Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
CH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDF
Загружено:
Aman ChauhanИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
CH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDF
Загружено:
Aman ChauhanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
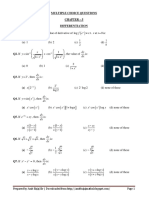
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
CHAPTER – 9 DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS
3
d 2 y dy
2
dy
Q1. The degree of the differential equation 2 sin 1 0 is:
dx dx dx
(a) 3 (b) 2 (c) 1 (d) not defined
d2y dy
Q2. The order of the differential equation 2 x 2
3 y 0 is:
2
dx dx
(a) 2 (b) 1 (c) 0 (d) not defined
Q3. The solution of the differential equation e x 1 y dy y 1 e x dx is:
(a) e y c e x 1 y 1
(b) e y c e x y 1
(c) y e x 1 y 1 (d) none of these
dy
Q4. The solution of the differential equation 1 x y xy is:
dx
x2 x2 x2
(a) e1 y x c (b) log 1 y x c (c) e y x c (d) none of these
2 2 2
dy 1 y 2
Q5. The solution of the differential equation 0 is:
dx 1 x2
(a) y sin 1 y sin 1 x c (b) sin 1 y sin 1 x c (c) sin 1 y sin 1 x c (d) none of these
Q6. The solution of the differential equation x 1 y 2 dx y 1 x 2 dy 0 is:
(a) sin 1 x sin 1 y c (b) 1 x 2 1 y 2 c (c) tan 1 x tan 1 y c (d) none of these
dy y 2 x 2
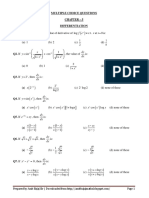
Q7. The solution of the differential equation is:
dx 2 xy
(a) x 2 y 2 cx (b) x 2 y 2 cy (c) x 2 y 2 cx (d) none of these
dy
Q8. The solution of the differential equation y tan x sec x is:
dx
(a) y sin x c cos x (b) y sin x c cos x (c) y sin x sin x c (d) none of these
Prepared by Amit Bajaj Sir | Downloaded from http://amitbajajmaths.blogspot.com/ Page 1
dy
Q9. The integrating factor of the differential equation x log x y 2log x is:
dx
(a) log log x (b) e x (c) log x (d) x
dy y
Q10. The solution of the differential equation sin x is:
dx x
(a) x y cos x sin x c (b) x y cos x sin x c (c) x y cos x cos x c (d) none of these
dy
Q11. The solution of the differential equation 2 x y 3 represents:
dx
(a) circles (b) straight lines (c) ellipses (d) parabolas
dy y
Q12. The solution of the differential equation x y x tan is:
dx x
x y x y
(a) sin xc (b) sin cx (c) sin cy (d) sin cy
y x y x
dy
Q13. The solution of the differential equation x 2 y 2 4 is:
dx
(a) x2 y 2 12 x c (b) x2 y 2 3x c `(c) x3 y3 3x c (d) x3 y3 12 x c
Q14. The solution of the differential equation x dx y dy x 2 y dy y 2 x dx is:
(a) x 2 1 c 1 y 2
(b) x 2 1 c 1 y 2
(c) x3 1 c 1 y 3
(d) x3 1 c 1 y 3
Q15. The solution of the differential equation x 2 1 dy
dx
y 2
1 0 is:
1 x 1 x
(a) y 2 x 2 (b) y (c) y x x 1 (d) y
1 x 1 x
dy x 2 xy y 2
Q16. The solution of the differential equation is:
dx x2
x y x
(a) tan 1 log y c (b) tan 1 log x c (c) tan 1 log x c (d) none of these
y x y
ANSWERS
1. d 2. a 3. a 4. b 5. c 6. b 7. c 8. b 9. c 10. a 11. d 12. b 13. d 14. a 15.
d 16. d
Prepared by Amit Bajaj Sir | Downloaded from http://amitbajajmaths.blogspot.com/ Page 2
Вам также может понравиться
- Pre Algebra Reference SheetДокумент2 страницыPre Algebra Reference SheetforeversccrОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)Документ7 страницCH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)CRPF School80% (41)
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-9Документ8 страницBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-9ASHISH NAIK100% (1)
- CH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersДокумент2 страницыCH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answersurooj fatimaОценок пока нет
- Servent Room Wardrobe Plan Linen Wardrobe: Fix Shelf Fix Shelf Fix Shelf Fix Shelf Fix ShelfДокумент1 страницаServent Room Wardrobe Plan Linen Wardrobe: Fix Shelf Fix Shelf Fix Shelf Fix Shelf Fix ShelfAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)Документ7 страницCH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)CRPF School100% (1)
- CH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFДокумент2 страницыCH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFVishal Kumar Singh100% (1)
- CH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersДокумент2 страницыCH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answerser.amitbajajОценок пока нет
- Emmet - Whitehead's Philosophy of OrganismДокумент317 страницEmmet - Whitehead's Philosophy of Organismziddasy100% (1)
- Answers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesОт EverandAnswers to Selected Problems in Multivariable Calculus with Linear Algebra and SeriesРейтинг: 1.5 из 5 звезд1.5/5 (2)
- CH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)Документ2 страницыCH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions (With Answers)CRPF School85% (26)
- 02 Linear EquationДокумент16 страниц02 Linear EquationmanjuramuОценок пока нет
- Worksheet No. 1 Grade 8 - Mathematics 1st Quarter Factors Completely Different Types of PolynomialsДокумент2 страницыWorksheet No. 1 Grade 8 - Mathematics 1st Quarter Factors Completely Different Types of PolynomialsKara BanzonОценок пока нет
- Differential Equation Question PDFДокумент19 страницDifferential Equation Question PDFvivek chandОценок пока нет
- Multiple Choice Questions on Differential EquationsДокумент2 страницыMultiple Choice Questions on Differential EquationsTejas Kankal100% (1)
- IITians PACE Coaching Classes in Andheri, Dadar, Chembur & Thane for Binomial Theorem Practice QuestionsДокумент11 страницIITians PACE Coaching Classes in Andheri, Dadar, Chembur & Thane for Binomial Theorem Practice QuestionsAditya SanjayBoobОценок пока нет
- Bernoulli Numbers and Zeta FunctionsДокумент278 страницBernoulli Numbers and Zeta FunctionsAssis GomesОценок пока нет
- Mat223 UTM Midterm UofTДокумент7 страницMat223 UTM Midterm UofTRevownSada100% (1)
- CH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFДокумент2 страницыCH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFpriya dharshiniОценок пока нет
- CH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersДокумент2 страницыCH 9 Differential Equations Multiple Choice Questions With AnswersPubudu NuwanОценок пока нет
- DetДокумент2 страницыDetcrr82440Оценок пока нет
- Differential Equations Practice Paper SolutionsДокумент5 страницDifferential Equations Practice Paper SolutionsKailash ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- 9 Differential EquationsДокумент31 страница9 Differential Equationshembrampriyanka07Оценок пока нет
- IIT-JEE differential equation practice problemsДокумент17 страницIIT-JEE differential equation practice problemsHarsh KumarОценок пока нет
- Exercise 1Документ3 страницыExercise 1OPT MECH ENTERPRISESОценок пока нет
- M 9 AUC, Differential Equation & Solution of Triangles ADV 1Документ28 страницM 9 AUC, Differential Equation & Solution of Triangles ADV 1Saket VisputeОценок пока нет
- Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 5Документ7 страницDifferentiation Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 5sudhishdadhich_68389Оценок пока нет
- CH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFДокумент7 страницCH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFscribОценок пока нет
- CH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFДокумент7 страницCH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFEladio LagosОценок пока нет
- Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 5Документ7 страницDifferentiation Multiple Choice Questions Chapter 5Swapnil Sahu100% (1)
- CH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFДокумент7 страницCH 5 Differentiation Multiple Choice Questions With Answers PDFAmandeep DhillonОценок пока нет
- JEE-Mathematics: Xii-Differential EquationДокумент4 страницыJEE-Mathematics: Xii-Differential EquationKuldeep MathematicsОценок пока нет
- 12 - Ordinary Differential EquationsДокумент2 страницы12 - Ordinary Differential Equationshoney1002Оценок пока нет
- Diffrential EqДокумент2 страницыDiffrential EqV MohithОценок пока нет
- Differential Equation-04-ExerciseДокумент23 страницыDifferential Equation-04-ExerciseRaju SinghОценок пока нет
- One Mark Questions (Updated)Документ3 страницыOne Mark Questions (Updated)Dhaya VОценок пока нет
- Differential Equation PracticeДокумент6 страницDifferential Equation PracticeGaming ManiacsОценок пока нет
- Differential Equation SolutionsДокумент5 страницDifferential Equation SolutionsKailash ChaudharyОценок пока нет
- Exams 2014Документ4 страницыExams 2014nyamsonevans90Оценок пока нет
- Ordinary Differential Equations SolvedДокумент2 страницыOrdinary Differential Equations SolvedRekha BhasinОценок пока нет
- A4P-Differential EquationsДокумент2 страницыA4P-Differential EquationsAimbotОценок пока нет
- Sample Paper 2 (2019-20) Class XII Maths SolutionsДокумент4 страницыSample Paper 2 (2019-20) Class XII Maths SolutionsSajal JainОценок пока нет
- Mock Test (Maths)-08 SolutionsДокумент8 страницMock Test (Maths)-08 SolutionsAman GoelОценок пока нет
- Code: D3 Kcet - 2021 Test Paper With Answer Key (HELD ON SATURDAY 28-08-2021)Документ10 страницCode: D3 Kcet - 2021 Test Paper With Answer Key (HELD ON SATURDAY 28-08-2021)Ryan AahilОценок пока нет
- Before Allen Class 11 29 JuneДокумент3 страницыBefore Allen Class 11 29 JuneYatharth KaranОценок пока нет
- Form Differential Equations from Families of CurvesДокумент5 страницForm Differential Equations from Families of CurvesJayNsteinОценок пока нет
- Differential EquationДокумент16 страницDifferential EquationSoham PandeyОценок пока нет
- 024e99d5874b2-Mock Test (Maths) - 05Документ8 страниц024e99d5874b2-Mock Test (Maths) - 05Aman GoelОценок пока нет
- XII-PTS-21 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTAДокумент8 страницXII-PTS-21 (2023-24) - by O.P. GUPTAmaanya.ailawadi3Оценок пока нет
- Question 9 - Differential EquationsДокумент2 страницыQuestion 9 - Differential EquationsSnehasish DasОценок пока нет
- Differentiation Formulas & ConceptsДокумент19 страницDifferentiation Formulas & ConceptsAnubhav vaishОценок пока нет
- Maths SQP 1Документ7 страницMaths SQP 1qutubkhan.nalwalaОценок пока нет
- Pratice Ordinary Diffential Equation Test 1Документ2 страницыPratice Ordinary Diffential Equation Test 1soreeОценок пока нет
- M1 Bit Bank PDFДокумент10 страницM1 Bit Bank PDFK Sushmanth ReddyОценок пока нет
- 02 Differential COefficientДокумент6 страниц02 Differential COefficienthoney1002Оценок пока нет
- BBa 202Документ3 страницыBBa 202Suman DasОценок пока нет
- MT112 Question Bank (1) GДокумент15 страницMT112 Question Bank (1) Garjunv_14Оценок пока нет
- Sample Paper 1Документ8 страницSample Paper 1Kanha BSОценок пока нет
- Math Warriors Test - 03: Time Allowed: 45 Minutes Max. Marks: 15Документ3 страницыMath Warriors Test - 03: Time Allowed: 45 Minutes Max. Marks: 15VinayОценок пока нет
- Basic Maths _ DPP-03 (Of lec 05)Документ3 страницыBasic Maths _ DPP-03 (Of lec 05)naunidhwiztechОценок пока нет
- Linear Differential Equations SolutionsДокумент21 страницаLinear Differential Equations SolutionsDemo Account 1Оценок пока нет
- Limits AssignmentДокумент5 страницLimits AssignmentRudraksh ChhibberОценок пока нет
- Calc Practice Test (Slope Fields and Differential Equations)Документ5 страницCalc Practice Test (Slope Fields and Differential Equations)Alina VoОценок пока нет
- I Integration-03 - Exercise 1Документ20 страницI Integration-03 - Exercise 1Raju SinghОценок пока нет
- Assign-1 Integration by Use of Basic FormulaeДокумент3 страницыAssign-1 Integration by Use of Basic FormulaeDhruv KuchhalОценок пока нет
- Definite & Indefinite Integration WAДокумент24 страницыDefinite & Indefinite Integration WARaju SinghОценок пока нет
- Quiz - Basic MathsДокумент3 страницыQuiz - Basic MathsShashwat MishraОценок пока нет
- (De) - Differential Equation PptfileДокумент52 страницы(De) - Differential Equation PptfileUtkarsh [ NIT Aurangabad ]Оценок пока нет
- 01 Rational NumberДокумент20 страниц01 Rational NumberAnuj MadaanОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент8 страницPDFAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- 523 Sci3 - 2019Документ11 страниц523 Sci3 - 2019Soumya xyxОценок пока нет
- 13th Oct SSC English QuestionsДокумент5 страниц13th Oct SSC English QuestionsAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Simple Interest - English 87Документ2 страницыSimple Interest - English 87Aman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Physics Force Unit Feburary 12 2020 PDFДокумент2 страницыPhysics Force Unit Feburary 12 2020 PDFAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Define TissueДокумент1 страницаDefine TissueAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Physics Force Unit Feburary 12 2020 PDFДокумент2 страницыPhysics Force Unit Feburary 12 2020 PDFAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- OptionformCHSL2018revised 06022020Документ2 страницыOptionformCHSL2018revised 06022020MANISH KUMARОценок пока нет
- Define TissueДокумент1 страницаDefine TissueAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- COM IVДокумент6 страницCOM IVanuj rajputОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Chapter 1 & 2 X iCSEДокумент4 страницыChemistry Chapter 1 & 2 X iCSEAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- GKДокумент5 страницGKHimanshuОценок пока нет
- Monthly Digest-April-2018-Eng - pdf-92 PDFДокумент21 страницаMonthly Digest-April-2018-Eng - pdf-92 PDFNadeem MalikОценок пока нет
- 50 Seating Arr PDFДокумент16 страниц50 Seating Arr PDFJIMMY ANTONYОценок пока нет
- 2000 Vocabulary PDF For Editorial 95Документ205 страниц2000 Vocabulary PDF For Editorial 95Raja Sandeep VubaОценок пока нет
- VII ICSE MathsДокумент2 страницыVII ICSE MathsAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- 13th Oct SSC English QuestionsДокумент5 страниц13th Oct SSC English QuestionsAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Phrasal Verbs 81Документ13 страницPhrasal Verbs 81Aman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- GK QuestionsДокумент31 страницаGK QuestionsAman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Vocab 22Документ208 страницVocab 22aditya srivastavaОценок пока нет
- Applications of Pigeonhole PrincipleДокумент21 страницаApplications of Pigeonhole Principlechaitucvs100% (1)
- Objective Trigonometry Level 1 (2015)Документ5 страницObjective Trigonometry Level 1 (2015)Aman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Straight Lines XI (Objective - Sheet)Документ9 страницStraight Lines XI (Objective - Sheet)Aman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Full Course MATHS 10 SA1Документ3 страницыFull Course MATHS 10 SA1Aman ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Greater Than and Less Than: Subject/Topic: 1st Grade Mathematics: Number & Operations in Base Ten RationaleДокумент6 страницGreater Than and Less Than: Subject/Topic: 1st Grade Mathematics: Number & Operations in Base Ten Rationaleapi-279517519Оценок пока нет
- Polar Codes Construction and Performance Analysis - Ramtin PedarsaniДокумент48 страницPolar Codes Construction and Performance Analysis - Ramtin PedarsaniguimanolОценок пока нет
- Linear ProgrammingДокумент19 страницLinear ProgrammingRemi DrigoОценок пока нет
- Monte Carlo MethodsДокумент19 страницMonte Carlo Methodsਸੁਖਪ੍ਰੀਤ ਸਿੰਘОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Modelling Principles ExplainedДокумент40 страницMathematical Modelling Principles ExplainedJanusОценок пока нет
- Cse2012 PPS3 w2022Документ3 страницыCse2012 PPS3 w2022Lazer TronОценок пока нет
- Actuarial Mathematics by Newton BowersДокумент766 страницActuarial Mathematics by Newton BowersTom Tran96% (56)
- Tolerance AnalysisДокумент5 страницTolerance Analysisdeepakgr79Оценок пока нет
- ExamДокумент7 страницExamChau Dinh HoanОценок пока нет
- A General Algorithm For Building Z-Matrix Based On Transitional MatricesДокумент4 страницыA General Algorithm For Building Z-Matrix Based On Transitional Matricesjaach78100% (1)
- LOGIC Mashad PresentationДокумент9 страницLOGIC Mashad Presentationapi-3709182Оценок пока нет
- Braybrook College Student Report 2023 - Semester OneДокумент11 страницBraybrook College Student Report 2023 - Semester OnebeeОценок пока нет
- JJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJДокумент16 страницJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJJNitin Suyan PanchalОценок пока нет
- Computer Science: Component 1 and Component 2Документ8 страницComputer Science: Component 1 and Component 2HappybabyОценок пока нет
- (J. G. Kalbfleisch) Probability and Statistical I PDFДокумент188 страниц(J. G. Kalbfleisch) Probability and Statistical I PDFZeus_plusОценок пока нет
- Sgems Quinta Parte Del MAnual para Uso GeoestadisticoДокумент27 страницSgems Quinta Parte Del MAnual para Uso GeoestadisticoMileedy Vanessa Narro LucanoОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1.1: Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesДокумент5 страницLesson 1.1: Introduction To Conic Sections and CirclesAerl XuanОценок пока нет
- BSABE Study ProgramДокумент4 страницыBSABE Study ProgramRaymarck PatricioОценок пока нет
- Basic Math & Logarithm - DPP 06 (Of Lec 09) - Arjuna JEE 2024Документ2 страницыBasic Math & Logarithm - DPP 06 (Of Lec 09) - Arjuna JEE 2024YASHОценок пока нет
- Improving Numeracy Performance Through Peer TutoringДокумент14 страницImproving Numeracy Performance Through Peer TutoringJomar Gasilla NavarroОценок пока нет
- Section A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 3 5 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 Mathematics (Standard) 041Документ6 страницSection A: Sample/Pre-Board Paper 3 5 Class X Term 1 Exam Nov - Dec 2021 Mathematics (Standard) 041Ashwani PathakОценок пока нет
- Difference Between DDA N BresenhamДокумент2 страницыDifference Between DDA N BresenhamSamudra NagОценок пока нет
- Ma 1252Документ25 страницMa 1252Nagalingaraja RnrОценок пока нет