Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Quantitative Research
Загружено:
Dave II CosteloОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Quantitative Research
Загружено:
Dave II CosteloАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
Used to examine the relationship between variables, quantify the problem by way of generating
numerical data and explain the phenomenon by way of gathering data.
QUANTITATIVE DATA COLLECTION METHOD:
1. Online Surveys
2. Questionnaire Surveys
3. Mobile Surveys
4. Face-to-face interviews
5. telephone interviews
6. longitudinal studies
7. Data Mining
8. Online polls
Quantitative approaches are best used to answer what, when and who questions and are not well suited
to how and why questions.
CHARACTERISTICS OF A QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH.
Purpose Explain, predict, and/or control phenomena through focused
collection of numerical data.
Approach to Inquiry Deductive, objective focused, and outcome-oriented
Hypothesis Specific,testable, and stated pro to a particular study
Theoretical-Conceptual Framework Provides an explicit explanation why the problem under study
exist by showing how the variables are related to each other;
extensive use of variables
Review of Related Literature Extensive, does significantly affect particular study.
Sampling Mostly random but not all the time. Intent to select large
representative sample in order to generalize results to
population.
Measurement Standarized, numerical,at the end
Data Collection Strategies Administration of test and questionnaires. Non participant
observation
Data Analysis Raw data are numbers performed at the end of the study,
involves statistics.
Data Interpretation and Conclusion Conclusions and generalizations formulated at end of the study,
stated with pre-determined degree of certainty
STRENGTHS AND WEAKNESSES OF QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH
STRENGTH WEAKNESS
1. Easy to analyze because it provides numerical 1. Improper representation of the target
data that can be easily interpreted. population might hinder the research for achieving
its desired purposes and objectives
2. The findings of the study can be generalized to 2. Related secondary data are sometimes not
the population about which information is available or accessing available data is difficult to
required. obtain through structured data collection
instruments
3. The data gathered can be very consistent, 3.Lack of resources for data collection.
precise and reliable
4. Clear documentation can be provided regarding 4. Difficult to understand the context of a
the content and application of the survey phenomenon.
instruments so that the other researchers can
assess the validity of the findings.
5.Quantitave studies can be replicated 5. Inability to control the environment
6. The effects of extraneous variables can be 6. Studies are expensive and time-consuming
controlled
KINDS OF QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH.
1. Survey Research -People questioned are sampled at random.
-Allow researchers to judge behavior and then
present the findings in a accurate way.
2. Descriptive Research -Describes what exist and may help uncover new
facts and meaning.
-Describe, Observe and Document
-Produce statistical information about aspects of
education that interest policy makers and
educators.
3. Correlational Research -Relationships between two variables.
4. Evaluation Research -Aims to assess the effects,impacts or outcomes of
practices,policies or programs.
5. Causal-Comparative Research -How different groups are affected by the same
circumtances.
-cause and effect relationship
IMPORTANCE OF QUANTITATIVE RESEARCH:
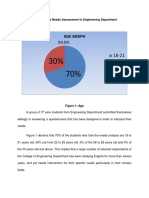
Quantitative research is useful when carrying out a large scale needs assessment or baseline survey. It is
a social research that employs empirical methods and empirical statements.
It is more objective and reliable
Test theories and hypothesis
Use statistics to generalize a finding
Less detailed
Researcher’s subjectivity is less recognized.
Вам также может понравиться
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryОт EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)От EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItОт EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaОт EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingОт EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyОт EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeОт EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnОт EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerОт EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreОт EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersОт EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceОт EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureОт EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaОт EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)От EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Рейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (98)
- 1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQsДокумент467 страниц1000 Electronic Devices & Circuits MCQskibrom atsbha67% (3)
- Dynamics of Bases F 00 BarkДокумент476 страницDynamics of Bases F 00 BarkMoaz MoazОценок пока нет
- Budokon - Mma.program 2012 13Документ10 страницBudokon - Mma.program 2012 13Emilio DiazОценок пока нет
- Rhodes Solutions Ch4Документ19 страницRhodes Solutions Ch4Joson Chai100% (4)
- Core 12-Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Tel. No. (082) 300-71-73Документ1 страницаCore 12-Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Tel. No. (082) 300-71-73Dave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Core 12-Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Tel. No. (082) 300-71-73Документ1 страницаCore 12-Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Tel. No. (082) 300-71-73Dave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- National Artists Famous Filipino Artists and Their Major WorksДокумент6 страницNational Artists Famous Filipino Artists and Their Major WorksDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Core 12-Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Tel. No. (082) 300-71-73Документ1 страницаCore 12-Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Tel. No. (082) 300-71-73Dave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- CORE 12-Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Tel. No. (082) 300-71-73Документ4 страницыCORE 12-Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Region: Tel. No. (082) 300-71-73Dave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Recognizing the Contributions of National Artists and GAMABA AwardeesДокумент5 страницRecognizing the Contributions of National Artists and GAMABA AwardeesDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- RMC Bldgs Final Exam for Core 12-Contemporary Philippine ArtsДокумент4 страницыRMC Bldgs Final Exam for Core 12-Contemporary Philippine ArtsDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- RMC Bldgs Midterm Exam on Philippine ArtsДокумент3 страницыRMC Bldgs Midterm Exam on Philippine ArtsDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Teaching Guide: Senior High SchoolДокумент5 страницTeaching Guide: Senior High SchoolDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Core 12 - Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions: 1 Semester A.Y.: 2019-2020Документ7 страницCore 12 - Contemporary Philippine Arts From The Regions: 1 Semester A.Y.: 2019-2020Dave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Midterm Exam Week: Senior High SchoolДокумент1 страницаMidterm Exam Week: Senior High SchoolDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Final Exam Week: Senior High SchoolДокумент1 страницаFinal Exam Week: Senior High SchoolDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Teaching Guide: Senior High SchoolДокумент5 страницTeaching Guide: Senior High SchoolDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Sculpture and Architecture in the PhilippinesДокумент6 страницSculpture and Architecture in the PhilippinesDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Pre-Lim Exam Week: Senior High SchoolДокумент1 страницаPre-Lim Exam Week: Senior High SchoolDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Appreciating Contemporary Philippine Visual ArtsДокумент6 страницAppreciating Contemporary Philippine Visual ArtsDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- LET Reviewer English Part 1 Answer KeysДокумент1 страницаLET Reviewer English Part 1 Answer KeysTherese June GregorioОценок пока нет
- Teaching Guide: The Rizal Memorial Colleges, IncДокумент2 страницыTeaching Guide: The Rizal Memorial Colleges, IncDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Course SyllabusДокумент2 страницыCourse SyllabusDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- SHS E-Class Record CORE 12 MACAPAGAL SUBJECT 2016 1ST SEMESTERДокумент17 страницSHS E-Class Record CORE 12 MACAPAGAL SUBJECT 2016 1ST SEMESTERDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Teaching Guide: Senior High SchoolДокумент2 страницыTeaching Guide: Senior High SchoolDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Irregular VerbsДокумент2 страницыIrregular VerbsLưu Thanh TâmОценок пока нет
- CorrelationДокумент2 страницыCorrelationAudrey RoseОценок пока нет
- Manuscript SUPER FULL BLOWNДокумент29 страницManuscript SUPER FULL BLOWNDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Needs AnalysisДокумент8 страницNeeds AnalysisDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- Get more Free English LET ReviewersДокумент5 страницGet more Free English LET Reviewersjerico julatonОценок пока нет
- Prof Ed 85 ItemsДокумент6 страницProf Ed 85 ItemsDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- CorrelationДокумент2 страницыCorrelationAudrey RoseОценок пока нет
- Description On Community ImmersionДокумент3 страницыDescription On Community ImmersionDave II CosteloОценок пока нет
- De Broglie's Hypothesis: Wave-Particle DualityДокумент4 страницыDe Broglie's Hypothesis: Wave-Particle DualityAvinash Singh PatelОценок пока нет
- Assignment Chemical Bonding JH Sir-4163 PDFДокумент70 страницAssignment Chemical Bonding JH Sir-4163 PDFAkhilesh AgrawalОценок пока нет
- Pengaruh Implementasi Sistem Irigasi Big Gun Sprinkler Dan Bahan Organik Terhadap Kelengasan Tanah Dan Produksi Jagung Di Lahan KeringДокумент10 страницPengaruh Implementasi Sistem Irigasi Big Gun Sprinkler Dan Bahan Organik Terhadap Kelengasan Tanah Dan Produksi Jagung Di Lahan KeringDonny Nugroho KalbuadiОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 12Документ5 страницProblem Set 12Francis Philippe Cruzana CariñoОценок пока нет
- TemplateДокумент1 страницаTemplatemaheshqwОценок пока нет
- Bunga Refira - 1830104008 - Allophonic RulesДокумент6 страницBunga Refira - 1830104008 - Allophonic RulesBunga RefiraОценок пока нет
- Jobgpt 9d48h0joДокумент6 страницJobgpt 9d48h0jomaijel CancinesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Introduction To Management and OrganisationДокумент34 страницыChapter 1 Introduction To Management and Organisationsahil malhotraОценок пока нет
- 11 Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis Caused by Food AllergyДокумент6 страниц11 Recurrent Aphthous Stomatitis Caused by Food AllergyramaОценок пока нет
- Elderly Suicide FactsДокумент2 страницыElderly Suicide FactsThe News-HeraldОценок пока нет
- Coek - Info Anesthesia and Analgesia in ReptilesДокумент20 страницCoek - Info Anesthesia and Analgesia in ReptilesVanessa AskjОценок пока нет
- Wave Optics Part-1Документ14 страницWave Optics Part-1Acoustic GuyОценок пока нет
- Electrostatics Formulas and Numerical ProblemsДокумент11 страницElectrostatics Formulas and Numerical ProblemsManish kumar100% (2)
- Modbus Quick StartДокумент3 страницыModbus Quick StartNash JungОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Project Cost ManagementДокумент48 страницChapter 7 Project Cost Managementafifah suyadiОценок пока нет
- Ductile Brittle TransitionДокумент7 страницDuctile Brittle TransitionAndrea CalderaОценок пока нет
- Placebo Studies Ritual TheoryДокумент10 страницPlacebo Studies Ritual Theoryapi-443830029Оценок пока нет
- Human Performance and LimitationsДокумент243 страницыHuman Performance and LimitationsListiyani Ismail100% (2)
- Evidence Law PDFДокумент15 страницEvidence Law PDFwanborОценок пока нет
- ATS - Contextual Theology SyllabusДокумент4 страницыATS - Contextual Theology SyllabusAts ConnectОценок пока нет
- Personal Branding dan Positioning Mempengaruhi Perilaku Pemilih di Kabupaten Bone BolangoДокумент17 страницPersonal Branding dan Positioning Mempengaruhi Perilaku Pemilih di Kabupaten Bone BolangoMuhammad Irfan BasriОценок пока нет
- Miranda V AgДокумент3 страницыMiranda V AgCARLO JOSE BACTOLОценок пока нет
- Jaimini Astrology - Calculation of Mandook Dasha With A Case StudyДокумент6 страницJaimini Astrology - Calculation of Mandook Dasha With A Case StudyANTHONY WRITER100% (3)
- 056 Set 1 C ChemistryДокумент16 страниц056 Set 1 C ChemistryEepen JohnОценок пока нет
- Development of Branchial ArchesДокумент4 страницыDevelopment of Branchial ArchesFidz LiankoОценок пока нет
- Report of Physical ExaminationДокумент6 страницReport of Physical ExaminationJerome Paul De VeneciaОценок пока нет