Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
TOS III Important Notes
Загружено:
Patrick CapillanАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TOS III Important Notes
Загружено:
Patrick CapillanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
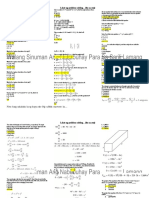
TOS III Important Notes B.
Two-Span Beams
Analysis of Indeterminate Beams
1. Two-Spans with Both Exterior Supports Fixed
Load, shear, moment, slope and deflection are related and the
relationships are shown below. A B C
V(x) = ∫ 𝑤(𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 w(x) = dV(x)/dx 1) Find DFs.
K EI
M(x) = ∫ 𝑉(𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 V(x) = dM(x)/dx DF = ,K=
K L
1/L1
EI dy(x)/dx = ∫ 𝑀(𝑥) 𝑑𝑥 M(x) = EI d[dy(x)/dx]/dx DFAB = DFBA = A
(1 / L1 ) (1 / L2 )
𝑑𝑦(𝑥) DFBC = DFCB = 1 - A B
y(x) = ∫[ ] 𝑑𝑥 dy(x)/dx = d[y(x)]/dx
𝑑𝑥
2) Find FEMs.
As an aside, from the above relationships, it can be seen that FEMAB C
FEMBA D
EIy(x) = ∬ 𝑀(𝑥)𝑑𝑥 FEMBC E
M(x) = ∬ 𝑤(𝑥)𝑑𝑥. FEMCB F
3) Use Cañete Cross Formulas
1
a. MA = FEMAB + 2 DFBA (FEMBA – FEMBC)
A. Single Span Beams 1
MA = C + 2 A (D – E)
With Overhang (eg. Frame with Overhang):
1. Simply Supported 1
a.1. MA = FEMAB + 2 DFBA [FEMBA – (FEMBC + Moverhang)]
Analysis of a simply supported beam is done in a straight
forward manner with the use of equilibrium equations since this
is determinate. b. MB = (FEMBA* DFBC) + (FEMBC*DFBA)
2. Fixed Ends MB = DB + EA
For beams with both ends fixed, determining the fixed-end With Overhang (eg. Frame with Overhang):
moments essentially completes the analysis. b.1. MB = (FEMBA* DFBC) + [(FEMBC + Moverhang) * DFBA]
3. Propped Cantilever
1
1) Determine the fixed-end moments. c. MC = FEMCB + 2 DFBC (FEMBC – FEMBA)
2) Balance the fixed-end moment in the simply supported end 1
MC = F + 2 B (E – D)
and carry-over half of this to the fixed end.
With Overhang (eg. Frame with Overhang):
1
c.1. MC = FEMCB + 2 DFBC [(FEMBC + Moverhang)– FEMBA]
2. Two-Spans with One Exterior End Fixed and the other Exterior 3. Two-Spans with Both Exterior Ends Simply Supported
End Simply Supported
A B C
1) Find DFs.
A B C K EI
DF = ,K=
K L
1) Find DFs. 1/L1
DFAB = DFBA = A
K EI (1 / L1 ) (1 / L2 )
DF = ,K=
K L DFBC = DFCB = 1 - A B
1/L1 2) Find FEMs.
DFAB = DFBA = A
(1 / L1 ) (0.75 / L2 ) FEMAB C
DFBC = DFCB = 1 - A B FEMBA D
2) Find FEMs. FEMBC E
FEMAB C FEMCB F
FEMBA D 3) Use Cañete Cross Formulas.
FEMBC E a. MA = 0 or moment of overhang
FEMCB F
3) Use Cañete Cross Formulas. 1
b. MB = DFBC (FEMBA + 2 FEMAB) + DFBA (FEMBC + 2 FEMCB)
1
1 1
a. MA = FEMAB + 2 DFBA [FEMBA – (FEMBC + 2 FEMCB)] 1 1
MB = B (D + 2 C) + A (E + 2 F)
1 1
MA = C + 2 A [D – (E + 2 F)] With Overhang:
With Overhang: 1 1
b.1. MB = DFBC [FEMBA + (FEMAB - MA)] + DFBA (FEMBC + ( FEMCB - MB)]
1 1 2 2
a.1. MA = FEMAB + 2DFBA{FEMBA – [FEMBC + 2 (FEMCB + Moverhang)]}
c. MC = 0 or moment of overhang
b. MB = (FEMBA* DFBC) + (FEMBC*DFBA) C. Three-Span Beams
MB = DB + EA
With Overhang:
1
a. Use “Three Moment Equation”
b.1. MB = (FEMBA* DFBC) + DFBA [FEMBC + 2 (FEMCB + Moverhang)]
6𝐴1𝑎1 6𝐴2𝑏2 ℎ𝐴 ℎ𝐶
MAL1 + 2MB (L1 + L2) + MCL2 + 𝐿1
+ 𝐿2
= 6EI ( 𝐿1
+ 𝐿2
)
c. MC = 0 or moment of overhang
Вам также может понравиться
- Error RulesДокумент2 страницыError RulesWong JiayangОценок пока нет
- ဒသမတန္း အခန္း (၉) mathДокумент11 страницဒသမတန္း အခန္း (၉) mathZakir Amad 320% (1)
- Improper Integrals: MATH23 Multivariable CalculusДокумент22 страницыImproper Integrals: MATH23 Multivariable CalculusRyan Jhay YangОценок пока нет
- Force Method Analysis of Indeterminate StructuresДокумент246 страницForce Method Analysis of Indeterminate StructuresSajawal iqbal gillОценок пока нет
- Menaka GC MAT129 Krug Assignment 1p7 Due 09/20/2020 at 11:59pm EDTДокумент6 страницMenaka GC MAT129 Krug Assignment 1p7 Due 09/20/2020 at 11:59pm EDTMenaka GcОценок пока нет
- Cycle 1 Review Part 3Документ2 страницыCycle 1 Review Part 3kiranmahal451Оценок пока нет
- Derivation of the free vibration decay formula with Coulomb frictionДокумент2 страницыDerivation of the free vibration decay formula with Coulomb frictionAnjaneya TiwariОценок пока нет
- Question Paper 1Документ3 страницыQuestion Paper 1Sanjeet KotaryaОценок пока нет
- International Competitions-International Zhautykov Olympiad-2007-155 PDFДокумент2 страницыInternational Competitions-International Zhautykov Olympiad-2007-155 PDFKetut LokaОценок пока нет
- Outline: - Motivation - Fuzzy Sets Basic ConceptsДокумент17 страницOutline: - Motivation - Fuzzy Sets Basic Conceptspankajbhatti1Оценок пока нет
- Analysis of Indeterminate Structures by Force MethodДокумент17 страницAnalysis of Indeterminate Structures by Force Methodatish k100% (2)
- Mathematics Question Paper 2017 BCA From D UniversityДокумент18 страницMathematics Question Paper 2017 BCA From D Universitywizyu freianОценок пока нет
- Krishna's - Integral Calculus, Edition-3Документ229 страницKrishna's - Integral Calculus, Edition-3Jayshri HuddarОценок пока нет
- Substitute Frame AnalysisДокумент5 страницSubstitute Frame Analysissiniann7100% (1)
- ALPS Mathematics 2201 - JEE 2022: SyllabusДокумент14 страницALPS Mathematics 2201 - JEE 2022: SyllabusYash Dhoke100% (1)
- Properties of Quadrilaterals: Mathematics IiiДокумент28 страницProperties of Quadrilaterals: Mathematics IiiRenel MapindanОценок пока нет
- Definite IntegralДокумент129 страницDefinite IntegralAnas MohammedОценок пока нет
- RD Sharma Class 12 Volume 2Документ958 страницRD Sharma Class 12 Volume 2Shital Niraj Mashru100% (2)
- Mindworkzz Formulae SheetДокумент66 страницMindworkzz Formulae SheetDeepak MОценок пока нет
- 5 - Moment-Area Method - R2.2Документ100 страниц5 - Moment-Area Method - R2.2F FОценок пока нет
- Wald - General Relativity: Kevin Chen October 29, 2017Документ2 страницыWald - General Relativity: Kevin Chen October 29, 2017Kevin ChenОценок пока нет
- Limit, Continuity & Differentiability - Agni Practice SheetДокумент39 страницLimit, Continuity & Differentiability - Agni Practice SheetNitin choudharyОценок пока нет
- Circle Geometry Part 4Документ6 страницCircle Geometry Part 4JonsJJJОценок пока нет
- Lahat NG Problem Solving... (Ito Na Yun)Документ4 страницыLahat NG Problem Solving... (Ito Na Yun)Juan Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- 1st Rev Maths G 12Документ9 страниц1st Rev Maths G 12Tesfamichael FufaОценок пока нет
- Mathematical Association of AmericaДокумент4 страницыMathematical Association of Americatim penttilaОценок пока нет
- NK C SI R: Exercise - 01Документ2 страницыNK C SI R: Exercise - 01Fahad warsiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Review Engineering StaticsДокумент6 страницChapter 6 Review Engineering StaticsMarcosОценок пока нет
- Ms 2012 s2 PaperДокумент17 страницMs 2012 s2 PaperVenu GeorgeОценок пока нет
- Topic 1 Theory Structure PDFДокумент17 страницTopic 1 Theory Structure PDFnrhdyaaОценок пока нет
- Slope Deflection Method (SDM) ExplainedДокумент6 страницSlope Deflection Method (SDM) ExplainedJayLord Mico PacisОценок пока нет
- Claypeyrons TheoremДокумент12 страницClaypeyrons TheoremGoutham NaikОценок пока нет
- 19.1 Vectors and ScalarsДокумент6 страниц19.1 Vectors and ScalarsisamalhassanОценок пока нет
- Solution of TrianglesДокумент57 страницSolution of TrianglesAvishkar JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Bismillah Presentasi B.inggДокумент1 страницаBismillah Presentasi B.inggppg.yovifitrianto91Оценок пока нет
- Problem 2.4: Given: Find: SolutionДокумент1 страницаProblem 2.4: Given: Find: SolutionKauê BrittoОценок пока нет
- Angle Chasing Techniques and Problems from Randolph High School Math LeagueДокумент4 страницыAngle Chasing Techniques and Problems from Randolph High School Math LeagueAngela Angie BuseskaОценок пока нет
- Simplification of Switching FunctionsДокумент72 страницыSimplification of Switching FunctionsAnkur BajpaiОценок пока нет
- Slope Deflection MethodДокумент9 страницSlope Deflection MethodPravin KenОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 TEST - AP Calculus PT: Part A No CalculatorДокумент12 страницChapter 2 TEST - AP Calculus PT: Part A No CalculatorAsh IvyОценок пока нет
- C4 Partial Fractions Maths RevisionДокумент15 страницC4 Partial Fractions Maths RevisionZanfalawy BashaОценок пока нет
- Integral Calculus - 2 Definite Integrals and AreaДокумент51 страницаIntegral Calculus - 2 Definite Integrals and Arearvnkrish24Оценок пока нет
- International Indian School worksheet on mathematicsДокумент5 страницInternational Indian School worksheet on mathematicsShweta GajbhiyeОценок пока нет
- LinearAlgebraI 2023 MatrdetsДокумент27 страницLinearAlgebraI 2023 Matrdetsguilhermeab2008Оценок пока нет
- Some Aspects of Structural Dynamics: Appendix BДокумент26 страницSome Aspects of Structural Dynamics: Appendix BEdgar Enrique Vilca RomeroОценок пока нет
- The Baker-Campbell-Hausdorff Formula Physics 341Документ3 страницыThe Baker-Campbell-Hausdorff Formula Physics 341Sana ElgamalОценок пока нет
- C 10 P T S M P: Hapter Hysical Reatments of OME Athematical RoblemsДокумент11 страницC 10 P T S M P: Hapter Hysical Reatments of OME Athematical RoblemsDestroyer74Оценок пока нет
- Parallel Reaction NetworkДокумент3 страницыParallel Reaction NetworkMahnoor AbbasОценок пока нет
- 4 M Ex LimitesДокумент3 страницы4 M Ex Limiteselizabethxsmith197Оценок пока нет
- Multiple choice exam on exponential and logarithmic functionsДокумент17 страницMultiple choice exam on exponential and logarithmic functionsValeria Olmos FernándezОценок пока нет
- X X X F: Worksheet On LinearizationДокумент3 страницыX X X F: Worksheet On LinearizationaiОценок пока нет
- Mensuration II (Important Results)Документ13 страницMensuration II (Important Results)Shubham SharmaОценок пока нет
- Continuous Uniform DistributionДокумент5 страницContinuous Uniform Distributionreviewamit100% (1)
- Trư NG PH ThôngДокумент9 страницTrư NG PH ThôngTien Dat LuuОценок пока нет
- CPP DEFINITE INTEGRATIONДокумент8 страницCPP DEFINITE INTEGRATIONAbhay SinghОценок пока нет
- Hermite-Hadamard Type Inequalities for (α, m) - Convex Functions via Fractional IntegralsДокумент11 страницHermite-Hadamard Type Inequalities for (α, m) - Convex Functions via Fractional IntegralsMuhammad Jamal KhanОценок пока нет
- M3PA50 chp1Документ11 страницM3PA50 chp1osama hasanОценок пока нет
- U2A9 - SummativeДокумент5 страницU2A9 - SummativeRina FakhryОценок пока нет
- Dianne Salarzon Barcelona: Cashier'SДокумент2 страницыDianne Salarzon Barcelona: Cashier'SDianneBarcelonaОценок пока нет
- Finite Element Simulation of Retrofitting of RCC Beam PDFДокумент5 страницFinite Element Simulation of Retrofitting of RCC Beam PDFPatrick CapillanОценок пока нет
- Abaca Manila Hemp PDFДокумент13 страницAbaca Manila Hemp PDFPatrick CapillanОценок пока нет
- Chapter3 PDFДокумент11 страницChapter3 PDFPatrick CapillanОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER2Документ8 страницCHAPTER2Patrick CapillanОценок пока нет
- Abaca Manila Hemp PDFДокумент13 страницAbaca Manila Hemp PDFPatrick CapillanОценок пока нет
- Preliminaries PDFДокумент3 страницыPreliminaries PDFPatrick CapillanОценок пока нет
- ASTM C293 Concrete CenterPointLoadingTestДокумент4 страницыASTM C293 Concrete CenterPointLoadingTestMark Lester Brosas TorreonОценок пока нет
- Fixed End MomentsДокумент1 страницаFixed End MomentsHarold DeanОценок пока нет
- The October 2019 Series of Earthquakes in Cotabato and VicinityДокумент1 страницаThe October 2019 Series of Earthquakes in Cotabato and VicinityPatrick CapillanОценок пока нет
- Grammarism Ed Ing Adjectives Test 4 1189424Документ2 страницыGrammarism Ed Ing Adjectives Test 4 1189424Royal Stars Drama AcademyОценок пока нет
- Hyundai Elevator Manual Helmon 2000 InstructionДокумент27 страницHyundai Elevator Manual Helmon 2000 InstructionReynold Suarez100% (1)
- Operating and Installation Guide For The Digital Instrument: Motoscope Tiny / Speedster / VintageДокумент12 страницOperating and Installation Guide For The Digital Instrument: Motoscope Tiny / Speedster / Vintagepeter timmermansОценок пока нет
- Civil Engineering Subjects (1st - 5th Year) - 1Документ5 страницCivil Engineering Subjects (1st - 5th Year) - 1Vincent TayagОценок пока нет
- Fe in Black TeaДокумент6 страницFe in Black TeaHerni Nur AeniОценок пока нет
- GSM Based Power Grid Monitoring SystemДокумент41 страницаGSM Based Power Grid Monitoring SystemPreetham SurepallyОценок пока нет
- 3.1 The Truth About Air TravelДокумент14 страниц3.1 The Truth About Air TravelСвітлана Свирид0% (1)
- Cardiopulmonary System: Relevant Anatomy & Physiology: HeartДокумент12 страницCardiopulmonary System: Relevant Anatomy & Physiology: HeartJulia SalvioОценок пока нет
- MACRO-ETCHING SOLUTIONS FOR ALUMINIUM ALLOYSДокумент1 страницаMACRO-ETCHING SOLUTIONS FOR ALUMINIUM ALLOYSsensoham03Оценок пока нет
- ASIAN LIVESTOCK PERSPECTIVESДокумент18 страницASIAN LIVESTOCK PERSPECTIVESMuadz AbdurrahmanОценок пока нет
- Module 6 - FormworksДокумент8 страницModule 6 - FormworksAldrich Francis Ortiz Peñaflor100% (1)
- Vapour Bar Exchange IMFL PackageДокумент4 страницыVapour Bar Exchange IMFL PackageNishank AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Nitration of Methyl BenzoateДокумент3 страницыNitration of Methyl BenzoateDaniel McDermottОценок пока нет
- Fault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - CriticalДокумент3 страницыFault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - Criticalhamilton miranda100% (1)
- Purification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneityДокумент9 страницPurification of Morphologically and Functionally Intact Human Basophils To Near HomogeneitySinaí GutierrezОценок пока нет
- Australian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1Документ32 страницыAustralian 9 Grade Physics Lesson 1binoyrajcrОценок пока нет
- History of Cancer ChemotherapyДокумент9 страницHistory of Cancer ChemotherapyJoydeep MajumdarОценок пока нет
- Lab Journal 4 14032023 104921amДокумент8 страницLab Journal 4 14032023 104921amHammad MashwaniОценок пока нет
- I Wanna Be Yours Arctic Monkeys Love SongДокумент3 страницыI Wanna Be Yours Arctic Monkeys Love SongAndréia E NiltonОценок пока нет
- Horizontal Projectile WSДокумент3 страницыHorizontal Projectile WSForsbergPhysicsОценок пока нет
- Service Manual: EQ1030T47D-820 Light Commercial TruckДокумент175 страницService Manual: EQ1030T47D-820 Light Commercial TruckYonny ColqueОценок пока нет
- Home Contents Vehicle Boat Cover Policy Sample Westpac NZДокумент27 страницHome Contents Vehicle Boat Cover Policy Sample Westpac NZRobin Rutter-BaumannОценок пока нет
- Shariff NДокумент4 страницыShariff NKruu ChinnuОценок пока нет
- Lab 1 Free Fall GEC - CEA21 - OERSTEDДокумент6 страницLab 1 Free Fall GEC - CEA21 - OERSTEDLee-Ann LimОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of VolleyballДокумент2 страницыFundamentals of VolleyballLawrence CezarОценок пока нет
- Difference Between AerospaceДокумент2 страницыDifference Between AerospaceSyawalMaulanaОценок пока нет
- Variants of NormalДокумент9 страницVariants of NormalFaizah HannyОценок пока нет
- NNDC Planning Applications 4oct - 11 OctДокумент4 страницыNNDC Planning Applications 4oct - 11 OctRichard SmithОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 5 Q1 W10Документ31 страницаMathematics 5 Q1 W10Aices Jasmin Melgar BongaoОценок пока нет
- Modeling Vessel Impacts for Lock Wall DesignДокумент15 страницModeling Vessel Impacts for Lock Wall DesignSalam FaithОценок пока нет