Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Unit 5 The Perfect Tense
Загружено:
Jorge LunaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Unit 5 The Perfect Tense
Загружено:
Jorge LunaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UNIT 5
THE PRESENT PERFECT
The present perfect is formed from the present tense of the verb have and the past participle of a verb.
1.1 USE
We use the present perfect tense:
A. for something that started in the past and continues in the present:
They’ve been married for nearly fifty years.
She has lived in Liverpool all her life.
We often use a clause with since to show when something started in the past:
I have worked here since I left school.
I’ve watched that programme every week since it started.
B. when we are talking about our experience up to the present:
Note: We often use the adverb ever to talk about experience up to the present:
My last birthday was the worst day I have ever had.
Note: and we use never for the negative form:
Have you ever met George?
Yes, but I’ve never met his wife.
C. For something that happened in the past but is important at the time of speaking:
I can’t get in the house. I’ve lost my keys.
Teresa isn’t at home. I think she has gone shopping.
I’m tired out. I’ve been working all day.
D. When the speaker wants to put emphasis on the result:
She has written five letters.
E. We can also use the present perfect to talk about something that happened recently:
She has cooked dinner.
I've just seen Lucy.
1.2 KEY WORDS
A. Since and for
Since is used with a point in time, and means “from that point in time until the present.”
Use since with dates (2011, January, Tuesday, etc.), times (6:15, noon, this morning, etc.), and past
Página 1
events (I was a child, he graduated from college, etc).
Unit 5 Inglés Técnico II
• “I’ve gone to the beach every year since I was a child.”
• “I've known Sam since 1992.”
For is used with a time period, and means “for that period of time until the present.”
Use for with times of any length (five seconds, eight hours, two days, six weeks, nine months, ten years,
a decade, centuries, etc.)
• “We’ve lived in Berlin for 6 months.” (and we live in Berlin now)
• “She's had a cold for a week.
B. Already and yet
Already can be used in positive statements and questions.
• “I’ve already read today’s newspaper.”
• “Have you already paid the electric bill?”
• “She’s finished the test already.”
Note: Already can go in between “have/has” and the past participle (as in the first two examples) or at
the end of the sentence.
Yet can be used in negative statements and questions.
• “We haven’t cleaned the house yet.”
• “Has he told you the good news yet?”
• “Have they booked their tickets yet?”
Note: Yet usually goes at the end of the sentence or phrase.
C. Recently, lately, and just
Recently and lately can be used in positive statements, negative statements, or questions:
Recently
• “He’s recently lost some weight.”
• “I haven’t seen her recently.”
• “Have you spoken to Beth recently?”
Lately
• “I’ve gotten a lot of spam e-mails lately.”
• “Adam and Jessica haven’t been to church lately.”
• “Have you seen any good movies lately?”
Just (usually means very recent) is typically only used in positive statements and questions:
• “Don’t touch the walls – I’ve just painted them and they’re still wet.”
• “What book have you just finished reading?”
D. Ever / never
Use ever in questions only – NOT in statements.
• Have you ever been to Japan?
• Has she ever seen Titanic?
• Have they ever ridden a motorcycle?
• Has Jason ever failed a test?
Use never in negative statements – but only with have/has, not with haven’t/hasn’t:
• “My sister hasn’t never seen Titanic.”
Página 2
• “My sister has never seen Titanic.”
• “My sister hasn’t seen Titanic.”
Unit 5 Inglés Técnico II
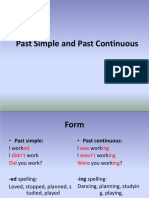
1.3 FORM
1.4 SPELLING
Página 3
Unit 5 Inglés Técnico II
Página 4
Unit 5 Inglés Técnico II
THE PAST PERFECT
The past perfect is formed from the present tense of the verb had and the past participle of a verb.
1.1 USE
We use the past perfect tense:
A. Together with the Simple Past
When two past actions are combined – the first action, which was completed before the second one
began, is put into Past Perfect.
E.g. Mary had read the book before she watched a film.
E.g. After Amy had gone home it started to rain.
E.g. After Sofie had finished her work, she went to lunch.
(First she finished her work and then she went to eat lunch.)
E.g. I washed the floor when the painter had gone.
(First the painter left and then I washed the floor.)
B. For something that started in the past and continued up to a given time in the past:
a) E.g. When George died he and Anne had been married for nearly fifty years.
E.g. She didn’t want to move. She had lived in Liverpool all her life.
C. When we are reporting our experience and including up to the present:
E.g. My eighteenth birthday was the worst day I had ever had.
E.g. I was pleased to meet George. I hadn’t met him before, even though I had met his wife several
times.
D. For something that happened in the past but is important at the time of reporting:
E.g. I couldn’t get into the house. I had lost my keys.
E.g. Teresa wasn’t at home. She had gone shopping.
Página 5
Unit 5 Inglés Técnico II
1.2 FORM
1.3 SPELLING
Página 6
Unit 5 Inglés Técnico II
Вам также может понравиться
- Paso Simple y Pasado ContinuoДокумент20 страницPaso Simple y Pasado ContinuoRobinson PilataxiОценок пока нет
- 4 The Present Perfect TenseДокумент6 страниц4 The Present Perfect TenseKate BarreraОценок пока нет
- New PP StructureДокумент31 страницаNew PP Structuregalih febriandryОценок пока нет
- How We LiveДокумент30 страницHow We LiveDaniela Juárez CastellanosОценок пока нет
- Past Tenses: - Liew Miao Huei - Jenny Kong Yug Ying - Chan Ngik Cheng - Li Li Ping - Liaw Yien SzeДокумент56 страницPast Tenses: - Liew Miao Huei - Jenny Kong Yug Ying - Chan Ngik Cheng - Li Li Ping - Liaw Yien SzeJenny KongyyОценок пока нет
- VT ReviewДокумент42 страницыVT ReviewalanОценок пока нет
- Past Tenses 1Документ47 страницPast Tenses 1Ичинноров МягмарсүрэнОценок пока нет
- Simple Present TenseДокумент6 страницSimple Present TenseKatherine JuleОценок пока нет
- Simple Past Vs Past Continuous Tense (1) - 231023 - 140832Документ17 страницSimple Past Vs Past Continuous Tense (1) - 231023 - 140832captaindear75Оценок пока нет
- VT ReviewДокумент44 страницыVT ReviewbeodethuongОценок пока нет
- Putri Raneta.D - 3336200012 - Bclass - EnglishДокумент8 страницPutri Raneta.D - 3336200012 - Bclass - EnglishPutri RanetaОценок пока нет
- Past TensesДокумент37 страницPast TensesInga Čurčić50% (2)
- English TensesДокумент9 страницEnglish TensesPaulo MarquesОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect Continuous TenseДокумент14 страницPresent Perfect Continuous Tenseshuga3100% (2)
- Past Tense HandoutДокумент7 страницPast Tense HandoutAnaNițuОценок пока нет
- Session 1 A JUST IN TIME Set B1Документ24 страницыSession 1 A JUST IN TIME Set B1Jorge MadridОценок пока нет
- Exercise Your Past Tense With KeyДокумент8 страницExercise Your Past Tense With KeyAnaNițuОценок пока нет
- 5) - Past TensesДокумент5 страниц5) - Past TensesNyJennyОценок пока нет
- Cities and HousesДокумент13 страницCities and HousesWeronika SzczepańskaОценок пока нет
- PAST Tenses - PPTДокумент24 страницыPAST Tenses - PPTbaba ioanaОценок пока нет
- Nelito Felizardo Coa Oscar Da Conceição Calisto Pinto Manual José Pinto Queresmino Octávio Agostinho Sábado ArturДокумент7 страницNelito Felizardo Coa Oscar Da Conceição Calisto Pinto Manual José Pinto Queresmino Octávio Agostinho Sábado ArturQueresminoctavio RupavaОценок пока нет
- TENSESДокумент17 страницTENSESJonathan AmadeusОценок пока нет
- The Simple Past Tense 1.1.use For The Relation of Past EventsДокумент6 страницThe Simple Past Tense 1.1.use For The Relation of Past EventsDjamal DjannadОценок пока нет
- Group: Hoàng Văn Tuấn Dương Văn ChungДокумент28 страницGroup: Hoàng Văn Tuấn Dương Văn ChungThang ToОценок пока нет
- 3rd MeetingДокумент22 страницы3rd MeetingIqbalsyahОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect: Have You Seen That Movie Many Times?Документ8 страницPresent Perfect: Have You Seen That Movie Many Times?maiktaОценок пока нет
- Module 5 Simple Past Regular Verbs Time ExpressionsДокумент9 страницModule 5 Simple Past Regular Verbs Time ExpressionsObed Escobar PerdomoОценок пока нет
- English Grammar First Stage Unit (1-10) 2020-2021: Ath J. M Ajee DДокумент23 страницыEnglish Grammar First Stage Unit (1-10) 2020-2021: Ath J. M Ajee DMikel ScoutОценок пока нет
- PRESENTPERFECTTENSEДокумент62 страницыPRESENTPERFECTTENSEMuhammad_Al_We_5107100% (1)
- The Past Perfect Simple TenseДокумент3 страницыThe Past Perfect Simple TenseMate1122Оценок пока нет
- B. Pat Tense 1. Simple PastДокумент9 страницB. Pat Tense 1. Simple PastDianSinthaОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect: How Do You Actually Use The Present Perfect?Документ8 страницPresent Perfect: How Do You Actually Use The Present Perfect?milicavasilic5720Оценок пока нет
- New Rich Text DocumentДокумент24 страницыNew Rich Text DocumentanaОценок пока нет
- Welcome English III: Luna Valdez Lucero FB: Teacherlucero LunaДокумент16 страницWelcome English III: Luna Valdez Lucero FB: Teacherlucero LunaLucero LunaОценок пока нет
- Session 1 English Tenses Theory and HomeworkДокумент21 страницаSession 1 English Tenses Theory and HomeworkAlejandra RamosОценок пока нет
- Simple Present: Theory and PracticeДокумент47 страницSimple Present: Theory and PracticeGabriela FlorentaОценок пока нет
- Review of TensesДокумент17 страницReview of TensesStefany Serret Trejo100% (1)
- Present Perfect RulesДокумент99 страницPresent Perfect RulesAngelina KostovaОценок пока нет
- Today'S Objective: - Reading Comprehension - Grammar: The Past Perfect - ExercisesДокумент31 страницаToday'S Objective: - Reading Comprehension - Grammar: The Past Perfect - ExercisesExcelsior SchoolОценок пока нет
- 4) - Present TensesДокумент9 страниц4) - Present TensesAnnas HanifОценок пока нет
- Grammar Adavanced LevelДокумент8 страницGrammar Adavanced LevelTxell Flix DuaigüesОценок пока нет
- Apuntes Ingles b2Документ25 страницApuntes Ingles b2Arancha ManeiroОценок пока нет
- RepasoДокумент11 страницRepasoMatias NicolasОценок пока нет
- Unit 6 Intermediate - Global - 2021Документ51 страницаUnit 6 Intermediate - Global - 2021Florcita Burgos MezaОценок пока нет
- Topic 2aДокумент14 страницTopic 2a黄奕Оценок пока нет
- Past TensesДокумент4 страницыPast TensesGlobal CellОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect TenseДокумент99 страницPresent Perfect TenseProfesores InglésОценок пока нет
- Past Simple Vs Past ContinuousДокумент4 страницыPast Simple Vs Past ContinuousPaula DiazОценок пока нет
- Guía de Actividades 4 Y 5: Nombre y Apellidos: Fecha: CursoДокумент5 страницGuía de Actividades 4 Y 5: Nombre y Apellidos: Fecha: CursoCora Sierra de RodriguezОценок пока нет
- Present Perfect Continuous and PastДокумент10 страницPresent Perfect Continuous and PastEstefany Ríos QuispeОценок пока нет
- Past TenseДокумент4 страницыPast TenseSiddhant RajakОценок пока нет
- Verb Tense QuestionДокумент41 страницаVerb Tense QuestionDuc PhamОценок пока нет
- Past PerfectДокумент12 страницPast PerfectIzuna MeburishviliОценок пока нет
- Past PerfectДокумент12 страницPast PerfectIzuna MeburishviliОценок пока нет
- Past Perfect: Izuna MeburishviliДокумент12 страницPast Perfect: Izuna MeburishviliIzuna MeburishviliОценок пока нет
- Past Tenses: Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect Simple, Past Perfect ContinuousДокумент34 страницыPast Tenses: Past Simple, Past Continuous, Past Perfect Simple, Past Perfect ContinuousmostarjelicaОценок пока нет
- Prepositions of Time - For, During, WhileДокумент3 страницыPrepositions of Time - For, During, WhileperdidalmaОценок пока нет
- Temas Língua Inglesa IIIДокумент22 страницыTemas Língua Inglesa IIIClenagela Paes RibeiroОценок пока нет
- AEF2e 4 GB 2AДокумент7 страницAEF2e 4 GB 2APhương Trần Thị ThanhОценок пока нет
- Unit 6 Relative ClausesДокумент5 страницUnit 6 Relative ClausesJorge LunaОценок пока нет
- Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDFДокумент3 страницыUnit 8 Conditional Clauses PDFJorge LunaОценок пока нет
- Vocabulary Unit 7 The Lab PDFДокумент5 страницVocabulary Unit 7 The Lab PDFJorge LunaОценок пока нет
- Unit 7 Passive Voice PDFДокумент4 страницыUnit 7 Passive Voice PDFJorge LunaОценок пока нет
- Unit 8 Conditional Clauses PDFДокумент3 страницыUnit 8 Conditional Clauses PDFJorge LunaОценок пока нет
- Vocabulary CellsДокумент6 страницVocabulary CellsJorge LunaОценок пока нет
- Back To School Decision Making ToolДокумент3 страницыBack To School Decision Making ToolXristosОценок пока нет
- Semi Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент5 страницSemi Detailed Lesson PlanYrraFranciscoОценок пока нет
- Group-8 Filipino-ScientistsДокумент11 страницGroup-8 Filipino-ScientistsAljondear RamosОценок пока нет
- ADMSHS Emp Tech Q2 M12 Multimedia and ICT FVДокумент10 страницADMSHS Emp Tech Q2 M12 Multimedia and ICT FVVinz Arvhil MatagayОценок пока нет
- Statement of PurposeДокумент13 страницStatement of Purposemuhammad adnanОценок пока нет
- Security Assessment and TestingДокумент43 страницыSecurity Assessment and Testingsubas khanalОценок пока нет
- Disha Darshan's ResumeДокумент2 страницыDisha Darshan's ResumeAastha SharmaОценок пока нет
- Developing Emotional IntelligenceДокумент9 страницDeveloping Emotional IntelligenceAnurag SharmaОценок пока нет
- The Tatra Mountains - The LandscДокумент18 страницThe Tatra Mountains - The LandscOLAОценок пока нет
- Pertanyaan Interview IismaДокумент5 страницPertanyaan Interview IismaMphoneid100% (1)
- Coaching Philosophy PortfolioДокумент2 страницыCoaching Philosophy PortfolioBella BastianОценок пока нет
- CASE STUDY - VAE Application - Quiz - Attempt ReviewДокумент6 страницCASE STUDY - VAE Application - Quiz - Attempt Reviewvinay MurakambattuОценок пока нет
- Behavioral DisorderДокумент2 страницыBehavioral DisorderJeffrey FostanesОценок пока нет
- Bhai GurdasДокумент260 страницBhai Gurdaswaheguru101100% (1)
- Mis VacacionesДокумент6 страницMis VacacionesYliana MoraОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 Texts and Authors From Each Region (Part 1) (Autosaved)Документ71 страницаLesson 2 Texts and Authors From Each Region (Part 1) (Autosaved)Rommel LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Lac SessionДокумент11 страницLac SessionANDREA OLIVASОценок пока нет
- Akhuwat Micro Finance BankДокумент8 страницAkhuwat Micro Finance BankAmna AliОценок пока нет
- Results of Your Language Assessment in EnglishДокумент2 страницыResults of Your Language Assessment in EnglishAtalay SeçerОценок пока нет
- The Design of Small Slot ArraysДокумент6 страницThe Design of Small Slot ArraysRoberto B. Di RennaОценок пока нет
- Julian Sowa General ResumeДокумент1 страницаJulian Sowa General Resumeapi-336812856Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Heat and TemperatureДокумент2 страницыLesson Plan Heat and TemperatureAlfred Angelo Cordura100% (1)
- Cep 800-Benson-Lesson Plan ReflectionДокумент4 страницыCep 800-Benson-Lesson Plan Reflectionapi-240037779Оценок пока нет
- MCSci1 OBE SYLLABUSДокумент9 страницMCSci1 OBE SYLLABUSBea Marie OyardoОценок пока нет
- 2 Annexure-IIДокумент297 страниц2 Annexure-IIStanley RoyОценок пока нет
- 7 - Integrating Circular Business Models and Development Tools in The Circular Economy TransitionДокумент12 страниц7 - Integrating Circular Business Models and Development Tools in The Circular Economy TransitionPós- Graduação Meio Ambiente UNINTERОценок пока нет
- English 6 DLL Q2 Week 3 11 21 25 2022Документ9 страницEnglish 6 DLL Q2 Week 3 11 21 25 2022Mary Grace Contreras100% (1)
- Lesson Plan 10-25-21Документ6 страницLesson Plan 10-25-21dasОценок пока нет
- Adrienne D Hunter - Art For Children Experiencing Psychological Trauma - A Guide For Educators and School-Based Professionals-Routledge (2018)Документ321 страницаAdrienne D Hunter - Art For Children Experiencing Psychological Trauma - A Guide For Educators and School-Based Professionals-Routledge (2018)Sonia PuarОценок пока нет
- SalcedoДокумент4 страницыSalcedoapi-317338108Оценок пока нет