Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
UTHM Engineering Statistics tutorial answers
Загружено:
Yusra HanisИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
UTHM Engineering Statistics tutorial answers
Загружено:
Yusra HanisАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
TUTORIAL 1 Page 1
Subject Code BSM2922
Subject Engineering Statistics Credit 2
1. A box has seven components, four are good and three are defective. Three components are selected at random
without replacement. Let Z be the number of good components.
a) Show your tree diagram. b) Find the probability distribution of Z.
2. A box contains 11 grey and 8 white bags. Two bags were taken from the box, without returning of the first bag
before taking the second bag. Find
a) P(exactly two white bags). b) P(two bags with different colour).
c) P(at most one grey bag).
3. The number of adults living in homes on a randomly selected city block is described by the following probability
distribution. What is the probability that 4 or more adults reside at a randomly selected home?
Number of adults, x 1 2 3 4 or more
P( X = x) 0.25 0.50 0.15 p
4. In a recent little league softball game, each player went to bat 4 times. The number of hits made by each player is
described by the following probability distribution. What is the mean of the probability distribution?
Number of hits, x 0 1 2 3 4
P( X = x) 0.10 0.20 0.30 0.25 0.05
5. The number of adults living in homes on a randomly selected city block is described by the following probability
distribution. What is the standard deviation of the probability distribution?
Number of adults, x 1 2 3 4
P( X = x) 0.25 0.50 0.15 0.10
6. Suppose a random variable X has the following probability function.
x 1 3 4 7 9 10 14 18
P( X = x) 0.11 0.07 0.13 0.28 0.18 0.05 0.12 0.06
Find a) X is at least 10 b) X is more than 10
c) X is less than 4 d) X is at least 4 and at most 9
e) X is more than 3 and less than 10
7. Suppose a discrete random variable X has probability function given by
x 3 5 7 8 9 10 12 16
P( X = x) 0.08 0.10 0.16 0.25 0.20 0.03 0.13 0.05
Find the probability that:
a) X > 9 b) X ≥ 9 c) X < 3 d) 5 < X ≤ 9
e) 4 < X < 11 f) X ≥ 7 g) X < 12
8. The probability distribution function for the random variables X is given as follows.
x -1 0 1 2
P( X = x) 1 2 1 3
7 7 7 7
a) Find P(−1 ≤ X < 2) b) Find E (2 x − 3)
c) Find V (4 x + 1)
9. The discrete random variable X takes the values between 0 and 6 inclusive, each with a probability given by
1 | 3 − x | . Find the expected value and variance of X.
P( X = x) = −
4 16
10. Given the probability distribution function of discrete random variable of Y.
(2 y + 1)
P (Y = y ) = ; y = 1, 2,3, 4 and 5.
k
a) Find the constant k. b) Construct a cumulative distribution function of Y.
11. Given the following unction :
x
81
P( X = x) = ; y = 1, 2,3.
72
a) Show that the function is probability distribution function of discrete random variable X.
b) Find P ( X > 1)
c) Find the mean of X
d) Find the variance of X.
12. Given the probability distribution function below.
1
8 (2 − x), 0 ≤ x ≤1
1
P ( X = x ) = x, 1≤ x ≤ 3
8
0, otherwise
a) Find the cumulative distribution function, F ( x).
b) Find P ( X ≥ 1) using the cumulative distribution function.
c) Find P (1 < X ≤ 3) using the cumulative distribution function.
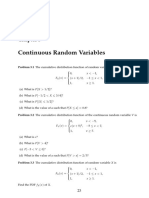
13. The following is a probability density function of continuous random variable.
2
(6 + x − x ) , 0≤ x≤3
2
f ( x) = 27
0, otherwise.
a) Calculate P (0 < X < 1 12 ) . b) Calculate P ( X > 2) .
c) Find the mean of X.
14. If X is a continuous random variable with probability density function,
kx
5, 0≤ x<2
2
x
f ( x) = , 2≤ x<3
7
0, otherwise
a) Find the value of k . b) Find the cumulative distribution function of X .
c) Evaluate P (1 ≤ X ≤ 4) d) Calculate E ( X ) and V ( X ).
Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia
TUTORIAL 1 (Answers) Page 1
Subject Code BSM2922
Subject Engineering Statistics Credit 2
z 0 1 2 3
1. b) P (Z = z) 1
35
12
35
18
35
4
35
28 88 116
2. a) 171 b) 171 c) 171
3. 0.1
4. 1.75
5. 0.79
6. a) 0.23 b) 0.18 c) 0.18 d) 0.59 e) 0.59
7. a) 0.21 b) 0.41 c) 0 d) 0.61 e) 0.74 f) 0.812 g) 0.82
8. a) 74 b) − 97 c) 20.245
9. 3, 52
0 ; y <1
3 ;1 ≤ y < 2
35
358 ; 2 ≤ y < 3
10. a) k = 35, b) F ( y ) = 15
35 ;3 ≤ y < 4
24 ;4 ≤ y < 4
35
1 y≥5
3
11. b) 7 c) 11
7 d) 26
49
0 ;x < 0
1 ;0 ≤ x < 1
4
12. a) F ( x) = 83 ;1 ≤ x < 2 b) 3
4 c) 5
8
5 ;2 ≤ y < 3
8
1 ;x ≥ 3
13. a) 0.667 b) 0.1605 c) 1.167
0 ;x < 0
x2 ;0 ≤ x < 2
14. a) 5
b) F ( x) = x3 42 8 c) 41
d) 2.448 e) 0.2263
21 − 21 ; 2 ≤ x < 3
21 42
1 ;x ≥3
Вам также может понравиться
- Dooley - Playing The MatrixДокумент39 страницDooley - Playing The MatrixCristian Catalina100% (5)
- The Law of Excluded Middle-Neil CooperДокумент21 страницаThe Law of Excluded Middle-Neil CooperMari VojvodovicОценок пока нет
- Herstein Topics SolnsДокумент34 страницыHerstein Topics SolnsJaspal Singh82% (11)
- Factoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)От EverandFactoring and Algebra - A Selection of Classic Mathematical Articles Containing Examples and Exercises on the Subject of Algebra (Mathematics Series)Оценок пока нет
- Fidp General MathematicsДокумент10 страницFidp General MathematicsDindo HiocoОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 10 Module 5: Week 5: First Quarter Problem Solving Involving SequencesДокумент8 страницMathematics 10 Module 5: Week 5: First Quarter Problem Solving Involving SequencesAngel Gwyneth Flores100% (2)
- Algebra Regents Content Review PacketДокумент26 страницAlgebra Regents Content Review Packetapi-264817418100% (1)
- Grade 9 Math Quiz Bee QuestionsДокумент2 страницыGrade 9 Math Quiz Bee QuestionsDiosdado II Marimon75% (4)
- Sage TutorialДокумент103 страницыSage TutorialLucian Cionca100% (1)
- Convolution LectureДокумент11 страницConvolution Lecturespong1ertzОценок пока нет
- Primary Progression Test - Stage 4 Math Paper 1 PDFДокумент10 страницPrimary Progression Test - Stage 4 Math Paper 1 PDFAhmed M. Anwar82% (11)
- Tutorial 5.0 Discrete Random Variable 2023Документ7 страницTutorial 5.0 Discrete Random Variable 2023AdliHakimОценок пока нет
- Math 208 Assignment - Problems on Discrete and Continuous Random VariablesДокумент9 страницMath 208 Assignment - Problems on Discrete and Continuous Random Variablesramesh pokhrelОценок пока нет
- EC2303 Additional Practice QuestionsДокумент7 страницEC2303 Additional Practice QuestionsSiya LimОценок пока нет
- Department of Mathematics Birla Institute of Technology Mesra, Ranchi Tutorial - 3Документ1 страницаDepartment of Mathematics Birla Institute of Technology Mesra, Ranchi Tutorial - 3Anonymous uGow9p7y8Оценок пока нет
- 1 of Chapter 3 Random Variables and Discrete Probability DistributionsДокумент16 страниц1 of Chapter 3 Random Variables and Discrete Probability DistributionsDmddldldldlОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2 PDFДокумент1 страницаTutorial 2 PDFUddeshya GuptaОценок пока нет
- Topic 3Документ17 страницTopic 3Ramli karamОценок пока нет
- Problems 3Документ2 страницыProblems 3Pratik LodhariОценок пока нет
- Statistics 2Документ121 страницаStatistics 2Ravi KОценок пока нет
- Probability and Queueing Theory: Question BankДокумент62 страницыProbability and Queueing Theory: Question BankajithОценок пока нет
- PQT Solved QB PDFДокумент62 страницыPQT Solved QB PDFDharumanОценок пока нет
- Isi JRF Stat 07Документ10 страницIsi JRF Stat 07api-26401608Оценок пока нет
- Exercise+Problems+for+MT 1Документ6 страницExercise+Problems+for+MT 1Necati Can ToklaçОценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Tutorial eДокумент2 страницыUnit 2 Tutorial eShivam vermaОценок пока нет
- 2009 Continuous Random VariableДокумент4 страницы2009 Continuous Random Variablefabremil7472100% (2)
- Tugas Variabel Random PDFДокумент3 страницыTugas Variabel Random PDFNatasyalika Ma'rufahОценок пока нет
- Probability & Statistics Problem Set 3 Random Variables & DistributionsДокумент5 страницProbability & Statistics Problem Set 3 Random Variables & DistributionsNguyễn Đức AnОценок пока нет
- Probability Distribution AssignmentДокумент2 страницыProbability Distribution AssignmentFaisalОценок пока нет
- PS IiДокумент6 страницPS IiAmazing cricket shocksОценок пока нет
- PSQT-QB-Unit 1Документ3 страницыPSQT-QB-Unit 1fabiomughilanОценок пока нет
- MSO 201a: Probability and Statistics 2019-20-II Semester Assignment-III Instructor: Neeraj MisraДокумент6 страницMSO 201a: Probability and Statistics 2019-20-II Semester Assignment-III Instructor: Neeraj MisraAdarsh BanthОценок пока нет
- 3 Semester BSC Model Examination Nov - 2019: Events Without A Common Element Are CalledДокумент2 страницы3 Semester BSC Model Examination Nov - 2019: Events Without A Common Element Are CalledBinu EMОценок пока нет
- Tutorial 2Документ4 страницыTutorial 2Lost BoyОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент2 страницыUntitledSmruti RanjanОценок пока нет
- Revision 1 (28 Ogos)Документ2 страницыRevision 1 (28 Ogos)SRI SIVABALASUNDRAM A/L KRISHNAN -Оценок пока нет
- B.Sc. Degree Examination, 2012: Register Number: Name of The CandidateДокумент3 страницыB.Sc. Degree Examination, 2012: Register Number: Name of The CandidatenirmalaОценок пока нет
- 1011sem1 Ma2213Документ4 страницы1011sem1 Ma2213jlee970125Оценок пока нет
- Topic 4 Random VariablesДокумент14 страницTopic 4 Random VariablesMULINDWA IBRAОценок пока нет
- Probability and Stochastic Processes (EE 591) Assignment-2: Prof. S. Dandapat August 17, 2022Документ4 страницыProbability and Stochastic Processes (EE 591) Assignment-2: Prof. S. Dandapat August 17, 2022Nibha RanjanОценок пока нет
- Master’s Written Examination Fall 2019Документ11 страницMaster’s Written Examination Fall 2019Robinson Ortega MezaОценок пока нет
- Assignment 8: Applications of Differentiation Page 27Документ8 страницAssignment 8: Applications of Differentiation Page 27YONGCHENG LIUОценок пока нет
- MA 501CAssignment 1Документ2 страницыMA 501CAssignment 1Sabir Ali0% (1)
- S2250 - Sheet 2 Random VariablesДокумент4 страницыS2250 - Sheet 2 Random Variablessandra.2015farhatadОценок пока нет
- Probability Distribution FunctionsДокумент23 страницыProbability Distribution FunctionsSantosh SanthuОценок пока нет
- 9.1 Random Variables 9.2 Discrete Random Variables: Lecture 1 0F 7Документ20 страниц9.1 Random Variables 9.2 Discrete Random Variables: Lecture 1 0F 7ajibpulasanОценок пока нет
- Tutorial For Random Variables and Stochastic Processes Eem2046 Engineering Mathematics Iv Multimedia UniversityДокумент9 страницTutorial For Random Variables and Stochastic Processes Eem2046 Engineering Mathematics Iv Multimedia UniversityNazmi AzizОценок пока нет
- PRPДокумент4 страницыPRPkibrom atsbhaОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6-1Документ7 страницChapter 6-1rezowansifatnavidОценок пока нет
- Ps 0Документ3 страницыPs 0Rupesh ParabОценок пока нет
- PDFДокумент66 страницPDFgajaОценок пока нет
- Continuous Random Variables: Problem 3.1Документ6 страницContinuous Random Variables: Problem 3.1Thanh NgânОценок пока нет
- STA347 Probability Problem SetДокумент7 страницSTA347 Probability Problem Setlawsonz1Оценок пока нет
- Ma8451 PRP Model Set BДокумент3 страницыMa8451 PRP Model Set BInfi Coaching CenterОценок пока нет
- Statistical MethodДокумент227 страницStatistical Methodmaria sanjaiОценок пока нет
- Midterm Sample Paper 1Документ18 страницMidterm Sample Paper 1ryann gohОценок пока нет
- Probability ps5Документ3 страницыProbability ps5Abhi TripathiОценок пока нет
- Problem Set 4: HANU - Faculty of Information and Technology Probability & StatisticsДокумент4 страницыProblem Set 4: HANU - Faculty of Information and Technology Probability & StatisticsNgọc TrâmОценок пока нет
- Probability & Random Process QBДокумент13 страницProbability & Random Process QBwizardvenkatОценок пока нет
- Chapter4 1Документ6 страницChapter4 1Suriya MahendranОценок пока нет
- PPT 37 - Ex 8C Discrete Random VariablesДокумент16 страницPPT 37 - Ex 8C Discrete Random VariablesRalph Rezin MooreОценок пока нет
- Sixth Exercise in Probability Discrete Distributions III and Continuous Distributions IДокумент2 страницыSixth Exercise in Probability Discrete Distributions III and Continuous Distributions IHans SchneidОценок пока нет
- Self Extra Exercises PolynomialsДокумент8 страницSelf Extra Exercises Polynomialsjazlina josephОценок пока нет
- Probability problems on random variablesДокумент3 страницыProbability problems on random variablesJames AttenboroughОценок пока нет
- Chapter Seven: Random Variable and Mathematical Expectation Random Variable Define Random Variable With ExampleДокумент7 страницChapter Seven: Random Variable and Mathematical Expectation Random Variable Define Random Variable With ExampleShuvoОценок пока нет
- PMMT100 FT 20 2020 1Документ12 страницPMMT100 FT 20 2020 1Kaoma MofyaОценок пока нет
- SST 204 ModuleДокумент84 страницыSST 204 ModuleAtuya Jones100% (1)
- HANU Probability & Statistics Problem Set 3Документ5 страницHANU Probability & Statistics Problem Set 3Ngọc ÁnhОценок пока нет
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970От EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallОценок пока нет
- What Is A Weighted Average?Документ12 страницWhat Is A Weighted Average?SachinОценок пока нет
- Pre Calculus11 Quarter1 Module9 Standardform of The Equation of A Hyperbola v1Документ36 страницPre Calculus11 Quarter1 Module9 Standardform of The Equation of A Hyperbola v1Chaine CandaОценок пока нет
- Quiz 6 SolutionsДокумент2 страницыQuiz 6 Solutionsrrro0orrrОценок пока нет
- A First LessonДокумент2 страницыA First LessonLeo LeniusОценок пока нет
- Statistics and Probability Course OverviewДокумент35 страницStatistics and Probability Course OverviewTnilc FernandezОценок пока нет
- 2 - Drills On Word Problems of LE2VДокумент2 страницы2 - Drills On Word Problems of LE2VTea JuanОценок пока нет
- All About NDA Written Exam and Pattern 2018: Code Subject Time Max MarksДокумент6 страницAll About NDA Written Exam and Pattern 2018: Code Subject Time Max MarksAmit SutarОценок пока нет
- Unit 08Документ39 страницUnit 08Faaz AlwahabОценок пока нет
- 100 Geometry Problems: Solutions: Alvin ZouДокумент26 страниц100 Geometry Problems: Solutions: Alvin ZouMuhammad TaufanОценок пока нет
- D AlgorithmДокумент71 страницаD AlgorithmKiran KumarОценок пока нет
- Gibbs Paradox and Boltzmann Entropy DefinitionДокумент4 страницыGibbs Paradox and Boltzmann Entropy Definitionsantiago bermudezОценок пока нет
- Limits of Functions of Two VariablesДокумент4 страницыLimits of Functions of Two VariablesHugo MayorgaОценок пока нет
- Question Bank Discrete MathsДокумент5 страницQuestion Bank Discrete Mathssureshkumar sambasivanОценок пока нет
- Unit 3 Z-Transform and Its ImplementationДокумент120 страницUnit 3 Z-Transform and Its ImplementationGemechisОценок пока нет
- 04 - Logarithms (OYCP-P) Mind MapДокумент1 страница04 - Logarithms (OYCP-P) Mind MapNepturiousОценок пока нет
- CPA Quantitative Techniques Notes: Probability Theory and DistributionsДокумент8 страницCPA Quantitative Techniques Notes: Probability Theory and DistributionsCaesarKamanziОценок пока нет
- Trigonometric Equations and Identities Solved ExamplesДокумент16 страницTrigonometric Equations and Identities Solved Examplesmazhar10325Оценок пока нет
- Count words by length in text file(40Документ7 страницCount words by length in text file(40queen setiloОценок пока нет
- Escuela de Sophia of Caloocan Inc.: 3 Quarterly Test Mathematics 6Документ6 страницEscuela de Sophia of Caloocan Inc.: 3 Quarterly Test Mathematics 6ROMNICK DIANZONОценок пока нет
- Algo - Mod12 - NP-Hard and NP-Complete ProblemsДокумент56 страницAlgo - Mod12 - NP-Hard and NP-Complete ProblemsISSAM HAMADОценок пока нет