Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Gastric Juice: I. Constituents of Gastric Juice Hydrochloric Acid (HCL)
Загружено:
pradeep kumar gandhamИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Gastric Juice: I. Constituents of Gastric Juice Hydrochloric Acid (HCL)
Загружено:
pradeep kumar gandhamАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
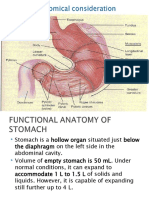
GASTRIC JUICE
Gastric juice is the mixture of secretions from all the glands present in the stomach
The total amount of gastric juice secreted per day is about 2 – 3 litres
Gastric juice is highly acidic in nature with a pH of 0.9-1.5.
The gastric juice contains 99.45 % water and 0.55% solid.
I. Constituents of Gastric Juice
Hydrochloric acid (HCl):
Gastric juice contains hydrochloric acid (HCL).
HCL is present in gastric juice in high amount about 40-60 meq/litre.
Oxyntic cells secrete HCL
HCL gives antiseptic property to the gastric juice
HCl converts pepsinogen into pepsin
HCl stimulates the secretion of different hormones from the small intestine.
Intrinsic Factor :
It is secreted by oxyntic cells of gastric mucous membrane
Intrinsic factor is a glycoprotein
It combines with Vit-B12 (extrinsic factor) and helps in its absorption
Gastric mucin:
Mucin is a glycoprotein
Provides defense against the damage which may be caused by the acid
Gastric mucin is of two types -Visible mucin and soluble mucin
Visible mucin is secreted by surface mucous cells of the gastric mucous membrane
Forms a slippery layer on gastric mucous membrane.
Prevents injury from solid food and moving fluids within the stomach
The soluble mucin secreted by the neck cells
Helps to buffer HCL to some extent
Pradeep Kumar.G Faculty of Medicine, Omar Al Mukhtar University 1
Enzymes of Gastric Juice
Pepsinogen & Pepsin:
Is an inactive precursor for enzyme pepsin
It is secreted by chief cells of gastric glands
Pepsinogen is activated to pepsin at a pH of 2.0 to 3 by HCL
Pepsin is a proteolytic enzyme which breaks down protein molecule into pep-tones
and peptides.
Rennin:
This enzyme coagulates milk, thus prevents rapid passage of milk from the stomach.
Gelatinase:
It liquifies gelatin, a protein contained in connective tissues.
Gastric lipase:
This is a weak fat splitting enzyme from stomach.
It acts at the optimal pH of 4 - 4.5.
Gastric lipase gets inactivated at pH 2.5.
Lysozyme: is a bactericidal enzyme.
Urease: The enzyme urease hydrolyze urea to produce ammonia.
Carbonic anhydrase : is present in small amounts.
II. Gastric acidity:
Free acidity: The acidity due to free HCl (not combined with other substances)
present in gastric juice
Total acidity: The acidity due to free HCl, HCl bound to mucin, organic acids, acid
proteins and other acidic substances in gastric juice.
Normal Range:
Free acidity: 18 – 25 mEq/L
Total acidity: 28 – 48 mEq/L
Pradeep Kumar.G Faculty of Medicine, Omar Al Mukhtar University 2
III. Clinical significance:
Hyperchlorhydria: increase of free acidity of gastric juice more than normal is
termed as hyperchlorhydria.
In individuals with duodenal ulcers
Hypochlorhydria: Decrease of free acidity of gastric juice less than normal is
termed as hypochlorhydria.
Achlorhydria: if the free gastric HCl concentration in zero then it is termed as
Achlorhydria.
Achlorhydria is divided in to true achlorhydria and False Achlorhydria.
In true achlorhydria the secretion of HCl is completely absent
In false achlorhydria free HCl in gastric juice is neutralized by alkaline substances
In false achlorhydria secretion of free HCL can be seen after injecting subject with
histamine
The slowing of the body's basal metabolic rate associated with hypothyroidism
Achlorhydria is seen in case of
Autoimmune disorders
The use of antacids
Helicobacter pylori infection
Pernicious anemia, stomach cancer. Etc.
Achylia gastrica: Both HCl and pepsin are not secreted
Pradeep Kumar.G Faculty of Medicine, Omar Al Mukhtar University 3
Estimation of free and total acidity of gastric juice
Principle: Free and total acidity of gastric juice is measured by titrating against
know concentration of NaOH using different indicators
Reagents:
NaOH (0.1 N solution)
Phenolphthalein indicator
Topfer’s reagent (dimethylaminobenzine 0.5 % w/v in 95% ethanol)
Procedure:
Total acidity:
Take 10 ml of gastric juice in a 100 ml conical flask
Add 2 – 3 drops phenolphthalein indicator
Titrate contents against 0.1 NaOH taken in a burette
Stop the titration when you observe pale pink color (end point)
Record the NaOH titer value
Free acidity:
Take 10 ml of gastric juice in a 100 ml conical flask
Add 2 – 3 drops of topfer’s reagent
Titrate contents against 0.1 NaOH taken in a burette
Stop the titration when the colour changes from red to orange-yellow color
Record the NaOH titer value
Pradeep Kumar.G Faculty of Medicine, Omar Al Mukhtar University 4
Calculation:
Note: 1 mEq of NaOH (40 mg) = 1 mEq of HCl (36.5 mg)
Total acidity = titer value (ml) X 100 = __________ mEq/L
Free acidity = titer value ( ml) X 100 = ___________ m Eq/L
Result:
Comment:
Pradeep Kumar.G Faculty of Medicine, Omar Al Mukhtar University 5
Вам также может понравиться
- Estimation of Free and Total Acidity in AДокумент19 страницEstimation of Free and Total Acidity in AAdlina Tajuddin92% (12)
- 238 Finial ExamДокумент10 страниц238 Finial Exammominamin100% (2)
- L5 Digestive and PFTsДокумент3 страницыL5 Digestive and PFTsMayank MeenaОценок пока нет
- Saliva and Gastric SecretionsДокумент36 страницSaliva and Gastric SecretionsfdafasfaОценок пока нет
- Control of Gastric SecretionsДокумент57 страницControl of Gastric SecretionsPhysiology by Dr Raghuveer100% (1)
- Gastric Function Test.... RohitДокумент28 страницGastric Function Test.... RohitJr Jc Rohit SahОценок пока нет
- Gastric AcidДокумент5 страницGastric Acidbrian3442Оценок пока нет
- Expt 10 DigestionДокумент10 страницExpt 10 DigestionRuby Sarai BelinoОценок пока нет
- Test For Gastric Duodenal Secretions 17Документ10 страницTest For Gastric Duodenal Secretions 17KaoriMarieSembranoОценок пока нет
- Gastric FluidДокумент33 страницыGastric FluidJaellah MatawaОценок пока нет
- Gastric Secretion-FinalДокумент107 страницGastric Secretion-FinalDr.Gomathi sivakumarОценок пока нет
- Estimation of Free and Totalacidity in A Gastric JuicesampleДокумент61 страницаEstimation of Free and Totalacidity in A Gastric Juicesamplebscmlt cctОценок пока нет
- Peptic Ulcers: PHRM 304Документ24 страницыPeptic Ulcers: PHRM 304Apurba Sarker Apu100% (1)
- Karaganda Medical University Pathphysiology Submitted By: Uppal Prachi GROUP: 3001 Task 1Документ4 страницыKaraganda Medical University Pathphysiology Submitted By: Uppal Prachi GROUP: 3001 Task 1Prachi UppalОценок пока нет
- Digestive-System NotesДокумент4 страницыDigestive-System NotesPiyush RoyОценок пока нет
- Bio AayushДокумент7 страницBio Aayushaayushjena54Оценок пока нет
- GIT Lect A2Документ43 страницыGIT Lect A2Ayurveda PgОценок пока нет
- All About GIT PhysiologyДокумент79 страницAll About GIT PhysiologyHarshavardhan AmancherlaОценок пока нет
- CM Gastric and Duodenal Contents Examination (Ocfemia, Eliazel G - BSMT4-PLTCI)Документ53 страницыCM Gastric and Duodenal Contents Examination (Ocfemia, Eliazel G - BSMT4-PLTCI)eliazel ocfemiaОценок пока нет
- Anti-Secretory & Anti-Ulcer Agents: Dr. Vinod Tiwari IIT (BHU), Varanasi Email: Vtiwari - Phe@iitbhu - Ac.inДокумент28 страницAnti-Secretory & Anti-Ulcer Agents: Dr. Vinod Tiwari IIT (BHU), Varanasi Email: Vtiwari - Phe@iitbhu - Ac.inNitesh SinghОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Investigatory Project: Stomach Acid, Its Composition and NeutralizationДокумент25 страницChemistry Investigatory Project: Stomach Acid, Its Composition and NeutralizationAkaar bellaneyОценок пока нет
- Gastric Secretions MineДокумент27 страницGastric Secretions MinesasamaterasuОценок пока нет
- PSG 252 Lecture 3 The StomachДокумент5 страницPSG 252 Lecture 3 The StomachMichael TobilobaОценок пока нет
- Peptic UlcerДокумент48 страницPeptic Ulcerscribd225Оценок пока нет
- Gastric Function TestsДокумент5 страницGastric Function TestssajjadОценок пока нет
- GIT Lect A2Документ45 страницGIT Lect A2Aira Jill PadernillaОценок пока нет
- The Digestive System: G.R. Pitts, PH.D., J.R. Schiller, Ph.D. and James F. Thompson, PH.DДокумент54 страницыThe Digestive System: G.R. Pitts, PH.D., J.R. Schiller, Ph.D. and James F. Thompson, PH.DAchmadPrihadianto100% (1)
- 3 7-CatabolismДокумент66 страниц3 7-CatabolismAlondra SagarioОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry of GitДокумент148 страницBiochemistry of GitMedical NotesОценок пока нет
- Git Agents Lecture Notes 1Документ29 страницGit Agents Lecture Notes 1Ravi KaushikОценок пока нет
- Fisio 5Документ12 страницFisio 5anaОценок пока нет
- Pancreatic Secretion SДокумент46 страницPancreatic Secretion SÑäd Éèm100% (2)
- GIT5Документ78 страницGIT5justiceboakyeОценок пока нет
- Pentagastrin TestДокумент13 страницPentagastrin TestMustafa KhandgawiОценок пока нет
- Gastric Juice - 1Документ31 страницаGastric Juice - 1wanderer_1010100% (1)
- Antiulcer and Antioxidant Effect of Enteric Coated Sodium Alginate Beads of Substituted Benzimidazole Proton Pump InhibitorДокумент7 страницAntiulcer and Antioxidant Effect of Enteric Coated Sodium Alginate Beads of Substituted Benzimidazole Proton Pump InhibitorkavitaОценок пока нет
- Gastric Secretions and Duodenal ContentДокумент53 страницыGastric Secretions and Duodenal ContentJanielle FajardoОценок пока нет
- Animal Models in Experimental Gastric Ulcer Screening-A ReviewДокумент6 страницAnimal Models in Experimental Gastric Ulcer Screening-A Reviewnareshph28Оценок пока нет
- Gastric Function TestsДокумент15 страницGastric Function TestsMustafa KhandgawiОценок пока нет
- Week 14 - OBF Analysis (Gastric Fluid)Документ19 страницWeek 14 - OBF Analysis (Gastric Fluid)Astrud LabradorОценок пока нет
- Acidifying Agents PDFДокумент1 страницаAcidifying Agents PDFShivi ShuklОценок пока нет
- Gastric Juice (Autosaved)Документ15 страницGastric Juice (Autosaved)ZahidKhanОценок пока нет
- Functional Diagnostic and Therapeutic Aspects of BGДокумент16 страницFunctional Diagnostic and Therapeutic Aspects of BGcetinaОценок пока нет
- Stomach PhysiologyДокумент12 страницStomach PhysiologyLazaros TsiatsiosОценок пока нет
- Secretion of Bile and The Role of Bile Acids in DigestionДокумент8 страницSecretion of Bile and The Role of Bile Acids in DigestionMarianne Kristelle NonanОценок пока нет
- Lipid Absorption Metabolism PPTX ModifiedДокумент81 страницаLipid Absorption Metabolism PPTX Modifiedkel GetanehОценок пока нет
- Biochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids: Dr. Amr S. MoustafaДокумент30 страницBiochemical Aspects of Digestion of Lipids: Dr. Amr S. Moustafaraanja2Оценок пока нет
- CM Lec Chemical Examination of UrineДокумент50 страницCM Lec Chemical Examination of UrineThea MallariОценок пока нет
- BIO 303-ManualДокумент27 страницBIO 303-ManualGum Naam SingerОценок пока нет
- Mouth: Lingual Lipase LipidДокумент9 страницMouth: Lingual Lipase LipidOscar Villados Jr.Оценок пока нет
- The Gastrointestinal Tract: صقن اهيب ةرضاحملا Cron disease Ulcerative colitis Lipase enzyme Calprotectin ليصافتДокумент31 страницаThe Gastrointestinal Tract: صقن اهيب ةرضاحملا Cron disease Ulcerative colitis Lipase enzyme Calprotectin ليصافتامجد حسين جواد كاظمОценок пока нет
- Clinical BiochemistryДокумент56 страницClinical Biochemistrysoumya palavalasa100% (1)
- Gastric AcidДокумент15 страницGastric AcidCaressa Marie EstradaОценок пока нет
- Chem Project HiteshДокумент16 страницChem Project HiteshSahil Sharma64% (14)
- Gastrointestinal Drugs IДокумент55 страницGastrointestinal Drugs IDewi Sindarayanti PurbaОценок пока нет
- Systemic VPT-Lecture NotesДокумент34 страницыSystemic VPT-Lecture NotesshОценок пока нет
- Digestive SystemДокумент33 страницыDigestive SystemSatyabrat DuttaОценок пока нет
- Investigation Into The Haematologic and Hepatotoxic EffectsДокумент18 страницInvestigation Into The Haematologic and Hepatotoxic EffectsMK WRITESОценок пока нет
- Excretion of DrugsДокумент43 страницыExcretion of DrugsBandameedi RamuОценок пока нет
- Alkaline Diet: the Quick & Easy Reference Guide for Beginners to the Effect of Foods on the Acid-Alkaline PH Body Balance, for Reversing Disease, Achieving Weight Loss and Restoring Glowing HealthОт EverandAlkaline Diet: the Quick & Easy Reference Guide for Beginners to the Effect of Foods on the Acid-Alkaline PH Body Balance, for Reversing Disease, Achieving Weight Loss and Restoring Glowing HealthОценок пока нет
- Illuminating: An NCBE / Unilever Educational GuideДокумент3 страницыIlluminating: An NCBE / Unilever Educational Guidepradeep kumar gandhamОценок пока нет
- Botany-GATE 2016 SyllabusДокумент2 страницыBotany-GATE 2016 Syllabuspradeep kumar gandhamОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry-GATE 2016 SyllabusДокумент1 страницаBiochemistry-GATE 2016 Syllabuspradeep kumar gandhamОценок пока нет
- Immuno Chemistry: Immunity: ImmunologyДокумент26 страницImmuno Chemistry: Immunity: Immunologypradeep kumar gandhamОценок пока нет
- Removable Partial Dentures: Reviewed byДокумент2 страницыRemovable Partial Dentures: Reviewed bypradeep kumar gandhamОценок пока нет
- Chemsheets-Empirical - Molecular-FormulaДокумент1 страницаChemsheets-Empirical - Molecular-FormulaMouli MishraОценок пока нет
- Composition of Foods: Raw Processed Prepared: USDA Nutrient Database For Standard Reference, Release No. 12Документ31 страницаComposition of Foods: Raw Processed Prepared: USDA Nutrient Database For Standard Reference, Release No. 12Ahmed El HawariОценок пока нет
- Spencer 1996Документ15 страницSpencer 1996M4shroomОценок пока нет
- 18 - Carbonyl CompoundsДокумент59 страниц18 - Carbonyl CompoundsenderothОценок пока нет
- IUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds AlkanesДокумент14 страницIUPAC Nomenclature of Organic Compounds AlkanesIRISH REEM LINAOTAОценок пока нет
- Test - 05 - AIATS - JEE (M) - 2024 - FS - GR - 01 & 02 - (Code-A) - 26-03-2023 - Sol.Документ13 страницTest - 05 - AIATS - JEE (M) - 2024 - FS - GR - 01 & 02 - (Code-A) - 26-03-2023 - Sol.rsjjain39Оценок пока нет
- Soils hwk5Документ3 страницыSoils hwk5api-535085475Оценок пока нет
- AdhesiveДокумент13 страницAdhesivenafiz imranОценок пока нет
- Bio 10 CH 2 Practice Exam 2012-13Документ6 страницBio 10 CH 2 Practice Exam 2012-13Aref DahabrahОценок пока нет
- Özlenen Erdem Is EcoprintingДокумент12 страницÖzlenen Erdem Is EcoprintingMuhammadDickyОценок пока нет
- Concepts of Acids and Bases-Theory & ExerciseДокумент53 страницыConcepts of Acids and Bases-Theory & ExerciseRaju SinghОценок пока нет
- Chromatographic Separation of Amino Acids Pre-Lab Activity: Visto, Pamela I. Bs Bio-IiiДокумент3 страницыChromatographic Separation of Amino Acids Pre-Lab Activity: Visto, Pamela I. Bs Bio-IiiPam VistoОценок пока нет
- Article WJPR 1513745964Документ12 страницArticle WJPR 1513745964Sivakumar LakshminarayananОценок пока нет
- Wood Coatings 101 Part 1Документ26 страницWood Coatings 101 Part 1No NameОценок пока нет
- Archive of SIDДокумент9 страницArchive of SIDFarhan RamadhanОценок пока нет
- Dynamar: The Application of Fluoropolymer Based Processing Aids in Polypropylene and Thermoplastic RubberДокумент10 страницDynamar: The Application of Fluoropolymer Based Processing Aids in Polypropylene and Thermoplastic Rubberhuy.dicОценок пока нет
- Experiment 17b 1bДокумент27 страницExperiment 17b 1bRajeev GangwarОценок пока нет
- Acids, Bases and SaltsДокумент20 страницAcids, Bases and SaltsTunde DabiriОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент3 страницыUntitledSURESH RAYAMAJHEEОценок пока нет
- CSM-Taishan-Chopped Strand Mat 450gsmДокумент1 страницаCSM-Taishan-Chopped Strand Mat 450gsmSina RastegarОценок пока нет
- Wilkote 2200 PIS 27-12-2021Документ1 страницаWilkote 2200 PIS 27-12-2021Atheer AliОценок пока нет
- Soap Production From Waste Cooking Oil PDFДокумент72 страницыSoap Production From Waste Cooking Oil PDFBizuye Shetie0% (1)
- Post Lab Finals3Документ21 страницаPost Lab Finals3AG SorianoОценок пока нет
- CHEMДокумент8 страницCHEMRyle AquinoОценок пока нет
- Lec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismДокумент12 страницLec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismyanОценок пока нет
- Microbes in Human Welfare-NotesДокумент2 страницыMicrobes in Human Welfare-NotesKomesh KumarОценок пока нет
- 11-Ion Exchange ProcessДокумент18 страниц11-Ion Exchange ProcessDr. Akepati Sivarami Reddy80% (5)
- Bpharm 2 Sem Biochemistry New S 2019Документ2 страницыBpharm 2 Sem Biochemistry New S 2019Abhay DeulkarОценок пока нет
- Project Report For Waste Plastic Processing Unit 1 TPDДокумент16 страницProject Report For Waste Plastic Processing Unit 1 TPDManju MysoreОценок пока нет