Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Additional Part of The Main Exercise Book: Chapter-Wise Preparation: Exam at Home
Загружено:
Shah Mohammad SabbirОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Additional Part of The Main Exercise Book: Chapter-Wise Preparation: Exam at Home
Загружено:
Shah Mohammad SabbirАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
1
Additional Part of the Main Exercise Book
Chapter-wise Preparation: Exam at Home
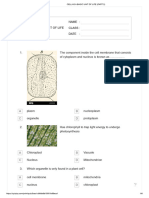
Ques.1 The absence of mitochondria in a cell would lead to its
death.
Mitochondria are organelles that act like a digestive
A system which takes in nutrients, breaks them down, and
creates energy rich molecules for the cell. The
B biochemical processes of the cell are known as cellular
respiration. Many of the reactions involved in cellular
respiration happen in the mitochondria. Mitochondria
are the working organelles that keep the cell full of
energy. So, its absence would make it impossible for the
cell to function and would lead to its eventual death.
a. What is cell membrane? 1
Ques.2
b. Write down three differences between plant and
animal cell. 2 Dw«¿` ˆKvl
Plant Cell cÉvYx ˆKvl
Animal Cell
c. Describe the function of the organelle “B”. 3
d. Imagine that the organelle “A” is absent in a cell. A B
What might be the consequence? Explain your
answer. 4 a. What is colour bearer? 1
Answer to the question no. 1 b. What does it mean by cell wall? 2
c. Draw a detailed diagram of B with labeling. 3
a The soft membrane present just below the cell wall
d. A is self-dependent but B is not. Why? Explain your
which surrounds the protoplasm entirely is called the cell
answer. 4
membrane.
Answer to the question no. 2
b Three differences between plant and animal cell are
a Plastid or colour bearer is a special type of organelle.
given below —
It is rich in stroma and grana, surrounded by a lipo-
Plant cell Animal cell protein membrane and is present in cytoplasm. A
i. Cell wall is present. i. Cell wall is not present. b A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some
types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It is made
ii. Contains plastid. ii. Does not contain plastid.
of nonliving material. It regulates the passage of various
iii. Stores food in the iii. Stores food in the form substances in and out of the cell. It also gives cell
form of starch. of glycogen. structural support and protection.
c The organelle “B” is a cell vacuole. Functions of cell
c The figure B of the stem is actually an animal cell.
vacuole are — A Detailed diagram of an animal cell is drawn below — A
i. Works as a reservoir of cell sap
ii. Various substances like inorganic salts, protein, Vacuole
carbohydrates, fatty substances, organic acid, Plasma membrane
pigments, water etc. are dissolved in the cell sap of
Nucleus
vacuoles. Endoplasmic reticulum
iii. Applying external pressure to the cell might cause Centriole
damage to it. Vacuoles protect cell from damages Mitochondria
that might occur due to external pressure.
d “A” labelled organelle is mitochondria. Figure: Animal cell
Mitochondria is considered as the powerhouse of the
d As per the question, ”A” or plant cell is self
cell. Mitochondria is an active part of the respiration dependent, wheres “B” or animal cell is not. Plant cells
system. The energy required to perform all the biological contain plastid. Green colour plastids are called
activities of a living cell is supplied by mitochondria. chloroplasts. Presence of chloroplast in leaves and other
2
parts of plant makes them appear green coloured. c The cell drawn by the teacher is redrawn here
Photosynthesis occurs in green leaves of plant. In labeling its different parts.
presence of sunlight, water stored in green leaves react
with CO2 gas from air react to produce glucose and Vacuole
oxygen. Glucose serves as the food for plant. So, plants
Plasma membrane
can make their own food.
On the other hand, plastid is absent in animal cell. Nucleus
Hence, no photosynthesis takes place and no food is
produced in animal cells. And so, animals depend on Endoplasmic reticulum
plants for their food.
Mitochondrion
From the discussion above, we can state the fact that
plant cell is self-dependent in terms of making its food
on its own while animal cell is not. Fig. An Animal cell
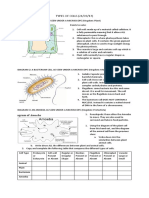
Ques.3 Mr. Ahmed was teaching cellular structure in
his class. He said, like a brick building, human body is
built with many cells. He drew an animal cell, labeled its d The cell inclusions mentioned by the teacher were:
parts and explained functions of - Protoplasm, Cell Protoplasm, Cell membrane, Cytoplasm and Vacuole.
membrane, Cytoplasm and Vacuoules. Their functions are analyzed below:
a. What is a cell? 1 The Protoplasm is the living material of a cell formed
b. Describe an organelle of animal cell that is absent in with a number of chemicals and exists in the form of
plant cell. 2 certain organelles. The cell membrane and cytoplasm are
c. Draw the diagram that was drawn by Mr. Ahmed parts of Protoplasm. The membrane controls the incoming
and label its different parts. 3 and outgoing of essential materials, like - water, mineral
d. Analyze the functions of the organelles mentioned salt, vitamin, protein, carbohydrate, fat, and certain gas.
by the teacher. 4 The cytoplasm contains different organelles to form the
Answer to the question no. 3 cellular structure, which is controlled by a central
a A cell is the structural and functional unit of life. Nucleus. The function of vacuoles is to support cell
functions by storing and delivering important materials
b Centrosome exists in animal cell, with two or more
through the direction of the Nucleus. All organelles
centrioles within it, which is never found in a plant cell.
mentioned by the teacher are very essential for existence
The centrosome produces Ester rays during the cell
of a cell.
division of an animal cell.
Вам также может понравиться
- Cell Structure SEДокумент7 страницCell Structure SENithya Majeti100% (1)
- DNA Puzzle Kit: Teacher'S Manual and Student GuideДокумент3 страницыDNA Puzzle Kit: Teacher'S Manual and Student GuideClven Fernandez0% (1)
- Assignment of Class VIIIДокумент4 страницыAssignment of Class VIIIMd A RAZZAKОценок пока нет
- GR 9 NS Cell Worksheet MemoДокумент4 страницыGR 9 NS Cell Worksheet MemoSyrus ZambiaОценок пока нет
- Bio RevisionДокумент58 страницBio RevisionKesithan AnandarashОценок пока нет
- QUIZ#3 - Cell Structure and FunctionsДокумент10 страницQUIZ#3 - Cell Structure and FunctionsLouiza Angelina LayugОценок пока нет
- EOCQ Ans 2Документ1 страницаEOCQ Ans 2Han SungОценок пока нет
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureДокумент8 страницStudent Exploration: Cell StructureMishaОценок пока нет
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureДокумент8 страницStudent Exploration: Cell Structurelingesh tamizhanОценок пока нет
- CellStructureSE LandonsmithДокумент5 страницCellStructureSE LandonsmithLandon SmithОценок пока нет
- Mastery Worksheet - Biology First TermДокумент5 страницMastery Worksheet - Biology First TermLaura Sofia Ramirez CardenasОценок пока нет
- Kami Export - Aubrianna Labonte-Postell - CellStructure GizmoДокумент5 страницKami Export - Aubrianna Labonte-Postell - CellStructure Gizmoaubrianna.postellОценок пока нет
- Science Form 1 Chapter 2Документ3 страницыScience Form 1 Chapter 2Nur Hidayah NohОценок пока нет
- 7 Science - Chapter 1-3 AnswerДокумент3 страницы7 Science - Chapter 1-3 Answermichael tanОценок пока нет
- Formative Assessment On CellДокумент2 страницыFormative Assessment On CellPoulomi SenguptaОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure-Module 1Документ14 страницCell Structure-Module 1maryann chanОценок пока нет
- Cell Sturcture, Osmosis & Diffusion (Answer Key)Документ7 страницCell Sturcture, Osmosis & Diffusion (Answer Key)maariamshamsi2Оценок пока нет
- Cells and Movement Across Cell MembraneДокумент10 страницCells and Movement Across Cell MembraneNisha JodhanОценок пока нет
- Cell Structure SEДокумент8 страницCell Structure SESandra FernandezОценок пока нет
- Student Exploration: Cell StructureДокумент7 страницStudent Exploration: Cell StructureTNT x TOXICОценок пока нет
- Initial Assement of Cell As A Basic Unit of Life (Part 2)Документ6 страницInitial Assement of Cell As A Basic Unit of Life (Part 2)astriОценок пока нет
- Chapter 01Документ40 страницChapter 01javed iqbal KhanОценок пока нет
- WorksheetsДокумент6 страницWorksheetsThe Chris LegaspiОценок пока нет
- Parts of A CellДокумент4 страницыParts of A CellLADY ANN GRACE LAGASОценок пока нет
- Biology Unit 1 Answers: 1 2 3 4 5 Ai II III IV BДокумент53 страницыBiology Unit 1 Answers: 1 2 3 4 5 Ai II III IV BDavid KimОценок пока нет
- GENBIO 1 Q1 Periodic TestДокумент6 страницGENBIO 1 Q1 Periodic TestCelsa ChicoОценок пока нет
- Biology 1 Exam 1st MonthlyДокумент2 страницыBiology 1 Exam 1st MonthlyBianca SuarezОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 Cell-Structure and FunctionsДокумент3 страницыChapter 8 Cell-Structure and Functionsniranjan bhagatОценок пока нет
- Cells Process QuestionsДокумент10 страницCells Process Questionsmofid monirОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 4 CellsДокумент9 страницCHAPTER 4 CellsNadeem IqbalОценок пока нет
- Student Handout 01 - Cell StructureДокумент6 страницStudent Handout 01 - Cell StructureJoslynn SlaytonОценок пока нет
- CellStructureSEДокумент7 страницCellStructureSEkumardarsheel65Оценок пока нет
- Cells and Microscope Practice TestДокумент6 страницCells and Microscope Practice TestlevchapОценок пока нет
- General Biology Module 2Документ11 страницGeneral Biology Module 2Jee-Anne HerbularioОценок пока нет
- Science7 Pretest CellsДокумент2 страницыScience7 Pretest Cellsrain sagotОценок пока нет
- 2022 Cells Revision AnswersДокумент11 страниц2022 Cells Revision Answersdantimtam33Оценок пока нет
- Grade 9 V2Документ3 страницыGrade 9 V2hanatabbal19Оценок пока нет
- Zoology 10th Edition Miller Test BankДокумент18 страницZoology 10th Edition Miller Test BankSandraJonescniqb100% (16)
- Cell Structure and FunctionДокумент4 страницыCell Structure and FunctionAngeelina AgarwalОценок пока нет
- Cells RevisionsДокумент11 страницCells Revisionsmofid monirОценок пока нет
- IG Science SA Biology SB Answers PDFДокумент9 страницIG Science SA Biology SB Answers PDFFaiyaz Rabby AlviОценок пока нет
- The Cell WorkbookДокумент6 страницThe Cell Workbooksaksham ostwalОценок пока нет
- Science 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Документ33 страницыScience 7 Animals and Plant Cells 3Welfredo Jr YuОценок пока нет
- Cells WebquestДокумент4 страницыCells Webquestapi-347555363Оценок пока нет
- Grade Nine Biology Cell AnswersheetДокумент4 страницыGrade Nine Biology Cell AnswersheetHitakshi BhanushaliОценок пока нет
- Genbio 1Документ14 страницGenbio 1Laiza Marie LopezОценок пока нет
- Cells & Tissues 9th BiologyДокумент8 страницCells & Tissues 9th Biologymhussainshigri786Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Manual Activity No. 2 Observing BacteriaДокумент9 страницLaboratory Manual Activity No. 2 Observing BacteriaMitzi CarreonОценок пока нет
- 2324 Level L (Gr10 UAE - GULF) Biology Course Questions SolutionsДокумент130 страниц2324 Level L (Gr10 UAE - GULF) Biology Course Questions SolutionsVan halenОценок пока нет
- Biological Science 6Th Edition Freeman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент37 страницBiological Science 6Th Edition Freeman Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFElizabethRuizrxka100% (9)
- 1St Quarterly Test in Science 7Документ4 страницы1St Quarterly Test in Science 7Joanne GodezanoОценок пока нет
- Cells WorksheetДокумент3 страницыCells WorksheetL NarineОценок пока нет
- BiologyДокумент2 страницыBiologyjsfowen18Оценок пока нет
- Types of CellsДокумент1 страницаTypes of CellsParis LiangОценок пока нет
- BiologyДокумент2 страницыBiologyPaul DgreatОценок пока нет
- Biology Exercise For Final Test - Semester 1 - 2023 - 2024Документ13 страницBiology Exercise For Final Test - Semester 1 - 2023 - 2024zugagantengОценок пока нет
- GCSE Cells Cut and Stick WorksheetДокумент5 страницGCSE Cells Cut and Stick WorksheetSara NahomОценок пока нет
- LabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellДокумент11 страницLabEx4 - Eukaryotic CellGlyndel ArcillasОценок пока нет
- Cell The Unit of Life - Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions Free PDF DownloadДокумент12 страницCell The Unit of Life - Class 11 Biology NCERT Solutions Free PDF Downloadmahendrakarvinay0Оценок пока нет
- Warm Up 9Документ2 страницыWarm Up 9api-474870562Оценок пока нет
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsОт EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers CellsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (2)
- USMLE Step One Rna Helical Virus MnemonicДокумент2 страницыUSMLE Step One Rna Helical Virus Mnemoniccschutt47Оценок пока нет
- Extract Your Own DNA at Home (Laganson-EOP1)Документ3 страницыExtract Your Own DNA at Home (Laganson-EOP1)cristhel joyОценок пока нет
- Comparative Veterinary Pharmacology, Toxicology and TherapyДокумент536 страницComparative Veterinary Pharmacology, Toxicology and TherapyWilton Calderon RuizОценок пока нет
- Baldassarre CVДокумент5 страницBaldassarre CVAncientChemistОценок пока нет
- Solving The Aggregation Problem of Human Embryonic Kidney 293 Cells Using The New Brunswick S41i CO Incubator ShakerДокумент9 страницSolving The Aggregation Problem of Human Embryonic Kidney 293 Cells Using The New Brunswick S41i CO Incubator ShakerCarlos Alfaro AlegríaОценок пока нет
- Drug Development Process Cleveland, 6.23.06Документ65 страницDrug Development Process Cleveland, 6.23.06Srinivasa Chary SriramadasuОценок пока нет
- Biology 2019 Answer SheetДокумент17 страницBiology 2019 Answer SheetTechno PointОценок пока нет
- Microbiology - Prokaryotic Cell Biology: Bacterial Surface Structures Bacterial Cell Wall StructureДокумент5 страницMicrobiology - Prokaryotic Cell Biology: Bacterial Surface Structures Bacterial Cell Wall StructureDani AnyikaОценок пока нет
- Genetic InheritanceДокумент7 страницGenetic InheritanceNur Amalina Khozari100% (1)
- Stem Cell Research (Rupendra)Документ4 страницыStem Cell Research (Rupendra)Rupendra ShresthaОценок пока нет
- Go TaqДокумент2 страницыGo TaqYogi ArismetОценок пока нет
- Nelson 2010Документ2 страницыNelson 2010juliopanzОценок пока нет
- MCQ S ZoologyДокумент102 страницыMCQ S ZoologySapath GuptaОценок пока нет
- Proceedings 2017Документ764 страницыProceedings 2017vedadsa100% (1)
- CSR SaladДокумент16 страницCSR SaladDaniel Caballero CerbonОценок пока нет
- 18 ACVVR FinalДокумент58 страниц18 ACVVR FinalElison J PanggaloОценок пока нет
- 236 Freezer InventoryДокумент1 страница236 Freezer InventorysammibrombackerОценок пока нет
- CAPE 1 Biology - Genetic EngineeringДокумент80 страницCAPE 1 Biology - Genetic EngineeringTamicka BonnickОценок пока нет
- Stage 3 Worksheets 8-11Документ5 страницStage 3 Worksheets 8-11api-314389226Оценок пока нет
- Biotechnology SyllabusДокумент111 страницBiotechnology SyllabusSatyam SinghОценок пока нет
- Plant Peptide Mimicry:: HOW Phytonematodes Outsmarts PlantsДокумент12 страницPlant Peptide Mimicry:: HOW Phytonematodes Outsmarts PlantsChristian OrjiОценок пока нет
- Important Notice: List of Life Members of AMI Enrolled Upto 31.3.2010Документ137 страницImportant Notice: List of Life Members of AMI Enrolled Upto 31.3.2010avinashdeo0% (1)
- PRODUCTДокумент38 страницPRODUCTSaroj MishraОценок пока нет
- AfafafДокумент1 страницаAfafafTUYA JOHNVICОценок пока нет
- Head Nurse For MinetteДокумент1 страницаHead Nurse For MinetteMiggy SikatОценок пока нет
- Week 4 CPH LEC - Introduction To Epidemiology: Fundamentals of Epidemiology in Public Health PracticeДокумент11 страницWeek 4 CPH LEC - Introduction To Epidemiology: Fundamentals of Epidemiology in Public Health PracticeQueency DangilanОценок пока нет
- POSTGRADUATE TEACHING DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY PPT NewДокумент18 страницPOSTGRADUATE TEACHING DEPARTMENT OF ZOOLOGY PPT NewChetan MasramОценок пока нет
- B.Sc. BotanyДокумент13 страницB.Sc. Botanyr prathapОценок пока нет
- Studying Wound Healing ActivityДокумент49 страницStudying Wound Healing ActivitymichaelОценок пока нет