Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Imaging of The Neck
Загружено:
nge2570 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
16 просмотров2 страницыThe document describes the anatomy of neck triangles and spaces. It outlines the boundaries and contents of the anterior and posterior neck triangles. It also defines the submental triangle and discusses the neck fasciae layers. Finally, it details the normal anatomy of important head and neck spaces above and below the hyoid bone, including the parapharyngeal, pharyngeal mucosal, carotid, and perivertebral spaces.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Imaging of the Neck.docx
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThe document describes the anatomy of neck triangles and spaces. It outlines the boundaries and contents of the anterior and posterior neck triangles. It also defines the submental triangle and discusses the neck fasciae layers. Finally, it details the normal anatomy of important head and neck spaces above and below the hyoid bone, including the parapharyngeal, pharyngeal mucosal, carotid, and perivertebral spaces.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
16 просмотров2 страницыImaging of The Neck
Загружено:
nge257The document describes the anatomy of neck triangles and spaces. It outlines the boundaries and contents of the anterior and posterior neck triangles. It also defines the submental triangle and discusses the neck fasciae layers. Finally, it details the normal anatomy of important head and neck spaces above and below the hyoid bone, including the parapharyngeal, pharyngeal mucosal, carotid, and perivertebral spaces.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
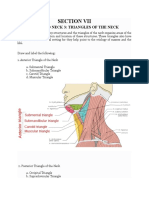
Imaging of the Neck Submental Triangle
Traditional Neck Triangles Boundaries:
− Used by clinicians to localize H&N lesions • Inferiorly – Hyoid bone.
2 Major subdivisions • Medially – Imaginary sagittal midline of the
− Anterior triangle neck.
− Posterior triangle • Laterally – Anterior belly of the digastric.
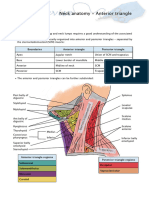
Anterior Triangle *mylohyoid muscle – forms the base of the submental
Boundaries: triangle
• Superiorly – Inferior border of the mandible Main content:
• Laterally – Medial border of the • Submental lymph nodes
sternocleidomastoid
• Medially – Imaginary sagittal line drawn along Posterior Triangle
the midline of the neck Boundaries:
Subdivisions: • Anterior: Posterior border of the
• Carotid Triangle sterncleidomastoid muscle.
• Muscular Triangle • Posterior: Anterior border of the trapezius
• Submental Triangle muscle.
• Submandibular Triangle • Inferior: Middle 1/3 of the clavicle
Carotid Triangle Subdivisions:
Boundaries: • Occipital Triangle
• Superior: Posterior belly of the digastric muscle. • Supraclavicular Triangle
• Lateral: Medial border of the Contents:
sternocleidomastoid muscle. • Muscles
• Inferior: Superior belly of the omohyoid muscle. – Omohyoid muscle (inferior belly)
Contents : – Vertebral muscles
• Common carotid artery • Splenius capitis
• Internal jugular vein • Levator scapulae
• Hypoglossal and Vagus nerves • Scalene muscles
Muscular Triangle • Vasculature
Boundaries: – External jugular vein
• Superiorly: Hyoid bone – Transverse cervical artery
• Medially: Imaginary midline of the neck – Subclavian artery and vein
• Supero-laterally: Superior belly of the Contents:
omohyoid muscle • Nerves
• Infero-laterally: Inferior portion of the – Accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI)
sternocleidomastoid muscle – Cervical plexus
Contents: – Phrenic nerve- arises from the anterior
• Infrahyoid strap muscles divisions of spinal nerves C3-C5,
• Pharynx innervate the diaphragms
• Thyroid gland – Brachial plexus
• Parathyroid gland Subdivisions
Submandibular Triangle • Occipital triangle- crossed by the accessory
Boundaries: nerve
• Superiorly: Body of the mandible • Subclavian triangle- contains the distal portion
• Anteriorly: Anterior belly of the digastric muscle of the subclavian artery
• Posteriorly: Posterior belly of the digastric
muscle Traditional Neck Triangles
Contents: • The traditional compartments are important for
• Submandibular gland describing the spread of superficial and
• Submandibular lymph nodes muscosa-based lesions.
• Facial artery and vein • In contrast to this divisions, multiple facial
planes divide the deep head and neck into
spaces that form true compartments.
• It is important to realize that these deep spaces Neck Division
are unrelated to the traditional division of the − SHN: Deep facial spaces above hyoid bone
head and neck and traverse the neck without including parapharyngeal (PPS), pharyngeal
regard to the traditional divisions. mucosal space (PMS), masticator (MS), parotid
• Most radiologist have adapted a spatial (PS), carotid (CS), buccal (BS), retropharyngeal
approach to the head and neck, popularized by (RS), danger space (DS), perivertebral space
Dr. Ric Harnsberger. (PVS)
Neck Fasciae − IHN: Spaces predominantly below hyoid bone
• Superficial Cervical Fascia with some continuing into mediastinum or SHN
• Deep Cervical Fascia including visceral space (VS), posterior cervical
– Superficial layer space (PCS), anterior cervical space (ACS), CS,
– Middle layer RPS & PVS.
– Deep layer
SL-DCF NORMAL ANATOMY SHN ANATOMIC SPACES
• SHN: circumscribes MS & PS, contributes to 1. Parapharyngeal space (PPS)
carotid sheath 2. Pharyngeal mucosal space (PMS)
• IHN: “invests” neck by surrounding strap, 3. Carotid space (CS)
Sternomastoid & trapezius muscle; contributes 4. Parotid space (PS)
to carotid sheath 5. Masticator space (MS)
ML-DCF 6. Retropharyngeal space (RPS)
• SHN: Defines PMS deep margin; contributes to 7. Perivertebral space (PVS)
carotid sheath
• IHN: circumbscribes VS; contributes to carotid Posterior Midline
sheath – Retropharyngeal space
DL-DCF • Danger space
• SHN & IHN – surrounds PVS with fascial slip to – Perivertebral space
transverse process dividing PVS into Skull Base Relation
prevertebral and paraspinal components; – Masticator Space
contricutes to carotid sheath. • F. Ovale
• F. Spinosum
Neck Division – Parotid Space
Hyoid Bone/ Cartilage • Stylomastoid foramen
• Suprahyoid Compartment – Carotid Space
• Infrahyoid Compartment • Int Carotid Artery
EXTENT: • Int Jugular Vein
• SHN: neck spaces from skull base to hyoid bone – Pharyngeal Mucosal Space
excluding orbit, sinonasal area and oral cavity • F. Lacerum
(OC) – Parapharyngeal Space
• IHN: Neck spces from hyoid above to – Retropharyngeal Space
cervicothoracic junction below
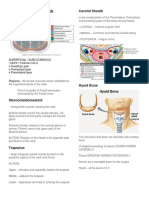
Hyoid Bone
− U-shape or horse shoe configuration
− Three components
− 2 horns, 1 body
Thyroid Cartilage
− V-shape configuration
− Two components
Cricoid Bone
− Complete cartilagenous ring
− Thicker and taller posteriorlly
Вам также может понравиться
- Anatomy of Head and NeckДокумент113 страницAnatomy of Head and NeckBenjamin Prabhu75% (4)
- Head - Neck Anatomy LectureДокумент91 страницаHead - Neck Anatomy Lecturen42.nayanОценок пока нет
- Surgical Anatomy of The Neck: Cervical Fascia: Head & Neck Surgery CourseДокумент10 страницSurgical Anatomy of The Neck: Cervical Fascia: Head & Neck Surgery CourseΑΘΑΝΑΣΙΟΣ ΚΟΥΤΟΥΚΤΣΗΣОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of The ARMДокумент17 страницAnatomy of The ARMJacob MasikaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy 06 - Axilla (Pre Med 101)Документ8 страницAnatomy 06 - Axilla (Pre Med 101)Navoda Dulshan PereraОценок пока нет
- Head and Neck TumorsДокумент14 страницHead and Neck TumorsBarda GulanОценок пока нет
- Updated Cours Ia Introuction Skull Ventricules CSFДокумент53 страницыUpdated Cours Ia Introuction Skull Ventricules CSFtiajaberrОценок пока нет
- 1414-11 The Spinal Cord 2021bbДокумент41 страница1414-11 The Spinal Cord 2021bbghazal safaviОценок пока нет
- Spine: Aggasid Azman Corpuz LagundiДокумент59 страницSpine: Aggasid Azman Corpuz LagundiJho AggasidОценок пока нет
- Neck + Thyroid GlandДокумент9 страницNeck + Thyroid GlandmarlyxsukiОценок пока нет
- Triangles of Neck (Anatomy)Документ36 страницTriangles of Neck (Anatomy)Dr Tahira Nihal100% (1)
- Clinical Anatomy NotesДокумент5 страницClinical Anatomy NotesYehansa WijethungaОценок пока нет
- Neck Anatomy - Anterior Triangle - MRCSДокумент6 страницNeck Anatomy - Anterior Triangle - MRCSathenhelОценок пока нет
- Ace Achievers: Anterior Triangle of NeckДокумент8 страницAce Achievers: Anterior Triangle of NeckaditryjeeОценок пока нет
- Week 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesДокумент53 страницыWeek 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesHephzibah JaporОценок пока нет
- Week 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesДокумент53 страницыWeek 3 Spinal Cord, Spinal NervesCyril Jay G. OrtegaОценок пока нет
- Shoulder JTДокумент30 страницShoulder JTEVELYN EZEKWEОценок пока нет
- Triangles of NeckДокумент59 страницTriangles of NeckParijat Chakraborty PJОценок пока нет
- Neck Dissections: DR P Lalityaswarna II ND Yr ResidentДокумент79 страницNeck Dissections: DR P Lalityaswarna II ND Yr ResidentSee GooMeОценок пока нет
- AtlasДокумент509 страницAtlasLasana Bayshawn SandyОценок пока нет
- Surgical Anatomy of NeckДокумент37 страницSurgical Anatomy of Neckaishwarya raviОценок пока нет
- Pectoral Region & AxillaДокумент18 страницPectoral Region & AxillaMohammad PharaonОценок пока нет
- Weight of An Adult BrainДокумент5 страницWeight of An Adult BrainjisarafaelОценок пока нет
- Parapharyngeal Space AnatomyДокумент31 страницаParapharyngeal Space AnatomyciciОценок пока нет
- NECK1 Part OneДокумент99 страницNECK1 Part OneZelallem AnileyОценок пока нет
- The Muscles and Triangles of The NeckДокумент35 страницThe Muscles and Triangles of The NeckKeesha AnneОценок пока нет
- 1 Introduction Organization of The Nervous SystemДокумент21 страница1 Introduction Organization of The Nervous Systemaaphiwe879Оценок пока нет
- Spinal Cord Injury IntroductionДокумент243 страницыSpinal Cord Injury Introductionfahad100% (1)
- Department of Anatomy: Dr. Sreekanth ThotaДокумент43 страницыDepartment of Anatomy: Dr. Sreekanth ThotadavidОценок пока нет
- 10,11,12-Head & Neck I, II and III (Only F1)Документ14 страниц10,11,12-Head & Neck I, II and III (Only F1)Safi MohammedОценок пока нет
- Upper LimbДокумент20 страницUpper LimbGabriel Botezatu100% (1)
- Scapular Region 9 Mar 2024Документ32 страницыScapular Region 9 Mar 2024aamna.nadeem101Оценок пока нет
- Imaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal (B. J. Manaster, Julia Crim) (Z-Lib - Org) Split-Merge - extractPDFpagesДокумент12 страницImaging Anatomy Musculoskeletal (B. J. Manaster, Julia Crim) (Z-Lib - Org) Split-Merge - extractPDFpagesChristian ToalongoОценок пока нет
- The Neck PDFДокумент67 страницThe Neck PDFAhmad Akram NatshehОценок пока нет
- Page of 1 3 Carotid Arteries L2 Vascular Biology: Musculofascial CollarДокумент3 страницыPage of 1 3 Carotid Arteries L2 Vascular Biology: Musculofascial CollarFazreena EleenaОценок пока нет
- 18 Posterior Compartment of ThighДокумент21 страница18 Posterior Compartment of ThighLaiba FaysalОценок пока нет
- HNF 03 Fascia Colli - IIДокумент40 страницHNF 03 Fascia Colli - IIthugsena39Оценок пока нет
- Arm and Cubital FossaДокумент40 страницArm and Cubital FossaAbdelrhman AbubakrОценок пока нет
- Facial Nerve Anatomy - Nithin NairДокумент25 страницFacial Nerve Anatomy - Nithin Nairnithin nairОценок пока нет
- Section Vii: Head and Neck 3: Triangles of The NeckДокумент3 страницыSection Vii: Head and Neck 3: Triangles of The NeckLeiraset WuОценок пока нет
- Anterior Thoracoappendicular MusclesДокумент3 страницыAnterior Thoracoappendicular MusclesTrisha HaОценок пока нет
- Head and Neck: Carotid SheathДокумент66 страницHead and Neck: Carotid SheathIrys GОценок пока нет
- Neck RegionДокумент47 страницNeck RegionShiela ClementeОценок пока нет
- 13 Triangles of The NeckNewДокумент43 страницы13 Triangles of The NeckNewsandyОценок пока нет
- ANAT523First Secondlectures 2021Документ89 страницANAT523First Secondlectures 2021pianistgirl99Оценок пока нет
- June 28, 2021Документ89 страницJune 28, 202171- MURALIKRISHNAОценок пока нет
- Mo Reda MrcsДокумент550 страницMo Reda MrcsS Muhammad Hashim RazaОценок пока нет
- NECK AnatomyzkkДокумент38 страницNECK AnatomyzkkzahidОценок пока нет
- 8 - Pectoral Region & AxillaДокумент21 страница8 - Pectoral Region & AxillaRaj BahiramkarОценок пока нет
- Hyoid Bone PPT FinalДокумент30 страницHyoid Bone PPT Finala30139286Оценок пока нет
- Head & Neck - Deep Cervical Fascia &cervical PlexusДокумент9 страницHead & Neck - Deep Cervical Fascia &cervical PlexusKomang Tri Adi SuparwatiОценок пока нет
- Neck Space 2Документ42 страницыNeck Space 2Sharan AnnapuraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 21 Back of The Neck NewДокумент63 страницыChapter 21 Back of The Neck NewMohan PalanimalaiОценок пока нет
- Suboccipital and Scapular Region 1125Документ50 страницSuboccipital and Scapular Region 1125qns8mhb7wyОценок пока нет
- Triangels of NeckДокумент86 страницTriangels of NeckNayela AkramОценок пока нет
- Trigonum Coli AnteriorДокумент22 страницыTrigonum Coli AnteriorPramudita DinarОценок пока нет
- Anatomy, Imaging and Pathologic Conditions of Brachial PlexusДокумент67 страницAnatomy, Imaging and Pathologic Conditions of Brachial PlexusChrista Levina DaniswaraОценок пока нет
- Blood and Tissue Roundworms (Filaria Worms)Документ5 страницBlood and Tissue Roundworms (Filaria Worms)nge257Оценок пока нет
- GrowthДокумент4 страницыGrowthnge257Оценок пока нет
- Agenesis Atresia Fistula: Mechanical ObstructionДокумент13 страницAgenesis Atresia Fistula: Mechanical Obstructionnge257Оценок пока нет
- Warthin Tumor Papillary Cystadenoma LymphomatosumДокумент8 страницWarthin Tumor Papillary Cystadenoma Lymphomatosumnge257Оценок пока нет
- Family CEAДокумент3 страницыFamily CEAnge257100% (1)
- Comparative - URT and PneumoniaДокумент4 страницыComparative - URT and Pneumoniange257Оценок пока нет
- Antiarrhythmic DrugsДокумент2 страницыAntiarrhythmic Drugsnge257Оценок пока нет
- Robbin'S and Cotran'S: Pathologic Basis of DiseaseДокумент6 страницRobbin'S and Cotran'S: Pathologic Basis of Diseasenge257Оценок пока нет
- Uncle Snell'S Notes in Gross Anatomy The FaceДокумент3 страницыUncle Snell'S Notes in Gross Anatomy The Facenge257Оценок пока нет
- AdodДокумент464 страницыAdodnge257Оценок пока нет
- AntibioticsДокумент8 страницAntibioticsnge257Оценок пока нет
- Rapid Musculoskeletal ScreenerДокумент4 страницыRapid Musculoskeletal Screenernge257Оценок пока нет
- GROSS HSB A Prelim 2018Документ18 страницGROSS HSB A Prelim 2018nge257Оценок пока нет
- Settlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Документ11 страницSettlement Geography: Unit No-1&2Arindam RoulОценок пока нет
- Fluid Mechanics Formulas Nov 2021Документ6 страницFluid Mechanics Formulas Nov 2021Benjie MorenoОценок пока нет
- Lescture OPACДокумент5 страницLescture OPACAgulto, Ivan R.Оценок пока нет
- Errors Affecting The Trial BalanceДокумент3 страницыErrors Affecting The Trial BalanceDarwin Lopez100% (1)
- Sample Invoice PDFДокумент3 страницыSample Invoice PDFMarcus OlivieraaОценок пока нет
- Zimbabwe National Code Ccorporate GovernanceДокумент96 страницZimbabwe National Code Ccorporate GovernanceHerbert NgwaraiОценок пока нет
- Soal Materi 1 KLS X IntroductionДокумент2 страницыSoal Materi 1 KLS X IntroductionFira AnandaОценок пока нет
- 70 Ijgm AsterДокумент12 страниц70 Ijgm AsterMc ManjuОценок пока нет
- PMAIZMTUSDMДокумент6 страницPMAIZMTUSDMLinh TranОценок пока нет
- Material Safety Data Sheet: Manufacturer Pt. Bital AsiaДокумент3 страницыMaterial Safety Data Sheet: Manufacturer Pt. Bital AsiaediОценок пока нет
- Emcee Script For CompetitionДокумент2 страницыEmcee Script For CompetitionArdini Izzati100% (3)
- VA RESUME HelloracheДокумент1 страницаVA RESUME HelloracheJessa AbadianoОценок пока нет
- UNIX Introduction 1Документ18 страницUNIX Introduction 1Akash SavaliyaОценок пока нет
- The Case For A Concentrated Portfolio 6-30-16Документ4 страницыThe Case For A Concentrated Portfolio 6-30-16Maria Gabriela PopaОценок пока нет
- (EN) Google Developer Policy - September 1, 2021Документ56 страниц(EN) Google Developer Policy - September 1, 2021JimmyОценок пока нет
- 20 Heirs of Alfredo Bautista VS LindoДокумент3 страницы20 Heirs of Alfredo Bautista VS LindoJerome LeañoОценок пока нет
- Peter Zumthor - Thinking Architecture PDFДокумент33 страницыPeter Zumthor - Thinking Architecture PDFDiana Sterian73% (11)
- Jeevan Tara, Sansad Marg NEW DELHI-11001 Regonal Office (North Zone) E MailДокумент3 страницыJeevan Tara, Sansad Marg NEW DELHI-11001 Regonal Office (North Zone) E MailGourav SharmaОценок пока нет
- CCSI - HDPE - Subduct 50-4240-33 32-27 32-28 - Rev.0 - TelkomДокумент1 страницаCCSI - HDPE - Subduct 50-4240-33 32-27 32-28 - Rev.0 - TelkomAlvan umaraОценок пока нет
- Alcatel 9400 PDFДокумент4 страницыAlcatel 9400 PDFNdambuki DicksonОценок пока нет
- YazdiДокумент7 страницYazditrs1970Оценок пока нет
- CREW Whitaker Recusal Letter DOJ 11-8-2018Документ9 страницCREW Whitaker Recusal Letter DOJ 11-8-2018Beverly TranОценок пока нет
- Natural Gas DistributionДокумент46 страницNatural Gas DistributionscribdmisraОценок пока нет
- BArch Thesis Proposal Form - 27march 2023 1 PDFДокумент3 страницыBArch Thesis Proposal Form - 27march 2023 1 PDFDevkalpaОценок пока нет
- Hitachi Zx330 3 Series Hydraulic ExcavatorДокумент15 страницHitachi Zx330 3 Series Hydraulic ExcavatorAgung ArdhanaОценок пока нет
- Detergent For Auto DishWashing Machine EДокумент5 страницDetergent For Auto DishWashing Machine EkaltoumОценок пока нет
- Clause: Extra Element + Independent Clause Dependent ClauseДокумент1 страницаClause: Extra Element + Independent Clause Dependent ClauseTieng HuangОценок пока нет
- Demand, Elasticity of Demand and Demand ForecastingДокумент16 страницDemand, Elasticity of Demand and Demand Forecastingankit thapliyal100% (1)
- Deferred Tax QsДокумент4 страницыDeferred Tax QsDaood AbdullahОценок пока нет
- STD 12 Accountancy1Документ264 страницыSTD 12 Accountancy1Chetan KhonaОценок пока нет
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)От EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)Рейтинг: 3 из 5 звезд3/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedОт EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (82)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityОт EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (32)
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionОт EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (404)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDОт EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОт EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsОценок пока нет
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsОт EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsОт EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (4)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (2)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeОт EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeРейтинг: 2 из 5 звезд2/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisОт EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (42)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.От EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Рейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (110)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeОт EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (254)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsОт EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (170)
- Manipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesОт EverandManipulation: The Ultimate Guide To Influence People with Persuasion, Mind Control and NLP With Highly Effective Manipulation TechniquesРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (1412)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaОт EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (266)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceОт EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceРейтинг: 3.5 из 5 звезд3.5/5 (51)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossОт EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (6)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryОт EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (46)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlОт EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (60)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessОт EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (328)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityОт EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityРейтинг: 4.5 из 5 звезд4.5/5 (6)
- How to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingОт EverandHow to ADHD: The Ultimate Guide and Strategies for Productivity and Well-BeingРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)