Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
To Describe and Demonstrate The Operation of An FSK Modem 2. To Describe and Demonstrate The Operation of A Two-Phase DPSK and A Dibit DPSK Modem
Загружено:
Athalia GalangОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
To Describe and Demonstrate The Operation of An FSK Modem 2. To Describe and Demonstrate The Operation of A Two-Phase DPSK and A Dibit DPSK Modem
Загружено:
Athalia GalangАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
OBJECTIVES
1. To describe and demonstrate the operation of an FSK modem
2. To describe and demonstrate the operation of a two-phase DPSK and a dibit DPSK modem
CONCLUSION
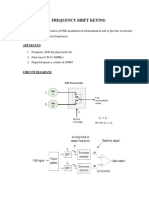
In the transmit section of an FSK Modem, digital signals from DTE enters the TXD (Transmit
Data) input and will be modulated in the FSK MODULATOR. The modulated signal is filtered
for transmission using TRANSMIT FILTER and exits from the ATO (Analog Transmit Output).
On the other hand, the bit clock signal from the DTE is applied to the TRANSMIT DPLL to
synchronize with the internal transmit clock .
In the receive section of the FSK Modem, the analog input enters the RAI (Receive Analog Input)
and will be filtered using the RECEIVE FILTER. The RFO (Receive Filter Output) will be
combined with the RDI (Receive Demodulator Input). The result will be amplified and
demodulated. Lastly, the signal will be produced from the RXD (Receive Data) pin. If a carrier
signal is detected from the RAI, the CARRIER DETECTION will output a logic 1 to the DCD
(Data Carrier Detect).
The RCLK is derived by the clock recovery from the RDI. Since FSK only uses
ASYNCHRONOUS Detection, RCLK frequency is 16 times the bit rate.
CONTROL and MODE SELECTION circuitry uses four switches as an external inputs (CM 4,
19, 18 and 17) to configure the modem.
In two-phase DPSK, phase is measured in two bit successive bit times to determine the phase
change.
In dibit DPSK, twice as many bits are transmitted in the same period so, baud rate is twice the bit
rate.
In the transmit section of an DPSK Modem, data from DTE enters the TXD input and transport to
asynchronous-to-synchronous converter. The output will then drive the scrambler, which
produces a continuously changing bit pattern if the input is continuous strings of ones or zeroes.
This scramble can be enabled or disabled (wherein signals are bypassed) using SEI (Scrambler
Enable Input). Then, signals will be modulated in the dibit DPSK modulator then filtered for
transmission using transmit filter and exits from the ATO.
In the receive section of the DPSK Modem, the analog input enters the RAI. It will be filtered
using the receive filter and output to RFO. The output will combine with the RDI and will be
amplified. The receiver decoder output will be descrambled if SEI is enabled and lastly, signal
will drive the synchronous-to-asynchronous converter and produced from the RXD pin. If SEI is
disabled, the receiver decoder output will be directed to TEST pin. Then, if a carrier signal is
detected from the RAI, the carrier detection will output a logic 1 to the DCD (Data Carrier
Detect).
Вам также может понравиться
- Generation and Detection of DPSKДокумент3 страницыGeneration and Detection of DPSKAmy OliverОценок пока нет
- Non-Linearities in Passive RFID Systems: Third Harmonic Concept and ApplicationsОт EverandNon-Linearities in Passive RFID Systems: Third Harmonic Concept and ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Generation and Detection of DPSKДокумент3 страницыGeneration and Detection of DPSKAmy OliverОценок пока нет
- Differential Phase Shift KeyingДокумент7 страницDifferential Phase Shift Keyingtaherakhans100% (1)
- Surya - First PhasereportДокумент10 страницSurya - First PhasereportSuribabuIppiliОценок пока нет
- Differential Phase Shift Keying Modulation and DemodulationДокумент9 страницDifferential Phase Shift Keying Modulation and DemodulationananthaprathimaОценок пока нет
- ATSC 8-VSB Demodulator and Decoder TDA8960: Philips Semiconductors Preliminary SpecificationДокумент2 страницыATSC 8-VSB Demodulator and Decoder TDA8960: Philips Semiconductors Preliminary SpecificationabbasdfОценок пока нет
- RFID Reader BasicsДокумент3 страницыRFID Reader BasicsP.h. ModiОценок пока нет
- DsPIC SW Receiver Rev1.1Документ7 страницDsPIC SW Receiver Rev1.1ngt881Оценок пока нет
- DC Manual Final PDFДокумент25 страницDC Manual Final PDFAsma FirdouseОценок пока нет
- 15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsДокумент28 страниц15EC306J Cycle 2 ExptsSanjeev KumarОценок пока нет
- II IP Core PSK DemodulatorДокумент5 страницII IP Core PSK DemodulatorfvseverОценок пока нет
- STM32 ADC Tutorial Complete Guide With ExamplesДокумент18 страницSTM32 ADC Tutorial Complete Guide With Examplessuper_faca100% (1)
- PC Controll Wireless Robot Using RF ModuleДокумент53 страницыPC Controll Wireless Robot Using RF ModuleanilОценок пока нет
- DSP Blocks InterfacingДокумент30 страницDSP Blocks Interfacingdolly aryaОценок пока нет
- RF Based Automatic Speed Limiter For VehiclesДокумент35 страницRF Based Automatic Speed Limiter For Vehiclesv3rajasekarОценок пока нет
- File 1406270302Документ25 страницFile 1406270302rupeshОценок пока нет
- Software Design of Digital Receiver Using FPGAДокумент5 страницSoftware Design of Digital Receiver Using FPGAAnonymous kw8Yrp0R5rОценок пока нет
- WarField Land Rover That Alerts On Sensing Panted Land MinesДокумент32 страницыWarField Land Rover That Alerts On Sensing Panted Land MinesPavan KPОценок пока нет
- Data Conditioning & Carrier Modulation Transmitter & Data Reconditioning & Carrier Demodulation ReceiverДокумент49 страницData Conditioning & Carrier Modulation Transmitter & Data Reconditioning & Carrier Demodulation ReceiverCauVong JustinОценок пока нет
- Experiment 08 Interfacing Codec TLV320AIC23, and Use of DAC and ADCДокумент6 страницExperiment 08 Interfacing Codec TLV320AIC23, and Use of DAC and ADCOmar JanjuaОценок пока нет
- PSKДокумент4 страницыPSKTushar PatilОценок пока нет
- Metal Detector Robotic Vehicle: Submitted byДокумент25 страницMetal Detector Robotic Vehicle: Submitted byDarshan ParmarОценок пока нет
- UNIT VI - Uart - Adc - SpiДокумент55 страницUNIT VI - Uart - Adc - SpiShubham MadneОценок пока нет
- UG - EC303 DSP Part-6 On-Chip Peripherals-Print PDFДокумент20 страницUG - EC303 DSP Part-6 On-Chip Peripherals-Print PDFapuurvaОценок пока нет
- Digital Communications Lab: List of ExperimentsДокумент50 страницDigital Communications Lab: List of ExperimentsNeel SarkarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Part1 PDFДокумент81 страницаChapter 2 Part1 PDFKrishna ChaitanyaОценок пока нет
- DTT Principles: N. Jethi, Dir (E) DDK, BhubaneswarДокумент34 страницыDTT Principles: N. Jethi, Dir (E) DDK, BhubaneswarShishir GuptaОценок пока нет
- Bapatla Engineering College Digital Communications Lab EC-451Документ30 страницBapatla Engineering College Digital Communications Lab EC-451nithyamnvОценок пока нет
- Single-Chip Modem Provides Low-Cost Data Communication: National Semiconductor Application Note 444 Wesley Lee July 1986Документ16 страницSingle-Chip Modem Provides Low-Cost Data Communication: National Semiconductor Application Note 444 Wesley Lee July 1986Luis CarlosОценок пока нет
- RAKE Receiver: Wireless Information Transmission System LabДокумент62 страницыRAKE Receiver: Wireless Information Transmission System Labmitso123Оценок пока нет
- 73K324L CCITT V.22bis, V.22, V.21, V.23, Bell 212A Single-Chip ModemДокумент32 страницы73K324L CCITT V.22bis, V.22, V.21, V.23, Bell 212A Single-Chip ModemRicardo MercadoОценок пока нет
- Phase Shift Keying: Exp - No:01Документ74 страницыPhase Shift Keying: Exp - No:01Sumit PatilОценок пока нет
- Rfid Interface TO 8051: Deepak GuptaДокумент4 страницыRfid Interface TO 8051: Deepak Guptamohitdaya14Оценок пока нет
- RF Based Wireless RemoteДокумент10 страницRF Based Wireless Remotetejasmodi21Оценок пока нет
- Unit 8 VTU Format PDFДокумент18 страницUnit 8 VTU Format PDFammayi9845_930467904Оценок пока нет
- Communication Systems Ii - LabmanualДокумент12 страницCommunication Systems Ii - LabmanualpramodОценок пока нет
- Automated Line FollowingДокумент8 страницAutomated Line FollowingManoj KumarОценок пока нет
- 2 FSKДокумент5 страниц2 FSKPranavОценок пока нет
- GPS U4Документ8 страницGPS U4espectra2k23Оценок пока нет
- DP8390 PDFДокумент57 страницDP8390 PDFJorBS57Оценок пока нет
- Circuit Diagram Wireless TransmitterДокумент17 страницCircuit Diagram Wireless Transmitterumaiya1990100% (2)
- Data Communication Assignment 1Документ4 страницыData Communication Assignment 1Ken MathewsОценок пока нет
- SPI Pins SPI Clock SPI Master Slave Connection SPI Registers DAC SpecificationsДокумент7 страницSPI Pins SPI Clock SPI Master Slave Connection SPI Registers DAC Specificationspiyushpandey100% (1)
- Wireless Communication-Digital Signaling For Fading ChannelsДокумент25 страницWireless Communication-Digital Signaling For Fading ChannelsPREMALATHA GOVINDОценок пока нет
- Design and Implement of QPSK Modem Based On FPGAДокумент3 страницыDesign and Implement of QPSK Modem Based On FPGAAnil PatilОценок пока нет
- VLSI Implementation OfdmДокумент40 страницVLSI Implementation Ofdmmanasverma21270% (1)
- A Novel FPGA-based LVDT Signal Conditioner: Kumardeb Banerjee, Bivas Dam, Kalyan MajumdarДокумент6 страницA Novel FPGA-based LVDT Signal Conditioner: Kumardeb Banerjee, Bivas Dam, Kalyan MajumdarnarayanОценок пока нет
- The Design and Construction of A DDS Based Waveform GeneratorДокумент12 страницThe Design and Construction of A DDS Based Waveform GeneratorWilson Fernando Rodríguez RodríguezОценок пока нет
- FPGA-based Implementation of Efficient Sample Rate Conversion For Software Defined RadiosДокумент5 страницFPGA-based Implementation of Efficient Sample Rate Conversion For Software Defined RadiosNitin MathurОценок пока нет
- Project of OFDM TransceiverДокумент4 страницыProject of OFDM TransceiverpratiksonuОценок пока нет
- Features Description: CMOS Manchester Encoder-DecoderДокумент14 страницFeatures Description: CMOS Manchester Encoder-DecoderKaty KimberlynОценок пока нет
- RPM Measurement (Tachometer)Документ10 страницRPM Measurement (Tachometer)19E45A0229 SDESEEEОценок пока нет
- Experiment No.5, Simulation of DPSK Aim: To Plot The Bit Error Rate (BER) of Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) Signal Using OCTAVEДокумент5 страницExperiment No.5, Simulation of DPSK Aim: To Plot The Bit Error Rate (BER) of Differential Phase Shift Keying (DPSK) Signal Using OCTAVEvanitha100% (2)
- Ijett V4i9p160Документ5 страницIjett V4i9p160kuzhaloliОценок пока нет
- Practical Session V: FSK Transceiver.: Laboratory of Electronic CommunicationsДокумент11 страницPractical Session V: FSK Transceiver.: Laboratory of Electronic CommunicationsAna Ort GОценок пока нет
- DP8390D/NS32490D NIC Network Interface Controller: General DescriptionДокумент55 страницDP8390D/NS32490D NIC Network Interface Controller: General DescriptionRaja MustafaОценок пока нет
- DP8390D Nic PDFДокумент56 страницDP8390D Nic PDFyairmtzОценок пока нет
- Brocade Compatibility Matrix Fos 7x MX PDFДокумент34 страницыBrocade Compatibility Matrix Fos 7x MX PDFbalaage2s5Оценок пока нет
- SSA TrainingДокумент48 страницSSA TrainingStats TutorОценок пока нет
- (PPT) Digital Electronics 2 For StudentsДокумент6 страниц(PPT) Digital Electronics 2 For StudentsJONNA ACABOОценок пока нет
- I Need Free Serial Key of Acrobat Xi Pro - FixyaДокумент3 страницыI Need Free Serial Key of Acrobat Xi Pro - FixyaRamesh Gowda33% (3)
- Computer and Network Security: Dan Boneh and John MitchellДокумент60 страницComputer and Network Security: Dan Boneh and John Mitchell19001015049 ROHITОценок пока нет
- Lab5 AnswerSheetДокумент3 страницыLab5 AnswerSheetnislam57Оценок пока нет
- CV-Sushil GuptaДокумент3 страницыCV-Sushil Guptaanurag_bahety6067Оценок пока нет
- Book PDF Reliability Maintainability and Risk Practical Methods For Engineers PDF Full ChapterДокумент18 страницBook PDF Reliability Maintainability and Risk Practical Methods For Engineers PDF Full Chaptermary.turner669100% (8)
- FINALEXAM-IN-MIL Doc BakДокумент4 страницыFINALEXAM-IN-MIL Doc BakObaidie M. Alawi100% (1)
- CIS201 Chapter 1 Test Review: Indicate Whether The Statement Is True or FalseДокумент5 страницCIS201 Chapter 1 Test Review: Indicate Whether The Statement Is True or FalseBrian GeneralОценок пока нет
- Visual Basic TipsДокумент21 страницаVisual Basic TipsbenoycОценок пока нет
- ASAP RoadmapДокумент2 страницыASAP RoadmapprakashssapОценок пока нет
- RS232STATUSMONДокумент1 страницаRS232STATUSMONashish.boradОценок пока нет
- A New Method For Encryption Using Fuzzy Set TheoryДокумент7 страницA New Method For Encryption Using Fuzzy Set TheoryAgus S'toОценок пока нет
- Field Visit PresentationДокумент33 страницыField Visit PresentationNib IndranilОценок пока нет
- Projects BCA MCAДокумент2 страницыProjects BCA MCAManojОценок пока нет
- RobotStudio Simulation of Industrial PDFДокумент140 страницRobotStudio Simulation of Industrial PDFcabecavil100% (1)
- BCI ICT ResilienceДокумент57 страницBCI ICT ResilienceOana DragusinОценок пока нет
- A Microsoft Teams OutlineДокумент2 страницыA Microsoft Teams OutlineMaheswaren MahesОценок пока нет
- Numerical Solution For Nonlinear MHD Jeffery-Hamel Blood Flow Problem Through Neural Networks Optimized TechniquesДокумент11 страницNumerical Solution For Nonlinear MHD Jeffery-Hamel Blood Flow Problem Through Neural Networks Optimized TechniquesMuhammad Imran KhanОценок пока нет
- Lab 1Документ8 страницLab 1Masud SarkerОценок пока нет
- Codesys Professional Developer Edition: Professional Add-On Tools For The IEC 61131-3 Development SystemДокумент3 страницыCodesys Professional Developer Edition: Professional Add-On Tools For The IEC 61131-3 Development SystemPauloRpindaОценок пока нет
- Huawei AC6805 Wireless Access Controller Datasheet - 2Документ16 страницHuawei AC6805 Wireless Access Controller Datasheet - 2irfanОценок пока нет
- IEEE Authorship WebinarДокумент1 страницаIEEE Authorship WebinarAnonymous PxkbBVwОценок пока нет
- Mobile Assisted Language Learning (MALL) Describes An Approach To Language LearningДокумент7 страницMobile Assisted Language Learning (MALL) Describes An Approach To Language Learninggusria ningsihОценок пока нет
- Hamidavi Et Al 2020 - Towards Intelligent Structural Design of Buildings AДокумент15 страницHamidavi Et Al 2020 - Towards Intelligent Structural Design of Buildings ARober Waldir Quispe UlloaОценок пока нет
- sjzl20070793-NetNumen M3 (ZXC10 BSSB) (V 3.08.19.01) Software Installation Manual (Windows) PDFДокумент243 страницыsjzl20070793-NetNumen M3 (ZXC10 BSSB) (V 3.08.19.01) Software Installation Manual (Windows) PDFGus RodriguezОценок пока нет
- CS201 Introduction To Programming Solved MID Term Paper 03Документ4 страницыCS201 Introduction To Programming Solved MID Term Paper 03ayesharahimОценок пока нет
- Lea Dardanos Efi-Controller eДокумент6 страницLea Dardanos Efi-Controller eadfumegaОценок пока нет
- Barneys Dream Cruise WalkthroughДокумент3 страницыBarneys Dream Cruise WalkthroughnoelzizonОценок пока нет