Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Week #20 - What's in My Noodles
Загружено:
Gareth James ParryАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Week #20 - What's in My Noodles
Загружено:
Gareth James ParryАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
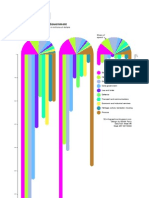
What’s in my noodles?!
The Codex Alimentarius was set up in 1963 by the United
Nations to codify what’s allowed in common food
products, like noodles.
So what does the Codex say is allowed in my
prepackaged noodles?
FLOUR
Acidity Regulators Antioxidants Colours Stabilizers and thickeners Emulsifiers Humectants Preservatives Flavour Enhancers Anticaking Agent Flour Treatment Agents
Acidity regulators are added Anti-oxidants are added to food Food colouring is any substance Stabilizers and thickeners give Emulsifiers keep water and oils Humectants stop food from Preservatives stop fungi, Flavour enhancers are added to Anticaking agents like Flour treatment agents are
to food change or maintain pH to help prevent deterioration. added to food or drink to foods a firmer texture. mixed together, rather than drying out. bacteria, and microorganisms commercially produced food to polydimethylsiloxane stop added to flour to make it
level (acidity or basicity). They Food begins to deteriorate change its colour. separating. from spoiling food. make it taste more savoury. powders from ‘caking’ or appear whiter (freshly milled
can be organic or mineral acids, by oxidation, when it gets • Calcium carbonate • Sodium lactate sticking together. flour is yellowish), to help
bases, neutralizing agents, exposed to oxygen and sun. • Curcumin • Agar • Lecthin • Monosodium orthophosphate • Sorbic acid • Glutamic acid (L(+)-) develop gluten, and to help
or buffering agents. They're Anti-oxidants help prevent • Riboflavin • Beta-cyclodextrin • Propylene glycol alginate • Disodium orthophosphate • Sodium sorbate • Monosodium glutamate, L- flour to bake.
shown by their E-number (like that oxidation. • Riboflavin • Alginic acid • Polyoxyethylene (8)stearate • Trisodium orthophosphate • Potassium sorbate • Disodium 5’-inosinate,
E260 acetic acid), or described 5'-phosphate, sodium • Sodium Alginate • Polyoxyethylene • Monopotassium • Calcium sorbate • Disodium 5’-guanylate • Sulpher dioxide
as "food acid". • Ascorbic acid (L-) • Tartrazine • Carob Bean Gum (40 stearate orthophosphate • Disodium 5’-ribonucleotides • Sodium sulphite
• Ascorbyl palmitate • Sunset yellow FCF • Carrageenan and its • Polyoxyethylene (20)sorbitan • Dipotassium orthophosphate • Sodium hydrogen sulphite
• Acetic acid, glacial • Ascorbyl stearate • Carmines Na, K, NH4 salts (includes monolaurate • Tripotassium orthophosphate • Sodium metabisulphite
• Sodium acetate • Mixed tocopherols • Chlorophyll copper complex furcellaran) • Polyoxyethylene (20)sorbitan • Tricalcium orthophosphate • Potassium metabisulphite
• Lactic acid (L-, D-, and DL-) concentrate • Chlorophyllin copper • Processed Eucheuma Seaweed monooleate • Disodium diphosphate • Potassium sulphite
• Malic acid (DL-) • Alpha-tocopherol complex, sodium and • Guar gum • Polyoxyethylene (20)sorbitan • Tetrasodium diphosphate • Calcium hydrogen sulphite
• Calcium lactate • Propyl gallate potassium salts • Gum Arabic (acacia gum) monopalmitate • Tetrapotassium diphosphate • Potassium bisulphite
• Citric acid • Tertiary butylhydroquinone • Fast green FCF • Karaya Gum • Polyoxyethylene (20)sorbitan • Dicalcium diphosphate • Sodium thiosulphate
• Trisodium citrate (TBHQ) • Caramel I-plain • Tara Gum monostearate • Pentasodium triphosphate
• Tartaric acid (L(+)-) • Butylated hydroxyanisole • Caramel II-caustic • Gellan Gum • Polyoxyethylene (20)sorbitan • Sodium polyphosphate
• Sodium malate (BHA) sulphite process • Curdlan tristearate • Potassium polyphosphate
• Sodium fumarates • Butylated hydroxytoluene • Caramel III-ammonia process • Pectins • Mono and di-glycerides of • Calcium polyphosphates
• Sodium carbonate (BHT) • Caramel IV-ammonia • Sodium carboxymethyl fatty acids • Ammonium polyphosphates
• Sodium hydrogen carbonate sulphite process cellulose • Diacetyltartaric and fatty • Sorbitol and sorbitol syrop
• Potassium carbonate • Beta carotene (synthetic) • Potassium chloride acid esters of glycerol • Propylene glycol
• Calcium sulphate • Carotenes, Vegetable • Acid treated starch • Sucrose esters of
• Calcium oxide • Beta-carotene • Alkaline treated starch fatty acids
(Blakeslea trispora) • Bleached starch • Polyglycerol esters of
• Beta-apo-carotenal • Oxdized Starch fatty acids
• Beta-apo-8'-carotenic acid, • Starches, enzyme-treated • Polyglycerol esters
methyl or ethyl ester • Monostarch phosphate of interesterified
• Beet red • Distarch phosphate ricinoleic acids
esterified with sodium • Propylene glycol esters of
trimetaphosphate; fatty acids
esterified with • Sodium stearoyl lactylate
phosphorous oxychloride • Calcium stearoyl lactylate
• Phosphated distarch • Sorbitan monostearate
phosphate • Sorbitan tristearate
• Acetylated distarch • Sorbitan monolaurate
phosphate • Sorbitan monopalmitate
• Starch acetate
• Acetylated distarch adipate
• Hydroxypropyl starch
• Hydroxypropyl distarch
phosphate
• Starch sodium
octenyl succinate
• Acetylated oxidized starch
52-infographics.blogspot.com
Data from the Codex Alimentarius and Wikipedia
Design by Gareth Parry
Week #20 20101128
Вам также может понравиться
- Week #51 - Who Owes What?Документ1 страницаWeek #51 - Who Owes What?Gareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #39 - What Just HappenedДокумент1 страницаWeek #39 - What Just HappenedGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #52 - The Making ofДокумент1 страницаWeek #52 - The Making ofGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #50 - CoffeeДокумент1 страницаWeek #50 - CoffeeGareth James Parry100% (4)
- Week #42 - Rivers of The World - E-Coli Bacteria Count Per Millilitre of River WaterДокумент1 страницаWeek #42 - Rivers of The World - E-Coli Bacteria Count Per Millilitre of River WaterGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #35 - Natural DisastersДокумент1 страницаWeek #35 - Natural DisastersGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #46 - HermeneuticsДокумент1 страницаWeek #46 - HermeneuticsGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #37 - SpendДокумент1 страницаWeek #37 - SpendGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #48 - The Creative ProcessДокумент1 страницаWeek #48 - The Creative ProcessGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #32 - Systems of GovernmentДокумент1 страницаWeek #32 - Systems of GovernmentGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #40 - A Simple Ratio of Civilian CasualtiesДокумент1 страницаWeek #40 - A Simple Ratio of Civilian CasualtiesGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #36 - Fruit, 2009Документ1 страницаWeek #36 - Fruit, 2009Gareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #21 - 21 Things I Did On Monday November 29Документ1 страницаWeek #21 - 21 Things I Did On Monday November 29Gareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #33 - There Are About 2703 Insects Per Square Meter of LandДокумент1 страницаWeek #33 - There Are About 2703 Insects Per Square Meter of LandGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #31 - A Timeline of Valentine's DayДокумент1 страницаWeek #31 - A Timeline of Valentine's DayGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #26 - Invasive Species of New ZealandДокумент1 страницаWeek #26 - Invasive Species of New ZealandGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #34 - Player Profile: Gareth ParryДокумент1 страницаWeek #34 - Player Profile: Gareth ParryGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #27 - American WarsДокумент1 страницаWeek #27 - American WarsGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #30 - Things That Are 30Документ1 страницаWeek #30 - Things That Are 30Gareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #29 - Animal RainsДокумент1 страницаWeek #29 - Animal RainsGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #18 - New Zealand BrandДокумент1 страницаWeek #18 - New Zealand BrandGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #17 - Energy Generation and UseДокумент1 страницаWeek #17 - Energy Generation and UseGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #14 - Stop TraffickДокумент1 страницаWeek #14 - Stop TraffickGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #15 - Things With Pig in ThemДокумент1 страницаWeek #15 - Things With Pig in ThemGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #16 - Affluence V PovertyДокумент1 страницаWeek #16 - Affluence V PovertyGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #9 - Stop RubbishДокумент1 страницаWeek #9 - Stop RubbishGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #8 - Universal Facial ExpressionsДокумент1 страницаWeek #8 - Universal Facial ExpressionsGareth James Parry100% (1)
- Week #13 - Working ConditionsДокумент1 страницаWeek #13 - Working ConditionsGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- Week #7 - Advice For DesignersДокумент1 страницаWeek #7 - Advice For DesignersGareth James ParryОценок пока нет
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Physical Science - Biological MacromoleculesДокумент18 страницPhysical Science - Biological MacromoleculesToni GraceОценок пока нет
- Nutritional Content and Health Benefits of SeafoodДокумент17 страницNutritional Content and Health Benefits of SeafoodElavarasan KrishnamoorthyОценок пока нет
- Bpo C Chapter 18Документ74 страницыBpo C Chapter 18Cristiano Hamdiansyah SempadianОценок пока нет
- Lipids Properties and FunctionsДокумент5 страницLipids Properties and FunctionsIyap LazatinОценок пока нет
- Fatty Alcohols Dhwrodleben deДокумент5 страницFatty Alcohols Dhwrodleben deharshОценок пока нет
- Vivek Rathore, Sudha Tyagi, Bharat Newalkar, R.P. Badoni: HighlightsДокумент12 страницVivek Rathore, Sudha Tyagi, Bharat Newalkar, R.P. Badoni: HighlightsFarah TalibОценок пока нет
- Food and Nutrition Quiz: Test Your Knowledge on Food Groups, Nutrients and MoreДокумент10 страницFood and Nutrition Quiz: Test Your Knowledge on Food Groups, Nutrients and MoreAu-au Hornido BulangОценок пока нет
- Product Catalogue 2016: © 2016 Zahidtransservice. All Rights ReservedДокумент47 страницProduct Catalogue 2016: © 2016 Zahidtransservice. All Rights ReservedMesfin MamoОценок пока нет
- NUTRITION & DIETETICS GUIDELINESДокумент147 страницNUTRITION & DIETETICS GUIDELINESmatrixtrinityОценок пока нет
- 2783 Ais - Database.model - file.PertemuanFileContent James Ralph Hanson Natural Products The Secondary Metabolites (Tutorial Chemistry Texts) 2003Документ149 страниц2783 Ais - Database.model - file.PertemuanFileContent James Ralph Hanson Natural Products The Secondary Metabolites (Tutorial Chemistry Texts) 2003Dyah Indah Rini100% (4)
- SAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 2 2Документ38 страницSAS For Biochemistry BIO 024 Module 2 2syriljen mamolangОценок пока нет
- An Experimental Investigation of Palm Oil As An Environment Friendly BiolubricantДокумент5 страницAn Experimental Investigation of Palm Oil As An Environment Friendly BiolubricantmohamedОценок пока нет
- Method For Manufacturing Rumen by Pass FatДокумент6 страницMethod For Manufacturing Rumen by Pass FatAnonymous 6HADGUEXDОценок пока нет
- Health Benefits of Eating MuttonДокумент4 страницыHealth Benefits of Eating MuttonAmal ami100% (1)
- PRICAT99xx Products - Tech Seminar - Updated 2016 SWДокумент56 страницPRICAT99xx Products - Tech Seminar - Updated 2016 SWKathe Molina CarvajalОценок пока нет
- Lipids Functions and StructuresДокумент2 страницыLipids Functions and StructuresCaryl Alvarado Silang0% (1)
- Ch13 Pages 390-422Документ33 страницыCh13 Pages 390-422rlawngus1Оценок пока нет
- Oils and Fats As Renewable Raw Materials in Chemistry: ReviewsДокумент18 страницOils and Fats As Renewable Raw Materials in Chemistry: ReviewsPaksi PujiantoОценок пока нет
- Chemical CompositionДокумент219 страницChemical CompositionPhan Huy100% (5)
- Azelaic Acid: Pharmacology, Toxicology and Mechanism of Action AcneДокумент5 страницAzelaic Acid: Pharmacology, Toxicology and Mechanism of Action AcneGlória BorgesОценок пока нет
- Carrier Oil Shelf LifeДокумент3 страницыCarrier Oil Shelf LifeAna ThesecretiveОценок пока нет
- Ebook Ebook PDF Personal Nutrition 10th Edition by Marie A Boyle PDFДокумент41 страницаEbook Ebook PDF Personal Nutrition 10th Edition by Marie A Boyle PDFtina.cousins322100% (36)
- Instructor: Dr. Vianney Curiel CervantesДокумент13 страницInstructor: Dr. Vianney Curiel CervantesRicardo Eduardo Martinez MartinezОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 - Milk CompositionДокумент46 страницLecture 1 - Milk CompositionAmirul AimanОценок пока нет
- Sample Lab Report 5 Alain NowДокумент10 страницSample Lab Report 5 Alain NowNur SetsuОценок пока нет
- Calamba Doctors' College Lecture on Digestion, Absorption, and MetabolismДокумент13 страницCalamba Doctors' College Lecture on Digestion, Absorption, and MetabolismMelody DoriaОценок пока нет
- IJSO Biology Module - 3Документ207 страницIJSO Biology Module - 3Ikhbaat Atiqur RehmanОценок пока нет
- 7 - Structur Lipid & As. Lemak TrisuspptДокумент47 страниц7 - Structur Lipid & As. Lemak TrisuspptNurul Sukmaning HabibieОценок пока нет
- Experiment 3Документ22 страницыExperiment 3Sophiah RachelleОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Lipids: Ms. Arianna S. Fernando NOVEMBER 6, 2022Документ13 страницIntroduction To Lipids: Ms. Arianna S. Fernando NOVEMBER 6, 2022BobbyОценок пока нет