Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDF
Загружено:
Ashish ChaharОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
12 Physics 2017 18 Pre Board Exam PDF
Загружено:
Ashish ChaharАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CBSE
Class 12 Physics
Pre-Board Exam (2017-18)
Time: 3 Hours. M.M:- 70 Marks
General Instruction:-
i. All questions are compulsory.
ii. This question paper have five sections: Section-A, Section-B, Section-C, Section-D and
Section-E
iii. Section A contains 5 questions of 1 marks each, Section B contains 5 questions of 2 marks
each, Section C contains 12 questions of 3 marks each, Section D contains 1 value based
question of 4 Marks and Section E contains 3 questions of 5 marks each.
iv. There is no overall choice, however, an internal choice has been provided in one question
of two marks, one question of three marks and all the three questions of five marks
weightage.
v. You may use the following values of physical constant:
mass of electron
mass of neutron
Section-A
1. Two charges of magnitude- 3Q and +2Q are located at point (a, 0) and (4a, 0) respectively.
What is the electric flux due to these charges through a sphere of radius 5a with its center
at origin.
2. A charge 'q' is moved from a point A above a dipole of dipole moment 'p' to a point B
below the dipole equatorial plane without acceleration. Find the work done in the
process.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 1 / 8
3. A concave lens of refractive index 1.5 is immersed in a medium of refractive index 1.65,
What is nature shown by lens?
4. Name any two types of transmission media that are commonly used for transmission of
signals ? Write the range of frequencies of the signals for which these transmission media
are used
5. Graph showing the variation of Current Versus voltage for material GaAs shown in figure
Identify the region of
i. Negative resistance
ii. Where ohm's law is obeyed
Section -B
6. A proton and an particle have the same de-Brogile wavelength, Determine the ratio of
i. their accelerating potentials
ii. their speed
7.
a. Distinguish between 'Analog' and 'Digital' forms of communication.
b. Explain briefly two commonly used application of the 'internet'.
8. Use the mirror equation to show that an object placed between 'f' and '2f' of a concave
mirror produces a real image beyond '2f'.
Or
A ray PQ incident normally on the refracting face BA is refracted in the prism BAC made
of material of refractive index 1.5 complete the path of ray through the prism. From
which face will the ray emerge ? Justify your answer.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 2 / 8
9. Define drift velocity. Write its relationship with relaxation time in terms of the electric
field E applied to conductor. A potential difference V is applied to a conductor of length L.
How is hte drift velocity affected when V is double and L is halved?
10. Calculate the shortest wavelength in the Balmer series of hydrogen atom. In which region
of the hydrogen spectrum does this wavelength lie?
Section - C
11.
a. Draw a labeled ray diagram of a compound microscope.
b. Derive an expression for its magnifying power.
c. Why is objective of a microscope of short aperture and short focal length? Give
reason.
12. The given graph shows the variation of photo - electric current (I) with the applied
voltage(v) for two different materials and for two different intensities of the incident
radiations. Identify and explain using Einstein's photo electric equation the pair to curves
that correspond to (i) different materials but same intensity incident radiations, (ii)
different intensities but same materials.
13.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 3 / 8
a. Write the basic nuclear involved in the emission ob in a symbolic form, by a radio
active nucleus.
b. In the reactions given below:
i.
ii.
Find the value of x, y and z and a, b and c.
Or
Distinguish between nuclear Fission and Fusion. Show how in both these
processes energy is released. Calculate the energy release in MeV in the
deuterium-tritium Fusion reaction:
Using the data:
14.
i. Why is communication using line of sight mode limited to frequencies above 40MHz.
ii. A transmitting antenna at the top of a tower has a height 32m and the height of the
receive antenna is 50m. What is the maximum distance between them for satisfactory
communication in line of sight mode?
15. A cell of emf 'E' and internal resistance 'r' is connected across a variable load resistor R.
Draw the plots of the terminal voltage V versus (i) R and (ii) current I.
It is found that when , the current is 1A when R is increased to , the current
reduces to 0.5A. Find the values of emf 'E' and internal resistance .
16.
i. Which segment of electromagnetic waves has highest frequency ? How are these
waves produced? Give one use of these waves?
ii. Which em waves lie near the highest frequency end of visible part of em spectrum ?
Give its one use. In what way this component of light has harmful effects on human?
17. State the principle of working of a galvanometer. A galvanometer of resistance G is
converted into a voltmeter to measure up to V volts by connecting a resistance R1 in
series with the coil. If a resistance R2 is connected in series with it, then it can measure
upto V/2 volts. Find the resistance, in terms of R1 and R2 required to be connected to
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 4 / 8
convert it into a voltmeter that can read upto 2v. Also find hte resistance G of the
galvanometer in terms of R1 and R2.
18.
i. Derive Snell's Law on the basis of Huygens's wave theory when light is traveling from
a denser to a rarer medium.
ii. Draw the sketches to differentiate between plane wave front and spherical wave
front.
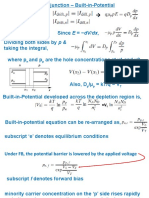
19. Draw V-I characteristics of p-n junction diode. Answer the following question, giving
reasons:
i. Why is the current under reverse bias almost independent of the potential up to a
critical voltage?
ii. Why does the semiconductor device which operates under the reverse bias in the
breakdown region.
20.
a. Why is the potential inside a hollow spherical charged conductor constant and has the
same value as on its surface?
b. Figure shows two identical capacitors, C1 and C2, each of capacitance connected
to a battery of 6v. Initially switch S is closed. After some time S is left open and
dielectric slabs of dielectric constant K = 3 are inserted to fill completely the space
between the plates of the two capacitors. How will the (i) charge and (ii) potential
difference between the plates of the capacitors be affected after the slabs are
inserted?
21. Write the expression for hte generalized of Ampere's Circuital law. Discuss its
significance and describe briefly how the concept of displacement current is explained
through charging/discharging of a capacitor in an electric circuit.
22. Identify the gates P and Q shown in the figure. Write the truth table for the combination
of the gates shown.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 5 / 8
Name the equivalent gate representing this circuit and write its logic symbol.
Section - D
23. Ram is a student of class x in a village school. His uncle gifted him a bicycle with a
dynamo fitted in it. He was very excited to get it. While cycling during night, he could
light the bulb and see the object on the road. He, however, did not know how this device
works. He asked this question to his teacher. The teacher considered it an opportunity to
explain the working to the whole class.
Answer the following question:
a. State the principle and working of a dynamo.
b. Write two values each displayed by Ram and his school teacher.
Section - E
24.
a. USe Gauss's law to find the electric field due to a uniformly charged in finite sheet.
What is the direction of field for positive and negative charge densities?
b. Find the ratio of the potential differences that must be applied across the parallel and
series combination of two capacitors C1 and C2, with their capacitances in the ratio 1:2
so that the energy stored in two cases becomes the same.
Or
a. Explain using suitable diagrams, the difference in hte behaviour of a (i) conductor
and (ii) dielectric in the presence of external electric field. Define the terms
polarization of a dielectric and write its relation with susceptibility.
b. A thin metallic spherical shell of radius R carries a charge Q on its surface. A point
charge Q/2 is placed at its centre C and another charge +2Q is placed outside the shell
at a distance x from the center as shown in figure. Find (i) the force on the charge at
the centre of shell and at the point A. (ii) the electric flux through the shell.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 6 / 8
25.
a. Express Biot-Savart Law in the vector form.
b. Use it to obtain the expression for the magnetic field at an axial point, distance 'd'
from hte centre of a circular coil of radius 'R' carrying current 'I'.
Or
a. A magnetic dipole is placed in a uniform magnetic field with its axis tilted with
respect to its position of stable equilibrium. Deduce an expression for the time period
of oscillation of this magnetic dipole about an axis, passing through its centre and
perpendicular to its plane
b. If this bar magnet is replaced by a combination of two similar bar magnets, placed
over each other, how will the time period vary?
26.
i. In Young's double slit experiment, deduce the condition for (a) constructive, and (b)
destructive interference at a point on the screen. Draw a graph showing variation of
intensity in the interference pattern against position 'x' on the screen.
ii. Compare the interference pattern observed in Young's double slit experiment with
single slit diffraction pattern, pointing out three distinguishing features.
Or
i. Plot a graph to show variation of the angle of deviation as a function of angle of
incidence for light passing through a prism derive an expression for refractive index
of the prism in terms of angle of minimum deviation and angle of prism.
ii. What is dispersion of light? What is its cause?
iii. A ray of light incident normally on one face of a right isosceles prism is totally
refracted as shown in fig, what must be minimum value of refractive index of glass?
Give relevant calculations.
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 7 / 8
Material downloaded from myCBSEguide.com. 8 / 8
Вам также может понравиться
- Geophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IОт EverandGeophysical Field Theory and Method, Part B: Electromagnetic Fields IОценок пока нет
- Cbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFДокумент9 страницCbse Class 12 Sample Paper 2017 18 Physics PDFIshika SinghОценок пока нет
- Principles of Solar Cells, LEDs and Related Devices: The Role of the PN JunctionОт EverandPrinciples of Solar Cells, LEDs and Related Devices: The Role of the PN JunctionОценок пока нет
- 12 Lyp Physics s1Документ7 страниц12 Lyp Physics s1jashwanth kumar58Оценок пока нет
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsОт EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 7Документ7 страницMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 7HemantОценок пока нет
- FLT - Iii (2016-17)Документ4 страницыFLT - Iii (2016-17)ChetanОценок пока нет
- 12 Physics sp02 PDFДокумент25 страниц12 Physics sp02 PDFaditya prabhakerОценок пока нет
- 12 Physics SP CbseДокумент20 страниц12 Physics SP CbsePrachi DwivediОценок пока нет
- Physice 2010 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFДокумент6 страницPhysice 2010 Unsolved Paper Outside Delhi PDFSunita AnandОценок пока нет
- Class 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24Документ3 страницыClass 12 Physics 1st Term 23 - 24PrinceОценок пока нет
- 2013 PDFДокумент7 страниц2013 PDFnandagopanОценок пока нет
- FT Gr-12 SET AДокумент8 страницFT Gr-12 SET ARAIRSОценок пока нет
- FLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsДокумент4 страницыFLT - I (2016 - 2017) : PhysicsChetanОценок пока нет
- Apeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsДокумент4 страницыApeejay School, Saket First Terminal Examination - 2016: Class Xii (Physics) General InstructionsabhilashagoelОценок пока нет
- New Microsoft Word DocumentДокумент3 страницыNew Microsoft Word DocumentRuprabh KumarОценок пока нет
- Physics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024Документ6 страницPhysics Class Xii Sample Paper Test 03 For Board Exam 2024xkryxxzОценок пока нет
- 1 Physics 2014 To 2018 JulyДокумент6 страниц1 Physics 2014 To 2018 JulyRavi Kumar100% (1)
- 5 MarkersДокумент9 страниц5 MarkersshiviОценок пока нет
- PB - I Physics Xii 2023-24Документ7 страницPB - I Physics Xii 2023-24hari008091Оценок пока нет
- Anant Achievement Classes Physics TestДокумент2 страницыAnant Achievement Classes Physics TestUTSAV JAINОценок пока нет
- Sample Papers Class 12 PhysicsДокумент53 страницыSample Papers Class 12 Physics0910ashuОценок пока нет
- XII PhysicsДокумент7 страницXII Physicsrandhir.kumar41Оценок пока нет
- 7 SQPДокумент7 страниц7 SQPlanfury45Оценок пока нет
- Preboard Physics 2023-24Документ5 страницPreboard Physics 2023-24rishitasarkar875Оценок пока нет
- 12TH PHYSICS FTДокумент10 страниц12TH PHYSICS FTABHISHEK PANDAОценок пока нет
- Phy 2015Документ5 страницPhy 2015ANASОценок пока нет
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper-01: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 20Документ20 страницCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper-01: Material Downloaded From - 1 / 20ANUP KUMARОценок пока нет
- CbseДокумент5 страницCbserockstar104Оценок пока нет
- CBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2010 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4Документ30 страницCBSE Board Class XII Physics - Set 1 Board Paper - 2010 Time: 3 Hours (Total Marks: 70) General Instructions: 1. 2. 3. 4zelОценок пока нет
- Class 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 1Документ6 страницClass 12 Cbse Physics Sample Paper 2013 Model 1Sunaina RawatОценок пока нет
- Electric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board QuestionsДокумент50 страницElectric Charges and Fields: 2006 Board Questionsgurveer sainiОценок пока нет
- Spty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFДокумент14 страницSpty, Yr6ti7iuhliphysics2013allindia PDFyeateshwarriorОценок пока нет
- Physice 2013 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFДокумент6 страницPhysice 2013 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFSunita AnandОценок пока нет
- Previous Year Question PapersДокумент19 страницPrevious Year Question PapersZareena JamadarОценок пока нет
- CBSE XII - Physics: Board Paper - 2006Документ5 страницCBSE XII - Physics: Board Paper - 2006venkithebossОценок пока нет
- CBSE 12th Physics Sample Paper 2019 Question PaperДокумент7 страницCBSE 12th Physics Sample Paper 2019 Question PapermisostudyОценок пока нет
- Phy Part I AssignmentДокумент16 страницPhy Part I Assignmentketan waghОценок пока нет
- PB Xii (2022 23) Set 1Документ4 страницыPB Xii (2022 23) Set 1Uday SinghОценок пока нет
- Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2 Indore Class Xii Physics Assignment For Summer Vacation 2019-20 ElectrostaticsДокумент6 страницKendriya Vidyalaya No.2 Indore Class Xii Physics Assignment For Summer Vacation 2019-20 ElectrostaticsRahul SinghОценок пока нет
- QP Xii Phy PB1 2023-24Документ7 страницQP Xii Phy PB1 2023-24Puskar SinghОценок пока нет
- Sample Paper Grade 12 PhysicsДокумент5 страницSample Paper Grade 12 PhysicsRohan ChackoОценок пока нет
- Class 12 Revision Sheet HW PDFДокумент5 страницClass 12 Revision Sheet HW PDFAditya ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Ii Pu Physics QPДокумент5 страницIi Pu Physics QPHarshith HachhuОценок пока нет
- PHYSICS Xii PB-1 QPДокумент10 страницPHYSICS Xii PB-1 QPAyaan HusainОценок пока нет
- II PUC Physics Paper 1Документ2 страницыII PUC Physics Paper 1narayanammagnarayanamma90Оценок пока нет
- Physics 2nd Obj Sub NДокумент3 страницыPhysics 2nd Obj Sub NMisbah sabirОценок пока нет
- Question Paper Physics PB I 2023-24Документ6 страницQuestion Paper Physics PB I 2023-24rishirajkaran2006Оценок пока нет
- 12 Science HHWДокумент26 страниц12 Science HHWOmkar VikalОценок пока нет
- Grade 12 - Physics PB2Документ9 страницGrade 12 - Physics PB2Nazneen AliОценок пока нет
- Class-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-1Документ8 страницClass-Xii - Final Cbse Board Physics Sample Paper-1kamali.v777Оценок пока нет
- Physics Code No. 1/2 Set: 2 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 General InstructionsДокумент5 страницPhysics Code No. 1/2 Set: 2 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 100 General InstructionsChandan PatraОценок пока нет
- 12 PhysicsДокумент8 страниц12 Physicsdhritibarak548Оценок пока нет
- Physice 2010 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFДокумент6 страницPhysice 2010 Unsolved Paper Delhi Board PDFSunita AnandОценок пока нет
- 12th First Book 2nd Book Test 2022Документ5 страниц12th First Book 2nd Book Test 2022Himanshu ThapliyalОценок пока нет
- Midterm 2023Документ5 страницMidterm 2023Thanushree.SОценок пока нет
- Angel Education Society: HALFYEARLY EXAMINATION (2017-20018) Subject: Physics Class - 12 F.M - 70 Time-3 HrsДокумент3 страницыAngel Education Society: HALFYEARLY EXAMINATION (2017-20018) Subject: Physics Class - 12 F.M - 70 Time-3 HrsAtul Verma0% (1)
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper 2018Документ3 страницыCBSE Class 12 Physics Sample Paper 2018Faculty, Shahid Matangini Hazra Government College for WomenОценок пока нет
- 10 Physics t2 sp08 220516 103652Документ9 страниц10 Physics t2 sp08 220516 103652Kshitij RanjanОценок пока нет
- CBSE 12th Physics Unsolved Overall Important Question Paper - IIIДокумент7 страницCBSE 12th Physics Unsolved Overall Important Question Paper - IIIShakti Singh ShekhawatОценок пока нет
- Electronics&Communication - PaperДокумент15 страницElectronics&Communication - PaperPrasanth P KorothОценок пока нет
- UNIT 4: Fundamentals of Semiconductor Devices and Digital CircuitsДокумент338 страницUNIT 4: Fundamentals of Semiconductor Devices and Digital CircuitsAyush GuptaОценок пока нет
- EEE225 - Pre-Final Exam Section 1 - Google FormsДокумент11 страницEEE225 - Pre-Final Exam Section 1 - Google FormsDavid Louie BediaОценок пока нет
- Module III IV Lasers Optical Fibers-1Документ13 страницModule III IV Lasers Optical Fibers-1OpenaiОценок пока нет
- CBSE XII Physics Notes SemiconductorДокумент20 страницCBSE XII Physics Notes Semiconductorkaushik2470% (1)
- Phy 363 ProjectДокумент9 страницPhy 363 ProjectMorongwa MaiselaОценок пока нет
- Semiconductor Diode: Prepared By: Presented ToДокумент16 страницSemiconductor Diode: Prepared By: Presented ToArif IstiaqОценок пока нет
- 30 TOP SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and Answers PDF SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and Answers PDFДокумент6 страниц30 TOP SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and Answers PDF SPECIAL PURPOSE DIODES Questions and Answers PDFsanaullahОценок пока нет
- Combine All Chapter (3.1-3.18)Документ665 страницCombine All Chapter (3.1-3.18)Jimmy CheungОценок пока нет
- TheoryДокумент3 страницыTheoryIonut PaladeОценок пока нет
- B.Tech. Syllabus Effective - Detailed Syllabus - 2021-2022-09.03.2022Документ125 страницB.Tech. Syllabus Effective - Detailed Syllabus - 2021-2022-09.03.2022M n LamaОценок пока нет
- MSE-21-Optical Properties (61) - 2007-05-31Документ61 страницаMSE-21-Optical Properties (61) - 2007-05-31Surendra PandaОценок пока нет
- Electonics Final HandoutsДокумент84 страницыElectonics Final HandoutsDiane BasilioОценок пока нет
- 10 - Sample Question Papers (SQPS) of Physics With Bps & Mss - Session - 2022-23.Документ141 страница10 - Sample Question Papers (SQPS) of Physics With Bps & Mss - Session - 2022-23.GAMING HACKSОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Bput - 2008 - EeeДокумент78 страницSyllabus Bput - 2008 - EeeSarAona HemBramОценок пока нет
- Analogue CircuitsДокумент156 страницAnalogue Circuitsdevender duaОценок пока нет
- Laser Diode & Application of It in Hematology, by Marwan FawziДокумент36 страницLaser Diode & Application of It in Hematology, by Marwan Fawzinoor deenОценок пока нет
- EDC Assignment #1Документ4 страницыEDC Assignment #1King KhanОценок пока нет
- Construction of Solar CellДокумент2 страницыConstruction of Solar CellAugustine FletcherОценок пока нет
- HP Pavilion G4-G6-G7 Quanta R23 AMD Sabin UMA-Muxless Schematic Diagram 1AДокумент14 страницHP Pavilion G4-G6-G7 Quanta R23 AMD Sabin UMA-Muxless Schematic Diagram 1AParv PatelОценок пока нет
- Deek ShaДокумент13 страницDeek ShaShivani SharmaОценок пока нет
- Edc Unit 1 PN DiodeДокумент28 страницEdc Unit 1 PN DiodeAravind SkipperОценок пока нет
- 3-Komponen Dasar ElektronikaДокумент42 страницы3-Komponen Dasar ElektronikaNovia Diajeng ArumsariОценок пока нет
- Depletion RegionДокумент2 страницыDepletion RegiongsigalaoОценок пока нет
- Solar CellДокумент3 страницыSolar CellET163018 Khaled ArjuОценок пока нет
- Questions On Transistor CharacteristicsДокумент72 страницыQuestions On Transistor Characteristicskibrom atsbha50% (2)
- PN Junction Diode: 5 March 2021 Physics of Semiconductor Devices 1 5 March 2021 1 5 March 2021 1Документ83 страницыPN Junction Diode: 5 March 2021 Physics of Semiconductor Devices 1 5 March 2021 1 5 March 2021 1Dhakshinamurthi .MОценок пока нет
- Basic Electronics Chap # 2 Diode: Engr. Farwa BatoolДокумент10 страницBasic Electronics Chap # 2 Diode: Engr. Farwa BatoolFarwa JaffriОценок пока нет
- PN Junction Diode: I-V Characteristics: Sung June KimДокумент42 страницыPN Junction Diode: I-V Characteristics: Sung June KimasadОценок пока нет
- Engineering Physics Text BookДокумент314 страницEngineering Physics Text BookShawn Waltz33% (3)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesОт EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2193)
- A Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceОт EverandA Beginner's Guide to Constructing the Universe: The Mathematical Archetypes of Nature, Art, and ScienceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (51)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessОт EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Dark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseОт EverandDark Matter and the Dinosaurs: The Astounding Interconnectedness of the UniverseРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (69)
- The Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectОт EverandThe Simulated Multiverse: An MIT Computer Scientist Explores Parallel Universes, The Simulation Hypothesis, Quantum Computing and the Mandela EffectРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (20)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingОт EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (5)
- Giza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyОт EverandGiza: The Tesla Connection: Acoustical Science and the Harvesting of Clean EnergyОценок пока нет
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceОт EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (23)
- Knocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldОт EverandKnocking on Heaven's Door: How Physics and Scientific Thinking Illuminate the Universe and the Modern WorldРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (64)
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowОт EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (49)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterОт EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (410)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidОт EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1395)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismОт EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (500)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayОт EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (125)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseОт EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (13)
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsОт EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (94)
- How to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionОт EverandHow to Teach Nature Journaling: Curiosity, Wonder, AttentionРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (3)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldОт EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (60)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldОт EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (8)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldОт EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (54)
- Chernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterОт EverandChernobyl 01:23:40: The Incredible True Story of the World's Worst Nuclear DisasterРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (264)