Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Basements For Housing
Загружено:
Bunkun15Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Basements For Housing
Загружено:
Bunkun15Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Basements for housing
Including a basement in residential developments helps maximises usage of available land,
o ers added value, more space and accommodation with additional performance bene ts.
Refurbishment or alterations to existing spaces below ground are also an e ective way of
providing additional habitable space to a property. It is possible to retro t a basement under or
adjacent to an existing property.
A basement storey is de ned within the Building Regulations of England and Wales as at least
1.2m below adjoining ground level.
Bene ts of domestic basements include:
Added value.
Additional habitable or useful space.
Increased oor area in locations with limited development potential above ground.
Creation of exible, adaptable space, due to creation of single span structure.
Spaces with extra sound insulation, expanding range of potential use, including home
working.
Spaces with good thermal mass and potential energy e ciency and cooling.
Good stable structural base, capable of supporting heavy loads above.
Resilience to climate change e ects in the soil, such as shrinkage or tree roots.
Flood resilience solution, by raising habitable spaces above ood level while providing
useful non-habitable storage space below.
Basement design
The appropriate design of basements is well established and achievable providing design and
construction guidance is implemented.
Basement design process simpli ed:
1. Establish current and anticipated future use of basement.
2. Site survey and exploratory works.
3. Design proposals to de ne type of construction water tight class and thermal
performance.
4. Detailed structural design integrated with design of waterproo ng.
Aspects of the design process are interrelated and a uni ed approach should be established
de ning roles and responsibilities of the design team. It is advisable to avoid complex
geometries to facilitate waterproo ng and to produce a three dimensional review of structure
and waterproo ng.
Basement construction
Concrete is the most common and appropriate material used in the construction of new
basement walls and oors. This is due in part to cost and availability but also its adaptability,
inherent resistance to water, durability underground and ability to provide a stable structural
surface for the support of waterproo ng membranes. Options include masonry or blockwork,
cast insitu, precast concrete, twinwall and insulating concrete formwork (ICF)
The method of concrete construction chosen will be in uenced by the type of waterproo ng
protection permitted according to the water table situation and proposed basement use as
described in BS8102 Code of Practice for the protection of below ground structures against
water from the ground.
For urther guidance on the bene ts of basements for housing and principles of construction
and design refer to Basements for Housing.
The publication ‘Concrete Basements: Guidance on the design and construction of in-situ
concrete basement structures’ provides comprehensive guidance on the design issues for the
design of deep basements, focusing on structural calculations.
Other useful resources:
The Basement Information Centre
Вам также может понравиться
- Performance Handbook Bell EquipmentДокумент142 страницыPerformance Handbook Bell EquipmentStefan TrollipОценок пока нет
- Earth Shelter: Traditional TechniqueДокумент20 страницEarth Shelter: Traditional TechniqueshrutiОценок пока нет
- How To Construct A Concrete Swimming Pool - (PDF) - The ConstructorДокумент13 страницHow To Construct A Concrete Swimming Pool - (PDF) - The ConstructorBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Building Envelope Design PrinciplesДокумент7 страницBuilding Envelope Design PrinciplesDezyne EcoleОценок пока нет
- Sto Design Considerations BrochureДокумент60 страницSto Design Considerations BrochureSam UriarteОценок пока нет
- Basements and Retaining WallДокумент49 страницBasements and Retaining WallSakshi Rawat100% (1)
- Deep Basements & Cut & Cover - 2Документ113 страницDeep Basements & Cut & Cover - 2bsitler100% (2)
- Concrete Centre Basements For HousingДокумент24 страницыConcrete Centre Basements For HousingFree_Beating_Heart100% (1)
- ETABS End OffsetДокумент2 страницыETABS End OffsetBunkun1567% (3)
- In Construction: Waterproofing Is The Process of Making An Object or Structure Waterproof or Water-Resistant SoДокумент63 страницыIn Construction: Waterproofing Is The Process of Making An Object or Structure Waterproof or Water-Resistant SoSuhaimi BohariОценок пока нет
- Cast in Place Concrete StructuresДокумент17 страницCast in Place Concrete Structuresmusiomi2005Оценок пока нет
- Insulating Flat RoofsДокумент30 страницInsulating Flat RoofsgencmetohuОценок пока нет
- Title - Section 6-1.29 - Swimming Pool Design Standards - New York Codes, Rules and RegulationsДокумент24 страницыTitle - Section 6-1.29 - Swimming Pool Design Standards - New York Codes, Rules and RegulationsBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Hemcrete, Biobric & Poroton: Sustainable & Solidwall Systems With Ecological MaterialsДокумент18 страницHemcrete, Biobric & Poroton: Sustainable & Solidwall Systems With Ecological MaterialsLucien SteilОценок пока нет
- Earth Shelter: Traditional TechniqueДокумент20 страницEarth Shelter: Traditional TechniqueshrutiОценок пока нет
- Starting A Bookstore BusinessДокумент11 страницStarting A Bookstore BusinessBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- How To Start A Bookstore BusinessДокумент5 страницHow To Start A Bookstore BusinessBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Brick CalculationsДокумент13 страницBrick CalculationsMirza Mustansir BaigОценок пока нет
- Stages For Construction: Retaining WallДокумент37 страницStages For Construction: Retaining WallIkhwan HasiffОценок пока нет
- IRSE Green BookДокумент2 страницыIRSE Green BookBunkun150% (1)
- Interlocking Compacted Earth Blocks (ICEB)Документ9 страницInterlocking Compacted Earth Blocks (ICEB)Zarah Ramirez100% (2)
- TCS-Q-113.01 (Rev 01) -沥青混凝土路面Документ41 страницаTCS-Q-113.01 (Rev 01) -沥青混凝土路面heng liu100% (1)
- Energy Efficiency and Historic Buildings: Insulating Solid Ground FloorsДокумент19 страницEnergy Efficiency and Historic Buildings: Insulating Solid Ground FloorsAnonymous lMTMFfmPlОценок пока нет
- Basement Study MaterialДокумент19 страницBasement Study MaterialParitosh JambhaleОценок пока нет
- IKO BUFR Design Guide Feb 2012Документ40 страницIKO BUFR Design Guide Feb 2012Deana WhiteОценок пока нет
- Concrete Masonry HousingДокумент12 страницConcrete Masonry HousingRoscii RulezОценок пока нет
- Guidance Document - Podium Decks & Buried Roofs: March 2017Документ8 страницGuidance Document - Podium Decks & Buried Roofs: March 2017fatimaОценок пока нет
- Cellular Light Weight Concrete PresentationДокумент20 страницCellular Light Weight Concrete PresentationPrince Kumar0% (1)
- 1 s2.0 S0360132322006266 MainДокумент20 страниц1 s2.0 S0360132322006266 MainSANTIAGOОценок пока нет
- Rehabilitation and The Building Enclosure: National Research Conseil Nationat Council Canada de Recherches CanadaДокумент8 страницRehabilitation and The Building Enclosure: National Research Conseil Nationat Council Canada de Recherches CanadasagarsunkaraОценок пока нет
- Lecture Notes 7Документ11 страницLecture Notes 7AMESHAОценок пока нет
- Masonry Failures: Neil R. Baer, P.EДокумент8 страницMasonry Failures: Neil R. Baer, P.EVenkatesh ArunaОценок пока нет
- Construction Technology AssignementДокумент17 страницConstruction Technology AssignementJibu KavugheОценок пока нет
- Slabs and Types: Post Tensioning - BenefitsДокумент4 страницыSlabs and Types: Post Tensioning - BenefitsRohit WhavalОценок пока нет
- Building Construction-Short NotesДокумент4 страницыBuilding Construction-Short NotesJeedaran Arshaad100% (1)
- 1-3 Ass PDFДокумент8 страниц1-3 Ass PDFfikru derejeОценок пока нет
- Exterior Wall Solutions For Hot Humid Climates PDFДокумент12 страницExterior Wall Solutions For Hot Humid Climates PDFBogdan MucenicaОценок пока нет
- What Is Construction SystemДокумент36 страницWhat Is Construction SystemHiro KiritoОценок пока нет
- Concrete Slab Floors: The Benefits of Concrete SlabsДокумент4 страницыConcrete Slab Floors: The Benefits of Concrete SlabsAdewale Adefemi JonathanОценок пока нет
- Insulating Solid Ground FloorsДокумент22 страницыInsulating Solid Ground FloorsgencmetohuОценок пока нет
- AДокумент2 страницыAathavanОценок пока нет
- Earth Sheltered BuildingДокумент7 страницEarth Sheltered BuildingDanut CalugarОценок пока нет
- Ea 75161Документ10 страницEa 75161Designs and Beyond BuildersОценок пока нет
- Civil Assignment ConceteДокумент9 страницCivil Assignment ConceteRaj KumarОценок пока нет
- Cooling Tower FundamentalsДокумент117 страницCooling Tower FundamentalsСергій ГейкоОценок пока нет
- AR213 ASSIGNMENT 1, Enersto NelsonДокумент47 страницAR213 ASSIGNMENT 1, Enersto Nelsonnelsonenersto99Оценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Resilient SystemsДокумент4 страницыCharacteristics of Resilient Systemsarkitektura489Оценок пока нет
- CEC 105 TheoryДокумент182 страницыCEC 105 TheorySamuel OladegaОценок пока нет
- Retaining Walls and Road PavementДокумент14 страницRetaining Walls and Road PavementPraise SamuelОценок пока нет
- Insulating Solid WallsДокумент25 страницInsulating Solid WallsCristina VoicuОценок пока нет
- RETROFITДокумент20 страницRETROFITShamsiya KhalidОценок пока нет
- Tropical ClimateДокумент15 страницTropical ClimatesabkebernОценок пока нет
- Module - 5 Special ConcreteДокумент9 страницModule - 5 Special ConcreteRavi TilaganjiОценок пока нет
- LANDSCAPE DESIGN STRUCTURES From Time-Saver Standards For Landscape Architecture BookДокумент142 страницыLANDSCAPE DESIGN STRUCTURES From Time-Saver Standards For Landscape Architecture Book10ahmedmazumderОценок пока нет
- Reinforced Ultra-Lightweight Cement Composite Flat Slabs: Experiments and AnalysisДокумент23 страницыReinforced Ultra-Lightweight Cement Composite Flat Slabs: Experiments and AnalysisNI KH ILОценок пока нет
- ARCHITECTURAL DESIGN RESEACH - Primary SchoolДокумент11 страницARCHITECTURAL DESIGN RESEACH - Primary SchoolElisha BautistaОценок пока нет
- Project WritingДокумент18 страницProject WritingMARSYA HANIS BINTI MOHAMAD AYOFОценок пока нет
- Retaining Wall BayuДокумент5 страницRetaining Wall BayurionovОценок пока нет
- Study On Strength and Durability Charactestics of Light Weight Aggregate ConcreteДокумент111 страницStudy On Strength and Durability Charactestics of Light Weight Aggregate ConcreteKashyap ChintuОценок пока нет
- Masonry Structures LectureДокумент10 страницMasonry Structures LecturemikramОценок пока нет
- A Sustainable Design For An Off-Grid Passive ContaДокумент8 страницA Sustainable Design For An Off-Grid Passive ContaVasilica SerbanОценок пока нет
- Retrofitting Guideline - Tamilnadu Final Compressed New-1Документ7 страницRetrofitting Guideline - Tamilnadu Final Compressed New-1mrramaОценок пока нет
- Chapter-5.2 Floor SystemДокумент68 страницChapter-5.2 Floor SystemFikaduKitessa67% (3)
- DeGroot Construction DetailsДокумент3 страницыDeGroot Construction DetailsSriramaBejadiОценок пока нет
- WALL CONSTRUCTION NotesДокумент5 страницWALL CONSTRUCTION NotesStephen MwangiОценок пока нет
- DCR BMP Spec No 5 Vegetated Roof Final Draft v2!3!03012011Документ17 страницDCR BMP Spec No 5 Vegetated Roof Final Draft v2!3!03012011Mark GoducoОценок пока нет
- RIE BUILDING TECH PresentationДокумент27 страницRIE BUILDING TECH PresentationBori GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Geotechnical Application of Soil MechanicsДокумент10 страницGeotechnical Application of Soil MechanicsHi HiОценок пока нет
- Sustainable Renovation: Strategies for Commercial Building Systems and EnvelopeОт EverandSustainable Renovation: Strategies for Commercial Building Systems and EnvelopeОценок пока нет
- Basic Requirements in Swimming Pool Construction - The ConstructorДокумент10 страницBasic Requirements in Swimming Pool Construction - The ConstructorBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Intake Tower Existing DamДокумент3 страницыIntake Tower Existing DamBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Swimming Pool Site PlanДокумент1 страницаSwimming Pool Site PlanBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Checklist ResPoolsДокумент7 страницChecklist ResPoolsBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Swimming Pool Sample LayoutsДокумент1 страницаSwimming Pool Sample LayoutsBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Swimming Pool Roofing OptionsДокумент2 страницыSwimming Pool Roofing OptionsBunkun15100% (1)
- Swimming Pool Details Structures SampleДокумент1 страницаSwimming Pool Details Structures SampleBunkun15100% (3)
- Stable Sprayed ConcreteДокумент2 страницыStable Sprayed ConcreteBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- ETABS Insertion PointДокумент3 страницыETABS Insertion PointBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- University OrganogramДокумент1 страницаUniversity OrganogramBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- 4 Ways To Book PublishingДокумент7 страниц4 Ways To Book PublishingBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Imperial College of Business Studies Employment Application FormДокумент3 страницыImperial College of Business Studies Employment Application FormBunkun15Оценок пока нет
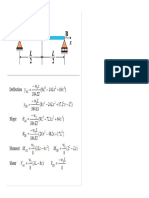
- Simple Beam Deflection - Uniform Load Partially Distributed at Left EndДокумент1 страницаSimple Beam Deflection - Uniform Load Partially Distributed at Left EndBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Imperial College: of Business StudiesДокумент1 страницаImperial College: of Business StudiesBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Live Load Distribution Factor CalculationsДокумент5 страницLive Load Distribution Factor CalculationsBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Import - SAP2000 MS Excel Spreadsheet .Xls File: New ModelДокумент1 страницаImport - SAP2000 MS Excel Spreadsheet .Xls File: New ModelBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- SAP2000 Command LineДокумент2 страницыSAP2000 Command LineBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- SAP2000 Sign CoventionДокумент5 страницSAP2000 Sign CoventionBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- ETABS Joint RestraintsДокумент2 страницыETABS Joint RestraintsBunkun15100% (3)
- ETABS Section PropДокумент1 страницаETABS Section PropBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- ETABS Property ModifierДокумент1 страницаETABS Property ModifierBunkun150% (1)
- ETABS Additional MassДокумент2 страницыETABS Additional MassBunkun15Оценок пока нет
- Caixa Modelo Bob BeeДокумент13 страницCaixa Modelo Bob BeeLair MorissonОценок пока нет
- RAMPДокумент1 страницаRAMPnanprОценок пока нет
- Highway Engineering 2Документ27 страницHighway Engineering 2Balogun IbrahimОценок пока нет
- The Whitney Museum at GansevoortДокумент116 страницThe Whitney Museum at GansevoortNgọc NguyênОценок пока нет
- Pud 21-01 Batton RV Park Staff ReportДокумент10 страницPud 21-01 Batton RV Park Staff ReportActionNewsJaxОценок пока нет
- Hicham Charkaoui .E CVДокумент2 страницыHicham Charkaoui .E CVAhmad Yani S NoorОценок пока нет
- Group Assignment On Reinforced Concrete Structures III (CEng554) ToДокумент3 страницыGroup Assignment On Reinforced Concrete Structures III (CEng554) ToMPH SGSОценок пока нет
- INFRA-TES-MST-CCC-CIV-00023 Rev. 0 - Excavation and BackfillingДокумент25 страницINFRA-TES-MST-CCC-CIV-00023 Rev. 0 - Excavation and BackfillingTaiwo OshinОценок пока нет
- Structural Design Ii Project: CIV4045FДокумент27 страницStructural Design Ii Project: CIV4045FMark JacobsОценок пока нет
- SIA Scope of Service Matrix-20180814-For WebsiteДокумент2 страницыSIA Scope of Service Matrix-20180814-For Websitesteven ZhaoОценок пока нет
- Baupanel Application Standard Seismic-Resistant ConstructionДокумент11 страницBaupanel Application Standard Seismic-Resistant Constructionİhsan TazeОценок пока нет
- Canal Brochure Reduced SizeДокумент28 страницCanal Brochure Reduced SizeVaibhav NautiyalОценок пока нет
- GL 15 Air ReceiversДокумент1 страницаGL 15 Air Receiverstp101267Оценок пока нет
- S2214785323044796 MainДокумент10 страницS2214785323044796 MainVincent P. PilienОценок пока нет
- PCPL - Pre. Cast ParabolicДокумент6 страницPCPL - Pre. Cast ParabolicMohammedОценок пока нет
- Major Project On Concrete RoadДокумент42 страницыMajor Project On Concrete Roadlalit gaurОценок пока нет
- Construction of Museum For The Buddhist Monastery at Jagjibanpur, Malda Under Malda Division, PWD During The Year 2018-19 (Balance Work)Документ5 страницConstruction of Museum For The Buddhist Monastery at Jagjibanpur, Malda Under Malda Division, PWD During The Year 2018-19 (Balance Work)matiur rahamanОценок пока нет
- Planned and Built Cities: Tel Aviv (Israel)Документ11 страницPlanned and Built Cities: Tel Aviv (Israel)Amrutha Pavithran100% (1)
- Brutalistic Architecture A RetrospectДокумент14 страницBrutalistic Architecture A RetrospectKathiresan ManoharanОценок пока нет
- Contract Doc AnalysisДокумент47 страницContract Doc AnalysisHazirah ZieraОценок пока нет
- AcousticДокумент10 страницAcousticKurnianda Dian WulandariОценок пока нет
- Hitachi Zaxis 210 F RP.: 700.000.000 NegoДокумент3 страницыHitachi Zaxis 210 F RP.: 700.000.000 Negoho gataОценок пока нет
- AC Purchase and Installation Living RoomДокумент4 страницыAC Purchase and Installation Living Roomps1amsОценок пока нет
- 3TEMPORARY STRUCTURE Fall Protection Working at HeightsДокумент85 страниц3TEMPORARY STRUCTURE Fall Protection Working at HeightsEunice GayetaОценок пока нет
- Gambar Kerja PondasiДокумент8 страницGambar Kerja PondasixcfОценок пока нет
- Ram Internship ReportДокумент65 страницRam Internship Report20135A0120 PINNIKA RAMESHОценок пока нет
- 8491-Article Text-32930-1-10-20151225 PDFДокумент7 страниц8491-Article Text-32930-1-10-20151225 PDFChetali SinghОценок пока нет