Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Word Tabassum
Загружено:
Ahmed Nouman0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров10 страницОригинальное название
word tabassum.docx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
13 просмотров10 страницWord Tabassum
Загружено:
Ahmed NoumanАвторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 10
978-1-5386-8125-1/19/$31.
00 ©2019 IEEE
Security Issues and Challenges in IoT
Dr. Kahkashan Tabassum
Dept. of Computer Sciences, CCIS,
Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman
University, Riyadh, KSA.
ktosman@pnu.edu.sa
0000-0001-7150-9830
Dr Ahmed Ibrahim
Dept. of Computer Sciences, CCIS,
Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman
University, Riyadh, KSA.
azibrahim@pnu.edu.sa
Dr Sahar A. El_Rahman
Faculty of Engineering, Shoubra Benha
University, Cairo, Egypt
Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman
University, Riyadh, KSA.
sahr_ar@yahoo.com
Abstract—The Internet of Things (IoT) supports a wide range of
applications including smart cities, traffic congestion, waste
management, structural health, security, emergency services,
logistics, retails, industrial control, and health care. IoT is megatechnology that can establish connection with anything,
anyone,
at any time, place, service on a platform and any network. It has
a great impact on the whole block chain of businesses, smart
objects and devices, systems and services that are enabled by
heterogeneous network connectivity and is developed as a smart
pervasive framework of smart devices. IoT devices are in use in
many fields, they connect to complex devices, interface with
hostile environments and are deployed on various uncontrolled
platforms, therefore faces many security issues and challenges.
Since the IoT offers a potential platform for integrating any type
of network and complex system it could encounter vulnerabilities
inherent to the individual systems which are available within the
integrated network. This research paper is a study of the security
issues of the individual systems responsible for IoT
interconnection and their impact towards the integrated IoT
system.
Keywords— Big Data Analytics, Network security, Device security,
Internet of Things.
I. INTRODUCTION
IoT devices are currently used in almost every area may it
be industrial, educational, medical or business. IoT connects
complex devices together, it can interface with a
heterogeneous set of environments deployed on various
platforms. Since the IoT provide integration of many types of
networks and complex systems, it is exposed to security
challenges and issues that are already a part of the individual
systems involved in its framework or available within its
integrated network. This paper targets the real challenges for
the clients from both the hardware (embedded server) and
software perspectives. Most of the connected devices that
seem to be functional are at a risk due to reasons that they
may be hacked by hackers and the whole business may suffer
drawbacks. These issues explain how critical are the privacy
and security to a system. The solution to these issues could be
providing the customer with personalized devices that offer
the system a high level of security through setting
personalized IDs, using MAC address security. public/private
keys, digital signatures and certificates within the system.
Unfortunately, there is no added cost for the system that
chooses to offer security but instead the cost exists only for the
system. IoT is the only technology in todays’ world which is
considered to have a fantastic prospective that can fill the gap
or barriers which existed within various technologies until
recently.
II. BACKGROUND AND RELATED WORK
This section discusses the security issues and challenges
in IoT in various fields and the survey is organized as
follows: First part of this section discusses general IoT
security[1], which is followed by a survey[2] based on deeper
insight on the IoT data transfer in the form of Big data. The
next part is organized from [3][4][5] and deals with the
description about the challenges that are faced by IoT and Big
Data security, the final section presents the secure applications
of IoT business analytics and Health informatics. The survey
in paper [6] expresses the IoT business collaboration, safety,
and confidentiality, the researchers in [7] discuss about IoT
business collaboration with financial perspective and
highlights its benefits. In [8] the researchers have illustrated a
real-life example about a specific industry and how the IoT
steps can be applied to a real-life scenario to secure it. In the
modern age, it is of the utmost importance for any business to
incorporate some features for optimal operation. One of which
is security, this links back to the huge size of data that is being
exchanged between devices. The current technology is striving
to advance towards development of deep learning analysis of
the security architecture and features of IoT. The research
status of key technologies including encryption mechanism,
security layers, cryptographic algorithms are reviewed and
discussed amongst these survey papers . All that was
discussed in [1] has an effect on business in the modern age.
[2] explores the potential impact of large data challenges,
research efforts directed towards the analysis of IoT data, and
various tools associated with its analysis. It discusses some
problems and challenges presented by big data, one of which
being the acquisition of knowledge from IoT data. The authors
discussed the relationship between Business Data
Analytics(BDA) and IoT, examined various research topics,
various opportunities generated by data analysis in the IoT
paradigm, challenges and tools used for BDA, and they
discussed the information security dimension of BDA. In the
article, numerous types of analysis techniques were used. The
authors suggested the use of platforms to explore big data in
numerous stages because Big Data platform has its own
individual approach. All types of devices communicate
together in numerous ways. They have to transfer enormous
amounts of data between each other. This article [3] has to do
with Big Data delivery over the IoT. The purpose of this
article is to develop suitable algorithms for efficient
transmission of big data. The authors represented an
architecture system that will be an entire automated system of
sensor and body area networks that will be built into the
appropriate topologies.
As mentioned previously there are many challenges in
IoT security regarding business. This paper [4] debates some
of these challenges and talks about IoT business analytics
security. The author’s research shows that almost all physical
devices will be connected by an IoT by the year 2020. All
major businesses are vying for the IoT market. Amongst this
market is the IoT security market which will be one of the
most imperative markets in the IoT driven digital marketplace
that the author’s research predicts. This article [5] aims to
present mature research or work-in-progress results in all areas
focused on security in IoT architecture based on business
processes and Business Analytics. It also discusses physical
linkage in IoT between devices. The authors speak about how
IoT device linkage can have real life application, such as
improving user experience. The article debates some problems
that businesses might face from a security perspective when
dealing with IoT, for example, hacker interception. It shows
the way to avoid this by saying that IoT’s for collaborative
business technologies must have a viable, efficient, and
resilient security solution. Which help businesses believe in
the IoT as a solution of collaborative technologies. Businesses
are aware of the financial and marketplace gain that IoT may
incur, but they’re unsure of how to approach its
implementation. Article [6] proposes a method that businesses
might be able to use for implementing IoT into themselves.
The article hinges on partner collaboration and it shows how
they might benefit from it. It also demonstrates how this
method has integrated the IoT framework strategy category,
and its tactics.
All businesses must care for the financial side of things,
and this also applies to the IoT marketplace. This article [7]
argues about financial technology (FinTech) which employs
technological advancements and sharing economy models to
improve financing services. The article shows a proactive
FinTech model that speaks of actual costs and potential
benefits in real time which they believe will offer attractive
service value. FinTech is a fast-growing technology that has
been implemented by many businesses and IoT has the
potential to be combined with it, which will mix these two
business powerhouses into a useful financial business tool.
The article acknowledges how this type of IoT implementation
might be an invasion into people’s privacy, it tries to outweigh
this con by arguing that some people might be willing to forgo
the potential invasion into their privacy by stating that most
people will find that monetary benefit is more appealing than
maximum privacy. It specifically states that implementation of
IoT will naturally invade people’s privacy, but there will be
benefits that will render the decrease in privacy acceptable.
One example of businesses are the oil and gas industries. This
article [8] discusses IoT business analytics security in this
specific field. This same knowledge can be transferred over to
other fields of industry, which ultimately means the
information can be applied to most businesses. The article
expresses the economical trend of implementing already tried
and tested methods in the oil and gas industry with a
technological aspect. Which helps simplify most tasks and
increases efficiency, cutting costs and increasing output. IoT is
a big way of facilitating tasks in these industries, in the sense
that IoT can be integrated into the infrastructure of these
industries. The article discusses IoT deployments and
protocols, which relates to IoT business analytics security. The
current article deals with a huge range of industries and cases
by implementing an equally huge number of devices and
network communication protocols. E.g. HTTPS, Access
control, etc.
III. PROPOSED APPROACH TO SECURE IOT
At first it may appear quite challenging to secure IoT but
it can be achieved through planning at the beginning, since if
the security is considered in the initial stage it can solve
substantial IoT security issues. Generally, security is
implemented at organizational level after understanding and
evaluating the overall risk related to the functionality of the
secure policies and standards. By evaluating the data security
risks and the controls required to manage data with respect to
the devices they operate on, as well as device security, any
organization can resolve IoT security issues maximum
possible extent. This strategy will simplify the implementation
of any IoT framework and also provides the additional benefit
to apply and integrate the existing proven security principles
into the current technological environment. Thus this strategy
involves thorough understanding of deployed components,
their restrictions and their implementation abilities. Therefore,
every IoT device is based on a network stack mostly
consisting of wireless networking design and technology since
these IoT have their own operating systems(OS). The OS
within the IoT devices could be locked down to secure them
from any vulnerability due to attacks and threats which require
regular monitoring of OS services or maintain proper
infrastructure security based on possible remedies. The
vulnerabilities due to insecurity leaves OS in a compromising
situation but protection can be achieved by constant vigilance
and organized maintenance programs or using a firewall.
However, to enable security using this strategy will be limited
to a system with few devices otherwise it is required to
automate and synchronize in case of many devices which may
assist the system in avoiding human errors.
Since IoT devices rely on wireless technology based on
wireless Ethernet or Bluetooth for communications, these
technologies can use critical updates and revisions of software
to address prior vulnerabilities or use newer versions of
framework to quickly address the security threats. 1) The
framework is dependent on the encryption techniques applied
between the communicating points to ensure end to end
communication among the peers by using unique keys. 2)
Another layer of security includes any device attempting to
connect to the network depends on the enterprise preferences
for successful authentication process implementation. 3) The
third important layer consists of controlling and dividing
communication paths which is accomplished by grouping
devices based on network types and functionality ( using
Routers and Switches). Bluetooth firewalls and IP-based
firewalls could be effective counter methods to implement
cyber threats apart from controlling other devices on the
network. The next section IV discusses a suitable IoT
framework based on three layers which could serve as a secure
reference framework for IoT elements.
IV. A SECURE IOT ARCHITECTURE
The IoT has a great potential, where its main aim is to
transform the way of performing different activities and
reform the living pattern of people in the recent world. Due to
this reason the IoT architecture differs based on type of
solution we intend to develop. IoT technology framework
mainly consists of four basic components( Sensors, Devices,
Gateways and Clouds). But there are several kinds of
challenges associated with IoT framework of devices and also
management of these devices. The focus of this paper is the
security issues and challenges from the IoT perspective which
in turn is based on internet security issues and security among
layers. A detailed discussion is provided below section. The
composition of IoT framework with respect to the three layers:
application layer, network layer and perception layer has to be
studied to understand the underlying issues and possible near
solutions to make the systems secure from the attacks (refer
Fig. 1) [11][12]. The major concerns in IoT development are
security and privacy issues as illustrated in [13]14]. The
security and privacy satisfaction requirements represent a
primary role where the requirements implicate access control
through IoT networks, data confidentiality and authentication,
privacy[15][18] and trust between things and users, and the
reinforcement of privacy and security regulations (refer Fig.
2). The main requirements to secure IoT is to ensure that the
data is available for the authorized users at all times [19][20].
IoT has different applications with different economic impact
ranging from home to industry (Fig. 3) and it is remarkably
growing to allow the daily tasks to be a part of the global
network. As IoT grows, security challenges increase and the
approaches to secure the devices and the networks move
towards a greater autonomy in reacting to attacks and
perceiving threats, based on a systemic cognitive technique
[21]. Fig. 4 indicates the evolution of security requirements
[22]. Consequently, efficient security techniques are required
for embedded computing that are based on scarce resources,
applications and secure network protocols, such as
authentication techniques, credential and key management
[18][23]. Security plays an important role in IoT application
development. Also, IoT applications gather enormous amount
of data from a number of sensors (Fig. 5).
Fig. 1. IoT Architecture
So, this data needs to be protected by information security
algorithms
Fig. 2. IoT Security Challenges
such as encryption where the most of this data is personal
[24][25],
Fig. 3. Impact of IoT in Industries
whereas, the collection and usage of personal data is a privacy
IoT challenge on its own. [26].
Fig. 4. Evolution of security requirements
Data collection
Security and Privacy
Services Semantics
Resources IoT Objects
Fig. 5. Integration Requirements of IoT data
A. Perception Layer Security issues
The main enabling technologies utilized in this layer are
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID), Wireless Sensor
Network (WSN) and other types of identification and sensing
techniques. The most popular threat types privileged by this
layer are [11]:
Malicious Node: In this type of security threat, the
malicious node is added to the existing system by the
antagonists over which they can disseminate malicious
data over the network, so as to infect the whole system.
Node Capture: The nodes that exist in the network
gateway have a greater potential to be exposed that may
result in the important information leakage that risks the
entire network’s security.
Replay Attack: In the replay attack, the antagonist
replays the previous messages to the destination node in
order to compromise the authentication scheme and
network trust.
Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack: Denial of
Service (DoS) DDoS attacks are the most popular and
easiest to conduct attacks through the networks. Where
they produce the unavailability of services and the
exhaustion of network resources.
B. Network and Transformation Layer Security issues
The main threats in this layer are Network Intrusion,
Man-in-the-middle, eavesdropping, and DoS/DDoS. These
threats relate to integrity, confidentiality, and availability
[15][25].
Issues of Scalability: IoT includes a huge number of
devices and sometimes large in size and these may
leave or enter the network many times, thus increasing
the challenges such as network congestion, lack of
authentication and authorization, a sharing
environment, etc. It also consumes more resources.
Heterogeneity: This makes the system vulnerable. The
main reason the system suffers heterogeneity is the
involvement (and utilization) of various technologies
[27], network coordination and protocols security are
difficult to preserve.
Data Revelation: The antagonist may be able to get
sensitive data from the network by utilizing social
engineering mechanisms. Although the IoT network has
a lot of devices that have a huge amount of data, it is
easy to retrieve the information from the nodes utilizing
certain information retrieval mechanisms.
C. Application Layer Security issues
This layer requires different security levels according to
the application requirements that make the securing
application tasks complicated and hard. At this layer, the
security and privacy issues[12].
Privacy: Personal privacy should be guaranteed for
each connection, where at times the methods that are
utilized to process and analyze the data may be weak
that can cause data loss and do huge damages to the
system over a long period.
Data Management: As the data collected in the system
is huge, its complexity grows that leads to a lot of
resources being exhausted and complicated
mechanisms for the data management and may also
produce data loss.
Node identification and Mutual authentication: For
identifying the node to perform authentication different
degrees of access privileges are required in each
application and it is dependent on the number of users
allowed by a specific application. This creates a serious
requirement for an effective Authentication scheme to
be implemented and utilized to prohibit any illegal
access.
Specific Vulnerabilities of Application: There exists
threats or vulnerabilities that can be used by the
antagonists resulting in development of application
modules anonymous to the user.
V. CONCLUSION
Today it is estimated that over 23 billion IoT connected
devices exist worldwide and it is anticipated to rise and reach
30 billion in near future within a year or two(by 2020)
and more than 60 billion by 2025. This gigantic wave of new
IoT gadgets are cost affective. As the IoT connected devices
continues to escalate in the upcoming years, so will the
security threats for Data privacy and security associated with
these will rise. So, there is a tremendous need for
implementing security throughout the platforms being used to
integrate IoT devices.
To summarize it is required to be thoughtful and make a
choice of IoT device based on the ability of security that can
be provided by the device. To design a secure IoT framework,
it is important to identify the limitation of IoT device, consider
the network infrastructure, the categories of vulnerabilities and
possibilities of organizational risks. It is required to build up a
strong network foundation to support IoT elements even
though they grow fast in the environments (network), still the
threats could be managed effectively and conveniently.
As a future work, our aim is to develop a real
implementation of a secure IoT Framework and illustrate
how to address the IoT Security threats using wireless network
simulation and present the potential importance for
supporting authenticated access to critical information.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We are thankful to the Head of Department of Computer
Sciences and the Research Unit of College of Computer and
Information Sciences, Princess Nourah Bint Abdulrahman
University for all the encouragement and support they have
extended to carry out the research activities at the department
and college level. We would like to extend our sincere thanks
for the research awareness and motivation they have
developed for women empowerment. I also extend my sincere
gratitude towards their constant cooperation and guidance to
get the required resources and information for the research.
REFERENCES
1. Hui Suo , Jiafu Wan , Caifeng Zou , Jianqi Liu, “Security in the Internet
of Things: A Review”, International Conference on Computer Science
and Electronics Engineering, IEEE Xplore Digital Library, 2012.
2. Fabián Constante Nicolalde, Fernando Silva, Boris Herrera,
António Pereira, “Big Data Analytics in IOT: Challenges, Open
Research Issues and Tools”, World Conference on Information Systems
and Technologies, Trends and Advances in Information Systems and
Technologies, 2018, Part of book pp 775-788.
3. Andreas P. Plageras , Kostas E. Psannis, “Algorithms for Big Data
Delivery over the Internet of Things”, IEEE 19th Conference on
Business Informatics (CBI), IEEE Xplore Digital Library, 2017.
4. Sachchidanand Singh , Nirmala Singh, “Internet of Things (IoT):
Security challenges, business opportunities & reference architecture for
E-commerce”, International Conference on Green Computing and
Internet of Things (ICGCIoT), IEEE Xplore Digital Library, 2015.
5. Layth Sliman , Hachemi Nabil Dellys, “Security, Safety and
Confidentiality in IoT for Collaborative Business Technologies (SSCIoT
Track of WETICE 2018)”, IEEE 27th International Conference on
Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises
(WETICE), IEEE Xplore Digital Library, 2018.
6. Hwaiyu Geng, “IoT Business Models”, Internet of Things and Data
Analytics Handbook, IEEE Xplore Digital Library, 2017.
7. Zahraa Marafie , Kwei-Jay Lin , Yanlong Zhai , Jing Li, “ProActive
Fintech: Using Intelligent IoT to Deliver Positive InsurTech Feedback”,
IEEE 20th Conference on Business Informatics (CBI), IEEE Xplore
Digital Library, 2018.
8. Cristian TOMA, Marius POPA, “IoT Security Approaches in Oil & Gas
Solution Industry 4.0”, Informatica Economica Academic Journal, vol.
22, no. 3/2018.
9. Aakanksha Tewari, B.B. Gupta, “Security, privacy and trust of different
layers in Internet of Things (IoTs) framework”, Future Generation
Computer Systems, May 2018. Available [Online]
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2018.04.027
10. Jianwei Hou, Leilei Qu, Wenchang Shi, “A survey on internet of things
security from data perspectives”, Computer Networks Journal, in press,
Dec 2018. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2018.11.026
11. Miao Wu, Ting-Jie Lu, Fei-Yang Ling, Jing Sun, Hui-Ying Du,
“Research on the architecture of Internet of Things”, in: Proceeding of
2010 3rd International Conference on Advanced Computer Theory and
Engineering(ICACTE), 2010, pp. 484-487.
12. Zhihong Yang, Yingzhao Yue, Yu Yang, Yufeng Peng, Xiaobo Wang,
Wenji Liu, “Study and application on the architecture and key
technologies for IoT”, in Proceeding of 2011 International Conference
on Multimedia Technology ( ICMT), 2011, pp. 747-751.
13. Ying-Cong Zhang, Jing Yu, “A study on the fire IOT development
strategy”, Procedia Engineering, Vol. 52, 2013, pp. 314-319.
14. Rishika Mehtaa , Jyoti Sahnib, Kavita Khannac, “Internet of Things:
Vision, Applications and Challenges”, International Conference on
Computational Intelligence and Data Science (ICCIDS 2018), Procedia
Computer Science, Vol. 132, 2018, pp. 1263-1269.
15. S. Sicari, A. Rizzardi, L.A. Grieco, A. Coen-Porisini, “Security, privacy
and trust in Internet of Things: The road ahead”, Computer Networks
Journal, Vol. 76, 2015, pp. 146–164.
16. Mardiana binti, Mohamad Noor, Wan Haslina Hassan, “ Current
research on Internet of Things (IoT) security: A survey”, Computer
Networks Journal, in press, Dec 2018.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.comnet.2018.11.025
17. Kazi Masum Sadique, Rahim Rahmani, Paul Johannesson, “Towards
Security on Internet of Things: Applications and Challenges in
Technology”, The 9th International Conference on Emerging Ubiquitous
Systems and Pervasive Networks (EUSPN 2018), Procedia Computer
Science, Vol. 141, 2018, pp. 199–206.
18. Mahmoud Ammar, Giovanni Russello, Bruno Crispo, “Internet of
Things: A survey on the security of IoT frameworks”, Journal of
Information Security and Applications, Vol. 38, 2018, pp. 8–27.
19. Kevin Ashton, “Internet of Things”, RFiD Journal, 2009.
20. Huansheng Ning ; Ziou Wang, “Future Internet of Things Architecture:
Like Mankind Neural System or Social Organization Framework?”,
IEEE Communications Letters, Vol. 15 , No. 4 , 2011, pp. 461–463.
21. Hugh Boyes, Bil Hallaq, Joe Cunningham, Tim Watson, “The industrial internet of things (IIoT): An analysis framework”, Computers in
Industry Jornal, Vol. 101, 2018, pp. 1–12.
22. Arbia Riahi Sfar, Enrico Natalizio, Yacine Challal, Zied Chtourou, “A
roadmap for security challenges in the Internet of Things “, Digital
Communications and Networks, Vol. 4, 2018, pp. 118–137.
23. Luigi Atzori, Antonio Iera, Giacomo Morabitoc, “The Internet of
Things: A survey”, Computer Networks Journal, Vol. 54, No. 15, 2010,
pp. 2787-2805.
24. Ira S. Rubinstein, “Big Data: The End of Privacy or a New Beginning?”
International Data Privacy Law, Vol. 3, No. 2, 2013, pp. 74–87.
25. Christos Stergioua, Kostas E. Psannisa, Brij B. Guptab, Yutaka
Ishibashic, “Security, privacy & efficiency of sustainable Cloud
Computing for Big Data and IoT”, Sustainable Computing: Informatics
and Systems, Vol. 19, 2018, pp. 174–184.
26. Xavier Caron, Rachelle Bosua, Sean B. Maynard, Atif Ahmad, “The
Internet of Things (IoT) and its impact on individual privacy: An
Australian perspective”, Computer Law & Security Review Journal,
Vol. 32, 2016, pp. 4–15.
27. Dr. Kahkashan Tabassum, Dr. A. Damodaram and S.V.S. Rama
Krishnam Raju, “An Energy-Efficient New Hierarchical Stable Election
Protocol for Wireless Sensor Networks”, Proceedings of 2nd
International Conference on Recent Advances in Design, Development
and Control of Micro-Air-Vehicles IC-RA-MAV-2013.
Вам также может понравиться
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- Uganda Electricity Connections Policy (2018 - 2027)Документ35 страницUganda Electricity Connections Policy (2018 - 2027)African Centre for Media Excellence80% (5)
- Regtronic Eh EngДокумент44 страницыRegtronic Eh Enggogame2014100% (1)
- Coconut Fatty Acid Diethanolamide - CDE 85Документ6 страницCoconut Fatty Acid Diethanolamide - CDE 85Iqbal batchaОценок пока нет
- Bosch Lambda Sensor LSU 1 & 4.9Документ10 страницBosch Lambda Sensor LSU 1 & 4.9Al CaracasОценок пока нет
- Data Communication NotesДокумент5 страницData Communication NotesitsmelittyОценок пока нет
- Low Impact Development Manual For Michigan September 2008Документ512 страницLow Impact Development Manual For Michigan September 2008Yadir Rodrìguez NùñezОценок пока нет
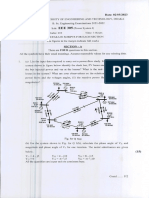
- L-3ff - lIEEE Date: 02/05/2023: Toomw 200MW 20 Mvar 9 Mvar Bus 2Документ26 страницL-3ff - lIEEE Date: 02/05/2023: Toomw 200MW 20 Mvar 9 Mvar Bus 2mahiyanintesirprethuprethuОценок пока нет
- Presentation First SolarДокумент36 страницPresentation First SolarkamalmuraОценок пока нет
- Actividades - Grupo Diana MabelДокумент22 страницыActividades - Grupo Diana MabelJhon Alejandro Hurtado ValenciaОценок пока нет
- XK3101 (HL-2065) IndicatorДокумент20 страницXK3101 (HL-2065) IndicatorEliana Cristina100% (1)
- AAFT Advertising PR Events BrochureДокумент91 страницаAAFT Advertising PR Events BrochureDeepak SethiОценок пока нет
- Detroit Diesel Training Manual Fans and Fan Shrouds AbbyДокумент11 страницDetroit Diesel Training Manual Fans and Fan Shrouds AbbyMohamed Abo elkhairОценок пока нет
- Anshul Srivastava: ObjectiveДокумент3 страницыAnshul Srivastava: Objectivealk_deepОценок пока нет
- Quick Start Guide Guía de Inicio Rápido: TH-46PZ850U TH-50PZ850UДокумент66 страницQuick Start Guide Guía de Inicio Rápido: TH-46PZ850U TH-50PZ850Ujeffreyspeck7119Оценок пока нет
- Prius 2004 - Brakes - BleedingДокумент17 страницPrius 2004 - Brakes - Bleedingburvi20011186Оценок пока нет
- Transaxle - TECUMSEH PEERLESS TRANSAXLE MST 205-535EДокумент3 страницыTransaxle - TECUMSEH PEERLESS TRANSAXLE MST 205-535EJindřich Nenza100% (1)
- End Prob. CengelДокумент5 страницEnd Prob. CengelErvz MissionОценок пока нет
- Y 54 y 45Документ10 страницY 54 y 45inayathОценок пока нет
- VISI ProgressДокумент4 страницыVISI Progressชัยรัตน์ ตันตืไพบูลย์วุฒิОценок пока нет
- Pp3090 Causal AnalysisДокумент5 страницPp3090 Causal AnalysisNitinchandan KumarОценок пока нет
- Spare Parts Supply ChainДокумент8 страницSpare Parts Supply ChainRaj ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- AMTE 130 - Lesson 2 - Types of Jet PropulsionДокумент48 страницAMTE 130 - Lesson 2 - Types of Jet PropulsionVince Renier RamosОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4.b (Method of Section)Документ22 страницыChapter 4.b (Method of Section)LogarithemОценок пока нет
- rt809h Mboot UpgredДокумент7 страницrt809h Mboot Upgredrabas_Оценок пока нет
- Soil Texture and Soil StructureДокумент24 страницыSoil Texture and Soil StructureRaquel Bona Viñas100% (4)
- Notes Collection Related With OopsДокумент135 страницNotes Collection Related With OopsPervasivetech BangaloreОценок пока нет
- Store 2Документ19 страницStore 2aymanОценок пока нет
- Pneu Portable ChairДокумент3 страницыPneu Portable ChairblessyОценок пока нет
- Canon Ir2200 Ir2800 Ir3300 User ManualДокумент362 страницыCanon Ir2200 Ir2800 Ir3300 User ManualMohamed Kabsha50% (2)
- July 10 HVACДокумент2 страницыJuly 10 HVACsandyolkowskiОценок пока нет