Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Explain X Ray Diffractometer With The Help of Schematic Diagram
Загружено:
Girdhar GopalОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Explain X Ray Diffractometer With The Help of Schematic Diagram
Загружено:
Girdhar GopalАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
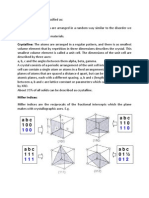
Explain X ray diffractometer with the help of schematic diagram.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a powerful nondestructive technique for characterizing
crystalline materials.
X-ray diffraction is now a common technique for the study of crystal structures and
atomic spacing.
X-ray diffractometers
X-ray diffractometers consist of three basic elements: an X-ray tube, a sample
holder, and an X-ray detector
X-ray diffraction is based on constructive interference of monochromatic X-rays and
a crystalline sample
X-rays are generated in a cathode ray tube by heating a filament to produce
electrons, accelerating the electrons toward a target by applying a voltage, and
bombarding the target material with electrons.
When electrons have sufficient energy to dislodge inner shell electrons of the target
material, characteristic X-ray spectra are produced.
The interaction of the incident rays with the sample produces constructive
interference (and a diffracted ray) when conditions satisfy Bragg’s law:
where n is an integer,
λ is the wavelength of the X-rays,
d is the interplanar spacing generating the diffraction,
and ϴ is the diffraction angle.
The geometry of an X-ray diffractometer is such that the sample rotates at an angle ϴ
while the X-ray detector is mounted on an arm to collect the diffracted X-rays and
rotates at an angle of 2 ϴ.
The instrument used to maintain the angle and rotate the sample is termed a
goniometer
A detector records and processes this X-ray signal and converts the signal to a count
rate, which is then output to a device such as a printer or computer monitor
Q descibe the principal of the particle size analyser. Explain in detail the sample preparation
and the process involved.
Particle size analyser is used to characterise the size distribution of particles in a given sample.
Particle size analysis can be applied to solid materials, suspensions, emulsions and even
aerosols.
The Nanoparticle Size Analyzer instrument is intended for accurate nano and micron size
particle size analysis of a wide variety of samples.
It works on the principle that when a beam of light (a laser) is scattered by a group of particles,
the angle of light scattering is inversely proportional to particle size (ie. the smaller the
particle size, the larger the angle of light scattering).
Вам также может понравиться
- R Don Steele - How To Date Young Women For Men Over 35Документ232 страницыR Don Steele - How To Date Young Women For Men Over 35gonzalo_barandiarán83% (6)
- Proofreading: Basic Guide (Research)Документ34 страницыProofreading: Basic Guide (Research)Mary Christelle100% (1)
- Hindu Succession-Male & FemaleДокумент14 страницHindu Succession-Male & FemaleKumar MangalamОценок пока нет
- Maha Nirvana Tantra EngДокумент200 страницMaha Nirvana Tantra EngDev Vyas100% (2)
- XRD Lab ManualДокумент29 страницXRD Lab ManualNicky198100% (1)
- Sir William Henry Bragg: Noble Prize 1915!Документ53 страницыSir William Henry Bragg: Noble Prize 1915!Harneysia JaneОценок пока нет
- XRDДокумент27 страницXRDBaraliya Jagdish DОценок пока нет
- Company ProfileДокумент15 страницCompany ProfileMuhammad Syaqil NgОценок пока нет
- Resume For Singapore Spass Civil EngineerДокумент8 страницResume For Singapore Spass Civil EngineerArul SD100% (1)
- Digital Logic FamiliesДокумент7 страницDigital Logic FamiliesGirdhar GopalОценок пока нет
- Price and Output Determination Under OligopolyДокумент26 страницPrice and Output Determination Under OligopolySangitha Nadar100% (1)
- Bragg's LawДокумент6 страницBragg's LawMuhammad Nauman Hafeez KhanОценок пока нет
- Xray DiffractionДокумент32 страницыXray Diffractionkunapareddy_anu100% (2)
- X Ray DiffractionДокумент12 страницX Ray DiffractionSiddraKhalidОценок пока нет
- My Kindergarten BookДокумент48 страницMy Kindergarten BookfranciscoОценок пока нет
- Characterization of NanoparticlesДокумент16 страницCharacterization of NanoparticlesPrasun SarkarОценок пока нет
- XRD AnalysisДокумент5 страницXRD Analysisbudhlada100% (2)
- Thesis TopicsДокумент9 страницThesis TopicsInayath AliОценок пока нет
- NMC CBT Sample Q&a Part 3 AcДокумент14 страницNMC CBT Sample Q&a Part 3 AcJoane FranciscoОценок пока нет
- Bragg's Law: What Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Документ2 страницыBragg's Law: What Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Jesus Gonzalez SanquisОценок пока нет
- Experiment-4: Aim: Synthesis and Characterization of Carbon Nanotube/Polypyrrole Requirements: Formula Used: TheoryДокумент4 страницыExperiment-4: Aim: Synthesis and Characterization of Carbon Nanotube/Polypyrrole Requirements: Formula Used: TheoryTush RohОценок пока нет
- III Growth of L-Proline Sodium Sulphate Single Crystals:) Group in Them (27) .Especially Some Amino Acid LikeДокумент16 страницIII Growth of L-Proline Sodium Sulphate Single Crystals:) Group in Them (27) .Especially Some Amino Acid LikeramОценок пока нет
- What Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Документ7 страницWhat Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD)Ahmad NawazОценок пока нет
- 5 Pages XRD AssignmentДокумент5 страниц5 Pages XRD AssignmentZia ud din KhanОценок пока нет
- RAW DATA Physical Methods in Biology and Medicine Biophysics Finals RequirementsДокумент38 страницRAW DATA Physical Methods in Biology and Medicine Biophysics Finals RequirementsALОценок пока нет
- Lec 7 - X-RayДокумент32 страницыLec 7 - X-RayNur Izzati KzmnОценок пока нет
- What Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) : Bragg's LawДокумент8 страницWhat Is X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRD) : Bragg's LawsafiОценок пока нет
- 1X RayДокумент9 страниц1X RayMaysoon YaghiОценок пока нет
- Characterization TechniquesДокумент6 страницCharacterization TechniquesKarunambika ArumugamОценок пока нет
- X RayДокумент8 страницX RayamehnrОценок пока нет
- XRD PDFДокумент6 страницXRD PDFHamza HassanОценок пока нет
- Lecture 15-16 XRDДокумент53 страницыLecture 15-16 XRDbsaimukeshreddy 820Оценок пока нет
- X-Ray DiffractionДокумент9 страницX-Ray DiffractionShashwat JainОценок пока нет
- X Ray DiffractionДокумент6 страницX Ray DiffractionYousef Adel HassanenОценок пока нет
- Xray DiffractionДокумент3 страницыXray DiffractionOsuizugbe Esom kennethОценок пока нет
- XRD FinalДокумент33 страницыXRD FinalprinceamitОценок пока нет
- X-Ray Diffraction 7Документ11 страницX-Ray Diffraction 7alina.tlekkabylova270202Оценок пока нет
- 1408100045-Nila Huda-Thesaurus of XRDДокумент3 страницы1408100045-Nila Huda-Thesaurus of XRDNilaHudaBaqirОценок пока нет
- Single CrystalДокумент6 страницSingle CrystalDolih Gozali100% (1)
- (XRD) Web - Intro Single-CrystalДокумент3 страницы(XRD) Web - Intro Single-CrystalJosé Francisco Blanco VillalbaОценок пока нет
- X-Ray Diffraction: A Powerful Method of Characterizing NanomaterialsДокумент3 страницыX-Ray Diffraction: A Powerful Method of Characterizing NanomaterialsFitra Isni RositaОценок пока нет
- 4481 PDFДокумент7 страниц4481 PDFSumeet Kumar K.K.U NalandaОценок пока нет
- 5 XRDДокумент13 страниц5 XRDAnushri VaidyaОценок пока нет
- ME427 Advanced Material Characterization 1Документ20 страницME427 Advanced Material Characterization 1UTPAL KUMARОценок пока нет
- Instrumental Techniques For Study of Orthodontic MaterialsДокумент18 страницInstrumental Techniques For Study of Orthodontic MaterialsSailusha BatchuОценок пока нет
- XRD TK 2023Документ71 страницаXRD TK 2023Meenakshi MakhijaniОценок пока нет
- First Laboratory X-Ray Diffraction Contrast Tomography For Grain Mapping of PolycrystalsДокумент7 страницFirst Laboratory X-Ray Diffraction Contrast Tomography For Grain Mapping of PolycrystalsXiaobing HuangОценок пока нет
- Basic X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) : In-Situ ExperimentsДокумент47 страницBasic X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) : In-Situ ExperimentsImran KhanОценок пока нет
- Physics 366 Lab Report 2: Michael Dobbs, Sonoma State University November 11, 2014Документ8 страницPhysics 366 Lab Report 2: Michael Dobbs, Sonoma State University November 11, 2014smoothieboyОценок пока нет
- Metal Detection by XRDДокумент29 страницMetal Detection by XRDDeb RathОценок пока нет
- X RaysДокумент7 страницX RaysHarshmeek KaurОценок пока нет
- 5752841Документ19 страниц5752841Anuj SoniОценок пока нет
- What Is Single-Crystal X-Ray DiffractionДокумент5 страницWhat Is Single-Crystal X-Ray DiffractionYousef Adel HassanenОценок пока нет
- Lecture 06Документ32 страницыLecture 06Retro lashОценок пока нет
- Single Crystal X Ray DiffractionДокумент4 страницыSingle Crystal X Ray Diffractioncutecat985351Оценок пока нет
- Xray 1Документ14 страницXray 1mamatamishra822822Оценок пока нет
- XRD (X - Ray Diffraction)Документ7 страницXRD (X - Ray Diffraction)summi64Оценок пока нет
- Material Report 1 StructuralallallДокумент11 страницMaterial Report 1 Structuralallallyassin elwakilОценок пока нет
- 8 X-Ray CrystallДокумент12 страниц8 X-Ray CrystallGustavo AraújoОценок пока нет
- X RaysДокумент17 страницX RaysMerlyn SylvesterОценок пока нет
- X-Ray DiffractionДокумент26 страницX-Ray DiffractionZain Ali KidwaiОценок пока нет
- XRF Report PDFДокумент11 страницXRF Report PDFIshtiaq AnjumОценок пока нет
- Characterization of Nanoparticles: DR - Rabia RazzaqДокумент40 страницCharacterization of Nanoparticles: DR - Rabia RazzaqHafsa MansoorОценок пока нет
- Kimia Analisis Instrumen 2: X-Ray DiffractionДокумент28 страницKimia Analisis Instrumen 2: X-Ray Diffractionsofi salasiОценок пока нет
- Report On Tour To Csir-National Institute For Interdisciplinary Science and Technology (Niist)Документ7 страницReport On Tour To Csir-National Institute For Interdisciplinary Science and Technology (Niist)Anandhu M SОценок пока нет
- Summary of XRDДокумент4 страницыSummary of XRDSofía Peñafiel VicuñaОценок пока нет
- Wiki X-Ray FluorescenceДокумент13 страницWiki X-Ray FluorescenceAsif AshrafiОценок пока нет
- Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research AДокумент7 страницNuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research Acordella_francescoОценок пока нет
- Photon Counting Detectors for X-ray Imaging: Physics and ApplicationsОт EverandPhoton Counting Detectors for X-ray Imaging: Physics and ApplicationsОценок пока нет
- Research Methodology and Design of ExperimentДокумент1 страницаResearch Methodology and Design of ExperimentGirdhar GopalОценок пока нет
- Research Methodology and Design of ExperimentДокумент1 страницаResearch Methodology and Design of ExperimentGirdhar GopalОценок пока нет
- RM & Doe Assignment 3 - 2019rec9550 PDFДокумент14 страницRM & Doe Assignment 3 - 2019rec9550 PDFGirdhar GopalОценок пока нет
- Mensuration Tricks, Formulas & Examples: Add CommentДокумент19 страницMensuration Tricks, Formulas & Examples: Add CommentGirdhar GopalОценок пока нет
- From Vector ModelДокумент9 страницFrom Vector ModelGirdhar GopalОценок пока нет
- UPPSC Combined State / Upper Subordinate Services (UPPCS) Preliminary Exam SyllabusДокумент6 страницUPPSC Combined State / Upper Subordinate Services (UPPCS) Preliminary Exam SyllabusGirdhar GopalОценок пока нет
- CO Formula Notes - PDF 62Документ11 страницCO Formula Notes - PDF 62Girdhar GopalОценок пока нет
- Region XiДокумент2 страницыRegion XiGarcia, Rafael Rico O.Оценок пока нет
- Arabic Unit 1 June 2011 Mark SchemeДокумент9 страницArabic Unit 1 June 2011 Mark SchemeGhaleb W. MihyarОценок пока нет
- GnatusДокумент36 страницGnatusNacer Mezghiche100% (1)
- Case Digest 2 S.C. MEGAWORLD CONSTRUCTIONДокумент3 страницыCase Digest 2 S.C. MEGAWORLD CONSTRUCTIONRomualdo CabanesasОценок пока нет
- BArch Thesis Proposal Form - 27march 2023 1 PDFДокумент3 страницыBArch Thesis Proposal Form - 27march 2023 1 PDFDevkalpaОценок пока нет
- PRP RationaleДокумент12 страницPRP Rationalemarquezjayson548Оценок пока нет
- J2 P IntroductionДокумент9 страницJ2 P IntroductionnitinvnjОценок пока нет
- Hazardous Location Division Listed LED Light: Model 191XLДокумент2 страницыHazardous Location Division Listed LED Light: Model 191XLBernardo Damas EspinozaОценок пока нет
- Allama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Secondary Teacher Education Department) WarningДокумент2 страницыAllama Iqbal Open University, Islamabad: (Secondary Teacher Education Department) WarningAiNa KhanОценок пока нет
- Moatiz Riaz - Area Sales ManagerДокумент1 страницаMoatiz Riaz - Area Sales ManagerMoatiz RiazОценок пока нет
- Method Statement Free Download: How To Do Installation of Suspended False CeilingsДокумент3 страницыMethod Statement Free Download: How To Do Installation of Suspended False Ceilingsmozartjr22100% (1)
- South WestДокумент1 страницаSouth WestDarren RadonsОценок пока нет
- Crim 2 Module 2 Atty A.D.G.Документ7 страницCrim 2 Module 2 Atty A.D.G.Badens DgОценок пока нет
- Buchanan, KeohaneДокумент34 страницыBuchanan, KeohaneFlorina BortoșОценок пока нет
- MAPEH 1 (4th Quarter)Документ27 страницMAPEH 1 (4th Quarter)JESSELLY VALESОценок пока нет
- SSP 861603 - EN - Tire Pressure Monitoring SystemsДокумент42 страницыSSP 861603 - EN - Tire Pressure Monitoring Systemsa.diedrichsОценок пока нет
- Biologic and Biophysical Technologies. FINALДокумент28 страницBiologic and Biophysical Technologies. FINALRafael Miguel MallillinОценок пока нет
- October 2014 1413376166 06 PDFДокумент3 страницыOctober 2014 1413376166 06 PDFDineshОценок пока нет
- Enga10 Speaking Test3Документ2 страницыEnga10 Speaking Test3luana serraОценок пока нет
- Ra 9293 Amending Ra 7836Документ2 страницыRa 9293 Amending Ra 7836vonoblesseОценок пока нет