Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Wind Power Applications
Загружено:
miguel itsonОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Wind Power Applications
Загружено:
miguel itsonАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
I N T E G R AT E D P O W E R S Y S T E M A N A LY S I S S O F T WA R E
DIgSILENT PowerFactory for
Wind Power Applications
DIgSILENT’s power system analysis software PowerFactory
incorporates extensive modelling capabilities with advanced
solution algorithms, to provide electrical engineers with tools to
carry out complex power system studies – from easily manage-
able calculations to very advanced simulations of the highest
complexity.
With more than 25 years of experience, DIgSILENT provides
state-of-the-art algorithms and models, as well as leading,
innovative developments to meet the needs of the future.
Especially in wind power applications, DIgSILENT PowerFactory
has become the de-facto standard tool, providing all required
models and simulation algorithms and achieving unrivalled
accuracy and performance.
POWER SYSTEM ANALYSIS NEEDS WITH
INCREASING WIND POWER GENERATION
During recent years, the growth in worldwide installed wind Testing and validation of wind turbine simulation models on the basis of
power generation capacity has substantially changed transmission field tests, parameter identification and benchmark analysis is necessary to
and distribution grid characteristics, introducing new engineering guarantee high model accuracy. Typical models cover fundamental frequency
tasks in system planning and grid operation. The increasing size level (dynamic RMS / stability), or electromagnetic transient level (EMT),
of wind turbines and wind parks has led to some of the greatest both including controllers and protection devices for fault-ride-through (FRT)
challenges currently present in the field of Power Systems engineering: simulations.
Voltage changes, loadings, and losses are analysed by using Load Flow The increasing use of power electronics converters in grids is leading to new
calculations. To undertake detailed analysis of grid losses, power generation challenges and new solutions in the field of power quality. Harmonic analysis
patterns and energy yields, wind time series covering periods of days, weeks, and flicker evaluation are becoming more and more important.
months, or even years have to be considered.
Non-dispatchable renewable generation with limited prediction accuracy
Synchronous generation, which has traditionally determined grid character- requires new considerations in generation planning and grid expansion
istics, is being replaced step by step by inverter fed generation systems. Such engineering: in particular, probabilistic load flow analysis and generation
systems introduce completely new dynamic characteristics, influencing short- adequacy assessment considering stochastic modelling of the network
circuit currents and network stability. including wind farms with stochastic wind models.
Grid impact studies covering steady state, fault analysis as well as dynamic For wind power integration studies and power system stability analysis,
aspects (stability and EMT type studies), must consider the behaviour of generic dynamic models of wind turbines/plants reflecting all relevant
power electronic interfaced generation systems. technologies are required. For grid code compliance studies, high precision
manufacturer-specific wind turbine models are necessary.
Grid codes determine the design and behaviour of wind turbine and wind
farm controllers. Calculation of steady-state results and simulation of
dynamic behaviour is essential for defining grid code rules, and for evaluat-
ing the behavior of wind turbines and wind farms according to grid code
requirements.
For more Information about DIgSILENT PowerFactory visit www.digsilent.de.
POWERFACTORY FEATURES TO SUPPORT WIND POWER APPLICATIONS
DIgSILENT GmbH has given priority to wind power applications for more than 15 years. DIgSILENT PowerFactory has been developed to satisfy the
needs and requirements of power system planners, certification and research institutes, transmission and distribution utilities and wind turbine
manufacturers. Among many unique PowerFactory features and capabilities, the following are most essential for wind power applications.
MODELLING ANALYSIS FUNCTIONS
Library of generic wind turbine models (generators connected via Steady-state load flow calculations considering voltage-dependent
fully-rated converters, doubly-fed induction generators, induction reactive power capability limits, wind farm controllers with setpoint
generators with variable rotor resistance) characteristics, automatically adjustable shunts, etc.
Dynamic wind turbine models according to IEC 61400-27-1 and WECC Medium to long term quasi-dynamic simulation taking into account
variable renewable generation
In addition, world-class manufacturers have their specific models
(validated acc. German TR4) implemented in PowerFactory. These Probabilistic load flow calculation based on Weibull distribution of wind
models may be requested from the manufacturer speed and wind-power curves NEW in PowerFactory 2018
Support of integrated single-phase and three-phase AC/DC grid Short-circuit calculation according to IEC 60909-0:2016
modelling with balanced and unbalanced operating conditions Short-circuit calculation based on complete method with options to include
Numerous models of power electronic devices such as voltage-sourced dynamic voltage support according to k-factor settings of wind turbines
converters (VSC), modular multi-level converters (MMC) for HVDC Dynamic time-domain simulations with adaptive step-size algorithm
systems, semiconductor valves for chopper applications, etc. allowing fast, efficient, robust simulations – for example for fault-ride-
Doubly-fed induction generator models of varying complexity, through (FRT) simulations
including the capability of crowbar switching Small Signal Stability Analysis (eigenvalue analysis; Arnoldi-
A general “Static Generator” model representing all kinds of generators Lanczos and QR-method) of power system models including wind
which are connected via fully-rated converters turbines, park controllers, HVDC systems, etc.
User-defined controller modelling for steady-state load flow and quasi- Electromagnetic transients (EMT) simulation for analysis of transformer
dynamic simulation inrush, fast actions of power electronic converters, etc.
User-defined dynamic modelling for RMS and EMT simulations Interface for real-time measurement data from DIgSILENT monitoring
system PFM for online grid code compliance supervision or model
Support of DLL interface according to IEC 61400-27-1 Annex F for user- validation NEW in PowerFactory 2018
specific external dynamic wind turbine models
Power quality assessment for harmonics and flicker propagation
DSL-to-C interface for model compilation according to IEC 61000-3-6, IEC 61400-21, as well as impedance
Injection of harmonics and existence of background harmonics, frequency sweeps
either phase-correct or defined by magnitudes according to Flickermeter according to IEC 61000-4-15 for analyzing measured or
IEC 61400-21 / IEC 61000-3-6: Ideal sources, frequency-dependent simulated curves
Norton and Thevenin equivalent sources are available
Generation adequacy assessment on basis of Monte Carlo Analysis for
determination of generation reliability indexes for capacity credit studies,
5,00
considering wind power characteristics and stochastic wind models
External Grid
SL
Uset=1,00
PCC 110kV 4,00
PQ Control with synch:
Wind Farm Trf
SynchMode
0
3,00
DIgSILENT
RampUp
Tramp
1,20
20kV Substation
1,00 Pstat Ptot
1 0
OnLine
0,80 Prot
3,00 km
2,00 0,60 id_max
S1.1
-
Pref Pref1 Pref2 Pref3
Reference Limiter
0,40 3 Tramp iP_ref idr
2,60 km
S1.4 S1.3 S1.2 S4.2 S4.3 S4.4 PI_d
S4.1
0 0
1,00 km 1,00 km 1,00 km 1,20 km 1,20 km 1,20 km Kp,Tp
ird_ref
0,20 0 1
0,00 0,20 0,40 0,60 dud_synch 0,80 [s] 1,00 1
4 2
WP-Klemme 1: Voltage Phasor, Magnitude in p.u.
Step-up Trf 1.4
Step-up Trf 1.2
Step-up Trf 1.3
Step-up Trf 1.1
Step-up Trf 4.4
Step-up Trf 4.1
Step-up Trf 4.2
Step-up Trf4.3
0 0 0 0 0
1,00 0 0 0 LV 1: Voltage Phasor, Magnitude in p.u. 0
PickDrop(1)
u sw flt
Tudelay,Tbackdelay,i_EEG
5 0 1 1
4,00 km
Dband(yi<(1-K))
S2.1
deltaU
LV-Bus 1.4 LV-Bus 1.3 LV-Bus 1.1 LV-Bus 4.1 LV-Bus 4.2 LV-Bus 4.4
3,00 iq_max,id_max
LV-Bus 1.2 LV-Bus 4.3
delt_u idrf_min
2,00 1 0 0 2 FaultLimits
1,00 Iq_fault idrf_max irq_ref
0,00 MagCurr
imag K_deltaU,i_max,deltaU,i_EEG 1 3 1 2
2,00 3,00 4,00 5,00 6,00 7,00 8,00 9,00 10,0 11,0 12,0 13,0 0,00
14,0 15,0 16,0 17,0[-] Xm 1
WTG 1.4 WTG 1.3 WTG 1.2 WTG 1.1 WTG 4.1 WTG 4.2 WTG 4.3 WTG 4.4 iqrf
Wind Farm Cable PCC: Current, Magnitude/Terminal i in A
-1,00 2 4
S3.1
-2,00 iq_max
S2.4
1,00 km
S2.3
1,00 km
S2.2
1,00 km 5,00 km
S3.2
1,00 km
S3.3
1,00 km 0,00 0,20 0,40 0,60 Qref 0,80 [s] Qr 1,00 Qref1 - Qref2 0
6
Reference Limiter_q iQ_ref iqr
DFIG 1: Current Phasor, Active Current in p.u. 1 PI_q 5
Kq,Tq
DFIG 1: Current Phasor, Reactive Current in p.u. 2
duq_synch
7 3 6
Step-up Trf 2.1
Step-up Trf 2.4
Step-up Trf 3.2
Step-up Trf 3.1
Step-up Trf 2.3
Step-up Trf 2.2
Step-up Trf 3.3
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Qstat
8
3,00
Qrot Qtot
2,00 9 3
LV-Bus 2.4 LV-Bus 2.3 LV-Bus 2.2 LV-Bus 2.1 LV-Bus 3.1 LV-Bus 3.2 LV-Bus 3.3
1,00 bypass
10
0,00
-1,00
WTG 2.4 WTG 2.3 WTG 2.2 WTG 2.1 WTG 3.1 WTG 3.2 WTG 3.3
-2,00
0,00 0,20 0,40 0,60 0,80 [s] 1,00
DFIG 1: Power-Phasor, Active Power in MW
DFIG 1: Power Phasor, Reactive Part in Mvar
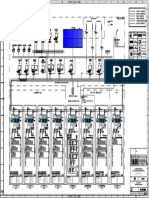
FRT Simulation WTG Date: 1/18/2013
DIgSILENT Wind Farm Annex: 1 /2
DIgSILENT GmbH T +49 7072 9168-0 DIgSILENT GmbH is certified
Heinrich-Hertz-Straße 9 F +49 7072 9168-88 to the ISO 9001:2015 standard.
72810 Gomaringen mail@digsilent.de More information is available at
Germany www.digsilent.de www.tuv-sud.com/ms-cert.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Battery Energy Storage Based Virtual Synchronous GeneratorДокумент6 страницA Battery Energy Storage Based Virtual Synchronous GeneratorRaja SekharОценок пока нет
- B&W Electrostatic PrecipitatorsДокумент4 страницыB&W Electrostatic PrecipitatorsPaul Ruel Gonzales QuintanaОценок пока нет
- Tan-Delta and Capacitance Test Set For HT Generator/Motor TestingДокумент3 страницыTan-Delta and Capacitance Test Set For HT Generator/Motor Testingmustafa180567% (3)
- A New Way To Model Current-Mode Control Part Two PDFДокумент6 страницA New Way To Model Current-Mode Control Part Two PDFTey Chin SoonОценок пока нет
- Fixed Mounted Circuit Breaker Switchgear - SiemensДокумент2 страницыFixed Mounted Circuit Breaker Switchgear - SiemensshahpinkalОценок пока нет
- Enlzt145258ra Inv 4kvaДокумент2 страницыEnlzt145258ra Inv 4kvaumair_aeОценок пока нет
- 9 10 enДокумент2 страницы9 10 enparth kananiОценок пока нет
- Electricity 3 Lpt012Документ3 страницыElectricity 3 Lpt012Nadah8Оценок пока нет
- Enlzt145260ra Inv 1kvaДокумент2 страницыEnlzt145260ra Inv 1kvaumair_aeОценок пока нет
- Said 2017Документ6 страницSaid 2017Riham abОценок пока нет
- Load Bank CatalogДокумент11 страницLoad Bank CatalognanilОценок пока нет
- MEK-2500 Datasheet PDFДокумент2 страницыMEK-2500 Datasheet PDFhenryhariyadiОценок пока нет
- Interface Technology in Modular Housings: Your Global Automation PartnerДокумент16 страницInterface Technology in Modular Housings: Your Global Automation PartnerJorge_Andril_5370Оценок пока нет
- GENERATORДокумент19 страницGENERATORANUSHIKAОценок пока нет
- Essential LEDtube 8W & 16W T8Документ9 страницEssential LEDtube 8W & 16W T8Jinus JieОценок пока нет
- Dimmer System Control SchematicДокумент2 страницыDimmer System Control SchematicCheah ChenОценок пока нет
- Combivert: Instruction ManualДокумент36 страницCombivert: Instruction Manualruisengo100% (1)
- Cost Benefit Analysis and Exploration of Cost Energy Perfo - 2016 - Procedia Com PDFДокумент5 страницCost Benefit Analysis and Exploration of Cost Energy Perfo - 2016 - Procedia Com PDFrifnaОценок пока нет
- AKRE 4lista ANG Koregirano 1Документ2 страницыAKRE 4lista ANG Koregirano 1JovanОценок пока нет
- BbomercitoДокумент5 страницBbomercitoOmar Espinoza sanchezОценок пока нет
- Reaffirmed 2017Документ17 страницReaffirmed 2017Suresh KrishnanОценок пока нет
- WeldForceKWF200S Om enДокумент22 страницыWeldForceKWF200S Om enValiBardaОценок пока нет
- Direct Ammonia Fuel CellДокумент1 страницаDirect Ammonia Fuel CellParijat MishraОценок пока нет
- Merlin NX Programmable Product DataДокумент12 страницMerlin NX Programmable Product Datamiseh keggahОценок пока нет
- MideaДокумент74 страницыMideaivanОценок пока нет
- MEA Testing Systems LTD CatalogДокумент105 страницMEA Testing Systems LTD CatalogPawin lothongОценок пока нет
- (Philips) Philips Ecofit LEDtube T8Документ8 страниц(Philips) Philips Ecofit LEDtube T8CommonОценок пока нет
- Plakat FESTO CPX MPA VTSAДокумент2 страницыPlakat FESTO CPX MPA VTSAtadОценок пока нет
- vthl884 EnglishДокумент6 страницvthl884 Englishtammam shamiОценок пока нет
- York 150.62-EG1Документ116 страницYork 150.62-EG1Kevin NovalОценок пока нет
- NotnotДокумент27 страницNotnotDanica CamagongОценок пока нет
- Standard Commissioning Procedure For Daylighting ControlsДокумент6 страницStandard Commissioning Procedure For Daylighting ControlsCarolina HernándezОценок пока нет
- Catalog - Air Cooled Twin Screw VSD YVAAДокумент54 страницыCatalog - Air Cooled Twin Screw VSD YVAAdanang hadi saputroОценок пока нет
- XikaxipesubewifujДокумент2 страницыXikaxipesubewifujbirjuОценок пока нет
- +3000036EN CarelДокумент4 страницы+3000036EN CarelFRANCISCO BRITO DIASОценок пока нет
- Televes Nova SwitchДокумент4 страницыTeleves Nova Switchnasser22Оценок пока нет
- Manual Servicio Mini Component Sound System Noblex MNX 3000sДокумент35 страницManual Servicio Mini Component Sound System Noblex MNX 3000sNey TrajanoОценок пока нет
- H-10207 00 0ea00-001f Fa-Cscs System Configuration Diagram - DДокумент1 страницаH-10207 00 0ea00-001f Fa-Cscs System Configuration Diagram - Dnguyen rinОценок пока нет
- Hoppecke Sun Power VR M BrochureДокумент2 страницыHoppecke Sun Power VR M Brochurediego santiago paucarОценок пока нет
- Evaluation of OpenFOAM For CFD of Turbulent Flow in Water TurbinesДокумент15 страницEvaluation of OpenFOAM For CFD of Turbulent Flow in Water TurbinesAghajaniОценок пока нет
- Development of A 500-kV DC XLPE Cable SystemДокумент6 страницDevelopment of A 500-kV DC XLPE Cable SystemalchernОценок пока нет
- ABBManobra A LineMidi2008Документ82 страницыABBManobra A LineMidi2008Claudia MartinsОценок пока нет
- Linde 393 Service Manual PDFДокумент126 страницLinde 393 Service Manual PDFnenad100% (7)
- In-Lab Work: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 2262 - Electric CircuitsДокумент4 страницыIn-Lab Work: Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering ECE 2262 - Electric CircuitsThiago Araújo de AssisОценок пока нет
- PS21255 EpДокумент6 страницPS21255 EpS.O.S MACTRONICAОценок пока нет
- And Excellent Service Worldwide Quality Heat Exchanger ProductsДокумент2 страницыAnd Excellent Service Worldwide Quality Heat Exchanger ProductsWINОценок пока нет
- 8.4 - Nozzle Theory PDFДокумент170 страниц8.4 - Nozzle Theory PDFJuan Navarro FernándezОценок пока нет
- 00 F 5 Sebk 320Документ40 страниц00 F 5 Sebk 320Mr.K chОценок пока нет
- Samsung-led-monitor-SA300 Service ManualДокумент41 страницаSamsung-led-monitor-SA300 Service ManualLuciano GerloОценок пока нет
- Third Year: Practical Work Book For The Course EE-394 Communication SystemДокумент22 страницыThird Year: Practical Work Book For The Course EE-394 Communication SystemMehmood ShahОценок пока нет
- IN Pulse Oximeter 7090Документ2 страницыIN Pulse Oximeter 7090klamaryОценок пока нет
- PTC Tempo - BiopharmaДокумент2 страницыPTC Tempo - Biopharmaakhil4006Оценок пока нет
- In Edit State:save Key: 0.4mV/V 6mV/VДокумент5 страницIn Edit State:save Key: 0.4mV/V 6mV/VJulian HortaОценок пока нет
- ST MicroInverter SchemeticДокумент12 страницST MicroInverter Schemeticpuspendu janaОценок пока нет
- Modelling of Vibrations of Overhead Line Conductors: Assessment of the TechnologyОт EverandModelling of Vibrations of Overhead Line Conductors: Assessment of the TechnologyGiorgio DianaОценок пока нет
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlОт EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Infineon-Technologies-SPP20N60C3 C27024 PDFДокумент15 страницInfineon-Technologies-SPP20N60C3 C27024 PDFmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Rjh3047 Mosfet DatasheetДокумент82 страницыRjh3047 Mosfet Datasheetmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- General Description: Silicon Diffused Power TransistorДокумент12 страницGeneral Description: Silicon Diffused Power Transistormiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Foshan Blue Rocket Elec 2N60 - C305393Документ6 страницFoshan Blue Rocket Elec 2N60 - C305393miguel itsonОценок пока нет
- MOSPEC-Semicon-M7 C138984Документ2 страницыMOSPEC-Semicon-M7 C138984miguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Xiner-Xnf6n60t C379739Документ1 страницаXiner-Xnf6n60t C379739miguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Getting Started With Oneliner & Power Flow V11Документ27 страницGetting Started With Oneliner & Power Flow V11miguel itsonОценок пока нет
- 01 Pilot Project PalauДокумент40 страниц01 Pilot Project Palaumiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Wind Power Applications PDFДокумент2 страницыWind Power Applications PDFmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Power Script V11 Reference ManualДокумент193 страницыPower Script V11 Reference Manualmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Getting Started With Oneliner & Power Flow V11Документ27 страницGetting Started With Oneliner & Power Flow V11miguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Overcurrent Curves ListДокумент326 страницOvercurrent Curves Listmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Overcurrent Curve Editor Version 4 User's Manual: AspenДокумент49 страницOvercurrent Curve Editor Version 4 User's Manual: Aspenmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Data Conversion Programs User's Manual: AspenДокумент23 страницыData Conversion Programs User's Manual: Aspenmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Data Conversion Programs User's Manual: AspenДокумент23 страницыData Conversion Programs User's Manual: Aspenmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Prof. Nazar M. Karyar Tuesday, September 16, 2014 Transmission Lines ofДокумент85 страницProf. Nazar M. Karyar Tuesday, September 16, 2014 Transmission Lines ofmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Relay Commissioning Tablesget8445Документ35 страницRelay Commissioning Tablesget8445miguel itsonОценок пока нет
- 11 - Chapter 3 PDFДокумент28 страниц11 - Chapter 3 PDFRainielОценок пока нет
- PF2018 - Brochure (EN) PDFДокумент16 страницPF2018 - Brochure (EN) PDFBRYAN ANDREY GALLEGO QUINTERO100% (1)
- Weller WDДокумент2 страницыWeller WDmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Ac Circuit Breaker: 2.1 What Is Circuit Breaker?Документ13 страницAc Circuit Breaker: 2.1 What Is Circuit Breaker?miguel itson100% (1)
- DIgSILENT PF 15.1.2 ManualДокумент1 427 страницDIgSILENT PF 15.1.2 Manualxvehicle97% (31)
- Network Protection & Automation Guide - NPAG 2011 AlstomДокумент508 страницNetwork Protection & Automation Guide - NPAG 2011 Alstomhenry100% (1)
- Power Systems Kuestion PDFДокумент37 страницPower Systems Kuestion PDFsanthosh0% (1)
- Single Line Diagram SLDДокумент8 страницSingle Line Diagram SLDmiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- Transmission LineДокумент84 страницыTransmission Linemiguel itsonОценок пока нет
- 16-Transformer and Transformer Feeder ProtДокумент26 страниц16-Transformer and Transformer Feeder ProtSristick100% (4)
- Extra High Voltage AcДокумент535 страницExtra High Voltage AcRachid HamianiОценок пока нет
- NormalizationДокумент36 страницNormalizationSmilie ChawlaОценок пока нет
- DS 2Документ70 страницDS 2Nayan GaulkarОценок пока нет
- NtbtlogДокумент35 страницNtbtlogRanzozo KizaОценок пока нет
- Javascript Quick ReferenceДокумент1 страницаJavascript Quick Referencenomaddarcy100% (1)
- CX ManualДокумент9 страницCX Manualramlijavier75% (4)
- Control and Management of Railway System Connected To Microgrid StationsДокумент4 страницыControl and Management of Railway System Connected To Microgrid StationsmbdtechnologiessolutionsОценок пока нет
- 9604552-00#3.10A Ocean 2014 - Users Manual - EnglishДокумент149 страниц9604552-00#3.10A Ocean 2014 - Users Manual - EnglishTedy XdxdОценок пока нет
- Plant Engineering 11-20117Документ84 страницыPlant Engineering 11-20117Michael J. BaneОценок пока нет
- Simple Gantt Chart Template - TemplateLabДокумент1 страницаSimple Gantt Chart Template - TemplateLabjparedesvillaltaОценок пока нет
- Dylan Stanford CertificateДокумент4 страницыDylan Stanford Certificateapi-443252259Оценок пока нет
- 6es7134 4GB11 0ab0 PDFДокумент24 страницы6es7134 4GB11 0ab0 PDFDeyanira Guzman EscobarОценок пока нет
- The Scavenger Hunt - Sample QuestionsДокумент11 страницThe Scavenger Hunt - Sample QuestionsJenesa SabilaoОценок пока нет
- GBD - Sesion 06 Sentencia Create Table AsДокумент3 страницыGBD - Sesion 06 Sentencia Create Table AsvcxzvzcОценок пока нет
- Lossless and Lossy CompressionДокумент7 страницLossless and Lossy CompressionNii LaryeaОценок пока нет
- International Programmes in Germany 2018 Automotive Software Engineering - Technische Universität Chemnitz - ChemnitzДокумент6 страницInternational Programmes in Germany 2018 Automotive Software Engineering - Technische Universität Chemnitz - ChemnitzAnkith ShettyОценок пока нет
- SR No Category Sub Category Course Name Enable / Disable D Hands On? Yes/No Handson DetailДокумент3 страницыSR No Category Sub Category Course Name Enable / Disable D Hands On? Yes/No Handson DetailSourav MallickОценок пока нет
- Knobology Image Optimization and Trans Views - ShookДокумент5 страницKnobology Image Optimization and Trans Views - ShookAmar Mahesh KalluОценок пока нет
- Thought Leader Formula Official Workbook Version Jan 19 2019 PDFДокумент14 страницThought Leader Formula Official Workbook Version Jan 19 2019 PDFNitro NexusОценок пока нет
- Commissioning: Commissioning P63X/Uk Cm/A54 Micom P631, P632, P633, P634Документ30 страницCommissioning: Commissioning P63X/Uk Cm/A54 Micom P631, P632, P633, P634Joseph Yap SabariaОценок пока нет
- AndroidДокумент12 страницAndroidSergio Darío LópezОценок пока нет
- Akshay KДокумент48 страницAkshay Kdenny josephОценок пока нет
- Wagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security Final Exam: (Last) (First)Документ23 страницыWagner Spring 2014 CS 161 Computer Security Final Exam: (Last) (First)Ahsan RamzanОценок пока нет
- About Oracle Apps - Interview Questions On Oracle AR (Account Receivables) PDFДокумент3 страницыAbout Oracle Apps - Interview Questions On Oracle AR (Account Receivables) PDFMadhavi SinghОценок пока нет
- Wonderware InTouch Machine Edition en 0814Документ9 страницWonderware InTouch Machine Edition en 0814Binh Thai HYОценок пока нет
- S-101 Info Paper Jun12 enДокумент13 страницS-101 Info Paper Jun12 envdevivОценок пока нет
- 10.1007 - 978 3 319 33003 7 - 11Документ10 страниц10.1007 - 978 3 319 33003 7 - 11Lowleary1942Оценок пока нет
- C. SGH-wall 3Документ61 страницаC. SGH-wall 3MoustafaОценок пока нет
- Getting Started With Mathematica - Raspberry Pi ProjectsДокумент14 страницGetting Started With Mathematica - Raspberry Pi ProjectsHans Sebastian Navarrete LopezОценок пока нет
- r007 MTS-5800 GettingStartedGuideДокумент178 страницr007 MTS-5800 GettingStartedGuideNtibileng MoloiОценок пока нет
- Name: Preston KhumbulaДокумент7 страницName: Preston KhumbulaPreston KhumbulaОценок пока нет