race for the Atom BombРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОт EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeОценок пока нет
- What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesОт EverandWhat is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (139)
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 1A: Basics of Physics & Newton's LawsОт EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 1A: Basics of Physics & Newton's LawsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityОт EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (75)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldОт EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (60)
- The Biggest Number in the World: A Journey to the Edge of MathematicsОт EverandThe Biggest Number in the World: A Journey to the Edge of MathematicsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (5)