Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
NCP Infection New
Загружено:
Xerxes Dejito0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
130 просмотров3 страницыОригинальное название
ncp infection new.docx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
130 просмотров3 страницыNCP Infection New
Загружено:
Xerxes DejitoАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
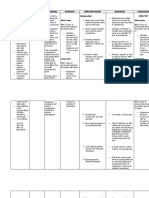
Patient: Gozo, M.
Age: 31 years old Diagnosis: S/P Craniotomy Excision of Brain Tumor
Date
& Assessment Needs Nursing Diagnosis Objective Interventions Evaluation
Time
Nov Subjective: H Risk for infection After 8 hours 1. Monitor vital signs regularly. GOAL MET
16, “Mahadlok mi E related to s/p of nursing R: Changes in vital signs may indicate
2019 kay gikan sya A craniotomy excision of interventions, infection. After 8 hours
ug surgery, L brain tumor the patient of nursing
3:00 basig ma T will be able 2. Monitor the patient for any signs of interventions,
pm – infect.” As H R: Invasive procedures to: swelling, purulent discharge or presence the patient was
11:00 verbalized by such as surgery, of pain from wound. able to:
pm the father of P involves opening the - remain free R: These are the cardinal signs of infection.
the patient. E skin and leading a from any - remain free
R lesion thereafter. This infection from any
Objective: C makes the patient 3. Perform handwashing when dealing with infection
E vulnerable to pathogens patient.
- surgical P as the first barrier of R: Handwashing is an effective technique to
incision on T protection is prevent the spread of infection. Dry surfaces
frontal I compromised. are better in preventing transfer of
tempoparietal O microorganisms.
area of the N Source: Nicoll, D.,
head McPhee, S., Pignone,
- bleeding on A M. and Nicoll, D. 4. Wear gloves during any contact with
the site N (2014). Diagnostic mucus, blood, and other body fluids. Use
D tests. 13th ed. [New goggles when appropriate.
- Vital Signs York, N.Y.]: McGraw- R: It prevents the transfer of microorganisms
recorded at: H Hill Companies, p.185. that are already on the hands and to protect
Temp: 36.7c E the hands from becoming contaminated.
BP: 120/80 A
RR: 20bpm L 5. Encourage adequate rest.
PR: 78 T R: It can reduce stress and boost the immune
H system.
M 6. Provide a clean environment.
A R: A sanitized environment creates a colossal
N effect when preventing infection, as this
A reduces contamination to the patient, making
G it less likely for the patient to develop
E infection post procedure.
M
E 7. Teach S/O how to perform procedures at
N home, like dressing changes and assessing IV
T site for signs of infection.
R: Patient and caregivers need to master
P these skills to make sure that they can
A continue preventing risk of infection even if
T they are already discharged.
T
E 8. Routinely monitor the patient’s white
R blood cell count, serum protein, and serum
N albumin.
R: These laboratory values are closely linked
to the patient’s nutritional status and immune
function.
9. Administer medications as ordered.
R: Not completing or skipping the required
dose of antibiotics can encourage antibiotic
resistance.
10. Coordinate with a dietician to create a
meal plan suitable or the patient and his
nutritional needs.
R: Proper nutritious diet helps support the
immune system by delivering the necessary
nutrients needed by the body.
Вам также может понравиться
- NCP LymphedemaДокумент1 страницаNCP Lymphedemayasira50% (2)
- Basic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityДокумент1 страницаBasic Concept Map - RH IncompatibilityTechnoShindoОценок пока нет
- SR Buyer Guide DIGITAL PDFДокумент449 страницSR Buyer Guide DIGITAL PDFMichael Carney0% (1)
- Purposeful Primitive Epilogue PDFДокумент18 страницPurposeful Primitive Epilogue PDFPikaboo31Оценок пока нет
- CaseanalysisДокумент2 страницыCaseanalysisChrislyn Dian Pene100% (1)
- SP CSДокумент4 страницыSP CSKhan HansОценок пока нет
- NCP Risk For InfectionДокумент3 страницыNCP Risk For InfectionXerxes Dejito0% (1)
- Nicardipine Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыNicardipine Drug StudyXerxes Dejito50% (2)
- NCP Risk For InfectionДокумент3 страницыNCP Risk For InfectionXerxes Dejito0% (1)
- KPJ Wellness & Lifestyle Programme (22.06.2014) Brand ManagementДокумент32 страницыKPJ Wellness & Lifestyle Programme (22.06.2014) Brand ManagementbennameerОценок пока нет
- Natures Hidden Health MiracleДокумент38 страницNatures Hidden Health MiracleGorneau100% (2)
- Yale Insulin Infusion ProtocolДокумент2 страницыYale Insulin Infusion ProtocolIffatNaeemОценок пока нет
- Breast Cancer Risk For InfectionДокумент6 страницBreast Cancer Risk For Infectionam peОценок пока нет
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Interventions Justification EvaluationДокумент7 страницAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Desired Outcome Interventions Justification EvaluationPJОценок пока нет
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation: VIII. Nursing Care PlanДокумент1 страницаAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluation: VIII. Nursing Care PlanKriz_sakuradreamОценок пока нет
- Normal Spontaneous DeliveryДокумент11 страницNormal Spontaneous DeliveryAyah GarciaОценок пока нет
- NCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISДокумент2 страницыNCP Acute Pain FURUNCOLOSISMaria Imogen MilambilingОценок пока нет
- Cutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыCutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanYayin Pestaño100% (1)
- Acute Pain OsteosarcomaДокумент8 страницAcute Pain OsteosarcomaMaryjoy Gabriellee De La Cruz100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Nitumusiina Billy Admitted With Acute Otitis Media and TonsillitisДокумент6 страницNursing Care Plan For Nitumusiina Billy Admitted With Acute Otitis Media and TonsillitisNatukunda Dianah100% (1)
- NCP PryllДокумент6 страницNCP PryllpjcolitaОценок пока нет
- FATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Документ4 страницыFATIGUE NCP Que Fransis A.Irene Grace BalcuevaОценок пока нет
- BFC NCPДокумент2 страницыBFC NCPMonica Melo HernandezОценок пока нет
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusДокумент3 страницыWord Ncp.......... TetanusYvounne Ananias Bautista RNОценок пока нет
- NCP (Acute Pain)Документ2 страницыNCP (Acute Pain)jennilois100% (1)
- FNCP TB As A Health DeficitДокумент5 страницFNCP TB As A Health Deficitkuu faalОценок пока нет
- NCP For StokeДокумент5 страницNCP For StokeMemedОценок пока нет
- Word Ncp.......... TetanusДокумент6 страницWord Ncp.......... TetanusaianrОценок пока нет
- NCP Ineffective Airway ClearanceДокумент1 страницаNCP Ineffective Airway Clearancejae_007Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationДокумент1 страницаNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationlaehaaaОценок пока нет
- NCP Acute PainДокумент3 страницыNCP Acute Painmanoelsterg50% (2)
- Deficient KnowledgeДокумент3 страницыDeficient KnowledgeCamilleAnneRoseRabinoОценок пока нет
- Head Nurse: General ObjectiveДокумент10 страницHead Nurse: General Objectiveeihjay-bravo-8041Оценок пока нет
- ASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoДокумент1 страницаASSESSMENT S: "Nanghihina Ako, Hindi Ko Magawa Yung Mga GustoCherie MayОценок пока нет
- Ncp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasДокумент4 страницыNcp-Impaired S.i.-NavidasFran LanОценок пока нет
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyДокумент3 страницыPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanОценок пока нет
- Skin IntegrityДокумент2 страницыSkin IntegrityJonica CamposОценок пока нет
- Hizon 2 NCP 1 Npi I Am SamДокумент5 страницHizon 2 NCP 1 Npi I Am SamDan HizonОценок пока нет
- Ameloblastoma PathophysiologyДокумент2 страницыAmeloblastoma PathophysiologyAshok KpОценок пока нет
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY TCHI Client BasedДокумент1 страницаPATHOPHYSIOLOGY TCHI Client BasedGem MarasiganОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan: Cues/Clues Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Objectives Nursing Intervention Rationale EvaluationJennirose JingОценок пока нет
- NCP AlteredДокумент3 страницыNCP AlteredShaira TillahОценок пока нет
- Objectives - Surgical WardДокумент3 страницыObjectives - Surgical WardAzhly AntenorОценок пока нет
- NCP of MGH PatientДокумент2 страницыNCP of MGH PatientMaverick LimОценок пока нет
- NCP Readiness RevisionДокумент3 страницыNCP Readiness RevisionimnasОценок пока нет
- NCP 2Документ3 страницыNCP 2klawdin100% (1)
- NCP For Parent and Child PDFДокумент3 страницыNCP For Parent and Child PDFMariana Mikaela AlagarОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NДокумент2 страницыNursing Care Plan: Date/ Time Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evaluatio NnananaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisДокумент3 страницыNursing Care Plan Rheumatoid ArthritisJashAnia MarIe EvArdo FloresОценок пока нет
- Chest Tube Reflective EssayДокумент2 страницыChest Tube Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoОценок пока нет
- Risk For InjuryДокумент1 страницаRisk For Injuryandycamille7Оценок пока нет
- Risk For InfectionДокумент5 страницRisk For InfectionRochelle Corneta JoreОценок пока нет
- Child - ImmunizationsДокумент1 страницаChild - ImmunizationsJOHN100% (1)
- Biopsy: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationДокумент5 страницBiopsy: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDan HizonОценок пока нет
- Acute Pain Related To Body Response To An Infective AgentДокумент2 страницыAcute Pain Related To Body Response To An Infective AgentSheril Sularte CasanesОценок пока нет
- You Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeДокумент2 страницыYou Are Caring For A Patient With An NG Feeding TubeWen Silver100% (1)
- Nursing Care PlansДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plansapi-19762967Оценок пока нет
- Nursing Care PlanДокумент3 страницыNursing Care PlanAnnahОценок пока нет
- Fdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaДокумент1 страницаFdar - Healthy Teaching - GarciaRuthangela GarciaОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan For LYING inДокумент4 страницыNursing Care Plan For LYING inKarissa CiprianoОценок пока нет
- NCP PpwardДокумент15 страницNCP PpwardKarl Vincent Soso100% (1)
- Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1Документ8 страницRisk For Ineffective Airway Clearance 1kint manlangitОценок пока нет
- NCP Risk For Infection Secondary To Vehicular AccidentДокумент2 страницыNCP Risk For Infection Secondary To Vehicular AccidentXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- Risk For InfectionДокумент5 страницRisk For InfectionVianah Eve EscobidoОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care Plan On SepsisДокумент6 страницNursing Care Plan On SepsisleoОценок пока нет
- NCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerДокумент5 страницNCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerJv Jore VillahermosaОценок пока нет
- NCP Inflamed TonsillitisДокумент3 страницыNCP Inflamed TonsillitisAubrey LafuenteОценок пока нет
- Last Requirement OB WardДокумент5 страницLast Requirement OB WardXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- Weekly Requirement OB WardДокумент12 страницWeekly Requirement OB WardXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- Ateneo de Davao University School of NursingДокумент2 страницыAteneo de Davao University School of NursingXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- Family Nursing Care PlanДокумент2 страницыFamily Nursing Care PlanXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- Oral Revalida Psychiatric NursingДокумент6 страницOral Revalida Psychiatric NursingXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- Pathophysiology of Varicella Zoster Virus-ChickenpoxДокумент8 страницPathophysiology of Varicella Zoster Virus-ChickenpoxXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- Morphine Drug StudyДокумент3 страницыMorphine Drug StudyXerxes Dejito100% (2)
- Losartan Drug StudyДокумент2 страницыLosartan Drug StudyXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- NCP Risk For Infection Secondary To Vehicular AccidentДокумент2 страницыNCP Risk For Infection Secondary To Vehicular AccidentXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- Doctor's Order SampleДокумент3 страницыDoctor's Order SampleXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- NCP Infection NewДокумент3 страницыNCP Infection NewXerxes DejitoОценок пока нет
- FYM Dress Size Reduction DietДокумент8 страницFYM Dress Size Reduction DietDaniela GuariniОценок пока нет
- Leaky Gut Syndrome in Plain English - and How To Fix It - SCD LifestyleДокумент81 страницаLeaky Gut Syndrome in Plain English - and How To Fix It - SCD Lifestylemusatii50% (4)
- Referat Compusi Biologic ActiviДокумент56 страницReferat Compusi Biologic ActiviAna-Maria SiminescuОценок пока нет
- Ayurvedic Skin Care Home RemediesДокумент13 страницAyurvedic Skin Care Home Remediesananth999Оценок пока нет
- Obat ObatДокумент8 страницObat ObatMuhammad Aulia KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Nutrition Plan For The Serious Basketball Player: Food ChoicesДокумент2 страницыNutrition Plan For The Serious Basketball Player: Food Choicesbetsi ozunaОценок пока нет
- ATHLETE COPY Tennis Annual Plan 2013-2014 GPP 1.1 PDFДокумент8 страницATHLETE COPY Tennis Annual Plan 2013-2014 GPP 1.1 PDFdgclarkeОценок пока нет
- Vitamin D Deficiency in Children-3 - 5Документ6 страницVitamin D Deficiency in Children-3 - 5anitn2020Оценок пока нет
- Formatted Food AssignmentДокумент12 страницFormatted Food AssignmentDylanRichards50% (2)
- ZYGO - Intro &methodsДокумент2 страницыZYGO - Intro &methodsDom GudezОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Dough Fermentation PDFДокумент303 страницыHandbook of Dough Fermentation PDFDeruiWilliamZhuОценок пока нет
- How To Improve Aerobic EnduranceДокумент10 страницHow To Improve Aerobic Enduranceshahbaz AkhtarОценок пока нет
- The Fit Body Hack E-BookДокумент30 страницThe Fit Body Hack E-BookDeep SavaliaОценок пока нет
- Chemical Changes During Extrusion Cooking - Camire PDFДокумент13 страницChemical Changes During Extrusion Cooking - Camire PDFmarmaduke32Оценок пока нет
- C4. Influence of Probiotics On The Growth and Digestive Enzyme Activity of White Pacific Shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei) - RДокумент4 страницыC4. Influence of Probiotics On The Growth and Digestive Enzyme Activity of White Pacific Shrimp (Litopenaeus Vannamei) - RBen BuddyОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 2 Literature ReviewДокумент12 страницCHAPTER 2 Literature ReviewAnas KamalОценок пока нет
- Fs11 Environmental and Genetic InteractionsДокумент3 страницыFs11 Environmental and Genetic InteractionsYuliandini Pangestika WiyonoОценок пока нет
- Ross 308 PS Nutrition SpecДокумент16 страницRoss 308 PS Nutrition SpecMosaad HashimОценок пока нет
- Nutritional Considerations For Healthy Aging and Reduction in Age-Related Chronic DiseaseДокумент10 страницNutritional Considerations For Healthy Aging and Reduction in Age-Related Chronic DiseaseSilvana RamosОценок пока нет
- Research ProposalДокумент9 страницResearch ProposalMika PatocОценок пока нет
- Class 6 PTДокумент4 страницыClass 6 PTs.kr. sirОценок пока нет
- Share 'FINAL RRL (Autosaved) 2Документ22 страницыShare 'FINAL RRL (Autosaved) 2Jeanelle DenostaОценок пока нет
- Ho Lester OlllДокумент6 страницHo Lester OlllVlad VladОценок пока нет
- Lyle McDonald - Applied Nutrition For Mixed Sports Companion (Slides) PDFДокумент23 страницыLyle McDonald - Applied Nutrition For Mixed Sports Companion (Slides) PDFabcds60% (5)
- P.4 Scie Package 26TH May To 2ND June 2020Документ8 страницP.4 Scie Package 26TH May To 2ND June 2020Monydit santinoОценок пока нет