Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Introduction To Risk Management
Загружено:
Venkatesh Pethuraj0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
26 просмотров3 страницыIntroduction to Risk Management
Оригинальное название
Introduction to Risk Management
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документIntroduction to Risk Management
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
26 просмотров3 страницыIntroduction To Risk Management
Загружено:
Venkatesh PethurajIntroduction to Risk Management
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 3
Introduction to Risk Management
Project risk management includes the processes concerned with
conducting risk management planning , identification , analysis ,
responses, and monitoring and control on a project , the objective is
to increase the probability and impact of positive events and
decrease probability and impact of negative events .
It’s not an optional activity , it’s a systematic and proactive
approach to taking control over projects instead of being controlled
by the project.
Project Risk is an uncertain event or condition that if occurs has a
negative or positive effect on the project objectives.
At the early stages of the project the level of risk exposure is at its
maximum but information on the project risks at it’s minimum , the
earlier in the project life cycle that the risks are recognized , the more
realistic the project plans and expectations of results will be .
Project risk management should be conducted for all projects , the
level of detail, sophistication tools and amount of time and resources
applied to project risk management should be in proportion to the
project characteristics .
Risk Factors are :
1. Probability, likelihood that risk will occur.
2. Impact , effect on the project if risk occur
3. When it will happen ( Expected Timing )
4. Frequency of the event.
Critical Success Factors for Project Risk management :
1. Recognize the value of risk management , it should be believed
specially by the organization that risk management will bring positive
potential return on investment.
2. Individual Commitment , Risk management is every body’s
responsibility.
3. Open and Honest Communications.
4. Organization Commitment , it can be obtained if risk management
goals are aligned with organization goals and values .
5. Risk effort scaled to project , as the cost of project risk
management should be appropriate with it’s potential value of the
project.
6. Integration with other project management activities.
Project management can be seen as an attempt to control the
project uncertain environment, it’s effectiveness is increased by using
information and results of risk management
Note that from risk definition the risk event affects the project
objectives , so objectives should be defined and stated before the
risk management starts.
It’s the project manager role to tailor risk management activities to
the needs of the project , it’s the initiation phase in risk management ,
main actions required includes :
1. Define objectives against which risks will be identified.
2. Define how risk management elements will be scaled for the
project.
3. Define risk thresholds , tolerances and appetite.
Risk management process will be iterative through the project life
cycle due to the emergent nature of risks.
Qualitative analysis used to gain understanding and evaluate
individual risks while Quantitative analysis evaluate project overall
risk.
Project Network diagram is an important input to Risk management
as you should look for :
1. Estimates , especially ones that contains padding
2. Path Convergence , where more than one path leads to one
activity.
3. Allocation of resources and expert level.
4. Parallel Activities.
5. Critical Path as it should be within project allocated time.
6. Number of near critical pathes.
7.
One point estimates for activities schedule and cost contains the
higher risk.
The best way to shorten project schedule is to identify and
eliminate risks,
Communication management plan is an important input to risk
management, reporting of risk activitites should be stated in
communication management plan.
There are some specific communication check points such as :
1. When charter is finalized.
2. When WBS is created.
3. When risks score is determined.
4. When risk response plans are created.
5. When creating monthly report.
6. More formal checkpoints are Go/No Go Decisions.
Organization Process assets are valuable input to risk
management as it provides some useful templates such as :
1. Reporting forms of risks
2. Standard Probability and Impact matrix.
3. Risk ranking standards for Go/No Go Decisions.
4. Procedures for Risk Audits.
Risk tolerance Areas are usually expressed in terms of project
constraints , Scope , Cost , time , Quality , Resources , Risks and
customer satisfaction.
Some Project Managers collect the risk thresholds and tolerances
from key stakeholders while they are collecting requirements.
Вам также может понравиться
- Project Risk ManagementДокумент16 страницProject Risk ManagementRishabhGuptaОценок пока нет
- Risk Management: Reported By: Darroca, John Rolde Augustine G. Deraper, Rachelle Mae Felismino, Mary R. Patoc, NinoДокумент31 страницаRisk Management: Reported By: Darroca, John Rolde Augustine G. Deraper, Rachelle Mae Felismino, Mary R. Patoc, NinoMary FelisminoОценок пока нет
- Project Management AssignmentДокумент12 страницProject Management AssignmentHimanshu yogiОценок пока нет
- Project Risk ManagementДокумент12 страницProject Risk ManagementRadeeshaОценок пока нет
- 18300038,14th, MGT 331, AssignmentДокумент8 страниц18300038,14th, MGT 331, AssignmentMd RifatОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - Looking at Projects RISKДокумент22 страницыChapter 2 - Looking at Projects RISKErmia MogeОценок пока нет
- 08 MarchewkaДокумент57 страниц08 Marchewkablackphoenix303Оценок пока нет
- #Assignment AbangДокумент5 страниц#Assignment AbangNurul SyahirahОценок пока нет
- The Importance of Risk ManagemДокумент5 страницThe Importance of Risk ManagemSerhat GünerОценок пока нет
- Gole ProjectДокумент73 страницыGole ProjectAaditya GoleОценок пока нет
- Project Risk Management - Area 8Документ49 страницProject Risk Management - Area 8Rutu BarveОценок пока нет
- Shaista Naz (Risk Management 1)Документ3 страницыShaista Naz (Risk Management 1)Shaista MalikОценок пока нет
- Bec 3324: Project Management Year Iii - Semester Ii Session 7Документ35 страницBec 3324: Project Management Year Iii - Semester Ii Session 7Tharindu PereraОценок пока нет
- Project Risk Management TemplateДокумент6 страницProject Risk Management TemplateJr HaumaОценок пока нет
- Session 5 Managing Risks in Project ManagementДокумент23 страницыSession 5 Managing Risks in Project Managementallahgodallah1992Оценок пока нет
- Lecture 1Документ21 страницаLecture 1habibrao253Оценок пока нет
- ManagementДокумент13 страницManagementMOHAMED SLIMANIОценок пока нет
- Risk ManagementДокумент6 страницRisk ManagementAlabi David oluwatobilobaОценок пока нет
- 4.5 PresentationДокумент13 страниц4.5 PresentationHajar SadikiОценок пока нет
- Risk ManualДокумент19 страницRisk ManualLoc Vinh PhungОценок пока нет
- Project Risk Management: Muhammad HasnainДокумент36 страницProject Risk Management: Muhammad Hasnainhweshid sjhjsjkОценок пока нет
- Risk Management in SoftwareДокумент14 страницRisk Management in SoftwareSyed Bilal MahmoodОценок пока нет
- CDC UP Risk Management Practices GuideДокумент7 страницCDC UP Risk Management Practices GuidePoli MarkovaОценок пока нет
- Risk Management PlanДокумент16 страницRisk Management Plandrsuresh26Оценок пока нет
- Risk Management GuideДокумент11 страницRisk Management GuideRajОценок пока нет
- Lecture 7 RiskДокумент59 страницLecture 7 RiskSidra Majeed100% (1)
- Project Risk Management: Nitishree Upadhyay Sanam Shrestha Sayar Prajapati Sushrut GautamДокумент26 страницProject Risk Management: Nitishree Upadhyay Sanam Shrestha Sayar Prajapati Sushrut GautamSushrutОценок пока нет
- Risk Management PlanДокумент27 страницRisk Management PlanJigneshОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6Документ15 страницChapter 6hailegebraelОценок пока нет
- Part 5 Risk ManagementДокумент17 страницPart 5 Risk ManagementPrincess Dayana Quiozon100% (1)
- HR ExecutiveДокумент16 страницHR ExecutiveAli AbbasОценок пока нет
- Risk Management in Software Engineering: Prepared by Sneha MudumbaДокумент14 страницRisk Management in Software Engineering: Prepared by Sneha MudumbameenahilОценок пока нет
- Risk Management in Software EngineeringДокумент14 страницRisk Management in Software EngineeringprincipelicОценок пока нет
- Risk Management Plan Preparation GuidelinesДокумент17 страницRisk Management Plan Preparation Guidelineszenagit123456Оценок пока нет
- CM659-Module 2 - Planning Project Risk ManagementДокумент15 страницCM659-Module 2 - Planning Project Risk Managementlyster badenasОценок пока нет
- Risk ManagementДокумент10 страницRisk ManagementharanaliveОценок пока нет
- Final Group 2 Risk Management Plan PDFДокумент23 страницыFinal Group 2 Risk Management Plan PDFadabotor7Оценок пока нет
- RiskДокумент4 страницыRiskadylanОценок пока нет
- Assignment 2Документ4 страницыAssignment 2Prosper ShumbaОценок пока нет
- 12 - Risk ManagementДокумент14 страниц12 - Risk ManagementHaseeb MianОценок пока нет
- Decision TMA2 AnswerДокумент5 страницDecision TMA2 AnswerYosef DanielОценок пока нет
- Project Risk ManagementДокумент3 страницыProject Risk ManagementMary FelisminoОценок пока нет
- Saction RisksДокумент10 страницSaction RisksSD Islam Al Azhar 36 BandungОценок пока нет
- Adventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementОт EverandAdventurer's Guide to Risk Management: Fictional Tales about Risk ManagementОценок пока нет
- Lecture 10 - ProjectManagement - RiskДокумент44 страницыLecture 10 - ProjectManagement - RiskDiana DmОценок пока нет
- 6.0 Risk ManagementДокумент43 страницы6.0 Risk ManagementAizuddinHakimBennyОценок пока нет
- Sri 3Документ7 страницSri 3Study BuddiesОценок пока нет
- Risk Flashcards PDFДокумент12 страницRisk Flashcards PDFNaveen PisatiОценок пока нет
- Basic Risk Analysis & Mitigation ProcessДокумент18 страницBasic Risk Analysis & Mitigation ProcessMd Mahadi Hasan RemalОценок пока нет
- Effective Management of RiskДокумент3 страницыEffective Management of RiskAbiОценок пока нет
- Hermela Risk AssignmentДокумент9 страницHermela Risk AssignmentHermela tedlaОценок пока нет
- 1 Explain in Detail Importance of Project Risk ManagementДокумент8 страниц1 Explain in Detail Importance of Project Risk ManagementRaj BhoreОценок пока нет
- Riskmanagement 12592328544536 Phpapp02Документ29 страницRiskmanagement 12592328544536 Phpapp02Jyothi RameshОценок пока нет
- Risk Management: Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis-The Process of Prioritising Risks For FurtherДокумент26 страницRisk Management: Perform Qualitative Risk Analysis-The Process of Prioritising Risks For FurthershifaОценок пока нет
- Risk ManagermentДокумент34 страницыRisk ManagermentAbbas WarsiОценок пока нет
- Pm652 Lm6 NotesДокумент5 страницPm652 Lm6 NotesNatasha ReavesОценок пока нет
- PM NOTES Chapter No 4Документ4 страницыPM NOTES Chapter No 4Ashish KhadakhadeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11Документ2 страницыChapter 11Zahrul ArafahОценок пока нет
- Event Enrolment Form: TWI Middle East FZ - LLCДокумент4 страницыEvent Enrolment Form: TWI Middle East FZ - LLCVenkatesh PethurajОценок пока нет
- Technical Integrity Engineering Is A Term Applied To The Engineering Disciplines Associated With TheДокумент5 страницTechnical Integrity Engineering Is A Term Applied To The Engineering Disciplines Associated With TheVenkatesh PethurajОценок пока нет
- Rtfi Assessment Report FormДокумент1 страницаRtfi Assessment Report FormVenkatesh PethurajОценок пока нет
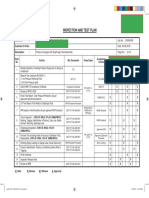
- ITPДокумент1 страницаITPVenkatesh PethurajОценок пока нет
- API 510 - Course NotesДокумент488 страницAPI 510 - Course NotesVenkatesh Pethuraj83% (6)
- AMCA Publication 511-10 - Certified Ratings Program Product Rating Manual For Air Control DevicesДокумент68 страницAMCA Publication 511-10 - Certified Ratings Program Product Rating Manual For Air Control DevicesSurajit PaulОценок пока нет
- 14C040F03 2675 VVV 9Q663 B C Coversheet PDFДокумент1 страница14C040F03 2675 VVV 9Q663 B C Coversheet PDFVenkatesh PethurajОценок пока нет
- Operations Management: BITS PilaniДокумент11 страницOperations Management: BITS PilaniVenkatesh PethurajОценок пока нет
- 14C040F03 2675 VVV 9Q663 B C Coversheet PDFДокумент1 страница14C040F03 2675 VVV 9Q663 B C Coversheet PDFVenkatesh PethurajОценок пока нет
- OM Global StrategyДокумент11 страницOM Global StrategyVenkatesh PethurajОценок пока нет
- Organizational Behavior-ZapposДокумент16 страницOrganizational Behavior-Zappostiko bakashviliОценок пока нет
- Soal B. Inggris Kelas X Semester 2Документ5 страницSoal B. Inggris Kelas X Semester 2Aliyah Al-IhsaniyahОценок пока нет
- CV - Elchin SalimovДокумент3 страницыCV - Elchin SalimovMicRoToneОценок пока нет
- A Step-by-Step Approach To Pump Selection Pumps & SystemsДокумент6 страницA Step-by-Step Approach To Pump Selection Pumps & SystemsABRAHAM ESTRADAОценок пока нет
- A869-6-44-0005 PMS For RevampДокумент950 страницA869-6-44-0005 PMS For RevampMastram HatheshОценок пока нет
- Soal Bahasa Inggris KLS IxДокумент5 страницSoal Bahasa Inggris KLS IxIrvan RiandiОценок пока нет
- A Reconsideration of The Social RitualДокумент16 страницA Reconsideration of The Social RitualFedeОценок пока нет
- Uise Turgeon: and TechniqueДокумент456 страницUise Turgeon: and TechniqueybiernasdonОценок пока нет
- Complex Analysis: Chapter V. Singularities V.1. Classification of Singularities-Proofs of TheoremsДокумент23 страницыComplex Analysis: Chapter V. Singularities V.1. Classification of Singularities-Proofs of TheoremsTOM DAVISОценок пока нет
- Why Choose A Sale CareerДокумент14 страницWhy Choose A Sale CareerMulong CabrillasОценок пока нет
- Exercise 4.9 Review Questions: Understanding and FluencyДокумент3 страницыExercise 4.9 Review Questions: Understanding and FluencySGillespieОценок пока нет
- Grade 7 CBC Business Studies Schemes of Work Term 1Документ14 страницGrade 7 CBC Business Studies Schemes of Work Term 1GEOFRY KIRUIОценок пока нет
- Styrolux 684D SBC Ineos TDS enДокумент3 страницыStyrolux 684D SBC Ineos TDS enfabianmendez2875Оценок пока нет
- Spin Your Self Talk: A Guide To Breaking Out of A Self-Talk RutДокумент11 страницSpin Your Self Talk: A Guide To Breaking Out of A Self-Talk RutAmelia HandayaniОценок пока нет
- AS Prac 4 - Effect of Temperature On Rate - GridДокумент2 страницыAS Prac 4 - Effect of Temperature On Rate - GridElla O'NEILLОценок пока нет
- CMO 92 S. 2017 BS Civil EngineeringДокумент408 страницCMO 92 S. 2017 BS Civil EngineeringDaniel DomingoОценок пока нет
- Rivets For Air Drum BrakesДокумент5 страницRivets For Air Drum BrakessreckoОценок пока нет
- Electrical and Electronincs MeasurementsДокумент51 страницаElectrical and Electronincs Measurementsrao asadОценок пока нет
- Ch2 Small Scale Fading and MultipathДокумент30 страницCh2 Small Scale Fading and MultipathaqilahОценок пока нет
- MacroenvironmentДокумент2 страницыMacroenvironmentAlan-Vital Samin Av-sОценок пока нет
- SW 306 Hydraulic OilДокумент4 страницыSW 306 Hydraulic OilgunawathyОценок пока нет
- SFS Academic Council Report On Map of The Modern World ChangesДокумент7 страницSFS Academic Council Report On Map of The Modern World ChangesJuliana BrintОценок пока нет
- MOdule GRADE 11 Module 1-2 Activity SHEETДокумент1 страницаMOdule GRADE 11 Module 1-2 Activity SHEETChristian Cabadongga100% (2)
- Mi CepДокумент9 страницMi CepSaad khanОценок пока нет
- Gamma 333 PC Gamma 333 PC - B: Operating InstructionsДокумент165 страницGamma 333 PC Gamma 333 PC - B: Operating InstructionsIsakov Igor100% (7)
- How A 4-20 Ma Transmitter WorksДокумент3 страницыHow A 4-20 Ma Transmitter WorksVraja KisoriОценок пока нет
- Nit New Test Series NTДокумент7 страницNit New Test Series NTMohommad ShoaibОценок пока нет
- Kami Export - End of Semester Assessment - Study GuideДокумент14 страницKami Export - End of Semester Assessment - Study GuideBarbz BitnickiОценок пока нет
- Coordination Chemistry ReviewsДокумент52 страницыCoordination Chemistry ReviewsAlejandro Estrella GutiérrezОценок пока нет
- OpenStax Psychology2e APA Guidelines MapДокумент17 страницOpenStax Psychology2e APA Guidelines MapmaritasvОценок пока нет