Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Teleimmersion Seminar Report
Загружено:
Kavya GopavaramОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Teleimmersion Seminar Report
Загружено:
Kavya GopavaramАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TELE IMMERSION
1. INTRODUCTION
In tele-immersion, immersive virtual reality environments are used over networks to provide
shared access to simulated virtual spaces for design, collaboration, entertainment, education.
Tele-immersion integrates collaborative Virtual Reality with audio and videoconferencing that
may involve data mining and heavy computation. When participants are tele-immersed, not
only can they virtually see and interact with each other, but when they leave, their
environment continues to evolve, autonomously controlling computation and data access. The
environment transmits gestures as well as audio and video, so users have a greater sense of
presence in the shared space. Scientists are also trying to tackle the problem of how to provide
both synchronous and asynchronous collaboration. When collaborators are on the same
continent, conducting synchronous sessions in the shared space is straightforward because
time differences are minimal. When collaborators are across the globe, however, the greater
time differences require asynchronous collaboration —collaborators working in the same
virtual space at different times so they can work during their normal work hours. Video
conferencing prices have plunged over the past few years with the advances in computer
technology and the advent of high-bandwidth telephone and Internet lines in the office.
However, there are limitations. Videoconferencing +today is like watching the remote person
on television. Although you can hear the person and see the non-verbal gestures and cues, it is
not really like sitting across the table from the person. People sometimes feel uncomfortable
on camera and feel disconnected from the people shown on the screen. It is also impossible to
make direct eye contact, because the camera and the display screen are not in the same spot.
In video-conferencing the image is close to real time but there are always delays that
cause distorted video. Also if someone walked out of the view of the camera the
person is no longer visible. So, to remove this problem a new technology came into
existence, called tele-immersion. Tele immersion is the next step of video conferencing.
Tele-immersion(National Tele-immersion Initiative - NTII ) will enable users at
geographically distributed sites to collaborate in real time in a shared, simulated
Environment as if they were in the same physical room. In a tele-immersive
environment computers recognize the presence and movements of individuals and
objects, track those individuals and images, and then permit them to be projected in
realistic, multiple, geographically distributed immersive environments or stereo-
immersive surfaces. Tele immersion environments will therefore facilitate not only
interaction between user themselves but also between users and computer-generated
models.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 1
TELE IMMERSION
1.1 What is tele-immersion?
According to Jason Leigh “The term Tele-immersion was first used … as the title of a
workshop … to bring together researchers in distributed computing, collaboration,
virtual reality and networking”.
According to Watsen & Zyda “It enables the interaction between geographically
remote participants within a shared, three-dimensional space.”
Tele-immersion is a new medium of human interaction that creates illusion that the
user is in the same physical space like the other participants, although in reality other
participants are thousands of miles away. This is a new telecommunication that
combines aspects of virtual reality with 3D videoconferencing. Tele-immersion enables
users at geographically distributed sites to collaborate in shared, simulated, hybrid
environment as if they were in the same physical room. It is the ultimate synthesis of
networking and media technologies to enhance collaborative environments. This
environment persists even when all the participants have left. Tele-immersive
applications must combine audio, video, virtual worlds, simulations, and many other
complex technologies. They will require huge bandwidth, very fast responses, and
guarantees of delivery.
The ideal tele-immersion system is not hard to imagine. Combine the best
computer graphics, audio, computer simulation, and imaging, connect with
networking, provide software and hardware to track gaze, gesture, facial
expression, and body position, offer it as a built-in feature on all personal computers
and video games. Obviously, we are far from achieving ubiquitous tele-immersion.
In the past people only dream about communicating geographically but the
advancement in telecommunication along with advancement in media techniques make
it possible. But still there was struggle to make them collaborate in a real time world,
like efforts to have users share the same physical space, during the meetings,
conferences, etc. This kind of tele-immersion differs significantly from conventional
video teleconferencing in that the user's view of the remote environment changes
dynamically as he moves his head.
Tele -immersion is the ultimate synthesis of * 3D environment scanning - 3D
reconstruction based on display * Projective and display technologies * tracking
technologies * Audio technologies * Robotics and haptics media technologies and
powerful networking. This application is therefore considered to be an ideal driver for
the research age of the Internet2 community. If the network can support network
requirements for tele-immersive (TI) sessions it is very probable that every other future
network application will be also supported.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 2
TELE IMMERSION
2. The History
It was way back in 1965 that the great pioneer of computer graphics, Ivan Sutherland,
proposed the concept of the ‘ultimate display’. It described a graphics display that
would allow the user to experience a completely computer rendered environment.
In 1998, Abilene, a backbone research project, was launched and now serves as a base
for Internet2 research. Internet2 needed an application that would challenge and stretch
its networks’ capabilities. The head of advanced network and services proposed Tele
immersion at the application that could drive internet2 research forward. That is how
the national. Tele immersion initiative as formed in may2000, researchers at the
Universities of North Carolina (UNC), the Universities of Pennsylvania and advanced
network and services reached a milestone in developing this technology. A user sitting
in an office at UNC in Chapel Hill, NC, was able to see life like, 3D images of
colleagues hundreds of miles away, one in Philadelphia and the other in New York.
Today scientists are still developing this new communication technology. There are
several groups working together on the national Tele immersion initiative (NTII) to
make this wonderful technology available to the common men.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 3
TELE IMMERSION
3. DEVELOPMENT OF TELE-IMMERSION
It was back in 1965 that the great pioneer of computer graphics Ivan Sutherland
proposed the concept of the “ultimate display”. It was National Tele-Immersion
Initiative - NTII team that leads the way to make Tele-immersion possible. They are
working on projects to have users share the same physical space in a real time world, as
if they are sitting in front of each other in the same room. This team is lead by Jaron
Lanier, who was one of the pioneers in development of Virtual Reality in 1980’s.
National Tele-Immersion team started the work in middle of 1997 and the collaborating
schools were Brown University, Providence Naval Post guard School, Monterey
University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill and University of Pennsylvania. In May
2000, researchers at the university of North Carolina, The University of
Pennsylvania and advance network and services reached a milestone in
developing this technology. In the time period from 1999 to 2001, entire work on
realization of tele immersive idea has been organized in two main research areas:
1. The Tele-immersion Media Technology: Vision-based 3D reconstruction, display
and projective technologies, tracking technologies.
2. The SOFT (Software Framework for Tele-immersion) area: Software systems to
support tele-immersion applications The TI concept was for the first time demonstrated
in May 2000. TI participants communicated using the next generation immersive
interface – tele cubicle.
NTII Demo In the year 2001, National Science Foundation announced Information
Technology Research award of 265 mil$ for three years to support tele-immersion
project. The goal of the project was to achieve real-time, high-quality 3D tele
immersion on greater distances. This goal was achieved by the first public
demonstration of TI system at the l S h Supercomputing conference in Baltimore in
November 16-22, 2002, Tele-immersion system gathered and displayed remote 3D
stereo-scopical scene in side-by-side booths at Baltimore Convention Center while the
actual data processing occurred 250 miles away at the Supercomputing Center.
Demonstrations of tele–immersion upon local computing power of the Pittsburgh
Previous have relied participating TI sites.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 4
TELE IMMERSION
4. TELE-IMMERSION AND VIRTUAL REALITY
Tele-immersion
Tele-immersion may sound like virtual reality but there are major differences between the
two technologies. While virtual reality allows you to move in a computer generated 3-D
environment. Tele-immersion can only create 3-D environment that you can see but not
interact with. Interaction is possible by combining the two technologies.
Virtual Reality
Virtual reality allows people to move around in a pre-programmed representation of an
environment, whereas tele-immersion is more like photography. It’s measuring the real world
and conveying the results to the sensory systems.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 5
TELE IMMERSION
5. TELEPORTEC
Teleportec has cleverly figured out a way to project a human image behind a desk, or
even on a stage to give the appearance that the person is sitting or standing there in real
life! Using ISDN or T1 lines and, ultimately, Internet2 technology (the next generation
of the Internet is much faster and is optimized for the transmission of moving images in
real time), this has the potential to revolutionize one-to-one videoconferences and has
enormous potential for presenters and educators as well.
FIG-1:Texas Governor Rick Perry’s
The picture shows Texas Governor Rick Perry's (right) life-size image being beamed on
stage to an auditorium at the University of Texas at Dallas while he was in Austin. The
presentation was fully interactive. An audience member asked the governor what it was
like for him. He replied that he could not reach out and touch the questioner but he
could see them and it was like being in the room with the audience. Although the
current technology provides only two-dimensional images, it is reportedly, very
convincing as it is full-color, life size image and there is depth between the image and
the background. Sitting in the back, it is very difficult to tell the image from a live
presenter. This has the potential for a huge impact for meetings. High-level keynote
speakers can be "beamed" to audiences at a fraction of the cost and time of flying them
there directly. Teleportec has proven high quality distance communication solutions
designed to provide your organization with a realistic alternative to travel. This unique
technology enables people to appear live, life-sized within an apparent 3-D
environment in a remote location and achieve eye-to-eye contact with all participants.
Group-to-group and multi-site communication is also possible.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 6
TELE IMMERSION
6. How Holographic Environment Will Work?
Scientists today are developing a new communications technology that will allow you
and your friends to interact inside a simulated environment even if you are thousands of
miles apart. It will allow everyone to come together in one virtual room, and no one
will have to leave their physical location to do so. Tele immersion will allow us to
manipulate holographic projections as if they were real objects. Most of the basic
components for this network are already in place to allow the development of tele-
immersion. Tele-immersion is the scientific community's answer to the holodeck. By
combining cameras and Internet telephony, videoconferencing has allowed the real-
time exchange of more information than ever without physically bringing each person
into one central room. Tele-immersion takes videoconferencing to the next level.
6.1 Beyond Videoconferencing
Videoconferencing via the Internet is not a perfect form of communication. The image
is close to real time, but there are delays that cause a jerking video. Also, if someone
walks out of view of that one camera, you can no longer see them. With tele-
immersion, people can't walk out of the view of the camera. In fact, you can peer
around their office just by looking at the display screen from different angles. It's like
having a window to look through. Holographic environments will be generated by
computers with computing speeds thousands of times faster than your PC. There are
several steps to constructing a holographic environment –
The computer recognizes the presence and movements of people.
Those images are tracked by the computer.
Those images are then projected on a stereo-immersive surface.
6.2 Building a Holographic Environment
The early prototypes of tele-immersive displays require users to wear special goggles, and
a head device that tracks the viewpoints of users looking at the screen. On the other end,
the people that appear as 3-D images are being tracked with an array of seven ordinary
video cameras, and two other video cameras that capture real light patterns projected in
each room to calculate distances. This enables the proper depth to be re-created on the
screen. So, if viewers move their heads to the right, they can see the corresponding images
that would be seen if the viewers were actually in the room with the person on the screen.
Images on the screen are split and polarized to create a different image for each eye. The
goggles then combine these images so that the brain recognizes only one 3-D image. This
process is similar to how those old 3-D movie glasses work.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 7
TELE IMMERSION
7. Need of Internet2
To cop up with the problems like communicating speed and better transmission of data
over the network, Tele-Immersion team collaborated with Internet2 and Internet
Protocol Performance Metrics. Main problem as obvious was that today’s internet is not
fast enough to transmit data, especially when you need to transmit a huge bulk of data
across the internet about people and their environment. Internet2, which will replace the
current Internet infrastructure. This new network will have a higher-bandwidth and
speeds 1,000 times faster than today's Internet. This high-bandwidth, high-speed
network is necessary to transfer the large amounts of data that tele-immersion will
produce. Display technologies, such stereo-immersive displays that can present a clear
view of the scenes being transmitted. A future addition to tele-immersion will be haptic
sensors that will allow people to touch projections as if they were real. Desktop
supercomputers 2will be needed to perform the trillions of calculations needed to create
a holographic environment. Another possibility to support these environments would be
a network of computers that share power.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 8
TELE IMMERSION
8. Components of a Holographic Environment
Tele immersive displays of earlier days required user to wear special goggles and a
head device that tracked the view point of the user looking at the screen. At the other
end, the people, who appeared as 3d image, where tracked with and array of 8 ordinary
video cameras while three other video cameras captured real life patterns projected in
each room to calculate distance. This enabled the proper depth to the recreated on the
screen. So if an observer move here head to the left, she could see the corresponding
image that would be seen if she were actually in the room with the person on the screen.
FIG-2: Views of cameras Tele immersed environment
Scientists are developing new technologies support this type of communication.
Apart of these new technologies is:
Tele-cubical:
Users will communicate by using this technology. It consist of a Stereo
immersive desk surface and two stereo immersive wall surfaces. These three
display surfaces join to form a virtual conference table in the centre. This will allow
the realistic inclusion of Tele immersion into the work environment, as it will take
up the usual amount of desk space.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 9
TELE IMMERSION
Internet2:
This will replace the current internet infrastructure. It is a consortium
made up of the US government, industry and academia (180universities) hat has
been formed for creating tomorrow’s internet. This new network will have a higher
bandwidth and speed that are 1000 times faster than today’s internet. This high
bandwidth, high speed network is necessary to transfer the large amounts of data
that Tele immersion will produce.
Bandwidth issues:
Network bandwidth required to make Tele immersion work is one of the main concerns
of this new technology. It is estimated that as much as 1.2 gigabits per sec will be
needed for future high quality effects. This is much higher than the average home
connection bandwidth. The exact amount of bandwidth needed for each scene depends
on the complexity of the background. With time, the number of megabits used will fall
as advanced compression techniques are established. Currently, the ‘last mile’ of
network connections for top computer science departments in US uses an OC3 line. This
can carry 155 megabits per second and supports, at a basic level, a three way
conversation. Although OC3 lines are 100 times faster than normal broadband, they are
also more expensive.
Initially, bandwidth-intensive application will have to be limited to the larger
organizations that can afford high connection speeds. The amount of data sent to render
this tele presence will also require fast processing power. This will need to be available
as required on the internet. A new network called the Grid could be a solution. The Grid
will use distributed computing. There are not enough supercomputers to ideal with the
enormous amount of data that will rush through the net in the future. As a solution,
network will connect their PCs so they can share processing power and hard disk space.
They will be locked into a grid-effectively creating one supercomputer.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 10
TELE IMMERSION
FIG -3:Bandwidth over time –bandwidth utilization graph
Display technologies:
Stereo immersive displays would have to present a clear view of the scenes being
transmitted.
Haptic sensors:
It would allow touching projections as if they were real.
Desktop supercomputers:
It would perform the trillions of calculations needed to create a holographic
environment. A network of computers that share power could also possibly support
these environment.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 11
TELE IMMERSION
9. How Tele immersion Works
In this simplified scheme for how a future tele immersion scheme might work,
two partners separated by 1,000 miles collaborate on a new engine design.
Following the flow of information tele immersion depends on intense data
processing at each end of a connection, mediated by high performance network.
FIG-4: WORKING OF TELE IMMERSION
From the sender:
Parallel processors accept visual inputs from the cameras and
reinterpret the scene as a 3-Dimensional computer model.
To the receiver:
Specific rendering of remote people and places are synthesized from the
model as it is received to match the point of view of each eye of a user. The whole
process repeats many times a second to keep up with the user head motion.
FIG-5: Array of cameras
Dept of CSE SREC Page 12
TELE IMMERSION
Generating the 3-D Image:
1. An array of cameras views people and their surroundings from different angle.
Each camera generates an image from its point of view many times in a second.
2. Each set of the images taken at a given instant is sorted into subsets of
overlapping trios of images
FIG-6: Views taken by cameras
3. From each trio of images, a “disparity map” is calculated, reflecting the degree
of variation among the images at all points in the Disparity map visual field. The
disparities are then analyzed to yield depths that would account for the differences
between what each camera sees. These depth values are combined into a “bas
relief” depth map of the scene.
4. All the depth maps are combined into a single viewpoint independent sculptural
model of the scene at a given moment. Process of combining the depth maps
provide maps opportunities.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 13
TELE IMMERSION
10. TELE CUBICLES
“A tele cubicle is an office that can appear to become one quadrant in a larger
shared virtual office space.” The main idea behind this work came directly from the
Tele-Immersion meeting on July 21, 1997 at the Advanced Network Office. At the
meeting each participant university (UIC, NPS, UNC, Columbia, and USC) brought
its individual designs of cubicles and together immersed the user and the desk. One
of the striking results of the meeting was the discovery of how future immersive
interfaces look like, and what were the needs and requirements at that time to make
this impossible looking task in the past, into reality.
10.1 How Tele Cubicles Works?
FIG-7: Working of Tele Cubical
In the above figure, the three display surfaces meet each other in the corner to make
a desk. At the moment four tele cubicles can be joined to form a large virtually
shared space. The walls appear to be transparent passage for other cubicles during
this linkage, and the desk surfaces join to form a large table in the middle. Objects
at each place can be shared for viewing across the common desk and through walls
can be seen the colleagues at other end and their environment. Figure below
describes how the participa22nts so far away share the same physical space,
through common immersed stereo desk and can see each other environment, virtual
objects place in the others environment, across the walls which looks like
transparent glasses when cubicles connected together. So the virtual world extends
through the desktop. The short term solution at that time was to have remote
environment pre-scanned which lead towards the goal which was obviously to have
environment automatically scanned.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 14
TELE IMMERSION
11. CHALLENGES OF TELE-IMMERSION
Tele-immersion has emerged as a high-end driver for the Quality of Service (QoS),
bandwidth, and reservation efforts envisioned by the Internet2 leadership.
From a networking perspective, tele-immersion is a very challenging technology for
several reasons:
Low latency, needed for 2-way collaboration, is hard to specify and guarantee.
The network must be in a place and tuned to support high bandwidth applications.
Data transmissions (called “flows”) needed to provide for and managed to the
networks.
The computers, too, are bandwidth limited with regard to handling very large data to
collaboration.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 15
TELE IMMERSION
12. APPLICATIONS
Tele-immersive holographic environment have a number of application. Imagine
a video game of joy sticks in which you become a participant in the game
fighting monsters or scoring touchdowns. Instead of traveling hundreds of miles
to visit your relatives during the holidays you can simply call them up and join
them in a shared holographic room. The list of applications is wide.
Some of them are described below:-
MEDICAL: Now with tele-immersion it is possible to treat a patient over
the phone or give instruction for tumour to be removed without physically
being there with the help of tele-immersion 3D surgical learning for virtual
operations is now in place and in the future the hope is to be able to carry out
real surgery on real patients. Tele-immersion will give surgeons the ability to
superimpose anatomic images right on their patients while they are being
operated on.
REMOTE SURGERY: Through advances in advanced networking applications such
as haptics (touch-sensitive or tactile enabling technologies), surgical simulation
training and collaborative videoconferencing technologies, Internet2 is enabling
pioneering scientists in medical and technical fields to make minimally-invasive,
Internet-based surgery techniques a future reality. Professor W. Le Roy Heinrichs of
Stanford University demonstrates the use of haptically-enabled laparoscopic tools to
demonstrate simulated surgical procedures across Internet2 advanced networks.
IN BUSINESS LIFE: The project “Office of the future” from the University of
North Carolina (Chapel Hill) is best for describing a level of business cooperation
that tele-immersion is going to give in the future using tele cubicles.
FIG-8: In business life
Dept of CSE SREC Page 16
TELE IMMERSION
The Office of the Future project is striving to bring together geographically distant
persons in a realistic, tele-collaborative environment. Using real-time computer vision
techniques, dynamic 3D images of your colleague in their office surroundings are
captured and transmitted to your Office of the Future where virtual reality technology
is used to create a life-size, visual portal into the distant space. By transmitting these
3D streams over the advanced networks of Internet2, participants in remote locations
are able to interact with each other and manipulate shared virtual objects in real-time.
IN EDUCATION: In education tele-immersion can be used to bring together
students at remote sites in a single environment. Relationship among
educational institutions could improve tremendously in the future with use of
tele-immersion. PEBBLES are the world's first fully functioning 'tele
presence' application - a revolutionary solution for hospitalized, homebound
and special children. PEBBLES connect children to their home classroom,
allowing for total participation in classroom activities and complete social
contact. PEBBLES were first used in 1997 at Toronto's Hospital for Sick
Children (Sick Kids) and as launched in 2001 in the United States at Yale-
New Haven Children's Hospital. The technology is now in use in Canada,
US, and the Netherlands.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 17
TELE IMMERSION
13. ADVANTAGES
Tele-immersion overcomes the drawback of video-conferencing
It uses haptic sensors by which we can touch & feel the projection
By this technology, it is very easy to see 3-D image of any project or model.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 18
TELE IMMERSION
14. DISADVANTAGES
Very Expensive.
High bandwidth requirement.
High speed internet is required (min of 60 MBPS).
Dept of CSE SREC Page 19
TELE IMMERSION
15. FUTURE SCOPE OF TELE-IMMERSION
Tele-immersion will blur the lines between real and computer-generated images. It
will be the ultimate tele-commuting technology; almost entirely eliminating the rush
hour drive to work Instead of commuting, people could attend those board meetings
by projecting themselves into the company's conference room.
In years to come, instead of asking for a colleague on the phone you will find it easier to
instruct your computer to find him. Once you do that, you will probably see a flicker on
one of your office walls and find that your colleague, who’s physically present in another
city, is sitting right across you as if he is right there. The person at the other end will
experience the same immersive connection. With the tele immersion bringing two or more
distant people together in a single, simulated office setting business travel will become
quite redundant.
Video conferencing via internet is not a perfect form of communication. The image is
closed to real time but there are delays that cause distorted video. Also, if someone walks
out of the view of a camera the person is no longer visible. However, with tele immersion,
people will always remain in view of the camera and you will be able to look around their
office just by looking at the display screen from different angles. Tele immersion takes
video conferencing to a higher level it is a dynamic concept, which will transform the way
humans interact with each other and the world in general.
Dept of CSE SREC Page 20
TELE IMMERSION
16. CONCLUSION
When tele-immersion becomes commonplace, it will probably enable a wide variety of
important applications. Teams of engineers might collaborate at great distances on
computerized designs for new machines that can be tinkered with as though they were real
models on a shared workbench. Archaeologists from around the world might experience
being present during a crucial dig. Rarefied experts in building inspection or engine repair
might be able to visit locations without losing time to air travel.
In fact, tele-immersion might come to be seen as real competition for air travel--unlike
videoconferencing. Although few would claim that tele-immersion will be absolutely as
good as "being there" in the near term, it might be good enough for business meetings,
professional consultations, training sessions, trade show exhibits and the like. Business
travel might be replaced to a significant degree by tele-immersion in 10 years. This is not
only because tele- immersion will become better and cheaper but because air travel will
face limits to growth because of safety, land use and environmental concerns.
Undoubtedly tele-immersion will pose new challenges as well. Some early users have
expressed a concern that tele-immersion exposes too much, that telephones and
videoconferencing tools make it easier for participants to control their exposure--to put the
phone down or move off-screen. We are hopeful that with experience we will discover
both user- interface designs and conventions of behavior that address such potential
problem
Dept of CSE SREC Page 21
TELE IMMERSION
17. REFERENCES
American Scientist magazine issue April 2001.
Information Technology magazine August 23.
GRID Today magazine issue December 2002.
www.wikipedia.com
www.google.com
www.studymafia.org
www.projectsreports.org
Dept of CSE SREC Page 22
Вам также может понравиться
- Unit IvДокумент15 страницUnit IvKavya GopavaramОценок пока нет
- Sumanth 68 IeeeДокумент27 страницSumanth 68 IeeeKavya GopavaramОценок пока нет
- Nokia MorphДокумент23 страницыNokia MorphKavya GopavaramОценок пока нет
- Teleimmersion Seminar ReportДокумент22 страницыTeleimmersion Seminar ReportKavya GopavaramОценок пока нет
- Visual Position SystemДокумент1 страницаVisual Position SystemKavya GopavaramОценок пока нет
- CSEIT183557Документ6 страницCSEIT183557Kavya GopavaramОценок пока нет
- Visual Position SystemДокумент1 страницаVisual Position SystemKavya GopavaramОценок пока нет
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Carestream DryView 5700 PDFДокумент44 страницыCarestream DryView 5700 PDFJose Quisca100% (1)
- Operation Manual: Daikin Room Air ConditionerДокумент92 страницыOperation Manual: Daikin Room Air ConditionerbenОценок пока нет
- Product Design Recommended Reading ListДокумент3 страницыProduct Design Recommended Reading ListSai Prasath100% (1)
- 6GK52160BA002AA3 Datasheet en PDFДокумент6 страниц6GK52160BA002AA3 Datasheet en PDFgrace lordiОценок пока нет
- 13 - Principles of Flight - QuestionsДокумент80 страниц13 - Principles of Flight - QuestionsEdgar Muñoz Fernández50% (4)
- Previews AGA XQ9902 PreДокумент6 страницPreviews AGA XQ9902 PreAldrin HernandezОценок пока нет
- As ISO 128.23-2005 Technical Drawings - General Principles of Presentation Lines On Construction DrawingsДокумент9 страницAs ISO 128.23-2005 Technical Drawings - General Principles of Presentation Lines On Construction DrawingsSAI Global - APAC0% (3)
- Physics Lab ReportДокумент2 страницыPhysics Lab ReportFelix SonsunОценок пока нет
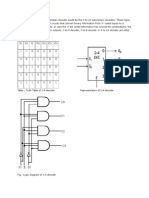
- 2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesДокумент6 страниц2:4 Decoder: DECODER: A Slightly More Complex Decoder Would Be The N-To-2n Type Binary Decoders. These TypesPavithraRamОценок пока нет
- The Tallest Buildings in The WorldДокумент2 страницыThe Tallest Buildings in The WorldW4G8989Оценок пока нет
- GRI 20RS-12-B Data SheetДокумент6 страницGRI 20RS-12-B Data SheetJMAC SupplyОценок пока нет
- Oil Analysis - Ruller and MPC TestДокумент81 страницаOil Analysis - Ruller and MPC Testmaidul.islamОценок пока нет
- Excellent Hex Key Wrench: English VersionДокумент54 страницыExcellent Hex Key Wrench: English Versionmg pyaeОценок пока нет
- AS1895/7 E-FLEX Sealing Solutions: Part Number AS1895/7 Reference Duct Size Seal DimensionsДокумент1 страницаAS1895/7 E-FLEX Sealing Solutions: Part Number AS1895/7 Reference Duct Size Seal DimensionsAlex Zambrana RodríguezОценок пока нет
- Hino 500S Catalog LR PDFДокумент8 страницHino 500S Catalog LR PDFZulОценок пока нет
- Method StatementДокумент2 страницыMethod StatementKumar Jbs100% (1)
- Master Opp GaveДокумент84 страницыMaster Opp GaveRizki Al AyyubiОценок пока нет
- Power and Simplicity: Pace ScientificДокумент16 страницPower and Simplicity: Pace ScientificAnonymous mNQq7ojОценок пока нет
- SRSUNTOUR General Fork GlossaryДокумент23 страницыSRSUNTOUR General Fork GlossaryThomas JunkersfeldОценок пока нет
- Racecar Engineering - September 2015Документ100 страницRacecar Engineering - September 2015MrRipleiОценок пока нет
- Caterpillar 914GДокумент28 страницCaterpillar 914GForomaquinas100% (3)
- Civil DEMOLITION OF BUILDINGДокумент12 страницCivil DEMOLITION OF BUILDINGShaik Abdul RaheemОценок пока нет
- JUS StandardsДокумент28 страницJUS StandardsgarejkaОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering Reference BooksДокумент2 страницыCivil Engineering Reference Booksdevbrat boseОценок пока нет
- Unit 6Документ13 страницUnit 6VeronicaОценок пока нет
- Apache Oozie - A workflow scheduler to manage Hadoop jobsДокумент5 страницApache Oozie - A workflow scheduler to manage Hadoop jobsarjuncchaudharyОценок пока нет
- Manual Service Aoc - E943fwskДокумент51 страницаManual Service Aoc - E943fwskEduardo BentoОценок пока нет
- Welding PositionДокумент30 страницWelding PositionTuah Negeri100% (1)
- Niveau S Longrine Type Pou05-S Section 20x25: A-A B-B C-C D-DДокумент1 страницаNiveau S Longrine Type Pou05-S Section 20x25: A-A B-B C-C D-DAWOUNANGОценок пока нет
- Cs 180 Notes UCLAДокумент3 страницыCs 180 Notes UCLAnattaq12345Оценок пока нет