Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Supply Chain - Blockchain
Загружено:
shalabh_hscАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Supply Chain - Blockchain
Загружено:
shalabh_hscАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
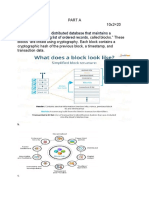
Blockchain can be visualized as a chain of blocks where each block maintains a record of valid
network activity. Each block is an encrypted piece of information and everybody is free to add data
into the network. Also, anyone can review the added data at any time but no one can modify it
without adequate authorisation. This technology helps two entities to transact with each other even
if they are complete strangers and do not trust each other. The validation of these transactions is
done through a process called mining which ensures the security of the data that is added. There are
several advantages of using this technology. Some of which are durability, transparency,
immutability and process integrity. As Blockchain is decentralized it does not have single point of
failure in the network. The risk is distributed among several points which make the system more
durable. At each of these points or nodes a copy of Blockchain is maintained which allow monitoring
in real time. Due to the need of validation the data stored at nodes is practically immutable. This also
boosts the integrity of Blockchain technology.
Blockchains have found vast variety of applications among different industries. Supply Chain
Management (SCM) is one such field where companies are analysing its utility. It consists of entities
such as physical resources, people, processes, knowledge and financial contracts etc. which assist
shipment of a product from supplier to consumer. If the supply chain system is very large it is
difficult to maintain an overall picture of transactions. The information of these transactions are
usually stored in different nodes within the Blockchain and accessible to certain systemic entities.
The customers in such system do not have access to complete information and in some case partial
information is commodity for a supplier. Hence, when the transparency is very low the entities are
indulged in transactions based on trust. The Blockchain technology comes into play here as it
increases the transparency within the supply chain in manufacturing sector as it is decentralized
distributed system. This system uses Blockchain technologies to collect, store and manage key
product information of each individual product throughout its life cycle. This distributed blocks
create a secure, shared record of transaction for each individual product with specific product
information. As a product moves through its life cycle, it is encompassed by a variety of entities such
as producers, suppliers, manufacturers, distributors, retailers and customer. Each of these entities
have an essential part to play in the system. Each product would have a unique digital profile
containing all relevant information in various lifestyle stages. The system consists of Registrars,
Standard Organizations, Certifiers, producers and distributors. Each product in the supply chain can
have an information tag in form of a barcode or QR code. This would represent a unique digital
cryptographic identifier that links a product to its identity in a network. Entities would have a digital
profile which is created while registering. The profile displays information such as description and
location associated with products. This visual identity can be presented to software as a part of the
digital profile. The system allows entities to change their privacy profiles. Entities have the option to
remain completely anonymous but it must be certified by a registered certifier to maintain the trust
in the system. The entities in the system register through a registrar which is an accreditation service
that provides a unique identity to the actors. After registration, a public and private cryptographic
key pair are generated for each entity. The public key identifies the entity in the network while the
private key can authenticate it when interacting with the system. Entities can interact with the
network by cryptographically authenticating themselves using their private key. This would allow
each product to be digitally signed by the entities when added in the supply chain.
References
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Radmehr_Monfared/publication/308163874_Blockchain_Rea
dy_Manufacturing_Supply_Chain_Using_Distributed_Ledger/links/57fe2dde08ae7275640133b0/Blo
ckchain-Ready-Manufacturing-Supply-Chain-Using-Distributed-Ledger.pdf
Вам также может понравиться
- Yellow King - Black Star MagicДокумент186 страницYellow King - Black Star Magicwijeesf797100% (1)
- Ebook Service Desk vs. Help Desk. What Is The Difference 1Документ18 страницEbook Service Desk vs. Help Desk. What Is The Difference 1victor molinaОценок пока нет
- Hindu Rashtra Darshan by Veer Vinayak Damodar SavarkarДокумент130 страницHindu Rashtra Darshan by Veer Vinayak Damodar SavarkarArya Veer100% (3)
- BlockChain Technologies (20CS32015)Документ16 страницBlockChain Technologies (20CS32015)srinivas kanakalaОценок пока нет
- GUBAnt BanwnaДокумент36 страницGUBAnt BanwnaMarc Philip100% (1)
- G.R. No. 172242Документ2 страницыG.R. No. 172242Eap Bustillo67% (3)
- Winter ParkДокумент7 страницWinter Parksadafkhan210% (1)
- Contemporary Issues in Management 2Документ13 страницContemporary Issues in Management 2joseph mbuguaОценок пока нет
- Supply Chain Blockchain Literature ReviewДокумент4 страницыSupply Chain Blockchain Literature ReviewSwaraОценок пока нет
- FOB Chapter-2Документ27 страницFOB Chapter-2Pratik KhuntОценок пока нет
- Blockchain, Also Known As Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), Was TheДокумент8 страницBlockchain, Also Known As Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), Was Thepartha_748385075Оценок пока нет
- Benefits of Blockchain TechnologyДокумент3 страницыBenefits of Blockchain TechnologydhoniОценок пока нет
- Blockchain Enhanced Security Applications Beyond CryptocurrencyДокумент7 страницBlockchain Enhanced Security Applications Beyond CryptocurrencyimxalОценок пока нет
- BlockchainДокумент11 страницBlockchainanilkumarak9532Оценок пока нет
- Blockchain Security, Accuracy, and Transparency Capabilities PDFДокумент3 страницыBlockchain Security, Accuracy, and Transparency Capabilities PDFmigdonОценок пока нет
- Unit 5Документ22 страницыUnit 5Prashan PatilОценок пока нет
- Supply Chain TraceabilityДокумент12 страницSupply Chain TraceabilityEmmanuelОценок пока нет
- 1.1 Introduction Block Chain SecurityДокумент4 страницы1.1 Introduction Block Chain Securityrajat ghardeОценок пока нет
- Blockchain Based Compliance Management System Ashish Jadhav Nitin Agarwal Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited PDFДокумент30 страницBlockchain Based Compliance Management System Ashish Jadhav Nitin Agarwal Reliance Jio Infocomm Limited PDFSirine HmlОценок пока нет
- Blockchain TechnologyДокумент6 страницBlockchain TechnologyMalik Muhammad Arslan Alam AwanОценок пока нет
- Actividad LogisticaДокумент10 страницActividad Logisticaaaxel0702Оценок пока нет
- Blockchain RAPORДокумент4 страницыBlockchain RAPORAylin ErdoğanОценок пока нет
- G-29 Project ProposalДокумент8 страницG-29 Project ProposalAjОценок пока нет
- CouldДокумент8 страницCoulddhoniОценок пока нет
- Anti-Counterfeit Detection System Using BlockchainДокумент10 страницAnti-Counterfeit Detection System Using BlockchainIJRASETPublicationsОценок пока нет
- Blockchain-Case Study (ETI)Документ13 страницBlockchain-Case Study (ETI)Omkar JadhavОценок пока нет
- Blockchain Technology and Its Synergy With General Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI)Документ6 страницBlockchain Technology and Its Synergy With General Artificial Intelligence (Gen AI)hacoj68463Оценок пока нет
- BlockchainДокумент4 страницыBlockchainSeng Cheong KhorОценок пока нет
- An Improved Banking Application Model Using BlockcДокумент21 страницаAn Improved Banking Application Model Using BlockcAakash GuptaОценок пока нет
- UNIT I Blockchain NotesДокумент19 страницUNIT I Blockchain Notesmanoj tilakchandОценок пока нет
- Block ChainДокумент6 страницBlock Chainsaksham guptaОценок пока нет
- Unit 1Документ92 страницыUnit 1rocky2003rajkumarОценок пока нет
- Blockchain SCE at VIITДокумент9 страницBlockchain SCE at VIITShivam MishraОценок пока нет
- How Blockchain Will Impact LogisticsДокумент2 страницыHow Blockchain Will Impact LogisticsdsdsdОценок пока нет
- The Futurist - XIMBДокумент3 страницыThe Futurist - XIMBRuchi AgrawalОценок пока нет
- The Role of Blockchain Technology in Transforming Supply Chain ManagementДокумент2 страницыThe Role of Blockchain Technology in Transforming Supply Chain ManagementJohn CarterОценок пока нет
- Block Chain CourseДокумент6 страницBlock Chain CoursePrince StefanОценок пока нет
- Blockchain Basics: Introduction To Distributed LedgersДокумент5 страницBlockchain Basics: Introduction To Distributed LedgersNelsonОценок пока нет
- Blockchain Technology: The Novelty and Business Transformation PotentialДокумент3 страницыBlockchain Technology: The Novelty and Business Transformation Potentialpriyam dixitОценок пока нет
- Application of Blockchain AWДокумент18 страницApplication of Blockchain AWS.K. PraveenОценок пока нет
- Making Cloud More Secure Using Blockchain Structured AnalysisДокумент3 страницыMaking Cloud More Secure Using Blockchain Structured AnalysisInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyОценок пока нет
- Blockchain ReflectionДокумент3 страницыBlockchain ReflectionNirakar BeheraОценок пока нет
- Blockchain TechnologyДокумент8 страницBlockchain Technology20CM052-Shravani Shinganwadikar. CMОценок пока нет
- Blockchain For SustainabilityДокумент22 страницыBlockchain For SustainabilityHarish NaikОценок пока нет
- New Tech Trends Impact Web DevДокумент12 страницNew Tech Trends Impact Web Devwarrior rawwriorОценок пока нет
- Blockchain in HealthcareДокумент7 страницBlockchain in HealthcarejoОценок пока нет
- DTT AssignmentДокумент12 страницDTT Assignmentsoniyap2443Оценок пока нет
- Strategic Marketing Assignment Submitted By:: Name: Exam Roll No.: Department of Business ManagementДокумент15 страницStrategic Marketing Assignment Submitted By:: Name: Exam Roll No.: Department of Business ManagementRiddhi PaulОценок пока нет
- Paper - Blockchain For Supply Chain ManagementДокумент14 страницPaper - Blockchain For Supply Chain Managementprat2607Оценок пока нет
- 6 Key Blockchain Features You Need To Know NowДокумент26 страниц6 Key Blockchain Features You Need To Know NowBankole AyoadeОценок пока нет
- BlockchainДокумент5 страницBlockchainGood for NothingОценок пока нет
- Blockchain: Distributed Ledger TechnologyДокумент5 страницBlockchain: Distributed Ledger Technologylife lineОценок пока нет
- Impactof Blockchaintechnologyon Supplychain ManagementДокумент15 страницImpactof Blockchaintechnologyon Supplychain ManagementPallavi EmadeОценок пока нет
- Understanding Blockchain: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessОт EverandUnderstanding Blockchain: Tips, Recommendations, and Strategies for SuccessОценок пока нет
- BlockChian Healthcare SynopsisДокумент9 страницBlockChian Healthcare SynopsisSantoshОценок пока нет
- Blockchain Technology ExplainedДокумент8 страницBlockchain Technology ExplainedMadalina AlexandraОценок пока нет
- Bank Record Storage Using BlockchainДокумент5 страницBank Record Storage Using BlockchaingeethakaniОценок пока нет
- Presentation SlideshowДокумент10 страницPresentation SlideshowsojimotiveОценок пока нет
- Block Chain Unit-1Документ18 страницBlock Chain Unit-1pilli maheshchandraОценок пока нет
- Crypto Currency UNIT - 1 NOTESДокумент14 страницCrypto Currency UNIT - 1 NOTESanishshree1207Оценок пока нет
- Unit - 1 NotesДокумент14 страницUnit - 1 NotesFbz AriОценок пока нет
- Mahnoor Qaisar - #1056 - Computer Application in Education Assignment-2Документ7 страницMahnoor Qaisar - #1056 - Computer Application in Education Assignment-2HaseeB MalikОценок пока нет
- Blockchain NotesДокумент3 страницыBlockchain NotesMadiha JavedОценок пока нет
- LMS 13Документ11 страницLMS 13prabakar1Оценок пока нет
- Block ChainДокумент4 страницыBlock ChainAnoopОценок пока нет
- Breusch Model TestДокумент2 страницыBreusch Model Testshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- Financial ModellingДокумент5 страницFinancial Modellingshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- Banking Crisis, Integration, and the Path to Banking UnionДокумент25 страницBanking Crisis, Integration, and the Path to Banking Unionshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- The Aurangzeb DebateДокумент4 страницыThe Aurangzeb Debateshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- Class Notes #1Документ6 страницClass Notes #1shalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- V-Mart Retail: Demand Pick-Up Likely From H2, BUYДокумент3 страницыV-Mart Retail: Demand Pick-Up Likely From H2, BUYshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- CO - MSc28 - FM - Avanced Corporate Finance 2019-2020 DEFДокумент12 страницCO - MSc28 - FM - Avanced Corporate Finance 2019-2020 DEFshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- GraphsДокумент3 страницыGraphsshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- Balu AppendixДокумент1 страницаBalu Appendixshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- Intro to Cirrus Test DemoДокумент1 страницаIntro to Cirrus Test Demoshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- Pre Class Exercise 2Документ2 страницыPre Class Exercise 2shalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- BRM Literature ReviewДокумент2 страницыBRM Literature Reviewshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- Letter To The DeanДокумент2 страницыLetter To The Deanshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- Food WastageДокумент3 страницыFood Wastageshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- Pakistan Could Be Included in Immigration Ban List in FutureДокумент2 страницыPakistan Could Be Included in Immigration Ban List in Futureshalabh_hscОценок пока нет
- 6 Cost AnalysisДокумент14 страниц6 Cost AnalysisNeha PrakashОценок пока нет
- Hitachi Energy BESS PQpluSДокумент9 страницHitachi Energy BESS PQpluSelpancaseroОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 Imc 407Документ14 страницChapter 1 Imc 407Mayson Chua ShangОценок пока нет
- GonorrhoeaДокумент24 страницыGonorrhoeaAtreyo ChakrabortyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 22Документ40 страницChapter 22bayu0% (1)
- Day1 S2 Gravity IntroДокумент21 страницаDay1 S2 Gravity IntroPedro Hortua SeguraОценок пока нет
- 19 Preposition of PersonalityДокумент47 страниц19 Preposition of Personalityshoaibmirza1Оценок пока нет
- Deportation of Jews of IoanninaДокумент7 страницDeportation of Jews of IoanninajaboninОценок пока нет
- Canada Immigration Forms: 5578EДокумент7 страницCanada Immigration Forms: 5578EOleksiy KovyrinОценок пока нет
- List of Solar Energy Operating Applications 2020-03-31Документ1 страницаList of Solar Energy Operating Applications 2020-03-31Romen RealОценок пока нет
- First CaseДокумент2 страницыFirst Caseaby marieОценок пока нет
- 3rd Yr 2nd Sem Business Plan Preparation Quiz 1 MidtermДокумент14 страниц3rd Yr 2nd Sem Business Plan Preparation Quiz 1 MidtermAlfie Jaicten SyОценок пока нет
- Operational Auditing Internal Control ProcessesДокумент18 страницOperational Auditing Internal Control ProcessesKlaryz D. MirandillaОценок пока нет
- Silent Night (2015) ProgramДокумент88 страницSilent Night (2015) ProgramLyric Opera of Kansas CityОценок пока нет
- Receivable Financing Pledge Assignment AДокумент34 страницыReceivable Financing Pledge Assignment AJoy UyОценок пока нет
- Career Lesson Plan Cheat SheetДокумент2 страницыCareer Lesson Plan Cheat Sheetapi-278760277Оценок пока нет
- The Ancient CeltsДокумент2 страницыThe Ancient CeltsArieh Ibn GabaiОценок пока нет
- Medicina Musica Amistad y Prejuicios BrahmsДокумент3 страницыMedicina Musica Amistad y Prejuicios BrahmsBreen MisiОценок пока нет
- WP (C) 267/2012 Etc.: Signature Not VerifiedДокумент7 страницWP (C) 267/2012 Etc.: Signature Not VerifiedAnamika VatsaОценок пока нет
- MCQ Human RightsДокумент30 страницMCQ Human RightsSameer PrasadОценок пока нет
- The Night Artist ComprehensionДокумент6 страницThe Night Artist ComprehensionDana TanОценок пока нет
- Tso C139Документ5 страницTso C139Russell GouldenОценок пока нет
- Winchel RM Stanley MДокумент13 страницWinchel RM Stanley MMariola AlamoОценок пока нет
- Bureau of Energy EfficiencyДокумент2 страницыBureau of Energy EfficiencyrkОценок пока нет
- Amazon InvoiceДокумент1 страницаAmazon InvoiceChandra BhushanОценок пока нет
- Audit Independence and Audit Quality Likelihood: Empirical Evidence From Listed Commercial Banks in NigeriaДокумент15 страницAudit Independence and Audit Quality Likelihood: Empirical Evidence From Listed Commercial Banks in NigeriaIdorenyin Okon100% (1)