Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Worksheet Oxidationnumber
Загружено:
MariaEzzaSyUy0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
544 просмотров1 страницаThis document provides rules for assigning oxidation numbers to elements in compounds and ions, and examples of oxidation numbers for various species. It also gives half reactions for oxidation-reduction examples, identifying the species being oxidized and reduced in each reaction. The rules state that pure elements have an oxidation number of 0, ions take the charge of the ion, fluorine is -1, oxygen is -2 except when combined with fluorine or in peroxides, and hydrogen is +1 except when combined with metals. Group 1 elements are +1, Group 2 are +2, and aluminum is +3. The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound or polyatomic ion equals the overall charge.
Исходное описание:
This is about chemistry. This is an exercise for oxidation numbers.
Оригинальное название
worksheet.oxidationnumber
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document provides rules for assigning oxidation numbers to elements in compounds and ions, and examples of oxidation numbers for various species. It also gives half reactions for oxidation-reduction examples, identifying the species being oxidized and reduced in each reaction. The rules state that pure elements have an oxidation number of 0, ions take the charge of the ion, fluorine is -1, oxygen is -2 except when combined with fluorine or in peroxides, and hydrogen is +1 except when combined with metals. Group 1 elements are +1, Group 2 are +2, and aluminum is +3. The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound or polyatomic ion equals the overall charge.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
544 просмотров1 страницаWorksheet Oxidationnumber
Загружено:
MariaEzzaSyUyThis document provides rules for assigning oxidation numbers to elements in compounds and ions, and examples of oxidation numbers for various species. It also gives half reactions for oxidation-reduction examples, identifying the species being oxidized and reduced in each reaction. The rules state that pure elements have an oxidation number of 0, ions take the charge of the ion, fluorine is -1, oxygen is -2 except when combined with fluorine or in peroxides, and hydrogen is +1 except when combined with metals. Group 1 elements are +1, Group 2 are +2, and aluminum is +3. The sum of oxidation numbers in a neutral compound or polyatomic ion equals the overall charge.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
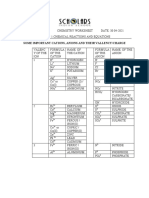
CHEM131 CHEMISTRY FOR ENGINEERS WORKSHEET – ASSIGNING OXIDATION NUMBERS
Oxidation Number Rules:
1. The oxidation number of any pure element is 0.
2. The oxidation of a monoatomic ion equals that charge on the ion.
3. The oxidation number of fluorine in a compound is always -1.
4. Oxygen has an oxidation number of -2 unless it is combined with F, in which it is +1 or +2, or it is in peroxide in
which it is -1.
5. Hydrogen is +1, unless combined with a metal, and then it is -1.
6. In compounds, Group I is +1, Group II is +2 and aluminum is +3.
7. The sum of oxidation numbers of all atoms in a neutral compound is 0.
8. The sum of the oxidation numbers in a polyatomic ion equals the charge of the ion.
A. Give the oxidation number of the indicated ion/atom.
1. N in N2O3 11. Cl in Fe(ClO2)3 21. O2
2. S in H2SO4 12. Fe in Fe(ClO2)3 22. P4
-
3. C 13. N in NO3 23. Na in Na2S
2+
4. C in CO 14. Cu 24. S in H2S
5. Na in Na2CO3 15. Zn2+ 25. Ca2+
6. H in H2O 16. C in CH4 26. C in CN-
7. Ba in BaCl2 17. Mn in MnO2 27. H in OH-
- 2-
8. N in NO2 18. S in SO3 28. Mn in KMnO4
2+
9. S in Al2S3 19. Mg 29. I in Mg(IO3)2
- -
10. S in HSO4 20. Cl 30. C in C2O42-
B. Identify the species being oxidized and reduced in each of the following reactions and write their half reactions:
1. 2Cr2+ + Sn4+ → 2Cr3+ + Sn2+
Oxidation: Reduction:
2. 3Hg2+ + 2Fe(s) → 3Hg2 + 2Fe3+
Oxidation: Reduction:
3. 2As(s) + 3Cl2(g) → 2AsCl3
Oxidation: Reduction:
4. Zn + Cu2+ → Zn2+ + Cu
Oxidation: Reduction:
5. C + H2SO4 → CO2 + SO2 + H2O
Oxidation: Reduction:
6. HNO3 + HI → NO + I2 + H2O
Oxidation: Reduction:
7. KMnO4 + HCl → MnCl2 + Cl2 + H2O KCl
Oxidation: Reduction:
8. Sb + HNO3 → Sb2O3 + NO + H2O
Oxidation: Reduction:
Вам также может понравиться
- Write20 Chapter Redox Reactions WorksheetДокумент4 страницыWrite20 Chapter Redox Reactions WorksheetAzain CardenasОценок пока нет
- Worksheet - Assigning Oxidation Numbers - KeyДокумент1 страницаWorksheet - Assigning Oxidation Numbers - KeyGopal PenjarlaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet - Assigning Oxidation Numbers - KeyДокумент1 страницаWorksheet - Assigning Oxidation Numbers - KeyRabia RafiqueОценок пока нет
- Worksheet - Assigning Oxidation Numbers - KeyДокумент1 страницаWorksheet - Assigning Oxidation Numbers - KeyJane IvanovaОценок пока нет
- Worksheet - Assigning Oxidation Numbers - KeyДокумент1 страницаWorksheet - Assigning Oxidation Numbers - KeyRabia RafiqueОценок пока нет
- Chapter 20 Redox Reactions WorksheetДокумент4 страницыChapter 20 Redox Reactions WorksheetMostafa Ahmed100% (1)
- Worksheet RedoxДокумент4 страницыWorksheet RedoxSyed asif HaleemОценок пока нет
- Rules For Oxidation StateДокумент2 страницыRules For Oxidation Statemanisha awasthiОценок пока нет
- W VCE 2019 Chemistry Oxidation Numbers Worksheet 1 FINALДокумент4 страницыW VCE 2019 Chemistry Oxidation Numbers Worksheet 1 FINALhtyhongОценок пока нет
- Balancing Chemical Equations 1Документ4 страницыBalancing Chemical Equations 1luis martinezОценок пока нет
- 2c Balancing EquationsДокумент1 страница2c Balancing EquationsKarina LeungОценок пока нет
- 2c ANSWERS Balancing Equations (2017)Документ1 страница2c ANSWERS Balancing Equations (2017)Karina LeungОценок пока нет
- Oxidation Numbers PracticeДокумент1 страницаOxidation Numbers PracticeMRMFARAHОценок пока нет
- RedoxДокумент14 страницRedoxsaraОценок пока нет
- P-Block Board Youtube Part-2Документ53 страницыP-Block Board Youtube Part-2vaibhav sainiОценок пока нет
- Practise Questions On BalancingДокумент1 страницаPractise Questions On BalancingDaksh SharmaОценок пока нет
- Redox WKSHTДокумент4 страницыRedox WKSHTMarco ConopioОценок пока нет
- Lol Za 121312Документ2 страницыLol Za 121312Alexandre GiglemianiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 20 Worksheet RedoxДокумент4 страницыChapter 20 Worksheet RedoxPerry Sin100% (1)
- Jasmine Carney - Set 1 Balancing Chemical EquationsДокумент3 страницыJasmine Carney - Set 1 Balancing Chemical Equationsapi-669467021Оценок пока нет
- Predicting Products of Chemical ReactionsДокумент3 страницыPredicting Products of Chemical ReactionsKiyu Mendez100% (1)
- WORKSHEETS KEY Balancing EquationsДокумент9 страницWORKSHEETS KEY Balancing EquationsFaye Lyka Mae ReyesОценок пока нет
- Redox Workbook HoДокумент43 страницыRedox Workbook HoMuhammad TauseefОценок пока нет
- CH 3 Chemical Reaction Worksheet 1Документ19 страницCH 3 Chemical Reaction Worksheet 1Alia ShabbirОценок пока нет
- Redox ReactionДокумент3 страницыRedox ReactionPranjal GuptaОценок пока нет
- Balancing Redox Reactions 2:: Chemistry 093 The Ion-Electron MethodДокумент13 страницBalancing Redox Reactions 2:: Chemistry 093 The Ion-Electron MethodfatimatumbiОценок пока нет
- Redox Question Paper 1Документ17 страницRedox Question Paper 1Uzair ZahidОценок пока нет
- For JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsДокумент56 страницFor JEE Aspirants: Complete Inorganic Chemistry ReactionsLakshmi AnandОценок пока нет
- Balancing Chemical Equations WorksheetДокумент2 страницыBalancing Chemical Equations WorksheetAye Pyae Pyae HtunОценок пока нет
- Oxidation AND ReductionДокумент60 страницOxidation AND ReductionSofea Alya SuhaiziОценок пока нет
- REDOXДокумент67 страницREDOXLeo PietroОценок пока нет
- 12 DChem Research SolubilityДокумент6 страниц12 DChem Research SolubilityRenzelle MelisseОценок пока нет
- In Your Textbook, Read About Redox Reactions.: PrawanДокумент5 страницIn Your Textbook, Read About Redox Reactions.: PrawanPrawan Chiewpanich THTMОценок пока нет
- 9 CH 2 - Types of ReactionsДокумент8 страниц9 CH 2 - Types of ReactionsVenkat SubramanianОценок пока нет
- Types of Chemical ReactionsДокумент2 страницыTypes of Chemical ReactionsHimeОценок пока нет
- REDOX ReactionДокумент12 страницREDOX Reactionpratiyushranjan80Оценок пока нет
- CHEMISTRY Chemical ReactionsДокумент5 страницCHEMISTRY Chemical ReactionsDanica AmigoОценок пока нет
- Chemistry-Bridging The Gap AnswerДокумент11 страницChemistry-Bridging The Gap AnswerMuhammad IzzuanОценок пока нет
- Table 1: Elements Symbols Atomic MassДокумент7 страницTable 1: Elements Symbols Atomic MassMadhavОценок пока нет
- Chemistry of Lighter Elements: Chapter HighlightsДокумент28 страницChemistry of Lighter Elements: Chapter HighlightsNatish JaglanОценок пока нет
- Yr 10 Chem Summer NoteДокумент22 страницыYr 10 Chem Summer NoteTokoni DanielОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and Reduction SPM Form 5Документ63 страницыOxidation and Reduction SPM Form 5Azie Nurul Akhtar85% (13)
- Chapter 9 Periodicity Revision (Документ5 страницChapter 9 Periodicity Revision (Ting NicholasОценок пока нет
- REDOX REACTIONSДокумент4 страницыREDOX REACTIONSajakazОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Reactions WorksheetДокумент2 страницыChemistry Reactions WorksheetGeorgia SimmsОценок пока нет
- Redox ReactionsДокумент44 страницыRedox ReactionsAnanthakrishnan Tinneveli VОценок пока нет
- Exercise C6 - Ans SchemeДокумент3 страницыExercise C6 - Ans Schemeknn233610437Оценок пока нет
- Lab 21Документ3 страницыLab 21KeenanОценок пока нет
- 1 Bba7tnid0ufci552ughpДокумент3 страницы1 Bba7tnid0ufci552ughpVijay PatilОценок пока нет
- Chemistry: Multiple Choice Questions With One Correct AlternativeДокумент12 страницChemistry: Multiple Choice Questions With One Correct AlternativeSooryaОценок пока нет
- Chem Basic FB Answer Key CH 22 (06.14.16)Документ4 страницыChem Basic FB Answer Key CH 22 (06.14.16)eman mamdohОценок пока нет
- Classify Chemical ReactionsДокумент4 страницыClassify Chemical ReactionsRain Simonette GuanОценок пока нет
- Some Important Cations, Anions and Their Vallency/ChargeДокумент3 страницыSome Important Cations, Anions and Their Vallency/ChargeAliОценок пока нет
- Oxidation and Reduction Workbook GuideДокумент113 страницOxidation and Reduction Workbook GuideRudi Berlian100% (1)
- Redox Reactions Worksheet 1 With Answer KeyДокумент6 страницRedox Reactions Worksheet 1 With Answer KeyCattleya Shariffa ChoОценок пока нет
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОт EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersОценок пока нет
- Structure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsОт EverandStructure and Properties of Inorganic Solids: International Series of Monographs in Solid State PhysicsОценок пока нет
- Coordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972От EverandCoordination Chemistry—XIV: Plenary Lectures Presented at the XIVth International Conference on Coordination Chemistry Held at Toronto, Canada, 22—28 June 1972A. B. P. LeverОценок пока нет
- Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry V2От EverandHandbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry V2Georg BrauerОценок пока нет
- Week 1 CoursewareДокумент9 страницWeek 1 CoursewareMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Planning Tools and Techniques for ManagersДокумент12 страницPlanning Tools and Techniques for ManagersMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Cebu Institute of Technology University College of Engineering and Architecture Department of Industrial Engineering COURSEWARE ES034 ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT Week 8 Leading and ControllingДокумент9 страницCebu Institute of Technology University College of Engineering and Architecture Department of Industrial Engineering COURSEWARE ES034 ENGINEERING MANAGEMENT Week 8 Leading and ControllingMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Introductory Topics StudentДокумент79 страницIntroductory Topics StudentMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Short Quiz 1 - Attempt Review - HTMLДокумент7 страницShort Quiz 1 - Attempt Review - HTMLMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Ducted Split Sentinel Series Product Brochure 10.21.21Документ2 страницыDucted Split Sentinel Series Product Brochure 10.21.21MariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- The Country I Want To VisitДокумент1 страницаThe Country I Want To VisitMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Basic Pump ConstructionДокумент90 страницBasic Pump ConstructionMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Flash and Fire Point of OilДокумент1 страницаFlash and Fire Point of OilMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Fuels For Internal Combustion EngineДокумент53 страницыFuels For Internal Combustion EngineMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Theoretical CyclesДокумент49 страницTheoretical CyclesMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Engine Design, Testing and PerformanceДокумент58 страницEngine Design, Testing and PerformanceMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Mixture of GasesДокумент20 страницMixture of GasesShane Michael BacalsoОценок пока нет
- QUIZ 1 Introduction To Kinematics of MachinesДокумент1 страницаQUIZ 1 Introduction To Kinematics of MachinesMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Tam, Sam, SomДокумент7 страницTam, Sam, SomMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Introduction and Principle of ThermodynamicsДокумент30 страницIntroduction and Principle of ThermodynamicsMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- B.V 10th of May 2021Документ1 страницаB.V 10th of May 2021MariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- RRRRRRДокумент1 страницаRRRRRRMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- B.V 23TH May 2021Документ1 страницаB.V 23TH May 2021MariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- B.V 16th of May 2021Документ1 страницаB.V 16th of May 2021MariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- SocsciДокумент1 страницаSocsciMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- B.V April 25,2021Документ1 страницаB.V April 25,2021MariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- B.V of May 02,2021Документ1 страницаB.V of May 02,2021MariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- An Act Strengthening Compliance With Occupational Safety and Health Standards and Providing Penalties For Violations Thereof (RA 11058) and IRR (DOLE DO 198 - 18)Документ44 страницыAn Act Strengthening Compliance With Occupational Safety and Health Standards and Providing Penalties For Violations Thereof (RA 11058) and IRR (DOLE DO 198 - 18)Miguel CuisiaОценок пока нет
- B.V 9th of May 2021Документ1 страницаB.V 9th of May 2021MariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Impulse and Reaction Turbines ExplainedДокумент68 страницImpulse and Reaction Turbines ExplainedMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Physics TermsДокумент7 страницPhysics TermsMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Physics TermsДокумент7 страницPhysics TermsMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- SONGДокумент2 страницыSONGMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Polyclar For Wine - ASI v2Документ47 страницPolyclar For Wine - ASI v2Giorgi GhambashidzeОценок пока нет
- 2-Mathematical Modeling and Simulation of Hydrotreating Reactors Cocurrent Versus Countercurrent Operations - Art5Документ14 страниц2-Mathematical Modeling and Simulation of Hydrotreating Reactors Cocurrent Versus Countercurrent Operations - Art5Vicente SosaОценок пока нет
- High Temp Grease Technical Data SheetДокумент2 страницыHigh Temp Grease Technical Data SheetErickОценок пока нет
- Disassembly & Assembly Instructions Multistage Centrifugal PumpsДокумент28 страницDisassembly & Assembly Instructions Multistage Centrifugal Pumpsjalw88100% (1)
- Unit 7 - Week 4: Assignment 4Документ3 страницыUnit 7 - Week 4: Assignment 4Ananda VijayasarathyОценок пока нет
- Ophthalmic InsertsДокумент28 страницOphthalmic InsertsShendi SuryanaОценок пока нет
- Lecture 2 - Clinical and Lab Steps - Preliminary Impression-Preliminary Cast (3.03)Документ42 страницыLecture 2 - Clinical and Lab Steps - Preliminary Impression-Preliminary Cast (3.03)Ioachim FriedmannОценок пока нет
- D 5117 - 96 - Rduxmtctukve PDFДокумент4 страницыD 5117 - 96 - Rduxmtctukve PDFchabibОценок пока нет
- Final Product 7 Learning Cycles - 6th Grade MatterДокумент46 страницFinal Product 7 Learning Cycles - 6th Grade Matterapi-310725472Оценок пока нет
- Motorized Butterfly Valve With Actuator JJ (WAFN3 - MSEENR)Документ10 страницMotorized Butterfly Valve With Actuator JJ (WAFN3 - MSEENR)hvacvn1984Оценок пока нет
- Physical Properties of SolutionДокумент3 страницыPhysical Properties of SolutionRhye Tabaday LopezОценок пока нет
- School WIFA Supplementation FormДокумент2 страницыSchool WIFA Supplementation FormSteffi100% (1)
- Cambridge Lower Secondary Progression Test: Science Paper 2Документ16 страницCambridge Lower Secondary Progression Test: Science Paper 2mahdi hassanОценок пока нет
- FT8 MOBILEPAC Gas Turbine PackageДокумент2 страницыFT8 MOBILEPAC Gas Turbine Packageudelmark100% (1)
- Alimentos Funcionais em UanДокумент12 страницAlimentos Funcionais em UanEduardo MartinsОценок пока нет
- LINGKUP PEKERJAAN Dan DED PERTASHOP GEN3 SENT (1) - Copy-DikonversiДокумент7 страницLINGKUP PEKERJAAN Dan DED PERTASHOP GEN3 SENT (1) - Copy-Dikonversiyovero aji dirgantara100% (3)
- Identification and Quantification of Secondary Metabolites .. - PDFДокумент16 страницIdentification and Quantification of Secondary Metabolites .. - PDFAmandaОценок пока нет
- Grain Size Vs Heat TreatmentДокумент24 страницыGrain Size Vs Heat TreatmentRyan ChenОценок пока нет
- FDA Guidance on Dosage Delivery Devices for Liquid OTC DrugsДокумент14 страницFDA Guidance on Dosage Delivery Devices for Liquid OTC DrugsmkyousufОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S1319610311002407 MainДокумент14 страниц1 s2.0 S1319610311002407 Mainspanu oanaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESДокумент7 страницChapter 17 - BREATHING AND EXCHANGE OF GASESprernatiwary508Оценок пока нет
- Coaxial Cables: Section VДокумент6 страницCoaxial Cables: Section VFrancisco CamposОценок пока нет
- Nu 5100 5100eg HalfДокумент19 страницNu 5100 5100eg HalfCristian AedoОценок пока нет
- Pittsburgh Coal ConferenceДокумент68 страницPittsburgh Coal ConferenceNileshОценок пока нет
- Industrial Training Presentation: PETRONAS Chemicals Methanol Labuan Sdn. BHDДокумент9 страницIndustrial Training Presentation: PETRONAS Chemicals Methanol Labuan Sdn. BHDAbdul AzizОценок пока нет
- 1 MergedДокумент8 страниц1 MergedNo NameОценок пока нет
- Cyanide-Free Gold Ore Dressing Agent PDFДокумент13 страницCyanide-Free Gold Ore Dressing Agent PDFAldemar Arciniegas100% (1)
- Cunningham 2011Документ3 страницыCunningham 2011januar fitrianaОценок пока нет
- Spent Coffee Grounds Heat Coffee RoastingДокумент15 страницSpent Coffee Grounds Heat Coffee RoastingMJundiОценок пока нет
- EP0070932B1Документ5 страницEP0070932B1bayuОценок пока нет