Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Assignment 0910 Spring Set2
Загружено:
Sarp Yiğit ŞirinОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Assignment 0910 Spring Set2
Загружено:
Sarp Yiğit ŞirinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
CE222 Spring 2009-2010
Assignment #2
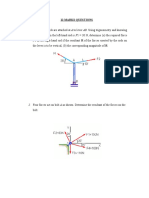
Q1. The motor M pulls in its attached rope causing
an acceleration of 6 m/s2 . Determine this towing force. The
coefficient of kinetic friction between the 50-kg crate and the
plane is µk=0.3. Neglect the mass of the pulleys and rope.
Q5The van is traveling at 20 km/h when the coupling of the
trailer at A fails. If the trailer has a mass of 250 kg and coasts
45 m before coming to rest, determine the constant horizontal
Q2. If a horizontal force of P=10 N is applied to block A,
force F created by rolling friction which causes the trailer to
determine the acceleration of block B. Neglect friction.
stop.
Hint: Show that aB=aA tan 15º.
Q6. A girl having a mass of 15 kg, sits motionless relative to
the surface of a horizontal platform at a distance of r = 5 m
from the platform’s center. If the angular motion of the
platform is slowly increased so that the girl’s tangential
component of acceleration can be neglected, determine the
maximum speed which the girl will have before she begins to
Q3. Block A has a mass of 10 kg and is hoisted using the rope- slip off the platform. The coefficient of static friction between
and-pulley system shown. If the collar is moving to the right at the girl and the platform is µk=0.2.
10 m/s and has a deceleration of 5 m/s2 at the instant shown, b) Solve the same problem by assuming that the platform starts
determine the tension in the cable connected to the collar at this rotating from rest so that the girl’s speed is increased uniformly
instant. at v̊ = 0.5 m/ s2 .
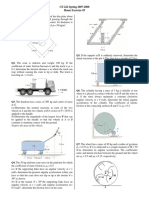
Q4. The 800-kg car at B is connected to the 350-kg car at A by
a spring coupling. Determine the stretch in the spring if
a) the wheels of both cars are free to roll, Q7. The 6-kg block is confined to move along the smooth
b) car B applies brakes to all four wheels. parabolic path. The attached spring restricts the motion and,
Take µB=0.4. Neglect the mass of the wheels. due to the roller guide, always remains horizontal as the block
descends. If the spring has a stiffness of k=10 N/m and an
unstretched length of 0.5 m, determine the normal force of the
path of the block and the instant x=1 m and the block has a
2
speed of 4 m/s. Also what is the rate of increase in speed of the
block at this point?
Neglect the mass of the roller guide and the spring.
Q10. The 0.5-kg ball of negligible size is fired up the vertical
circular track using the spring plunger. The plunger keeps the
spring compressed 0.08 m when s=0. Determine how far s it
must be pulled back and released so that the ball will just make
it around the loop and land on the platform at B. What is the
ball’s speed when it reaches the platform?
b) Determine how far s it must be pulled back and released so
Q8. The 6000-N (~600-kg) “wrecking ball”, suspended from a that the ball begins to leave the track when θ=135°.
15-m chain, swings from rest at point A, θ=30°, toward a wall.
After striking the wall it rises to point B, φ=20°. Determine the
amount of energy which is lost during the collision and
compute the tension in the chain just before the collision, θ=0°.
Neglect the size of the ball for the calculation. Point C does not
move, and when θ=0° the ball is at its lowest point.
Q11. The 50-N (=5-kg) crate is hoisted by the motor M. If the
crate starts from rest and by constant acceleration attains a
speed of 12 m/s after rising s=10m, determine the power that
must be supplied to the motor at the instant s=10m. The motor
has an efficiency ε=0.65. Neglect the mass of the pulley and
cable.
Q9. The 1-kg brick slides down a smooth roof, such that when
it is at A it has a velocity of 1.5 m/s. Determine the speed of the
block just before it leaves the surface at B, the distance d from
the wall to where it strikes the ground, and the speed at which it
hits the ground.
3
Q12. The 100-N (=10-kg) collar starts from rest at A and is
lifted by applying a constant force of F=250 N to the cord. If
the rod is smooth, determine the power developed by the force
at the instant θ=60°.
Q16. Determine the velocity of the 20-kg block A after it is
released from rest and moves 2 m down the plane. Block B has
a mass of 10 kg and the coefficient of kinetic friction between
the plane and block A is µk = 0.2. Also, what is the tension in
the cord?
Q13. If the1-kg smooth collar is given a velocity of 1.8 m/s to
the right when s=0.9m, determine the maximum distance,
s=smax, the collar travels before momentarily stopping. The
spring has an unstrecthed length of 0.6m.
Q17. Determine the height h to the top of the incline D to
which the 200-kg roller coaster car will reach, if it is launched
at B with a speed just sufficient for it to round the top of the
loop at C without leaving the track. The radius of curvature at C
is ρc = 25 m.
Q14. The car and its contents have a weight of 600kg, whereas
block B has a weight of 200kg. If the car is released from rest,
determine its speed when it travels 30m down the 20° incline.
Suggestion: To measure the gravitational potential energy, Q18. The girl throws the 0.5 kg ball toward the wall with an
establish separate datum at the initial elevations of B and C. initial velocity vA = 10 m/s. Determine
a) the velocity at which it strikes the wall at B.
b) the velocity at which it rebounds from the wall if e=0.5
c)the distances from the wall to where it strikes the ground at C.
Q15. The 2-kg ball of negligible size is fired from point A with
an initial velocity of 10 m/s up the smooth inclined plane.
Determine the distance from point C to where it hits the
horizontal surface at D. Also, what is its velocity when it strikes
the surface?
Вам также может понравиться
- Strength of MatrialДокумент36 страницStrength of MatrialahmedanyОценок пока нет
- Of The Bar by Equating The Strain: Problem 2.7-9Документ16 страницOf The Bar by Equating The Strain: Problem 2.7-9EDiane LlanosОценок пока нет
- 10 Years of Electrostatic QuestionsДокумент6 страниц10 Years of Electrostatic QuestionsBharti KakkarОценок пока нет
- Bs Experiment 1Документ5 страницBs Experiment 1Hui Zhi100% (2)
- Problems FluidmechanicsДокумент5 страницProblems Fluidmechanicsanon_182348362Оценок пока нет
- MEP 4th Ed 2019 Worked Sols Chap 03Документ16 страницMEP 4th Ed 2019 Worked Sols Chap 0319-133 Joy Frando PinemОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 1Документ24 страницыChapter 3 Steady State Single Phase AC Circuit Analysis Part 1temesgen adugnaОценок пока нет
- Chapter-16 Planar Kinematics of A Rigid BodyДокумент26 страницChapter-16 Planar Kinematics of A Rigid BodyhamzaОценок пока нет
- QUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 2 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer Key 1Документ26 страницQUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 2 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer Key 1AicelleОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 - Center of Mass and Linear MomentumДокумент20 страницChapter 9 - Center of Mass and Linear MomentumVV Cephei100% (1)
- 2 CorrectionДокумент37 страниц2 CorrectionJeah Joyce LagrimasОценок пока нет
- Ps 5Документ1 страницаPs 5Dawit B Melka100% (1)
- Calculator TechniquesДокумент8 страницCalculator TechniquesRafael DeocuarizaОценок пока нет
- Practice Problems - Strema Part 1Документ4 страницыPractice Problems - Strema Part 1Meverlyn RoqueroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13. Filter Inductor DesignДокумент29 страницChapter 13. Filter Inductor DesignNestor EspinozaОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент29 страницPDFSaurabh PatelОценок пока нет
- Auto TransformerДокумент5 страницAuto TransformerAugy HaerudyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 17Документ9 страницChapter 17michaelanunag26Оценок пока нет
- QUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 1 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer KeyДокумент15 страницQUIZ ASSIGNMENT NO. 1 Dynamic of Rigid Bodies Answer KeyAicelleОценок пока нет
- Exercises For Lecture 5-6-7 - SOLUTIONДокумент8 страницExercises For Lecture 5-6-7 - SOLUTIONLam Pham Phuoc Loc100% (1)
- HW1 A SolutionsДокумент5 страницHW1 A SolutionsAli Abbas SheriffОценок пока нет
- ch31 PDFДокумент26 страницch31 PDFRodrigo S QuirinoОценок пока нет
- Statics AnДокумент13 страницStatics AnIsaac Davy100% (1)
- Kajidaya Bahan - Shear and Moment Diagrams Case StudyДокумент8 страницKajidaya Bahan - Shear and Moment Diagrams Case StudyzalОценок пока нет
- CH-2-DC MachineДокумент83 страницыCH-2-DC MachineÙm ØrthøbøyОценок пока нет
- Circuit Lab Div. B Tryout Test PDFДокумент6 страницCircuit Lab Div. B Tryout Test PDFMadhavi VangipurapuОценок пока нет
- Pressure and Pressure Measuring Devices: Brownian Motion", Due To WhichДокумент23 страницыPressure and Pressure Measuring Devices: Brownian Motion", Due To WhichSamuel GaétanОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics: SolutionДокумент4 страницыEngineering Mechanics: SolutionasluznetОценок пока нет
- November 2023 - PSAD 1Документ2 страницыNovember 2023 - PSAD 1Viele Antonette NaranjoОценок пока нет
- IES - Objective Paper I & II Electrical - 1997 - 2008Документ343 страницыIES - Objective Paper I & II Electrical - 1997 - 2008hasinimangaОценок пока нет
- Statics hw3Документ3 страницыStatics hw3nageshОценок пока нет
- Reading 1Документ20 страницReading 1Hwee Peng YeoОценок пока нет
- Solution 08Документ44 страницыSolution 08楊顗融Оценок пока нет
- Basicthermo Compiled TnshridharДокумент129 страницBasicthermo Compiled Tnshridharsohan2902Оценок пока нет
- Simple Stress StrainДокумент141 страницаSimple Stress StrainvelavansuОценок пока нет
- DC Machine 2Документ20 страницDC Machine 2Fadhil A. HasanОценок пока нет
- Plates in EnerconДокумент38 страницPlates in EnerconJevan Calaque100% (1)
- Problem - 7A PDFДокумент9 страницProblem - 7A PDFMonicaОценок пока нет
- 12 MarksДокумент23 страницы12 Markslakshmigsr6610Оценок пока нет
- Assignment 3Документ2 страницыAssignment 3bilal afzalОценок пока нет
- PTDU Lab No. 10 Study of Real Time Operation of Bus Bars Abdul Wahab Nasir (02) Bsee 16-20Документ2 страницыPTDU Lab No. 10 Study of Real Time Operation of Bus Bars Abdul Wahab Nasir (02) Bsee 16-20Ali ArshadОценок пока нет
- RF Review Center Weekly Exam 1Документ2 страницыRF Review Center Weekly Exam 1Hary KrizОценок пока нет
- EE-5 AC 1-PhaseДокумент15 страницEE-5 AC 1-PhaseZen GarciaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5a Equilibrium of ForcesДокумент2 страницыChapter 5a Equilibrium of ForcesPathmanathan NadesonОценок пока нет
- Lab9 BeamLabSolДокумент8 страницLab9 BeamLabSolPatrick LeeОценок пока нет
- Zener Diode and Diode ApplicationДокумент62 страницыZener Diode and Diode Applicationnibar dyllanОценок пока нет
- Applied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedДокумент20 страницApplied Mechanics I Tutorials and Assignment - RemovedYoukesh GautamОценок пока нет
- E.Mech Tutorials Mod 1Документ8 страницE.Mech Tutorials Mod 1rajee101Оценок пока нет
- Republic of The Philippines Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of Engineering: (Документ2 страницыRepublic of The Philippines Mindanao State University - Iligan Institute of Technology College of Engineering: (Gillian AmbaОценок пока нет
- Lab 5 - BJT As InverterДокумент3 страницыLab 5 - BJT As InverterKamal ChapagainОценок пока нет
- Contoh SoalДокумент24 страницыContoh SoalNovia RezaОценок пока нет
- CE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant ClockwiseДокумент2 страницыCE 222 Spring 2007-2008 Home Exercise #5: A. If The Rotor Always Maintains A Constant ClockwiseSean TraverОценок пока нет
- Problem Set ForceAndAccelerationV01Документ2 страницыProblem Set ForceAndAccelerationV01Benedick Jayson P. Marti100% (1)
- Tutorial 7 8Документ3 страницыTutorial 7 8Zahida ParnisОценок пока нет
- Work Energy-6Документ2 страницыWork Energy-6Zahida ParnisОценок пока нет
- Addpro 7Документ1 страницаAddpro 7Mary Izere MutabaziОценок пока нет
- CL4Документ2 страницыCL4Harvey BautistaОценок пока нет
- Dynamics: Review - Structural Engineering and ConstructionДокумент2 страницыDynamics: Review - Structural Engineering and ConstructionVincent NavaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 0910spring Set2 AnsДокумент1 страницаAssignment 0910spring Set2 AnsSarp Yiğit ŞirinОценок пока нет
- Assignment 0910spring Set1Документ2 страницыAssignment 0910spring Set1Sarp Yiğit ŞirinОценок пока нет
- CVE303 Syllabus 2017Документ9 страницCVE303 Syllabus 2017Sarp Yiğit ŞirinОценок пока нет
- GooglepreviewДокумент65 страницGooglepreviewSarp Yiğit ŞirinОценок пока нет
- CHP 18Документ16 страницCHP 18Abhiram Reddy100% (1)
- Kinematics of Machines Compiled HariraoДокумент94 страницыKinematics of Machines Compiled HariraoUpender DhullОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Biomechanics KINE 3300Документ110 страницChapter 3 Biomechanics KINE 3300Selviya AvaurumОценок пока нет
- A Study On Human Fall Detection Systems Daily Activity ClassificationДокумент9 страницA Study On Human Fall Detection Systems Daily Activity Classificationyy74Оценок пока нет
- Dynamics: Vector Mechanics For EngineersДокумент61 страницаDynamics: Vector Mechanics For Engineersgerango2010Оценок пока нет
- PHYSICS FOR ENGINEERS Chapter 2Документ30 страницPHYSICS FOR ENGINEERS Chapter 2Leo Prince GicanaОценок пока нет
- Fisica 1 TemasДокумент36 страницFisica 1 TemasUsuario 1023Оценок пока нет
- Fpy 0316 - Mid Sem 1 (2021-22) QuestionДокумент11 страницFpy 0316 - Mid Sem 1 (2021-22) QuestionDurga ShrieОценок пока нет
- Mechanical PDFДокумент104 страницыMechanical PDFDeepak MalusareОценок пока нет
- Satellite and Planetary MotionДокумент5 страницSatellite and Planetary MotionExpertsmindEduОценок пока нет
- Physics Rules 5Документ10 страницPhysics Rules 5Chris_Barber09100% (6)
- FSMQ Newtonian ModellingДокумент7 страницFSMQ Newtonian ModellingnaylinaungОценок пока нет
- PHYS 369 Formula Sheet CombinedДокумент4 страницыPHYS 369 Formula Sheet Combineddarro d92Оценок пока нет
- AP Physics Question BankДокумент99 страницAP Physics Question BankElianne Gabbay100% (2)
- Hydraulics Chapter 3Документ73 страницыHydraulics Chapter 3Yoni RebumaОценок пока нет
- Physics I EM FinalIДокумент104 страницыPhysics I EM FinalINaveen VasalaОценок пока нет
- VRX J Series 99j266313e0-1309Документ28 страницVRX J Series 99j266313e0-1309bhandge880% (1)
- Aristotle 180314024203Документ17 страницAristotle 180314024203Karla Jenica PatlunagОценок пока нет
- SJBIT Notes PDFДокумент144 страницыSJBIT Notes PDFMohammed Umar Farooq PatelОценок пока нет
- Form Four Physics HandbookДокумент108 страницForm Four Physics Handbookmosesreuben416Оценок пока нет
- Velocity and Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms (Analytical Method)Документ35 страницVelocity and Acceleration Analysis of Mechanisms (Analytical Method)Vijaykumar H KОценок пока нет
- Determination of Initial VelocityДокумент4 страницыDetermination of Initial VelocityGneiss Louie Gem AlmazanОценок пока нет
- CIE A-Level Mechanics 1Документ205 страницCIE A-Level Mechanics 1Hyungryul Daniel YangОценок пока нет
- Gyro NotesДокумент12 страницGyro NotesManupriya Singh100% (2)
- Are You Ready For SMT359Документ8 страницAre You Ready For SMT359nuphormОценок пока нет
- Grade 11 Physics Study Guide Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Документ23 страницыGrade 11 Physics Study Guide Notes For Final Exam SPH3U1Kamil GhoshОценок пока нет
- USAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Документ311 страницUSAPhO Problems (2007-2014)Science Olympiad Blog95% (19)
- Mec 291: Dynamics and Materials LAB Mechanism and Machine ElementsДокумент22 страницыMec 291: Dynamics and Materials LAB Mechanism and Machine ElementsHaFiy HaZimОценок пока нет
- InertiaДокумент10 страницInertiaZalini AbdullahОценок пока нет