Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Principles of Management Lecture 1
Загружено:
api-495201002Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Principles of Management Lecture 1
Загружено:
api-495201002Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
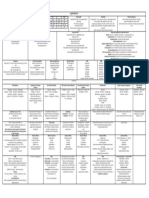
Principles of Management Lecture 1 Planning – goals, objectives, methods, resources Responsibility – the duty to carry out an assignment or
needed conduct a certain activity
Majority of healthcare expenditures are from: Organizing resources Delegation – process of assigning a task to a
Hospital Care (30%) Leading- set direction for the organization subordinate
Providers/physicians (20%) Controlling or coordinating the systems Authority – formally granted influence of a position
RX drugs (10%) Modern Views Line authority – the type of authority where managers
The system is “Broken” Energize have formal authority over their subordinate’s activity
Access – underinsured, uninsured Empower Staff authority – the type of authority where
Affordability – cost to patients and healthcare Communicate managers’ influence line managers through staff’s
Accountability – outcomes DO NOT justify the costs Support specialized advice – HR, legal, finance
Factors Impacting Health Care - PESTEL Management Theories Environmental Scan
Political Scientific management theory – large industries, Strengths - internal
Economic measurement and specification of activities and Weaknesses - internal
Social results, standardize tasks, reward and punishment Opportunities – external
Technological system Threats – external
Legal Bureaucratic management theory – divide Analyze the Market (5C’s or market audit)
What kind of structure does the US healthcare system have? organizations into hierarchies and establish strong Company
NONE lines of authority and control, standard operating Consumers
Subsystem model of healthcare in the US procedures Competition
Middle class Human relations movement – more attention to Channel of distribution
Poor individuals, organizations would prosper if workers Controls (regulations)
VA prospered as well, contemporary theories Components of Business Plan
Military Strategic Planning Executive summary
Public programs Clearly defines purpose of organization and its goals Background and description
Titles of ACA Communicates goals to organization and externally Market analysis and strategy
Title I: quality, affordable health care for all Americans Develops a sense of ownership of the plan Operational structure and process
Title II: the role of public programs Efficient use of resources Financial projections
Title III: improving the quality and efficiency of health Provides a base from which progress can be measured Schedule and action plan
care Incorporates all opinions Critical risks and opportunities
Title IV: prevention of chronic disease and improving Provides the glue to keep employees together Exit strategy
public health When should strategic planning be done? Conclusion
Title V: healthcare workforce When an organization is just starting Supportive documents
Title VI: transparency and program integrity In preparation for a new venture Planning, Organizing, Leading, Controlling
Title VII: improving access to innovative medical Review once a year for budget Leadership styles
therapies Strategic planning process Affiliative – people first, task second
Title VIII: community living assistance services and Describe the organization Directive – the autocrat – Do as I tell you!
supports act Identify strategic direction (vision, mission, values) Authoritative – the visionary
Title IX: revenue provisions Conduct an environmental scan The participative – democrat
Title X: reauthorization of the Indian health care Specify goals, objectives, strategies and tactics Coaching – the transformational or servant leader
improvement act Link objectives and outcomes (monitoring and The pacesetter – Do it Myself
Purpose of ACA evaluation plan) CMS – single largest purchaser of healthcare
High rate of uninsured Implementation Elements of Marketing
Unsustainable spending Monitoring and feedback Product/service
Focus on preventative care Components of organizational structure Price
Improve health outcomes Horizontal – types of people or units or job functions Place
Address disparities in health and respect to income Spatial – physical separation between units Promotion
and demographics Vertical – reporting structure (chain of command) Market Audit
Management Formalization – of job functions (defined roles) Consumer or stakeholders
The organization and coordination of the activities of a Centralization – scope of decision making Competition
business in order to achieve defines objectives Other terminology Channels of distribution
Production based on: men, machines, materials, Division of labor – dividing up tasks Controls (Regulations)
money, management of these factors Span of control – scope of control of a manager Company (industry)
Departmentalization – grouping based on tasks
Demand Type of marketing Example
Negative Conversional Anti-vaxxers
No Stimulational MTM
Latent (unfulfilled) Developmental Demand, no drug
Declining Remarketing
Irregular Synchromarketing Seasonal (allergy)
Full Maintenance BOGO
Overfull Demarketing Limit product
Unwholesome Countermarketing Opioids
Types of Product Differentiation
Undifferentiation One product Any/all groups Ear drops, tablets
Concentrated One product One specific group Any new RX drug
Partially Many product One group Diff doses, dosage
differentiated forms forms, combos
Fully Many product Many groups Diff doses, dosages,
differentiated forms and for diff indications
Product
Branding
Brand awareness
Brand image
Brand equity
Types of strategies
Market penetration
Market development
Product development
Diversification
Pricing policy and strategy
Factors that impact price Factors that pricing impacts
Cost Sales volume
Demand sales revenue
Competition Market share
Experience Competitive position
Customer perceptions Company image
Profit goals Profitability
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (120)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- VinamilkДокумент7 страницVinamilkTran VietsonОценок пока нет
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Conceptual SkillsДокумент21 страницаConceptual SkillsKarthick Kumaravel100% (1)
- ATHE Level 7 Strategic Management Specification v1.0 FINAL 020223Документ108 страницATHE Level 7 Strategic Management Specification v1.0 FINAL 020223Ahmed AttallaОценок пока нет
- Strategic Plan by SameerДокумент12 страницStrategic Plan by SameerHardik PanchalОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management Final NotesДокумент308 страницStrategic Management Final Notesbhartisharma93% (28)
- Stable Ischemic Heart DiseaseДокумент1 страницаStable Ischemic Heart Diseaseapi-495201002Оценок пока нет
- Hypertensive CrisisДокумент1 страницаHypertensive Crisisapi-495201002Оценок пока нет
- HTN Tran IratДокумент1 страницаHTN Tran Iratapi-495201002Оценок пока нет
- DyslipidemiaДокумент2 страницыDyslipidemiaapi-495201002Оценок пока нет
- Thromboembolic DisordersДокумент3 страницыThromboembolic Disordersapi-495201002Оценок пока нет
- Vision Ans MissionДокумент11 страницVision Ans MissionValarmathiОценок пока нет
- Module 1 HRMДокумент14 страницModule 1 HRMrebecca lisingОценок пока нет
- NGO Self-Assessment Through A SWOT ExerciseДокумент13 страницNGO Self-Assessment Through A SWOT ExerciseAvital ShapiroОценок пока нет
- Comprehensive Review in LEAДокумент239 страницComprehensive Review in LEArayco.philip89% (9)
- Coa Qms ManualДокумент241 страницаCoa Qms ManualEricka Joi OjerioОценок пока нет
- Strategic LeadershipДокумент34 страницыStrategic Leadershipakypc9Оценок пока нет
- Performance ManagementДокумент8 страницPerformance ManagementKJuneОценок пока нет
- Implementation of Balanced ScorecardДокумент30 страницImplementation of Balanced ScorecardParamjit Sharma100% (13)
- Dwnload Full Principles of Marketing 16th Edition Kotler Solutions Manual PDFДокумент36 страницDwnload Full Principles of Marketing 16th Edition Kotler Solutions Manual PDFabsterseabattoir9g7ox100% (9)
- MargawinataДокумент14 страницMargawinataMargawinataОценок пока нет
- CSR Strategy FormulationДокумент20 страницCSR Strategy FormulationEr Vipul VermaОценок пока нет
- A Future Back Approach To Creating Long Term Growth StrategyДокумент5 страницA Future Back Approach To Creating Long Term Growth StrategyFrancisco Fierro CarrilloОценок пока нет
- 1.3 Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling (P-O-L-C)Документ15 страниц1.3 Planning, Organizing, Leading, and Controlling (P-O-L-C)Leo HiterozaОценок пока нет
- Strategic Report QuestionnaireДокумент4 страницыStrategic Report QuestionnairemadihashkhОценок пока нет
- TFV As A Strategic ToolДокумент8 страницTFV As A Strategic ToolAxl BenaventeОценок пока нет
- Housing Authority Strategic Plan 2011Документ34 страницыHousing Authority Strategic Plan 2011Muhammad ZakiОценок пока нет
- Marketing Strategy SuzukiДокумент42 страницыMarketing Strategy SuzukiAmit PasiОценок пока нет
- Best Practices Organizational AgilityДокумент23 страницыBest Practices Organizational AgilityAnkur Dhir100% (1)
- PM Footprints - Project Portfolio Management: Niladri Mallick Choudhuri 16 January 2014Документ12 страницPM Footprints - Project Portfolio Management: Niladri Mallick Choudhuri 16 January 2014VijaysinhJadejaОценок пока нет
- Minztberg 10 RolesДокумент8 страницMinztberg 10 RolesDon Mcarthney TugaoenОценок пока нет
- MGMT 4 - Business Policies & Strategic ManagementДокумент4 страницыMGMT 4 - Business Policies & Strategic ManagementTomas del Rosario CollegeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11 Lecture Note Building An Organization Capable of Good Strategy ExecutionДокумент13 страницChapter 11 Lecture Note Building An Organization Capable of Good Strategy ExecutionManje Gowda HSОценок пока нет
- FIA Strategic Plan PDFДокумент35 страницFIA Strategic Plan PDFDaniel K chiwonaОценок пока нет
- Revision MarketingДокумент8 страницRevision MarketingAnna FossiОценок пока нет
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of Strategic ManagementДокумент3 страницыThe Advantages and Disadvantages of Strategic ManagementBrian KerrОценок пока нет