Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
DME - New Paper Analysis 4 - Belt and Chain Drive
Загружено:
darshit dadhaniyaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
DME - New Paper Analysis 4 - Belt and Chain Drive
Загружено:
darshit dadhaniyaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GTU Paper Analysis
Chapter 4 – Belt and Chain Drive
May – 16
May – 17
May – 18
May – 19
Nov – 16
Nov – 17
Nov – 18
Dec – 15
Sr.
Questions
No.
Theory
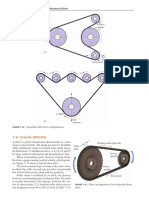
1. Explain any two type of chain with neat sketches. 05
2. Explain the polygon action of chain. 02
3. Compare the belt and chain drives. 03
4. Explain tooth correction factor for roller chain. 03
5. Explain load and power transmitting capacity of chain drive. 04
Derive the expression of a ratio of driving tensions for the flat belt drive. Explain the effect of
6. 07 07
centrifugal tension on ratio of driving tensions in brief.
7. Derive an expression for the ratio of driving tensions of a V-belt drive. 07 07
8. What is crowning of the pulley? State the objectives of providing crowning. 03 04
9. Explain the step by step procedure used for design of chain drive system. 07 03
Why is the cross-section of the pulley an elliptical arm? Why is major axis of the cross-section in the 03
10.
plane of rotation?
11.State the advantage and disadvantage of the chain drive over belt and rope drive. 04
12.Sketch the cross section of a V-belt and label its important parts. 03
13.Explain the difference between belt slip and belt creep. 03
14.Explain the design of belt. 04
Design of Machine Elements (2151907)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology
GTU Paper Analysis
15.State the advantages of chain drive over belt drive 04
16.Explain effect of slip and creep on belt drive 03
17.List advantages and disadvantages of chain drive 04
18.Explain effect of initial tension on belt drive 03
19.Explain working of (1) Compound belt drive (2) Fast and loose pulley belt drive with neat sketch 04
20.What is the purpose of providing steel or nylon cords in the inner case of V-belt? 03
21.What are the application of Flat, V, Round and Timing belt belts in engineering? 04
22.What is polygon effect in chain drive? How it is minimized? 03
23.Explain the procedure for selection of a standard V belt. 04
Examples
A flat belt drive transmits 50 kW at 25 m/s. The mass of the belt is 1.75 kg per metre of belt length and
width the belt is 180 mm. The belt drive is cross belt drive having driver pulley of 350 mm and driven
1. pulley of 1050 mm. The centre distance between two pulleys is 5 m. Calculate the length of belt; angle 07
of contact; belt tensions and thickness of belt. Take mass density of belt = 1000 kg/m3 and coefficient
of friction between belt and pulley surface =0.35.
Two V Belts of section B are transmitting power on grooved pulleys. Angle of Groove is 35 0. Belt angle
is 400. The driver pulley of 300 mm runs at 1500 rpm and driven pulley is 600 mm diameter. The
coefficient of friction between belt and pulley is 0.3. If the power transmitted is 150 kW, determine (i)
2. 07
Centrifugal tension (ii) maximum tension, (iii) length of the belt for open drive. (iv) designation of the
belt, (v) the speed at which maximum power can be transmitted The mass of the belt is 0.193 kg per m
length For Section B Belt. Assume centre distance between pulleys is 900 mm.
Design a 10 mm thick rubber belt to drive a dynamo generating 20 KW at 2250 R.P.M. and fitted with a
3. pulley 200 mm diameter. The dynamo efficiency to be 85%. Allowable stress for belt = 2.1 MPa, 07
Density of rubber = 1000 kg/m3, Angle of contact for dynamo pulley = 1650, μ = 0.3.
4. A compressor, requiring 90 KW, is to run at about 250 R.P.M. The drive is by V-belts from an electric 07
Design of Machine Elements (2151907)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology
GTU Paper Analysis
motor running at 750 R.P.M. The diameter of pulley on compressor shaft must not be greater than 1
metre while the centre distance between the pulleys is limited to 1.75 metre. The belt speed should not
exceed 1600 meters/min. Determine the number of V-belts required to transmit the power if each belt
has a cross-sectional area of 375 mm2, density 1000 kg/m3 and an allowable tensile stress of 2.5 MPa.
The groove angle of the pulleys is 350. The coefficient of friction between the belt and the pulley is 0.25.
Calculate also the length required of each belt.
A fan is driven by open belt from a motor runs at 880 rpm. A leather belt 8 mm thick and 250 mm wide
is used. The diameter of motor pulley and driven pulley are 350 mm and 1370 mm respectively. The
5. centre distance is 1370 mm and both pulleys are made of cast iron. The coefficient of friction of leather 07
on cast iron is 0.35. The allowable stress for the belt is 2.5 MPa, which allows for factor of safety. The
belt mass is 975 kg/m3. Determine the power capacity of belt drive.
A cast iron pulley transmits 20 kW at 300 rpm. The diameter of pulley is 550 mm and has four straight
6. arms of elliptical cross-section in which the major axis is twice the minor axis. Find the dimensions of 04
the arm if the allowable bending stress is 15 MPa.
A leather belt 9 mm x 250 mm is used to drive cast iron pulley 900 mm in diameter at 336 r.p.m. If the
7. active arc on smaller pulley is 1200 and the stress in the tight side is 2 N/mm 2, find the power capacity 07
of the belt. The density of leather may be taken as 980 kg/m3, and μ = 0.35.
Two parallel shafts whose center lines are 4.8 m apart, are connected by an open belt drive. The
diameter of the larger pulley 1.5 m and that of smaller pulley 1.05 m. The initial tension in the belt
8. when stationery is 3 KN. The mass of the belt is 1.5 kg/m length. The co-efficient of friction between 07
the belt and the pulley is 0.3 Taking centrifugal tension in to account, calculate the horse power
transmitted, when smaller pulley rotates at 400 r.p.m.
A centrifugal blower driven by horizontal belt drive running at 600 r.p.m. by a 15 kW, 1750 r.p.m.
electric motor. The center distance is twice the diameter of the larger pulley. The density of the belt
9. material = 1500 kg/m3; maximum allowable stress = 4 MPa; Coefficient of friction at motor pulley and 07
blower pulley is 0.5 and 0.4 respectively; peripheral velocity of the belt = 20 m/s. Determine the
following: 1. Pulley diameters; 2. belt length; 3. cross-sectional area of the belt; 4. minimum initial
Design of Machine Elements (2151907)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology
GTU Paper Analysis
tension for operation without slip.
A 15 KW power transmitting leather belt drive running at 1440 rpm to 480 rpm. The center distance
10.between the pulleys is twice the diameter of the bigger pulley. The belt should operate at 20 m/s 04
approximately. Calculate the diameters pulleys and the length of the belt for open belt drive.
Two shafts 1.2 m apart connected by pulley having multiple V-grooves. The system is required to
transmit 84 kW power. The driving pulley is running at 900 rpm and has an effective diameter of 240
mm while the driven pulley diameter is 640 mm. groove angle of the pulley is 450. The belt used can
11. 07
safely withstand a pull of 1890 N and each has cross section area of 395 mm 2. Density of the belt
material is 1200 kg / m3. Coefficient of friction is 0.23. Calculate the number of belts required to
accomplish the job.
Design a chain drive to actuate a compressor from 15 kW electric motor at running 970 rpm and
12.compressor running at 330 rpm. Minimum center distance should be 550 mm. The chain tension may 07
be adjusted by shifting the motor rails. The compressor is to work 16 hr/day.
The centre distance between two shafts is 4 m for a flat belt drive. The thickness of the belt is 10 mm.
13.The driving pulley having 350 mm diameter is rotating with 1800 RPM. Driven pulley is rotating with 07
600 RPM. Considering slip of 5% determine outer diameter of driven pulley and belt length for (1)
open belt drive (2) crossed belt drive
Design a V-belt drive from the given data. Motor power = 3.75 KW, Belt Width = 17 mm, Speed of
14.motor = 1440 RPM, Belt thickness = 11 mm, Speed reduction = 4, Belt area = 140 mm 2, Density of belt= 07
1.5 x 10(-5) N/mm3, Endurance limit for belt is 10N/mm2
A Leather belt, 160 mm wide and 7 mm thick is used to transmit 3kW under light shock load conditions
for which service factor is 1.2.the driving pulley is of 160 mm diameter and operates at 1440 rpm. The
driven pulley is 480 mm in diameter and centers of pulley are 2.4 m apart. Considering open belt drive,
w=11,200 N/mm3 for belt, μ = 0.4 between pulley and belt, and allowable tension per mm width at
15.3m/s is equal to 7.2 n/mm. Determine 07
Centrifugal tensions,
Tensions on tight and slacks sight,
Factor of safety and
Design power.
16.A simple chain no.06 B is used to transmit power from a transmission shaft running at 1000 rpm to 07
another shaft running at 500 rpm. There are 21 teeth on driving sprocket wheel and operation is
Design of Machine Elements (2151907)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology
GTU Paper Analysis
smooth without any shock.
Calculate:
1. power transmission capacity of the chain
2. chain velocity
3. chain tension
4. factor of safety based on breaking load
5. Length of chain if centre distance is 50p
Design of Machine Elements (2151907)
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Darshan Institute of Engineering & Technology
Вам также может понравиться
- Dish Washer Mcachine ProjectДокумент43 страницыDish Washer Mcachine ProjectVijay Powar60% (5)
- Slide 1: No-Churn TelecomДокумент11 страницSlide 1: No-Churn Telecomleongladxton100% (1)
- MD GTU Study Material GTU-Paper-Analysis ALL 18092019084700AM PDFДокумент20 страницMD GTU Study Material GTU-Paper-Analysis ALL 18092019084700AM PDFD VОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 - Design of Springs: Sr. No. QuestionsДокумент5 страницChapter 3 - Design of Springs: Sr. No. Questionsdarshit dadhaniyaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - Pressure Vessels: Sr. No. QuestionsДокумент5 страницChapter 5 - Pressure Vessels: Sr. No. Questionsdarshit dadhaniyaОценок пока нет
- TOM GTU Study Material GTU-Paper-Analysis All-Units 05102019072605AMДокумент23 страницыTOM GTU Study Material GTU-Paper-Analysis All-Units 05102019072605AMSanat PatelОценок пока нет
- GTU-Paper-Analysis PDF All 20052019032318PMДокумент13 страницGTU-Paper-Analysis PDF All 20052019032318PMrockbharat130% (2)
- Chapter 1 - Introduction: Sr. No. QuestionsДокумент21 страницаChapter 1 - Introduction: Sr. No. QuestionsAniruddh PatelОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Introduction: Sr. No. QuestionsДокумент2 страницыChapter 1 - Introduction: Sr. No. Questionsdarshit dadhaniyaОценок пока нет
- Theory of Machine AssignmentДокумент3 страницыTheory of Machine AssignmentshehzadОценок пока нет
- Gnanamani College of TechnologyДокумент15 страницGnanamani College of TechnologyRajueswarОценок пока нет
- ME6601 Design of Transmission Systems 2 Marks With AnswersДокумент6 страницME6601 Design of Transmission Systems 2 Marks With Answerspremgmech762Оценок пока нет
- RequestДокумент22 страницыRequestOmar MuñozОценок пока нет
- ANNA UNIVERSITY Dts Two MarkДокумент7 страницANNA UNIVERSITY Dts Two MarkkarthisanОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Subject Name-Theory of Machine Branch - Production Engineering Subject Code - BPE2402 Semester - 4Документ2 страницыLesson Plan Subject Name-Theory of Machine Branch - Production Engineering Subject Code - BPE2402 Semester - 4Raja RamachandranОценок пока нет
- 3machine Elements in Mechanical DesignДокумент14 страниц3machine Elements in Mechanical DesignNachoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 & 2 - Metal Casting Process: Sr. No. QuestionsДокумент8 страницChapter 1 & 2 - Metal Casting Process: Sr. No. QuestionsRutvikОценок пока нет
- DTS ALL UNITS-PART A QsДокумент3 страницыDTS ALL UNITS-PART A QsntsdharmaОценок пока нет
- EM - II GTU Study Material GTU-Paper-Analysis All 04072020090955AMДокумент6 страницEM - II GTU Study Material GTU-Paper-Analysis All 04072020090955AMDharam100% (3)
- Chapter 1 - Gear Design: Sr. No. QuestionsДокумент8 страницChapter 1 - Gear Design: Sr. No. QuestionsRushabh PatelОценок пока нет
- BRAKE SYSTEM HyundaiДокумент6 страницBRAKE SYSTEM HyundaiAfshin GhafooriОценок пока нет
- DTS Univ QPДокумент29 страницDTS Univ QPAnand NagarajanОценок пока нет
- Re-Balancing of Generalized Assembly Lines - Searching Optimal Solutions For SalbpДокумент7 страницRe-Balancing of Generalized Assembly Lines - Searching Optimal Solutions For Salbpsitam_nitj4202Оценок пока нет
- Design of Transmission SystemДокумент23 страницыDesign of Transmission Systemspsurya2013100% (2)
- Mech-Iv-Kinematics of Machines (10me44) - Notes PDFДокумент196 страницMech-Iv-Kinematics of Machines (10me44) - Notes PDFgopalОценок пока нет
- Model 2 Marks DtsДокумент1 страницаModel 2 Marks DtsnivasmechanicalОценок пока нет
- 073 - ME8651, ME6601 Design of Transmission Systems - 2 Marks With AnswersДокумент19 страниц073 - ME8651, ME6601 Design of Transmission Systems - 2 Marks With AnswersJ O NОценок пока нет
- KOM LAB IVSem PDFДокумент24 страницыKOM LAB IVSem PDFvenkatksr1987Оценок пока нет
- E45-70XN SERIES Technical GuideДокумент12 страницE45-70XN SERIES Technical GuideEmilio CortesОценок пока нет
- MP-I - Paper Analysis - 29072018 - 051415PM PDFДокумент12 страницMP-I - Paper Analysis - 29072018 - 051415PM PDFSantosh jhaОценок пока нет
- Assignment DME 2Документ3 страницыAssignment DME 2prabhjotbhangalОценок пока нет
- 073 - ME8651, ME6601 Design of Transmission Systems - 2 Marks With Answers 5Документ23 страницы073 - ME8651, ME6601 Design of Transmission Systems - 2 Marks With Answers 5002-ABISHEK GОценок пока нет
- Kinematics of Machinery Anna University Question Papers CompiledДокумент77 страницKinematics of Machinery Anna University Question Papers CompiledNatesha SundharanОценок пока нет
- DTSДокумент23 страницыDTSDhaneshОценок пока нет
- TransmissionДокумент4 страницыTransmissionrnkridiОценок пока нет
- Me2352 - DTS 2 Marks With AnswersДокумент23 страницыMe2352 - DTS 2 Marks With AnswersSuresh NatarajanОценок пока нет
- DTSДокумент7 страницDTSmithundme659Оценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan Subject Name-Design of Machine Elements Branch-Production Engineering Subject Code - BPE 2501 Semester - 5 Period/ HoursДокумент1 страницаLesson Plan Subject Name-Design of Machine Elements Branch-Production Engineering Subject Code - BPE 2501 Semester - 5 Period/ HoursRaja RamachandranОценок пока нет
- DTS COACHING QUESTION PAPER (Autosaved) - UNIT-1Документ1 страницаDTS COACHING QUESTION PAPER (Autosaved) - UNIT-1sangeethkumarmОценок пока нет
- Lec 18Документ23 страницыLec 18ayushОценок пока нет
- TESCO MLT Torque Ring Field Make-Up Handbook PDFДокумент44 страницыTESCO MLT Torque Ring Field Make-Up Handbook PDFRene Torres HinojosaОценок пока нет
- Theory of TMДокумент2 страницыTheory of TMBinal TivarОценок пока нет
- Tom QB 030320Документ2 страницыTom QB 030320Arvind YadavОценок пока нет
- Yamaha YZFR6X Service Manual 2008 (197-245)Документ49 страницYamaha YZFR6X Service Manual 2008 (197-245)Harold CruzОценок пока нет
- MTM CYCLE Test 11 Question BankДокумент2 страницыMTM CYCLE Test 11 Question BankRanilprabhu MОценок пока нет
- Design and Development of Gear Test RigДокумент10 страницDesign and Development of Gear Test RigAnonymous CUPykm6DZОценок пока нет
- Piston Rings DesignДокумент35 страницPiston Rings Designkumar_yogesh223881100% (1)
- ME6401 SCAD MSM by EasyEngineering - Net 1Документ122 страницыME6401 SCAD MSM by EasyEngineering - Net 1shankar0% (1)
- DTS Question Bank Jan 2016-1Документ17 страницDTS Question Bank Jan 2016-1AnirudhОценок пока нет
- Machine Design II CHPT 17Документ122 страницыMachine Design II CHPT 17sysevgisy45Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 13 - Chain and SprocketsДокумент78 страницChapter 13 - Chain and SprocketsSugeng Ciko DarmintoОценок пока нет
- Simple Mechanisms: (2 Marks) 1. What Are The Materials Used For Making Ropes?Документ3 страницыSimple Mechanisms: (2 Marks) 1. What Are The Materials Used For Making Ropes?RahulОценок пока нет
- Questions For 2 Marks: Question Bank Unit Test:-II Course: - TOM (22438) Program: - Mechanical Sem: - ME4iДокумент2 страницыQuestions For 2 Marks: Question Bank Unit Test:-II Course: - TOM (22438) Program: - Mechanical Sem: - ME4iindrajitbhise10Оценок пока нет
- Four Bar LinkageДокумент13 страницFour Bar LinkageAnupGautamОценок пока нет
- PaperДокумент23 страницыPapersachin patelОценок пока нет
- ME6601-Design of Transmission SystemsДокумент16 страницME6601-Design of Transmission SystemsSecret SecretОценок пока нет
- Camshaft Lobe DesignДокумент7 страницCamshaft Lobe Designagandoel100% (1)
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachОт EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachОценок пока нет
- Analytical Kinematics: Analysis and Synthesis of Planar MechanismsОт EverandAnalytical Kinematics: Analysis and Synthesis of Planar MechanismsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (3)
- Internal Combustion Engine Bearings Lubrication in Hydrodynamic BearingsОт EverandInternal Combustion Engine Bearings Lubrication in Hydrodynamic BearingsОценок пока нет
- MICOM P12x-TechnicalDataSheetДокумент28 страницMICOM P12x-TechnicalDataSheetSeba GonzálezОценок пока нет
- SPE15010Документ11 страницSPE15010Leandro NavarroОценок пока нет
- Astm C97/C97M-09Документ3 страницыAstm C97/C97M-09Azuriak150% (2)
- Mesh Based Multicast Routing ProtocolДокумент10 страницMesh Based Multicast Routing ProtocolArul JothiОценок пока нет
- Cell Biology: Science Explorer - Cells and HeredityДокумент242 страницыCell Biology: Science Explorer - Cells and HeredityZeinab ElkholyОценок пока нет
- Differentiation11 21Документ75 страницDifferentiation11 21Maryam ShahidОценок пока нет
- RF Optimization Tips - TCH Block Rate Optimization Tips in Huawei GSMДокумент4 страницыRF Optimization Tips - TCH Block Rate Optimization Tips in Huawei GSMdolisieОценок пока нет
- Web Application Penetration TestingДокумент11 страницWeb Application Penetration TestingRohitОценок пока нет
- Tapchanger Dual Assessment Raka Levi31102011 PDFДокумент12 страницTapchanger Dual Assessment Raka Levi31102011 PDFYuri OmonteОценок пока нет
- Pump Station System Curves Session 1Документ29 страницPump Station System Curves Session 1Toan LeОценок пока нет
- GP 1 Module 3Документ46 страницGP 1 Module 3Raymund EspinoОценок пока нет
- Ali Math Competition 3 English Reference SolutionsДокумент11 страницAli Math Competition 3 English Reference SolutionsJEREMIAH ITCHAGBEОценок пока нет
- Maintenance Component Main Function Level Activity Frequency Line DepartmentДокумент7 страницMaintenance Component Main Function Level Activity Frequency Line DepartmentBarathОценок пока нет
- Quiz 3 Basic ProbabilityДокумент38 страницQuiz 3 Basic ProbabilityjacobtianОценок пока нет
- 1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryДокумент23 страницы1 Kinetic Molecular TheoryAeron Kurt AcuñaОценок пока нет
- MADNotes J2MEДокумент34 страницыMADNotes J2MEKanchana MorumpalliОценок пока нет
- Chm361-Chapter 3 SolidДокумент60 страницChm361-Chapter 3 Solidfatin harrisОценок пока нет
- Class Problems Sentences 13 The DДокумент20 страницClass Problems Sentences 13 The DKnowledgeIsTruePowerОценок пока нет
- 2210 w18 Ms 12Документ12 страниц2210 w18 Ms 12Fiyazul HaqueОценок пока нет
- Automotive Solutions: Setting The Pace For InnovationДокумент36 страницAutomotive Solutions: Setting The Pace For InnovationAda TopanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 Approaches To Software DesignДокумент25 страницChapter 2 Approaches To Software DesigntarunkakkarОценок пока нет
- All The Questions of Section - A Are in Google Form and The Link To Attempt Them Is " Https://Forms - Gle/Jfvq8Wszicewchrj7 " 12 M Section - BДокумент4 страницыAll The Questions of Section - A Are in Google Form and The Link To Attempt Them Is " Https://Forms - Gle/Jfvq8Wszicewchrj7 " 12 M Section - BKamal AnandОценок пока нет
- Prob AnswersДокумент4 страницыProb AnswersDaniel KirovОценок пока нет
- Sap Basis Transaction CodesДокумент2 страницыSap Basis Transaction CodeskatrinbreaksОценок пока нет
- Practical - 1: 1.1 CommitДокумент8 страницPractical - 1: 1.1 CommitRoy BokhiriyaОценок пока нет
- Cree CGH40006pДокумент15 страницCree CGH40006pQazi KamalОценок пока нет
- TCL CommandsДокумент52 страницыTCL Commandssurya_gaddeОценок пока нет
- Just in Time AlgebraДокумент289 страницJust in Time AlgebraamaiscОценок пока нет