Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
MATHMW Unit 4
Загружено:
Jomes Aunzo0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
24 просмотров2 страницыStatistics is the branch of science dealing with collecting, organizing, and interpreting data. It has two main divisions: descriptive statistics, which describes data samples, and inferential statistics, which makes inferences about populations from samples. Key terms include data, population, sample, parameter, variable, and sampling method. Variables can be discrete, continuous, independent, or dependent. Data can be measured at the nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio level. Common methods of data collection include direct interviews, indirect questionnaires, registration, experimentation, and observation. Measures of central tendency include the mean, median, and mode. Measures of variation include the range, quantiles like quartiles and percentiles, interquartile range, standard deviation,
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
MATHMW Unit 4.txt
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документStatistics is the branch of science dealing with collecting, organizing, and interpreting data. It has two main divisions: descriptive statistics, which describes data samples, and inferential statistics, which makes inferences about populations from samples. Key terms include data, population, sample, parameter, variable, and sampling method. Variables can be discrete, continuous, independent, or dependent. Data can be measured at the nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio level. Common methods of data collection include direct interviews, indirect questionnaires, registration, experimentation, and observation. Measures of central tendency include the mean, median, and mode. Measures of variation include the range, quantiles like quartiles and percentiles, interquartile range, standard deviation,
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
24 просмотров2 страницыMATHMW Unit 4
Загружено:
Jomes AunzoStatistics is the branch of science dealing with collecting, organizing, and interpreting data. It has two main divisions: descriptive statistics, which describes data samples, and inferential statistics, which makes inferences about populations from samples. Key terms include data, population, sample, parameter, variable, and sampling method. Variables can be discrete, continuous, independent, or dependent. Data can be measured at the nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio level. Common methods of data collection include direct interviews, indirect questionnaires, registration, experimentation, and observation. Measures of central tendency include the mean, median, and mode. Measures of variation include the range, quantiles like quartiles and percentiles, interquartile range, standard deviation,
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате TXT, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
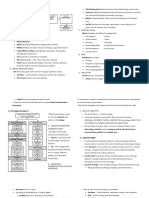
STATISTICS
- Branch of Science that deals with:
Collection
Organization
Presentation
Computation
Interpretation of data
I. Division of Statistics
1. Descriptive Statistics - deals with the collection, organization,
presentation and computation of data to describe the sample under investigation
2. Inferential Statistics - gives information, inferences and implications
regarding the population by studying its representative sample.
II. Definition of Terms
1. Data - Set of observation, values, elements or objects under consideration
2. Population - complete set of all possible observation or elements.
3. Sample - small representative cross-section of the population
4. Parameter - arbitrary constant whose value characterizes a member of a
system.
5. Sampling Method - process choosing a representative part of the population
6. Variable - Statistical quantity that is capable of assuming several values.
III. Kinds of Variables
1. Discrete - Variables whose values can be counted such as the number of
enrollees.
2. Continuous - variable on the other and may progess from one value to the
next without a break and may represented by a whole number or a fraction.
3. Independent and Dependent - two variables are independent, if the
occurrence of the first is not relative to the existence of the second.
IV. Level of Data measurement
1. Normal level - categorical data, frequency data, attribute data or
enumeration data ------
2. Ordinal level - involves data that may be arrange in some meaningful order.
3. Interval level (of measurements) - similar to ordinal level, but meaningful
amounts of differences or equality can be determined between data. This level may
lack an inherent zero starting point.
4. Ratio level (of measurements) - interval level modified to include the
inherent zero starting point.
V. Summation Notation
--------
VI. Kinds of data according to Source
1. Internal data - taken from the company's own records of operation such as
sales, records, personnel records etc.
2. External data - comes from outside sources and not from the company's owns
record
VII. Method of Data Collection
1. Direct or Interview Method - method of person-to-person exchange between
the interviewer and interviewee.
2. Indirect or Questionnaire Method - Written responses are given to prepared
questions intended to elicit answer to the problem of a study.
3. Registration Method - Gathering information forced by a certain laws.
4. Experimental Method - used when the objective is to determine the cause and
effect relationship of certain phenomena under controlled condition.
5. Observation Method - Mostly used to observes the behavior of person
organizations and their outcome.
VIII. Measure of Central Tendency
Mean=Average
Median=Mid-Most
Mode=Appears Most Frequently
A. Two Groups of Data
1. Ungrouped Data = data are NOT arranged in frequency distribution table
2. Group Data = data arranged in frequency distribution table
B. Ungrouped Data------
Mean
Median
C. Types of Mode
1. Unimodal 1,2,3,3,4,5
2. Bimodal 1,1,2,3,4,4,5
3. Multimodal 1,1,2,3,3,4,5,5
IX. Measure of Variation
1. Range - Simplest of the measure of spread or variability
2. Quantiles - is the natural extension of the median concept which divides a
set of data into equal parts
KINDS OF QUANTILES
Quartiles - Divides the data into 4 equal parts
Deciles - Divides the data into 10 equal parts
Percentiles - Divides the data into 100 equal parts
3. Interquartile Range (IQR) - difference between the third and the first
quartiles
4. Standard Variation - It is simply the square root of the variance.
5. Variance - the mean of the standard deviation from the mean
Вам также может понравиться
- Express Review Guide - Algebra 1Документ176 страницExpress Review Guide - Algebra 1Margaret100% (4)
- Chapter 1 StatisticsДокумент41 страницаChapter 1 StatisticsIrish Mae LabragueОценок пока нет
- 2500 Solved Problems in Differential EquationsДокумент452 страницы2500 Solved Problems in Differential EquationsOnard FS100% (7)
- STAT 1N NotesДокумент16 страницSTAT 1N NotesLabLab Chatto100% (2)
- Catia V5 Parameters and Formulas TutorialДокумент25 страницCatia V5 Parameters and Formulas Tutorialananthrengaraj100% (4)
- Module 1 Statistic PDFДокумент7 страницModule 1 Statistic PDFKi xxiОценок пока нет
- STATISTICS ANALYSIS - Reviewer Week 1Документ5 страницSTATISTICS ANALYSIS - Reviewer Week 1Lovely De SalasОценок пока нет
- Statistical Analysis - MODULES 1,2 & 3Документ19 страницStatistical Analysis - MODULES 1,2 & 3Allana MierОценок пока нет
- MYP 5 Domain and Range NotesДокумент3 страницыMYP 5 Domain and Range NotesSamia AkterОценок пока нет
- Simple Linear RegressionДокумент24 страницыSimple Linear RegressionBie JhingcHayОценок пока нет
- A Detailed Lesson PlanДокумент6 страницA Detailed Lesson PlanRaquel NavarezОценок пока нет
- Probability and Statistic1Документ42 страницыProbability and Statistic1Mayette Rose Sarroza100% (1)
- Basic Statistics 18 19 20Документ6 страницBasic Statistics 18 19 20Mirage LeeОценок пока нет
- Criminological ResearchДокумент4 страницыCriminological ResearchKirstein Pran PangodОценок пока нет
- Advanced Calculus For Applications - Francis B Hilderand 1962Документ657 страницAdvanced Calculus For Applications - Francis B Hilderand 1962prabu201Оценок пока нет
- Desmet, Pieter - Designing Emotions (2002)Документ273 страницыDesmet, Pieter - Designing Emotions (2002)Jomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Kemeng ReviewerДокумент8 страницKemeng ReviewerVinabie PunoОценок пока нет
- Module 1 NotesДокумент5 страницModule 1 NotesLovely De SalasОценок пока нет
- STATISTICS - Is A Branch of Mathematics That Deals With The CollectionДокумент14 страницSTATISTICS - Is A Branch of Mathematics That Deals With The CollectionCares OlotrabОценок пока нет
- Sasa ReviewerДокумент8 страницSasa ReviewerPatrick John LumutanОценок пока нет
- Statistics: Statistical Inference Would Not Be Necessary Statistical Methods Are Applicable To EachДокумент3 страницыStatistics: Statistical Inference Would Not Be Necessary Statistical Methods Are Applicable To EachzellyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1Документ2 страницыLecture 1Agustine AcelajadoОценок пока нет
- Module 1Документ6 страницModule 1Khent Ives Acuno SudariaОценок пока нет
- Biostatistics NotesДокумент3 страницыBiostatistics NotesMarnellete Latoja InsoОценок пока нет
- Week 1 Introduction To Statistics 1Документ3 страницыWeek 1 Introduction To Statistics 1Evelyn VelascoОценок пока нет
- Introduction On StatДокумент55 страницIntroduction On StatAndrea Monique R. GalasinaoОценок пока нет
- Introduction To StatisticsДокумент24 страницыIntroduction To Statisticssunhyep.kimОценок пока нет
- Ann Genevieve Flores (Math Activity)Документ6 страницAnn Genevieve Flores (Math Activity)Olsen SoqueñaОценок пока нет
- PAS 111 Week 1Документ3 страницыPAS 111 Week 1Franz PampolinaОценок пока нет
- StatisticsДокумент5 страницStatisticsMachi KomacineОценок пока нет
- Chapter One: 1. Basic Concepts, Methods of Data Collection and PresentationДокумент111 страницChapter One: 1. Basic Concepts, Methods of Data Collection and PresentationGebru GetachewОценок пока нет
- Module 1 STAT GSДокумент5 страницModule 1 STAT GSJohn Rainier QuijadaОценок пока нет
- Stat 1-3 ChaptersДокумент36 страницStat 1-3 ChaptersGizachew NadewОценок пока нет
- ELECTIVEДокумент5 страницELECTIVEmavel ayingОценок пока нет
- Math 4Документ4 страницыMath 4Arceta, Alia Mae M.Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2Документ72 страницыUnit 2Sai priyadarshini SОценок пока нет
- Statistics IntroДокумент5 страницStatistics IntroMai Mgcini BhebheОценок пока нет
- CH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1 PDFДокумент106 страницCH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1 PDFMuket AgmasОценок пока нет
- 2013 CH 1 Up 9 Probability NoteДокумент104 страницы2013 CH 1 Up 9 Probability NoteZemenu mandefroОценок пока нет
- Fish Pond ActivityДокумент13 страницFish Pond ActivityMERAKI ILYОценок пока нет
- Stat I CH - IДокумент19 страницStat I CH - Ibrucknasu279Оценок пока нет
- CH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1Документ91 страницаCH 1 Up 9 Probability Note-1Onetwothree Tube100% (1)
- CHAPTER 5 Data ManagementДокумент2 страницыCHAPTER 5 Data ManagementDonita BinayОценок пока нет
- Unit-2 StatisticsДокумент64 страницыUnit-2 StatisticsJyothi PulikantiОценок пока нет
- Statistics and Probablity Note For EngineersДокумент79 страницStatistics and Probablity Note For EngineerstasheebedaneОценок пока нет
- Module For R-3Документ14 страницModule For R-3Amber EbayaОценок пока нет
- Class Notes Introduction To StatisticsДокумент3 страницыClass Notes Introduction To StatisticsAlex Dee Music HubОценок пока нет
- Statistics With Computer ApplicationДокумент17 страницStatistics With Computer ApplicationMica MellizoОценок пока нет
- Statistics Mod 1Документ4 страницыStatistics Mod 1Jannelle TanОценок пока нет
- From Weakest To Strongest in Terms of Statistical Inference)Документ1 страницаFrom Weakest To Strongest in Terms of Statistical Inference)Cj B. GastanesОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Basic Concepts of StatisticsДокумент12 страницChapter 1 - Basic Concepts of StatisticsFLIPTOP ANALYSISОценок пока нет
- CH 1 Up 9 Probability Note (For Engineering) - 1Документ93 страницыCH 1 Up 9 Probability Note (For Engineering) - 1tazeb AbebeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Full Gned 03Документ30 страницChapter 4 Full Gned 03joseph.mrk24Оценок пока нет
- Statistics For MGMT I & IIДокумент161 страницаStatistics For MGMT I & IIewnetuОценок пока нет
- Generalstatistics 091020092539 Phpapp01Документ129 страницGeneralstatistics 091020092539 Phpapp01Penny BesidОценок пока нет
- Lecture 03Документ25 страницLecture 03mwantelaОценок пока нет
- Overview of Data Processing and AnalysisДокумент6 страницOverview of Data Processing and AnalysisBete AmdОценок пока нет
- Statistical Analysis With Software ApplicationДокумент6 страницStatistical Analysis With Software ApplicationFiona Ramirez RomeroОценок пока нет
- PR 2 FINALS Test 2Документ4 страницыPR 2 FINALS Test 2Sunshine FrigillanaОценок пока нет
- Reviewer Stat MidtermДокумент4 страницыReviewer Stat MidtermSeok Jin KimОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 IntroductionДокумент6 страницChapter 1 Introductionasuasan151Оценок пока нет
- Sta 2260 NotesДокумент118 страницSta 2260 Notesibrahim salimОценок пока нет
- Probability and Statistics NotesДокумент118 страницProbability and Statistics Notesqueenmutheu01Оценок пока нет
- Midterm Exam in Reading and WritingДокумент3 страницыMidterm Exam in Reading and WritingGabriel JaloconОценок пока нет
- Average: Sagni D. 1Документ85 страницAverage: Sagni D. 1keebeekОценок пока нет
- Module 1-Introduction To StatisticsДокумент4 страницыModule 1-Introduction To StatisticsJessa Mae LavadoОценок пока нет
- Tabulation and Presentation of Data - Unit IIДокумент17 страницTabulation and Presentation of Data - Unit IIVidhya BОценок пока нет
- Aunzo - Screening TestДокумент11 страницAunzo - Screening TestJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- The Bet by Anton ChekhovДокумент6 страницThe Bet by Anton ChekhovJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- DEADLINES As of 21-09-19Документ2 страницыDEADLINES As of 21-09-19Jomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- DEADLINES As of 21-10-28Документ2 страницыDEADLINES As of 21-10-28Jomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- DEADLINES As of 21-10-07Документ2 страницыDEADLINES As of 21-10-07Jomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Week 1 2022-08-07 To 13Документ3 страницыWeek 1 2022-08-07 To 13Jomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Aunzo - Ja - WS 3Документ4 страницыAunzo - Ja - WS 3Jomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- IV. Notes On Chinese LiteratureДокумент17 страницIV. Notes On Chinese LiteratureJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- WS 3 - Analysis of Highly Acclaimed WorksДокумент4 страницыWS 3 - Analysis of Highly Acclaimed WorksJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- I. Introduction To LiteratureДокумент37 страницI. Introduction To LiteratureJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Locker Form - CFADSC'sДокумент2 страницыLocker Form - CFADSC'sJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Advertising Practice - Creative SideДокумент8 страницAdvertising Practice - Creative SideJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Aunzo JA PlotTaskДокумент2 страницыAunzo JA PlotTaskJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- LIM, AliciaДокумент38 страницLIM, AliciaJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- ANG, SandyДокумент34 страницыANG, SandyJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- II. Literary ElementsДокумент84 страницыII. Literary ElementsJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- LIM, IsaacДокумент27 страницLIM, IsaacJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- HENG, JoyiДокумент28 страницHENG, JoyiJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- LEE, Kathy Tan ChiaДокумент38 страницLEE, Kathy Tan ChiaJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Chang, Dooley, Tuovinen - Gestalt Theory in Visual Screen Design - A New Look at An Old Subject (2002)Документ8 страницChang, Dooley, Tuovinen - Gestalt Theory in Visual Screen Design - A New Look at An Old Subject (2002)Jomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Strati, Antonio - Aesthetics of Organization (2003)Документ5 страницStrati, Antonio - Aesthetics of Organization (2003)Jomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Bayunitri & Putri - The Effectiveness of Visualization The Logo Towards Brand AwarenessДокумент6 страницBayunitri & Putri - The Effectiveness of Visualization The Logo Towards Brand AwarenessJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Adir, Adir, and Pascu - How To Design A Logo (2014)Документ5 страницAdir, Adir, and Pascu - How To Design A Logo (2014)Jomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- University of Lincoln - Scoring and Making Likert Style QuestionsДокумент9 страницUniversity of Lincoln - Scoring and Making Likert Style QuestionsJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Good Day, 2AD4!: Topic: Encoding Data, Analysis and Interpretation of TablesДокумент17 страницGood Day, 2AD4!: Topic: Encoding Data, Analysis and Interpretation of TablesJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Thumbnails and Comprehensive Sketches FOR Thematic Promotional PostersДокумент12 страницThumbnails and Comprehensive Sketches FOR Thematic Promotional PostersJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- Storyboard Title: PG:: SC# DialogueДокумент2 страницыStoryboard Title: PG:: SC# DialogueJomes AunzoОценок пока нет
- 6.01 - Identifying FunctionsДокумент7 страниц6.01 - Identifying FunctionsZachary StarkОценок пока нет
- Experiment 5 - On-Off ControllerДокумент7 страницExperiment 5 - On-Off ControllerJitender YadavОценок пока нет
- A Thermal Hydrodynamic Lubrication Model of Pivoted Plane-Pad Thrust BearingsДокумент72 страницыA Thermal Hydrodynamic Lubrication Model of Pivoted Plane-Pad Thrust BearingsArisang Ceciea JojobaОценок пока нет
- Unit IV Modelling and Prediction of PerformanceДокумент40 страницUnit IV Modelling and Prediction of PerformancenithinkОценок пока нет
- The Theory Production NotesДокумент14 страницThe Theory Production NotesAmrishaОценок пока нет
- N Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 1.variables and ExpressionsДокумент4 страницыN Gen Math Algebra I.Unit 1.lesson 1.variables and Expressionsarg456Оценок пока нет
- Two-Point Estimates in ProbabilitiesДокумент7 страницTwo-Point Estimates in ProbabilitiesrannscribdОценок пока нет
- LESSON 2.3: The Language of Relations and FunctionsДокумент5 страницLESSON 2.3: The Language of Relations and FunctionsShan DidingОценок пока нет
- Differential EquationДокумент11 страницDifferential EquationMapple VergaraОценок пока нет
- Essential MathematicsДокумент381 страницаEssential MathematicsLaw MirОценок пока нет
- The PQR and Uvw Method PhoenixfireДокумент35 страницThe PQR and Uvw Method PhoenixfireLin LiuОценок пока нет
- 6 STD Text Book Part 2Документ112 страниц6 STD Text Book Part 2Parthasarathy SeshadriОценок пока нет
- Generalization of Laguerre Matrix Polynomials For Two VariablesДокумент11 страницGeneralization of Laguerre Matrix Polynomials For Two VariablesRana HusnainОценок пока нет
- Grade 6 Ratios & Proportional Relationships Sample Unit PlanДокумент47 страницGrade 6 Ratios & Proportional Relationships Sample Unit Plannaiyar alamОценок пока нет
- Tutorial-12 (Non-Dimensionalisation)Документ8 страницTutorial-12 (Non-Dimensionalisation)anik bhowmickОценок пока нет
- Tedds Quick Start Guide (GB)Документ58 страницTedds Quick Start Guide (GB)manoj444_777Оценок пока нет
- Combination of Variable Sol.Документ4 страницыCombination of Variable Sol.Merve EserОценок пока нет
- M3L1 Concept and Definitions of Random VariablesДокумент6 страницM3L1 Concept and Definitions of Random VariablesabimanaОценок пока нет
- Advanced Control System Design Prof. Radhakant Padhi Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Science, BangaloreДокумент38 страницAdvanced Control System Design Prof. Radhakant Padhi Department of Aerospace Engineering Indian Institute of Science, BangaloreJai SebastianОценок пока нет
- First Prelims in GenmathДокумент3 страницыFirst Prelims in GenmathMs. Jhallaine MauricioОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 of MathsДокумент6 страницChapter 6 of MathssanjayОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 - Equations, Inequalities and Absolute ValuesДокумент72 страницыTopic 2 - Equations, Inequalities and Absolute ValuesChandra MohganОценок пока нет