Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Hydrocarbons
Загружено:
Leonard SawyerИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Hydrocarbons
Загружено:
Leonard SawyerАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Name:____________________________
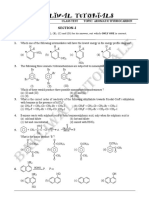
Unit VIII: Hydrocarbons test 3.1
Note: For clarity hydrogens have been omitted from most structures on this test. Whenever carbon
does not appear to have the required number of bonds, it is understood that the “missing”
bonds go to hydrogen atoms.
Multiple Choice
___ 1. A saturated compound is one that (1) contains only carbon-carbon sigma bonds; (2) contains
at least one carbon-carbon pi bond; (3) contains at least one carbon-carbon double or triple
bond; (4) both 1 and 3; (5) both 2 and 3; (1,2) is not described by any of the above answers.
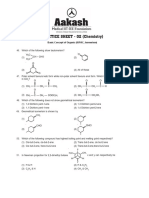
___ 2. Which of the following structures best describes an unsaturated compound?
C C C
C C C C C C C C C C
C C C C C C C
(1) (2) (3) C (5)
(4)
(1,2) both 2 and 5 (1,3) all but 2 (1,4) all but 5 (1,5) all but 4 and 5
___ 3. The first three members of a homologous series are: CH4O, C2 H6O2 , C3 H8O 3. The fourth
member of this series would be (1)C4 H10O4 ; (2) C4 H10O; (3) C 10H4O 4; (4) C 4H10O 2; (5) none
of the above.
___ 4. The geometry associated with carbon-carbon triple bonds is (1) linear; (2) tetrahedral;
(3) planar; (4) octahedral; (5) biplanar.
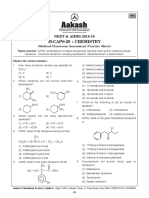
___ 5. Which of the following structures contain a chiral or asymmetric carbon atom?
Cl Cl Br
Cl I Cl
CH3 CH3 CH3
C C Br I C CH3 C C C
C C
Br Br Br Cl
Br I
(1) (2) (4)
(3)
___ 6. Isomers are compounds that (1) have the same number of carbon atoms but a different
number of hydrogen atoms; (2) have the same number of hydrogen atoms but a different
number of carbon atoms; (3) have the same number and kind of atoms in a molecule but
differ in structure; (4) have the same kind of atoms in their molecular formulas but differ in
the number of these atoms present; (5) none of the above.
___ 7. The two carbons joined by a triple bond in an alkyne are connected by (1) three sigma bonds;
(2) one sigma bond and two pi bonds; (3) three pi bonds; (4) two identical sp3 bonds;
(5) two sigma and one pi bond.
Hydrocarbons test 3.1 1998 page 1 of 5
___ 8 Which of the following illustrate the process of hydrogenation?
(1) C C C C
C C + H2 C C
(2) C C + H2 C C
C C C C
(3) C C C C + H2
C C C C
Br
(4) C C + Br 2 C C + H2
C C C C
Br
___ 9. In a certain laboratory exercise Snoopy mixed 5 drops of a solution of bromine water with
one milliliter of each of the following substances: butane, 2-butene, 1, butene, benzene, and
methyl benzene. The experiment was carried out at room temperature. Which of the
substances should react rapidly with the bromine? (1) butane; (2) 1-butene and 2-butene;
(3) benzene and methyl benzene; (4) 2-butene and benzene; (5) all but butane.
___ 10. Whenever two or more equally valid structures can be drawn for a molecule involving only
the relative positions of double and single bonds, ___________ is said to occur? (1) resonance;
(2) geometric isomerism; (3) stereoisomerism; (4) cis configuration; (5) trans configuration.
___ 11. Which of the following best explain why there are so many carbon compounds?
(1) concatenation; (2) isomerism; (3) multiple oxidation states are possible for carbon; (4) both
1 and 2; (5) both 2 and 3.
___ 12. Hydrogenation is the process of (1) adding hydrogen to unsaturated compounds; (2) adding
hydrogen to saturated compounds; (3) removing hydrogen from saturated compounds;
(4) removing hydrogen from unsaturated compounds.
___ 13. The formula for 2-nonacontene, an 90 carbon alkyne, would be
(1)C90 H182 ; (2) C90 H180 ; (3) C90 H178 ; (4) C90 H176.
___ 14. In order to explain the geometry of organic compounds, among other properties, hybrid
orbitals are postulated to exist. What type of hybridization exists for the carbon atom in
order to explain the geometry associated with a carbon-carbon single bond?
(1) sp3; (2) s3 p; (3) s2 p; (4) sp2 ; (5) sp.
___ 15. As explained in class, resonance structures occur when a (1) sigma bond attempts to form in
two places at the same time; (2) pi bond attempts to form in two places at the same time;
(3) two pi bonds attempt to form between adjacent hydrogen atoms; (4) two pi bonds attempt
to form an arene without carbon atoms; (5) a hybrid warp orbital orientates perpendicular
to the axis of a sigma-pi intercept vector involving six carbon atoms.
Hydrocarbons test 3.1 1998 page 2 of 5
___ 16. Which of the following illustrates the formation of a pi bond? (Note: The following legend
applies to the various figures used in all answers.)
Carbon atom Carbon atom
• p orbital
s orbital
oribital overlap
(1) +
oribital overlap
(2) + • •
(3) + orbital overlap
oribital overlap
(4) • + • • •
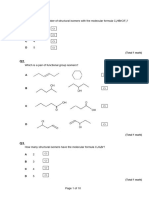
___ 17. Which of the structures below is not an isomer of pentane?
C C
C C C C C C C C C C
C C C C C C C
C
(1) (2) (3) (4)
___ 18. The process of breaking up large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller molecules is known
as (1) resonance; (2) hydrogenation; (3) dehydrogenation; (4) cracking.
Hydrocarbons test 3.1 1998 page 3 of 5
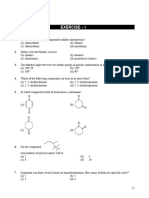
Matching
Questions 19-29 pertain to the structures below and to the right. Match up the IUC name with a
corresponding structure, if a structure exists.
C C C C
C C C C C C C
C C C C C C C C C C C C
C C C C
C C
C C (4)
(3) (5) (1,2)
C
(1)
(2)
CH3
C C C C
C C C
___ 19. 2,3 dimethyl 1-butene C C
C C C
___ 20. 2,3 dimethyl 1-butyne C C
CH3
___ 21. 1, 3 dimethyl benzene (1,3) (1,4)
(1,5)
___ 22. 1, 4 dimethyl benzene
___ 23. anthracene CH3 CH3
___ 24. 3 methyl heptane CH3
CH3 CH3 CH3
___ 25. 2 pentene
(2,3) (2,4) (2,5)
___ 26. hexane
___ 27. 3 ethyl pentane
___ 28. an isomer of heptane (3,5) no structure matches.
(3,4)
___ 29. 2,3 dimethyl butane
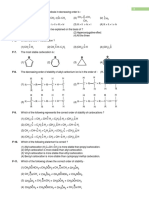
___ 30. Which of the following is in favor of hurt?
C C C C C
C C C C C C C C
C
(1) (2) (3) (4)
Hydrocarbons test 3.1 1998 page 4 of 5
Short Answer
1. Name each of the six structures below. (Note: If you feel a structure cannot exist, for whatever
reason, you must answer with “impossible”.)
a) b) C c)
C2 H5 C C C
C C
C C
C2 H5 C
C
d) C C e) f) C
C
C C C C C C
C C C C C C C C
C
a) _________________________ b) __________________________
c) _________________________ d) __________________________
e) _________________________ f) ___________________________
2. Draw a structure for benzene, showing all hydrogen atoms.
Hydrocarbons test 3.1 1998 page 5 of 5
Вам также может понравиться
- Solution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringОт EverandSolution Manual for The Elements of Polymer Science and EngineeringРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (3)
- G.O.C & Isomerism - DPP 04 (Of Lec 07) - (Arjuna JEE 2023)Документ3 страницыG.O.C & Isomerism - DPP 04 (Of Lec 07) - (Arjuna JEE 2023)jeemainsmaterial97Оценок пока нет
- PRACTICE SHEET - 02 (Chemistry) : Basic Concept of Organic (IUPAC, Isomerism)Документ5 страницPRACTICE SHEET - 02 (Chemistry) : Basic Concept of Organic (IUPAC, Isomerism)ABD 17Оценок пока нет
- Inorganic DPP PDFДокумент3 страницыInorganic DPP PDFashutosh99878Оценок пока нет
- M-Caps-29: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Документ3 страницыM-Caps-29: Chemistry: NEET & AIIMS 2018-19Vishal SinghОценок пока нет
- NCERT - OrganicДокумент106 страницNCERT - OrganicSridhar ChowdaryОценок пока нет
- Isomerism DPP - With Solution PDFДокумент20 страницIsomerism DPP - With Solution PDFPiyush Agarwal50% (2)
- Classification and Nomenclature of Organic Compound: BR BR BR BRДокумент6 страницClassification and Nomenclature of Organic Compound: BR BR BR BRShin ChanОценок пока нет
- ViewpdfДокумент12 страницViewpdfBhargav SinghaОценок пока нет
- Assessed Homework Mark SchemeДокумент4 страницыAssessed Homework Mark SchemelfcluishoughtonОценок пока нет
- ExerciseДокумент50 страницExerciseAbhiОценок пока нет
- PRACTICE SHEET - 03 (Chemistry) : CH - CH - CH CN CN CNДокумент3 страницыPRACTICE SHEET - 03 (Chemistry) : CH - CH - CH CN CN CNABD 17Оценок пока нет
- Chemistry Max Marks: 88 Section - I (Integer Answer Type)Документ10 страницChemistry Max Marks: 88 Section - I (Integer Answer Type)Thatipally AadithhyaОценок пока нет
- Isomerism Review 2Документ10 страницIsomerism Review 2ayesha sheikhОценок пока нет
- Ocd PP Special On Taut Omer Is MДокумент3 страницыOcd PP Special On Taut Omer Is MKartik YadavОценок пока нет
- C1102 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Lebanese University Faculty of SciencesДокумент84 страницыC1102 Introduction To Organic Chemistry: Lebanese University Faculty of SciencesBlack InsomniaОценок пока нет
- 65125b4ef6556b001895c29c - ## - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - DPP 05 (Of Lec 12)Документ2 страницы65125b4ef6556b001895c29c - ## - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - DPP 05 (Of Lec 12)pattarkaustubhОценок пока нет
- Chem 2016Документ4 страницыChem 2016Shubhankar ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- 02 - Coordination CompoundsДокумент8 страниц02 - Coordination CompoundsNithin KarthikeyanОценок пока нет
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination of CompoundsДокумент12 страницNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 9 Coordination of Compoundskahargulab71Оценок пока нет
- Christ King Academy: Subject:CHEMISTRY Test Max Marks: 30 General Organic ChemistryДокумент5 страницChrist King Academy: Subject:CHEMISTRY Test Max Marks: 30 General Organic ChemistryajaybolarОценок пока нет
- Coordination Compounds ExercisesДокумент55 страницCoordination Compounds Exercisesaamir siddiquiОценок пока нет
- DPP 6Документ3 страницыDPP 6ashutosh99878Оценок пока нет
- 01 Funda Gen OrgДокумент21 страница01 Funda Gen OrgnilsghОценок пока нет
- 12th NEET ANSWERS - 30 - 04 - 2023Документ9 страниц12th NEET ANSWERS - 30 - 04 - 2023studyloverx1234Оценок пока нет
- 235practice Exam 1Документ11 страниц235practice Exam 1Zia RathoreОценок пока нет
- Thoi Khoa BieuДокумент6 страницThoi Khoa BieuDinh Oanh TacОценок пока нет
- General Organic Chemistry GocДокумент21 страницаGeneral Organic Chemistry GocsquadralsupremeОценок пока нет
- Goc Stereo PDFДокумент32 страницыGoc Stereo PDFDeepak GargОценок пока нет
- 6.DAY-8 CHE - Organic Chemistry Electron Migration Effects & Reagents - 25-05-2020 PDFДокумент7 страниц6.DAY-8 CHE - Organic Chemistry Electron Migration Effects & Reagents - 25-05-2020 PDFRamakrishna ReddyОценок пока нет
- SR Elite, Aiims s60, MPL & LTC Aits Grand Test - 19 Paper (29!04!2023)Документ30 страницSR Elite, Aiims s60, MPL & LTC Aits Grand Test - 19 Paper (29!04!2023)vulurakashsharma2005Оценок пока нет
- JEE Advanced Paper 1 Chemistry SolutionДокумент11 страницJEE Advanced Paper 1 Chemistry SolutionIndian Placid TuberОценок пока нет
- Isomers Exam QДокумент10 страницIsomers Exam Qarychan418Оценок пока нет
- Questions in TEST BOOKLET: 100 MAX MARKS: 400 (+4/-1) : Minor 9Документ8 страницQuestions in TEST BOOKLET: 100 MAX MARKS: 400 (+4/-1) : Minor 9Sanskar SahuОценок пока нет
- Exam #2 PracticeДокумент7 страницExam #2 PracticeNiel Felix Villanueva BalakidОценок пока нет
- General Organic Chemistry - DPP 01 - Goc-dpp-01-Lakshya (Jee)Документ4 страницыGeneral Organic Chemistry - DPP 01 - Goc-dpp-01-Lakshya (Jee)SS MENTOR100% (3)
- 2.10 Alcohols Extra Questions Ms 1.: Mill Hill High School 1Документ15 страниц2.10 Alcohols Extra Questions Ms 1.: Mill Hill High School 1Emil Van Der MeerОценок пока нет
- JEE Main 2019 Paper Answer Chemistry 10-01-2019 2ndДокумент5 страницJEE Main 2019 Paper Answer Chemistry 10-01-2019 2ndDeepak SainiОценок пока нет
- Coordination Compounds 109 QuestionsДокумент19 страницCoordination Compounds 109 QuestionsAnkit kumarОценок пока нет
- First Term Test Papers ScienceДокумент5 страницFirst Term Test Papers ScienceDinhas SenulОценок пока нет
- IsomerismДокумент2 страницыIsomerismricardobabu6t9Оценок пока нет
- Black Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7Документ8 страницBlack Board Problems For JEE Advanced Set-7DikshantОценок пока нет
- AHC TestДокумент4 страницыAHC TestArpan KumarОценок пока нет
- Organic Chem Mcqs PDFДокумент18 страницOrganic Chem Mcqs PDFDIPA NAGОценок пока нет
- Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University: School of Technology, GandhinagarДокумент2 страницыPandit Deendayal Petroleum University: School of Technology, GandhinagarHarsh ThakurОценок пока нет
- Dhisha Jee Mains and Neet-185-206Документ22 страницыDhisha Jee Mains and Neet-185-206jeevavelayyaОценок пока нет
- 474 - CHM 222Документ68 страниц474 - CHM 222Tariq AbdullahiОценок пока нет
- Isomerism Tut Ans Q1 To Q10 PDFДокумент5 страницIsomerism Tut Ans Q1 To Q10 PDFSundaravadivel Prabhav (Njc)Оценок пока нет
- Upload 2Документ5 страницUpload 2k.prarthu0909Оценок пока нет
- ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-30-07 - 13th ObjectiveДокумент6 страницORGANIC CHEMISTRY-30-07 - 13th ObjectiveRaju SinghОценок пока нет
- 13FINALSHEET06STEREOISOMERДокумент23 страницы13FINALSHEET06STEREOISOMERarryan keshanОценок пока нет
- IsomerismДокумент26 страницIsomerismsharmaekta1801Оценок пока нет
- Part Ii: Chemistry Section - I Single Correct Choice TypeДокумент7 страницPart Ii: Chemistry Section - I Single Correct Choice Typerupal108Оценок пока нет
- JEE Main 2019 Paper Answer Chemistry 09-01-2019 1stДокумент6 страницJEE Main 2019 Paper Answer Chemistry 09-01-2019 1stDeepak SainiОценок пока нет
- Coordination Compounds 19-06-2020Документ6 страницCoordination Compounds 19-06-2020Vanshaj GuptaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry - Aromatic HydrocarbonsДокумент4 страницыChemistry - Aromatic Hydrocarbonswakeetha cОценок пока нет
- Green Park Educational Institutions, Namakkal: Long Term - Chemistry (Worksheet)Документ4 страницыGreen Park Educational Institutions, Namakkal: Long Term - Chemistry (Worksheet)Monalisa PremkumarОценок пока нет
- Organics, Synthesis and Enthalpy MSДокумент47 страницOrganics, Synthesis and Enthalpy MSAnh Nguyễn VănОценок пока нет
- Covalent Bonding NotesДокумент39 страницCovalent Bonding NotesAmaris HopkinsОценок пока нет
- Grade 9 Activity Sheet On Chemical Bonding Activity: 5 "Balloon Volleyball"Документ1 страницаGrade 9 Activity Sheet On Chemical Bonding Activity: 5 "Balloon Volleyball"Junard AsentistaОценок пока нет
- A Hirshfeld Surface Analysis and Crystal StructureДокумент8 страницA Hirshfeld Surface Analysis and Crystal StructureLidiane MicheliniОценок пока нет
- Prelim Yearly Kiss NotesДокумент83 страницыPrelim Yearly Kiss NotesPercy Jack100% (1)
- 有机化学作业帮助Документ6 страниц有机化学作业帮助afefhrxqv100% (1)
- SRSEB Chem Module-1Документ73 страницыSRSEB Chem Module-1msani hibatuОценок пока нет
- University of Gour Banga: M.Sc. in Physics Two Years (Four Semesters) SyllabusДокумент23 страницыUniversity of Gour Banga: M.Sc. in Physics Two Years (Four Semesters) SyllabusBaishali BanerjeeОценок пока нет
- Questions & Answers: Indian Olympiad Qualifier in Junior Science 2020-21 (IOQJS) Part-IIДокумент13 страницQuestions & Answers: Indian Olympiad Qualifier in Junior Science 2020-21 (IOQJS) Part-IIYash PatelОценок пока нет
- Topic 3Документ22 страницыTopic 3ChaudhryAbdullahОценок пока нет
- Sz2-A MPC Final Mcs 2Документ4 страницыSz2-A MPC Final Mcs 2Kartik ThotaОценок пока нет
- Chinmaya Vidyalaya, Kannamaly: Sample Paper - 1Документ19 страницChinmaya Vidyalaya, Kannamaly: Sample Paper - 1Deanne Joe JohnsonОценок пока нет
- Exam 1 and Solutions (MEEN 464)Документ13 страницExam 1 and Solutions (MEEN 464)RotaveraОценок пока нет
- SESSION 9-10 - CHEMICAL BONDING PDFДокумент46 страницSESSION 9-10 - CHEMICAL BONDING PDFakiaОценок пока нет
- Bhavna LambaДокумент23 страницыBhavna LambaNithinОценок пока нет
- Lecture Presentation: Remembering General ChemistryДокумент73 страницыLecture Presentation: Remembering General ChemistryshahjafferОценок пока нет
- Adhesive Bonding 2Документ67 страницAdhesive Bonding 2Saud Aidrus100% (1)
- Royal Society of Chemistry Organometallic Chemis 048Документ468 страницRoyal Society of Chemistry Organometallic Chemis 048Hien During Thah67% (3)
- h2 Chem ChecklistДокумент3 страницыh2 Chem ChecklistJohn TanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 15 Water and Aqueous SystemДокумент12 страницChapter 15 Water and Aqueous System尼克 NickОценок пока нет
- Gamsat Notes FinalДокумент32 страницыGamsat Notes FinalBrickОценок пока нет
- Tetrachlorides and Oxides of Group 14 ElementsДокумент9 страницTetrachlorides and Oxides of Group 14 ElementsXue Yi LamОценок пока нет
- Experiment On Melting PointsДокумент6 страницExperiment On Melting PointsZira PiangОценок пока нет
- Apsis O1 Final Term SyllbussДокумент4 страницыApsis O1 Final Term SyllbussSnowYTОценок пока нет
- Hybridization: Definition: The Phenomenon of Mixing Up of Atomic Orbitals ofДокумент48 страницHybridization: Definition: The Phenomenon of Mixing Up of Atomic Orbitals ofIke Jayson RollonОценок пока нет
- 2023 Usnco Local Exam Local OriginalДокумент9 страниц2023 Usnco Local Exam Local Originalmuhammademiralyavich9876Оценок пока нет
- Kaplan + UWorldДокумент49 страницKaplan + UWorldELIOMAR ROSA-RAMONОценок пока нет
- Empirical & Molecular Formula 2 QPДокумент8 страницEmpirical & Molecular Formula 2 QPjade.davis0019Оценок пока нет
- Sample MCQs For Students of Semester IV Organic ChemistryДокумент5 страницSample MCQs For Students of Semester IV Organic ChemistryAppa ShitoleОценок пока нет
- Carbon and Its Compounds: Class 10 Science (Chemistry)Документ33 страницыCarbon and Its Compounds: Class 10 Science (Chemistry)Sarfraz AnsariОценок пока нет
- Sains - KBSM - Additional Science Form 4Документ14 страницSains - KBSM - Additional Science Form 4Sekolah Portal79% (14)