Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Coal India Limited CE Schedule
Загружено:
Rahul jorwalОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Coal India Limited CE Schedule
Загружено:
Rahul jorwalАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Full Length Mock Tests
No. of Max Date of
Test No Mock codes Duration
Questions Marks Activation
Full Length Mock Test-1
Test-01 200 200 3 hours 10-01-2020
(Paper-I + Paper-II)
Full Length Mock Test-2
Test-02 200 200 3 hours 18-01-2020
(Paper-I + Paper-II)
Full Length Mock Test-3
Test-03 200 200 3 hours 25-01-2020
(Paper-I + Paper-II)
Full Length Mock Test-4
Test-04 200 200 3 hours 01-02-2020
(Paper-I + Paper-II)
Full Length Mock Test-5
Test-05 200 200 3 hours 08-02-2020
(Paper-I + Paper-II)
Full Length Mock Test-6
Test-06 200 200 3 hours 15-02-2020
(Paper-I + Paper-II)
Note:
The Syllabus considered as per previous Notification of COAL INDIA. ACE Engineering Academy does not take
any responsibility for deviations in syllabus in the final Coal India exam. As per Notification of Coal India each
question carries ‘1’ mark and there is no negative marks for wrong answer.
Tests will be activated at 6:00 pm on scheduled day
Paper-I_Syllabus
Subject Name Syllabus
Everyday Science, Scientific Research, Sports, Indian Culture, Indian History, Indian national
General Knowledge/ movement, World & Indian Geography, Natural resources Indian Economy, Indian Polity,
awareness Indian C0nstituti0n,Nati0nal & International current affairs, Environment, India’s Agriculture,
Trade & Commerce, Basic Information technology.
Analogies, similarities and differences, space Visualization, spatial orientation, problem solving,
analysis, judgement, decision making, Visual memory, discrimination, observation, relationship
concepts, arithmetical reasoning and figural classification, arithmetic number series, non-
Reasoning
verbal series, coding and decoding, Word Building statement conclusion, syllogistic reasoning
,puzzle, Venn Diagrams , Space Visualization , Symbolic/Number Classification, Figural
Classification etc.
Number System,decimals,fracti0ns and relationships between numbers, Percentage. Ratio &
Proportion, Square roots, Averages, Interest, Profit and Loss, Discount, Mixture and Allegation,
Numerical ability
Time and distance, Time & Work, Basic algebraic identities of School Algebra, , Factor, Heights
and Distances. AP. & G.P.Series
Error recognition, fill in the blanks (verbs,Prep0siti0n etc.) synonyms, antonyms,
spelling/detecting Mis—spelt words, idioms & phrases, one word substitution, sentences
General English
structure, Sentence completion, shuffling of sentence parts, shuffling of sentences in a
passage, comprehension passage
Paper-II_Syllabus
Subject Name Syllabus
System of forces, free-body diagrams, equilibrium equations; Internal forces in structures;
Engineering Mechanics Friction and its applications; Kinematics of point mass and rigid body; Centre of mass; Euler’s
equations of motion; Impulse-momentum; Energy methods; Principles of Virtual work.
Bending moment and shear force in statically determinate beams; Simple stress and strain
Solid Mechanics relationships; Theories of failures; Simple bending theory, flexural and shear stresses, shear
centre; Uniform torsion, buckling of column, combined and direct bending stresses.
Statically determinate and indeterminate structures by force/ energy methods; Method of
superposition; Analysis of trusses, arches, beams, cables and frames; Displacement methods:
Structural Analysis
Slope deflection and moment distribution methods; Influence lines; Stiffness and flexibility
methods of structural analysis.
Construction Materials: Structural steel - composition, material properties and behaviour;
Concrete - constituents, mix design, shortterm and long-term properties; Bricks and mortar;
Construction Materials and
Timber; Bitumen. Construction Management: Types of construction projects; Tendering and
Management
construction contracts; Rate analysis and standard specifications; Cost estimation; Project
planning and network analysis - PERT and CPM.
Working stress, Limit state and Ultimate load design concepts; Design of beams, slabs,
Concrete Structures columns; Bond and development length; Prestressed concrete; Analysis of beam sections at
transfer and service loads.
Working stress and Limit state design concepts; Design of tension and compression members,
beams and beam- columns, column bases; Connections - simple and eccentric, beam-column
Steel Structures
connections, plate girders and trusses; Plastic analysis of beams
and frames.
Origin of soils, soil structure and fabric; Three-phase system and phase relationships, index
properties; Unified and Indian standard soil classification system; Permeability - one
dimensional flow, Darcy’s law; Seepage through soils - two-dimensional flow, flow nets, uplift
Soil Mechanics pressure, piping; Principle of effective stress, capillarity, seepage force and quicksand
condition; Compaction in laboratory and field conditions; Onedimensional consolidation, time
rate of consolidation; Mohr’s circle, stress paths, effective and total shear strength
parameters, characteristics of clays and sand.
Sub-surface investigations - scope, drilling bore holes, sampling, plate load test, standard
penetration and cone penetration tests; Earth pressure theories - Rankine and Coulomb;
Stability of slopes - finite and infinite slopes, method of slices and Bishop’s method; Stress
distribution in soils - Boussinesq’s and Westergaard’s theories, pressure bulbs; Shallow
Foundation Engineering
foundations - Terzaghi’s and Meyerhoffls bearing capacity theories, effect of water table;
Combined footing and raft foundation; Contact pressure; Settlement analysis in sands and
clays; Deep foundations - types of piles, dynamic and 2/4 static formulae, load capacity of
piles in sands and clays, pile load test, negative skin friction.
Properties of fluids, fluid statics; Continuity, momentum, energy and corresponding
Fluid Mechanics equations; Potential flow, applications of momentum and energy equations; Laminar and
turbulent flow; Flow in pipes, pipe networks; Concept of boundary layer and its growth.
Forces on immersed bodies; Flow measurement in channels and pipes; Dimensional analysis
and hydraulic similitude; Kinematics of flow, velocity triangles; Basics of hydraulic machines,
Hydraulics specific speed of pumps and turbines; Channel Hydraulics - Energydepth relationships,
specific energy, critical flow, slope profile, hydraulic jump, uniform flow and gradually varied
flow
Subject Name Syllabus
Hydrologic cycle, precipitation, evaporation, evapo-transpiration, watershed, infiltration, unit
hydrographs, hydrograph analysis, flood estimation and routing, reservoir capacity, reservoir
Hydrology
and channel routing, surface run-off models, ground water hydrology - steady state well
hydraulics and aquifers; Application of Darcy’s law.
Duty, delta, estimation of evapo-transpiration; Crop water requirements; Design of lined and
unlined canals, head works, gravity dams and spillways; Design of weirs on permeable
Irrigation
foundation; Types of irrigation systems, irrigation methods; Water logging and drainage;
Canal regulatory works, cross-drainage structures, outlets and escapes.
Quality standards, basic unit processes and operations for water treatment. Drinking water
standards, water requirements, basic unit operations and unit processes for surface water
treatment, distribution of water. Sewage and sewerage treatment, quantity and
Water and Waste Water characteristics of wastewater. Primary, secondary and tertiary treatment of wastewater,
effluent discharge standards. Domestic wastewater treatment, quantity of characteristics of
domestic wastewater, primary and secondary treatment. Unit operations and unit processes
of domestic wastewater, sludge disposal.
Air Pollution: Types of pollutants, their sources and impacts, air pollution meteorology, air
pollution control, air quality standards and limits.
Air Pollution , Municipal Municipal Solid Wastes: Characteristics, generation, collection and transportation of solid
Solid Wastes & Noise wastes, engineered systems for solid waste management (reuse/ recycle, energy recovery,
Pollution treatment and disposal).
Noise Pollution: Impacts of noise, permissible limits of noise pollution, measurement of
noise and control of noise pollution.
Highway alignment and engineering surveys; Geometric design of highways - cross-sectional
Transportation
elements, sight distances, horizontal and vertical alignments; Geometric design of railway
Infrastructure
track; Airport runway length, taxiway and exit taxiway design.
Highway materials - desirable properties and quality control tests; Design of bituminous
paving mixes; Design factors for flexible and rigid pavements; Design of flexible pavement
Highway Pavements
using IRC: 37-2012; Design of rigid pavements using IRC: 58- 2011; Distresses in concrete
pavements.
Traffic studies on flow, speed, travel time - delay and 0-D study, PCU, peak hour factor,
parking study, accident study and analysis, statistical analysis of traffic data; Microscopic and
Traffic Engineering macroscopic parameters of traffic flow, fundamental relationships; Control devices, signal
design by Webster’s method; Types of intersections and channelization; Highway capacity
and level of service of rural highways and urban roads.
Principles of surveying; Errors and their adjustment; Maps - scale, coordinate system;
Distance and angle measurement - Levelling and trigonometric levelling; Traversing and
Surveying: triangulation survey; Total station; Horizontal and vertical curves. Photogrammetry - scale,
flying height; Remote sensing - basics, platform and sensors, Visual image interpretation;
Basics of Geographical information system (GIS) and Geographical Positioning system (GPS).
Вам также может понравиться
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5795)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2259)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (121)
- Sample Construction ScheduleДокумент10 страницSample Construction Scheduleyusuf abdinasirОценок пока нет
- 003 - LICO Light Weight Column FormworkДокумент8 страниц003 - LICO Light Weight Column FormworksmaliscribdОценок пока нет
- Pipe Supports - Product TrainingДокумент25 страницPipe Supports - Product TrainingmurugesanОценок пока нет
- OCF by Jaspal SirДокумент2 страницыOCF by Jaspal SirAnkur SinhaОценок пока нет
- Concrete Beam Design (CSA A23.1-94)Документ2 страницыConcrete Beam Design (CSA A23.1-94)marijean catuiraОценок пока нет
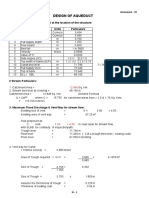
- DESIGN AqueductДокумент89 страницDESIGN AqueductmukhleshОценок пока нет
- DB Wiring DiagramДокумент1 страницаDB Wiring DiagrammhofuОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5-Fundamentals of Fluid FlowДокумент26 страницChapter 5-Fundamentals of Fluid FlowJerico Torres AdajarОценок пока нет
- Module1 - Basics of HVACДокумент7 страницModule1 - Basics of HVACanita shindeОценок пока нет
- Reinforcing Steel Bars Price List: Structural (Astm Grade 33)Документ1 страницаReinforcing Steel Bars Price List: Structural (Astm Grade 33)Mark Ryan NagalesОценок пока нет
- 6 Student Manual PSO User ExpertДокумент212 страниц6 Student Manual PSO User Expertagusnurcahyo66Оценок пока нет
- FOI Cengkareng - SchedulleДокумент238 страницFOI Cengkareng - SchedulleAnnisa SafitriОценок пока нет
- Installation Manual: Chamclad® by ChameleonДокумент34 страницыInstallation Manual: Chamclad® by ChameleonBoraОценок пока нет
- Cooler 171110 (r0) Seleccion de Enfriador y Calculo Tlr-4225-UДокумент1 страницаCooler 171110 (r0) Seleccion de Enfriador y Calculo Tlr-4225-UloretoОценок пока нет
- HMT 2Документ19 страницHMT 2ME 26 PRADEEP KUMARОценок пока нет
- Study On Slope Stability of Earthen DamsДокумент7 страницStudy On Slope Stability of Earthen Damssharvan10Оценок пока нет
- Perencanaan Struktur Gedung PusatДокумент12 страницPerencanaan Struktur Gedung Pusatastuti masdarОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 1Документ8 страницLab Report 1w fОценок пока нет
- Cast in PlatesДокумент18 страницCast in Plates贾天伟Оценок пока нет
- Scrutiny of Shamli-AmbalaДокумент16 страницScrutiny of Shamli-AmbalaAbhishek PathakОценок пока нет
- Kirby SpecificationДокумент23 страницыKirby SpecificationTuanQuach0% (1)
- CENGR 3270 Ce Laws, Ethics and Contracts: The Engineering Education, Personal and Ethical Relations Research Work No. 1Документ15 страницCENGR 3270 Ce Laws, Ethics and Contracts: The Engineering Education, Personal and Ethical Relations Research Work No. 1Bao yifanОценок пока нет
- MyBook 11Документ278 страницMyBook 11ali mustafaОценок пока нет
- Equivalent Frame Method Applied To Concrete Shear Walls by Angelo MattacchioneДокумент8 страницEquivalent Frame Method Applied To Concrete Shear Walls by Angelo Mattacchionegulilero100% (1)
- HVAC Approved Manufacturers ListДокумент2 страницыHVAC Approved Manufacturers ListJoshuaОценок пока нет
- Pile DebondingДокумент4 страницыPile DebondingjtjtfghОценок пока нет
- JNTUA Concrete Technology Notes R20Документ101 страницаJNTUA Concrete Technology Notes R20Shaik SabeetОценок пока нет
- Fire Protection Systems: Continuing Education From Plumbing Systems & DesignДокумент25 страницFire Protection Systems: Continuing Education From Plumbing Systems & DesignKyi TharОценок пока нет
- SJS - DHT-Downhole Oil ToolsДокумент156 страницSJS - DHT-Downhole Oil ToolsTHUNDER KESAR1000Оценок пока нет
- Structural Analysis Report of Hospital BuldingtДокумент35 страницStructural Analysis Report of Hospital BuldingtPrasanth Nair50% (2)