Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Fig 2 - Brushless DC Motor Driver - EFY June 14
Загружено:
bahriun syahriОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Fig 2 - Brushless DC Motor Driver - EFY June 14
Загружено:
bahriun syahriАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
dIy: circuit
Parts List
Brushless DC Motor Driver Semiconductors:
IC1
IC2
- NE555 timer IC
- DRV10866, 3-phase BLDC
motor driver
Abhijeet Rai (IC2) and a few other compo- D1, D2 - BAT41 Schottky diode
nents. Resistors (all 1/4-watt, ±5% carbon):
U
R1 - 10-kilo-ohm
se of brushless DC mo- chabhaiy
a DRV10866 driver IC from R2 - 100-kilo-ohm
vivek pan
tors (BLDCs) is on the Texas Instruments is used R3 - 3.8-kilo-ohm
VR1 - 5-kilo-ohm potmeter
rise. But their control to drive a small three-phase
Capacitors:
usually requires rotor-position BLDC motor (M1). The circuit C1, C3 - 10nF ceramic disk (X7R
information for selecting the appro- is of a three-phase, sensor-less motor recommended)
C2 - 0.1µF ceramic disk (X5R
priate commutation angle. Normally, driver with integrated power MOS- recommended)
a Hall Effect sensor is used to sense FETs having drive-current capabil- C4 - 2.2µF ceramic disk (X7R
rotor position. But in cost-sensitive ap- ity up to 680mA peak. DRV10866 is recommended)
Miscellaneous:
plications, a sensor-less commutation specifically designed for low noise CON1 - 2-pin terminal block
scheme is often desirable. The circuit and low component-count fan-motor connector
described here uses a DRV10866 driver drive applications. A 150° sensor-less M1 - 5V, 3-phase BLDC motor
IC to drive a small BLDC fan, without back emf scheme is used to control the
using any position sensors. A BLDC three-phase motor.
Test Points
fan’s speed can be varied smoothly, A 100k pull-up resistor (R2) is used
without the usual steps associated with at pin 1 of IC2. Pins 2, 4, 7 and 6 of Test point Details
a normal AC fan. IC2 are connected to common, phase TP0 0V
A, phase B and phase C of the BLDC TP1 5V
Circuit and working motor, respectively. Pin 10 of IC2 is TP2 PWM pulse
Fig. 1 shows the circuit of a sensor-less connected to pin 7 of IC1 to get the
BLDC motor driver. The circuit is built pulse-width modulated (PWM) signal BLDC motor.
around an NE555 (IC1), a DRV10866 from IC1 to control the speed of the The output signal (PWM) is avail-
able at IC1’s pin 7 (DIS) and not from the
+ TP1 TP2 usual output pin 3 of the IC. The 25kHz
− (approx.) PWM signal’s duty cycle can
5V R2 be adjusted from 5% to 95% using po-
100K
CON1
R1 7 DIS RESET 4
D1 1
FG PWM 10
tentiometer VR1. The speed of the BLDC
10K
2
R3 motor can be controlled by varying the
TP0 COM CS 9
6
TH
IC1
Vcc 8
3.8K duty cycle of the PWM signal. Turning
C2 3 IC2 8
NE555 0.1u C4
Vcc FGS VR1 counter-clockwise lowers the duty
2
O/P 3 VR1 DRV10866
TRI
5K
4
U V
7
cycle which, in turn, lowers the speed of
2.2u
1
GND CV
5 5 GND W 6
the motor, and vice versa.
C1 C3
10n 10n B Construction and testing
A C
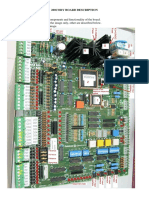
D2 M1 An actual-size, single-side PCB for the
GND
D1− D2 = BAT41
COM BLDC MOTOR brushless DC motor driver is shown in
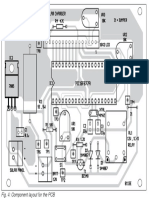
Fig. 2 and its component layout in Fig. 3.
Fig. 1: Circuit of brushless DC motor driver Assemble the circuit on the recommended
PCB to minimise assembly errors. IC2
should be fitted on solder side of the PCB.
After assembling the components,
connect a 5V DC supply to CON1 con-
nector. To test the circuit for proper
functioning, verify correct 5V supply
for the circuit at TP1 with respect to
TP0. Turn VR1 clockwise or counter-
clockwise to increase or decrease the
speed of the motor.
Fig. 2: An actual-size, single-side PCB for the Fig. 3: Component layout for the PCB The author is a B.Tech (electronics and communica-
brushless DC motor driver tion) from GGSIPU, New Delhi
www.efymag.com Electronics For You | June 2014 91
Вам также может понравиться
- Programming 16 Bit Timer On Atmega328Документ9 страницProgramming 16 Bit Timer On Atmega328VisitOn.T.witte.r100% (1)
- FCCCGGGGДокумент4 страницыFCCCGGGGYorvic GodoyОценок пока нет
- ListДокумент197 страницListAnonymous sCJntbrОценок пока нет
- Delay 1.0K Millis 2.3K Micros 1.0K Delaymicroseconds 359 Analogwrite 274 Tone 1.4K Notone 76 Servo Library 1.6KДокумент11 страницDelay 1.0K Millis 2.3K Micros 1.0K Delaymicroseconds 359 Analogwrite 274 Tone 1.4K Notone 76 Servo Library 1.6KOthmane Bouzarzar100% (1)
- 16-Channel Relay Module Board 16 - Channel Relay Module BoardДокумент2 страницы16-Channel Relay Module Board 16 - Channel Relay Module BoardAliОценок пока нет
- Iraudamp1 PDFДокумент22 страницыIraudamp1 PDFamijoski6051Оценок пока нет
- ADAS Description enДокумент10 страницADAS Description enIonut-alexandru IordacheОценок пока нет
- PID Buck-BoostДокумент8 страницPID Buck-BoostIvan RahmanОценок пока нет
- Component IdentificationДокумент22 страницыComponent Identificationjactopple0% (1)
- 150A Watt MeterДокумент2 страницы150A Watt Meterjhon_212100% (2)
- CONPRA - Enginer Tuning Under Numerical and Nominal Data-2011Документ16 страницCONPRA - Enginer Tuning Under Numerical and Nominal Data-2011Bolia KornevičОценок пока нет
- Arduino Timer and InterrupДокумент10 страницArduino Timer and InterrupFabian Monteleone100% (1)
- Tf10 Technical GuideДокумент25 страницTf10 Technical GuideFülöp LászlóОценок пока нет
- HV Resonance CollectionДокумент4 страницыHV Resonance CollectionfreiwildОценок пока нет
- Engine Control Module (Ecm) I/O SignalДокумент5 страницEngine Control Module (Ecm) I/O Signalkofo3000Оценок пока нет
- Microwave InfoДокумент36 страницMicrowave InforamjoceОценок пока нет
- Using The MOSFET As A SwitchДокумент4 страницыUsing The MOSFET As A Switchadrian665100% (2)
- ReadmeДокумент1 страницаReadmeNicholas HarmonОценок пока нет
- Using Winols To Find EDC15 Passat PD 100 BHP MapsДокумент24 страницыUsing Winols To Find EDC15 Passat PD 100 BHP MapsMacarena MolanoОценок пока нет
- Bk-Precision 1476 Dual-Trace Oscilloscope SMДокумент47 страницBk-Precision 1476 Dual-Trace Oscilloscope SMLazaro Guajardo Garza100% (1)
- 1000 WattДокумент3 страницы1000 WattAmjad Ali KhokharОценок пока нет
- 12v To 18v ConverterДокумент7 страниц12v To 18v ConverterLuis Paulo100% (1)
- Power Supply For 8051 MicrocontrollerДокумент5 страницPower Supply For 8051 MicrocontrollerAshok Ekanath KalangeОценок пока нет
- DSM Ecu Extended Map GuideДокумент4 страницыDSM Ecu Extended Map GuideJohn MongielloОценок пока нет
- Engine Data ListДокумент48 страницEngine Data ListYordano PerezОценок пока нет
- LT-856 RAX-LCD Installation and Wiring ManualДокумент24 страницыLT-856 RAX-LCD Installation and Wiring ManualIatan AlexandruОценок пока нет
- 2008-11-14 003029 Es Code CheckДокумент6 страниц2008-11-14 003029 Es Code CheckRaysian K. SetoОценок пока нет
- Installing Tiny Core On A USB Drive - The Ext2 WayДокумент4 страницыInstalling Tiny Core On A USB Drive - The Ext2 WayDoru Barbu100% (1)
- Immobilizer 3 Measuring BlocksДокумент4 страницыImmobilizer 3 Measuring BlocksMauricioОценок пока нет
- Designandconstructionofa1 5kvainverterusing12vbatteriesMODIFIEDfinal16022016Документ13 страницDesignandconstructionofa1 5kvainverterusing12vbatteriesMODIFIEDfinal16022016shah pallav pankaj kumarОценок пока нет
- Diagnostic Sales Evening Component TestingДокумент124 страницыDiagnostic Sales Evening Component TestingbibОценок пока нет
- Guide To Choosing Generator To Motor Size - RELДокумент3 страницыGuide To Choosing Generator To Motor Size - RELdhayalasundaram5689Оценок пока нет
- cj125 Product Info 2019-02Документ5 страницcj125 Product Info 2019-02Joao HerreraОценок пока нет
- AC Current Measurement Using CTДокумент22 страницыAC Current Measurement Using CTKoushik MaityОценок пока нет
- 9A04401 Switching Theory and Logic DesignДокумент4 страницы9A04401 Switching Theory and Logic DesignsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Kdfi V1.4: User Manual (English)Документ13 страницKdfi V1.4: User Manual (English)Dot3xe Nicolas100% (1)
- Inverter 12v 3kv PDFДокумент13 страницInverter 12v 3kv PDFirfz44Оценок пока нет
- Tiny Giant Build PDF Rev2Документ6 страницTiny Giant Build PDF Rev2mini998Оценок пока нет
- Maintenance Manual of Chery Karry - Circuit DiagramДокумент16 страницMaintenance Manual of Chery Karry - Circuit DiagramUmar ShamsudinОценок пока нет
- LCD MicrochipДокумент40 страницLCD Microchipgorea_grigОценок пока нет
- Product Introduction Product Introduction: LEXUS LS600h/LS600hL Hybrid System Power Control Unit (PCU)Документ4 страницыProduct Introduction Product Introduction: LEXUS LS600h/LS600hL Hybrid System Power Control Unit (PCU)Вячеслав ГлушакОценок пока нет
- Rfid Security Access Control System: Submitted byДокумент20 страницRfid Security Access Control System: Submitted byVale Conde CuatzoОценок пока нет
- Bipolar SramДокумент33 страницыBipolar SramRavinder VijayranОценок пока нет
- Project 15 MOTOR BASICSДокумент7 страницProject 15 MOTOR BASICSDarwin VargasОценок пока нет
- 555 TimerДокумент76 страниц555 TimerSai Krishna KodaliОценок пока нет
- AllData 10.40 Domestic - Asian - Europe (2011)Документ1 страницаAllData 10.40 Domestic - Asian - Europe (2011)JoséLuisОценок пока нет
- Easy Start Guide LS Ic5 PDFДокумент15 страницEasy Start Guide LS Ic5 PDFMarina Cecilia TorresОценок пока нет
- rr322404 Automotive Electrical and AutotronicsДокумент4 страницыrr322404 Automotive Electrical and AutotronicsSRINIVASA RAO GANTAОценок пока нет
- Rebuilding The Yamaha Vision Motorcycle TCI Electronic Igniter Module / Electronic Ignition / Transistor Controlled IgnitionДокумент11 страницRebuilding The Yamaha Vision Motorcycle TCI Electronic Igniter Module / Electronic Ignition / Transistor Controlled Ignitionxplod11Оценок пока нет
- V850ESДокумент6 страницV850ESVictor Ramalho100% (1)
- 42LS3450, 345S, 345TДокумент53 страницы42LS3450, 345S, 345TAndres Fermin OchoaОценок пока нет
- AN8008 Eeprom Temperature Mod PDFДокумент4 страницыAN8008 Eeprom Temperature Mod PDFHéctor López Viveros100% (1)
- Reduction of Power MOSFET Losses in Hard-Switched ConvertersДокумент2 страницыReduction of Power MOSFET Losses in Hard-Switched ConvertersWesley de PaulaОценок пока нет
- Gauge Control Module 2013-2018 TroubleshootingДокумент67 страницGauge Control Module 2013-2018 TroubleshootingTotall AutomotrízОценок пока нет
- ELM327DSДокумент0 страницELM327DSБаба ЏајаОценок пока нет
- Capacitor Power Supply Design NoteДокумент8 страницCapacitor Power Supply Design NoteIvez StrausseОценок пока нет
- Diesel Edc 2Документ14 страницDiesel Edc 2DanielCostaXinaОценок пока нет
- Components Side PCBДокумент1 страницаComponents Side PCBsohail nasirОценок пока нет
- PG 106 (Smart Solar Charger - Jan 13 - Fig 4 - Component For The PCBДокумент1 страницаPG 106 (Smart Solar Charger - Jan 13 - Fig 4 - Component For The PCBHaris MehmoodОценок пока нет
- Stepper Motor Control Using MicrocontrollerДокумент4 страницыStepper Motor Control Using MicrocontrollerkrishnnadevОценок пока нет
- DL 47 Enannual Report 2012Документ204 страницыDL 47 Enannual Report 2012bahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- A. Analisa Daun C. Analisa Kompos: Form Pesanan Jasa Analisa Laboratorium Analitik PT - SocfindoДокумент1 страницаA. Analisa Daun C. Analisa Kompos: Form Pesanan Jasa Analisa Laboratorium Analitik PT - Socfindobahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Ataman BP17 ManualДокумент17 страницAtaman BP17 Manualbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Standar Vegetasi Bibitan DXP SocfindoДокумент1 страницаStandar Vegetasi Bibitan DXP Socfindobahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Form Pesanan Jasa Analisa PDFДокумент1 страницаForm Pesanan Jasa Analisa PDFbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- 302 02 04 PDFДокумент64 страницы302 02 04 PDFbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- BMP'S For Facing Drought Stress On Oil Palm: Marihat, September, 29 2016Документ36 страницBMP'S For Facing Drought Stress On Oil Palm: Marihat, September, 29 2016bahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- 302 02 04 PDFДокумент64 страницы302 02 04 PDFbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- 2012 KTM 450 SX-F PDFДокумент98 страниц2012 KTM 450 SX-F PDFbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Manual Nissan UdДокумент308 страницManual Nissan UdFranciscoGumiel79% (24)
- AF RifleManual0114PROOFv4Документ20 страницAF RifleManual0114PROOFv4bahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- 1997 Aprilia RS 250 PDFДокумент92 страницы1997 Aprilia RS 250 PDFbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Ideapad Y460 Hardware Maintenance Manual PDFДокумент97 страницIdeapad Y460 Hardware Maintenance Manual PDFbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- 555 Diodes PDFДокумент14 страниц555 Diodes PDFbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- 82menus PDFДокумент9 страниц82menus PDFbanboОценок пока нет
- ElektronikДокумент15 страницElektronikbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Cummins 161110083846 PDFДокумент18 страницCummins 161110083846 PDFMuhammad IshfaqОценок пока нет
- Cs ReportДокумент5 страницCs Reportbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Lenovo Ideapad Y460P/Y560P: User Guide User GuideДокумент145 страницLenovo Ideapad Y460P/Y560P: User Guide User Guidebahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Mounting Instructions: Racing Steering Damper ECU Kawasaki ZX10RДокумент2 страницыMounting Instructions: Racing Steering Damper ECU Kawasaki ZX10Rbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Using The Small Loop Antenna: Joe Carr's Radio Tech-NotesДокумент8 страницUsing The Small Loop Antenna: Joe Carr's Radio Tech-Notesbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Decree of The Minister of Communication and Information Technology NUMBER: 34/PER/M.KOMINFO/8/2009 ON Provision of Inter-Inhabitant Radio CommunicationДокумент23 страницыDecree of The Minister of Communication and Information Technology NUMBER: 34/PER/M.KOMINFO/8/2009 ON Provision of Inter-Inhabitant Radio Communicationbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Jual HT Alinco DJ-CRX5 (Dual Band)Документ2 страницыJual HT Alinco DJ-CRX5 (Dual Band)Multiarya100% (1)
- Catalog37PDF PDFДокумент556 страницCatalog37PDF PDFbahriun syahri100% (1)
- Owner'S Manual: M4 A1 Carbine - M4 CQB - M4 CQCДокумент28 страницOwner'S Manual: M4 A1 Carbine - M4 CQB - M4 CQCbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Security On The Water: Marine Power For Security and DefenseДокумент6 страницSecurity On The Water: Marine Power For Security and Defensebahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Stinger 22 ManualДокумент7 страницStinger 22 Manualbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- M Lok Modular Accessory System Owners Manual2Документ11 страницM Lok Modular Accessory System Owners Manual2bahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент20 страницPDFbahriun syahriОценок пока нет
- Unit Ut582+Документ1 страницаUnit Ut582+George Benny Miranda ArrunateguiОценок пока нет
- SCR-6 SCR-8 - Manual de Serviço (En) (2012.04)Документ52 страницыSCR-6 SCR-8 - Manual de Serviço (En) (2012.04)Thiago AzevedoОценок пока нет
- Technical Data Schedule 60mva, 132/33 KV Mobile Substation: Power TransformerДокумент7 страницTechnical Data Schedule 60mva, 132/33 KV Mobile Substation: Power TransformermahnoorОценок пока нет
- Bistable MultivibratorsДокумент9 страницBistable MultivibratorsihtishamuddОценок пока нет
- A TV Pattern Generator Part1Документ4 страницыA TV Pattern Generator Part1riverajluizОценок пока нет
- (Codientu - Org) - 29M41-CHASSIS TB97-VN (CRT CHUNGHWA)Документ1 страница(Codientu - Org) - 29M41-CHASSIS TB97-VN (CRT CHUNGHWA)GioVoTamОценок пока нет
- G2X Certificate ATEX 1Документ2 страницыG2X Certificate ATEX 1Iwan NugrohoОценок пока нет
- Amercable - VFDДокумент16 страницAmercable - VFDmgentry128Оценок пока нет
- Electrical 2x18MW Rev0Документ12 страницElectrical 2x18MW Rev0skthen72Оценок пока нет
- ICS 92 52 ManualДокумент56 страницICS 92 52 ManualPawan Kumar JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Siemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 152Документ1 страницаSiemens Power Engineering Guide 7E 152mydearteacherОценок пока нет
- BEE Three Phase CircuitsДокумент27 страницBEE Three Phase CircuitsPrasanth KumarОценок пока нет
- Guentner GDRD Manual Version4.2 enДокумент47 страницGuentner GDRD Manual Version4.2 enehsan haleem100% (1)
- ANSI C82.6 For Lamp Ballasts. Ballasts For High-Intensity Discharge Lamps - Methods of MeasurementДокумент29 страницANSI C82.6 For Lamp Ballasts. Ballasts For High-Intensity Discharge Lamps - Methods of MeasurementJose Luis Perez RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Linde Service GuideДокумент5 страницLinde Service GuideMário AndradeОценок пока нет
- Paneles de Distribucion GeДокумент89 страницPaneles de Distribucion GeLuis D UrciaОценок пока нет
- Kavo 4425 4426 Easydrive ConverterДокумент70 страницKavo 4425 4426 Easydrive ConverterdinhdtdОценок пока нет
- Semikron SKIIP 11NAB126V1 DatasheetДокумент4 страницыSemikron SKIIP 11NAB126V1 DatasheetGabriel EscamillaОценок пока нет
- 200cory Board DescriptionДокумент2 страницы200cory Board DescriptionChang ChangОценок пока нет
- Octal 3-State Noninverting Buffer/Line Driver/Line Receiver: SL74HC244Документ5 страницOctal 3-State Noninverting Buffer/Line Driver/Line Receiver: SL74HC244José AdelinoОценок пока нет
- Wheatstone-Bridge Readout Interface For ISFET REFET ApplicationsДокумент10 страницWheatstone-Bridge Readout Interface For ISFET REFET ApplicationsLykaios VllpndoОценок пока нет
- Electric Guitar: Service ManualДокумент6 страницElectric Guitar: Service ManualSri KṛṣṇaОценок пока нет
- Features: Ratings Accuracy IndicatorsДокумент2 страницыFeatures: Ratings Accuracy IndicatorsLochana DeshappriyaОценок пока нет
- 9f55d1 - Introduction To Vlsi DesignДокумент4 страницы9f55d1 - Introduction To Vlsi DesignAman ShivachhОценок пока нет
- Commissioning RM6Документ31 страницаCommissioning RM6pemanr1914100% (3)
- Unit4questions 100415042439 Phpapp01Документ4 страницыUnit4questions 100415042439 Phpapp01Mohamad HishamОценок пока нет
- CFU-M.. Datasheet En-ApДокумент2 страницыCFU-M.. Datasheet En-ApbadslayerОценок пока нет
- En Acs800 107 HW CДокумент112 страницEn Acs800 107 HW CHENRY HERNAN SALINAS CASTAÑEDAОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Word - Notes On DC GeneratorДокумент40 страницMicrosoft Word - Notes On DC GeneratorDr. Deepika YadavОценок пока нет
- SPM20-20-05-00 (See Page 23 of 38) PDFДокумент38 страницSPM20-20-05-00 (See Page 23 of 38) PDFroshan mungurОценок пока нет