Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Seamless VS Welded Tubes
Загружено:
hirenkumar patelАвторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Seamless VS Welded Tubes
Загружено:
hirenkumar patelАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
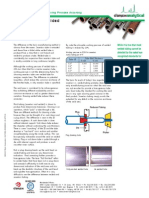
Integrated Solutions Improving Process Accuracy
Seamless vs. Welded
Tubing
The difference in the basic manufacturing method is By code the allowable working pressure of welded While it is true that most
obvious from the names. Seamless tube is extruded tubing is reduced by 20%. welded tubing cannot be
and drawn from a billet while welded tube is
produced from a strip that is roll formed and Working pressure in PSIG for seamless detected by the naked eye
welded to produce a tube. Welded tube is 316SS tubing at 70°F.
recognized standards for
considerably less expensive than seamless tube and Tube Wall Thickness
Tube OD working the weld area of
is readily available in long continuous lengths. 0.028 0.035 0.049
1/8" 8,500 10,900 — tubing are very open and
Although the working pressure of welded tube is 1/4" — 5,100 7,500
3/8" — 3,300 4,800 allow great latitude in the
20% less than that for a similar seamless tube,
working pressure is not the determining factor for 1/2" — 2,600 3,700 degree of homogeneity in
For welded tubing multiply pressure rating by 0.80.
choosing seamless tube over welded tube for Temperature Conversion for 400°F: multiply above by 0.96 the final product.
analyzer sample lines. The difference in potential
impurities, which reduce the corrosion resistance of The basis for much of today’s bias regarding
the finished tube, is why seamless tube is specified. seamless vs. welded tubing probably stems from
early manufacturing processes when the weld area
The weld area is considered to be inhomogeneous was not reworked to provide a homogeneous tube
thus exhibiting different malleability and less wall. Even today the standard for working the weld
corrosion resistance as well as greater dimensional area is very open allowing great variance in the
variation. Drawing welded tube reduces these final product. Seamless tubing simply avoids the
anomalies. potential for any defect in the corrosion resistance
of the weld area.
Most tubing (seamless and welded) is drawn to
produce final dimensional tolerances. Drawing is an
operation, which “pulls” a tube through a die.
There are different methods for drawing a tube
however they can be thought of as sunk drawn and
©2003 O’Brien Corporation • QLT-OBA-SEAMWLD • 25 APR 03
a plug drawn. The difference is seen in the ID
surface roughness. A sunk drawn tube is done
without internal support. Sink drawn tube reduces
the diameter without controlling the wall thickness.
There is some “crunching” of the ID and the tube
develops a “sun burst” cross section and wrinkles
circumferentially along the inside surface. This can
Plug drawing tube
be especially noticeable around the weld on welded
tubing. Plug or rod drawn tube is pulled through a
die with internal support and produces a much
smoother inner surface.
Rod or plug drawing breaks up the weld bead on
welded tubing and removes any dimensional
indication. Final annealing further promotes a
homogeneous tube. The term “full finished” refers
to welded tubes that have been rod or plug drawn
and annealed sufficiently to both remove any
dimensional indication of the weld area and also
break up the dendritic structure of the weld bead Fully worked welded tube As welded tube
and expedite homogenization. Often it is very
difficult to see the difference between welded and
seamless tubing.
ISO 9001:2000
Worldwide Offices:
1900 Crystal Industrial Ct. • St. Louis, MO 63114 • Ph 314/236-2020 • Fax 314/236-2080
Mallekotstraat 65 • B 2500 Lier Belgium • Ph (+32) 3 491 9875 • Fax (+32) 3 491 9876
Suite 400 • 609 14th Street NW • Calgary, AB T2N 2A1 • Ph 403/730-7277 • Fax 403/730-7279
Certificate No.
CC1504-0 001122
obcorp@obcorp.com • www.obrien-analytical.com
Вам также может понравиться
- Pipe SMLS VS Welded PDFДокумент1 страницаPipe SMLS VS Welded PDFLim PaОценок пока нет
- Seamless vs. Welded TubingДокумент1 страницаSeamless vs. Welded Tubingzero_cool_oooОценок пока нет
- Pipe GlossaryДокумент3 страницыPipe Glossarybavarian_sheepОценок пока нет
- Seamless or Welded Pipes PDFДокумент4 страницыSeamless or Welded Pipes PDFPeterWangОценок пока нет
- Weatherford CORODДокумент6 страницWeatherford CORODclass 96Оценок пока нет
- Jointing Systems: - PVC Pipe Jointing - Rubber Ring Jointing - Solvent Cement JointingДокумент16 страницJointing Systems: - PVC Pipe Jointing - Rubber Ring Jointing - Solvent Cement JointingFrancisco M. RamosОценок пока нет
- MS-06-117 Tubing Data-Engineered CombinationsДокумент6 страницMS-06-117 Tubing Data-Engineered CombinationsJacques StrappeОценок пока нет
- Prochem: Stainless Steel SpecialistsДокумент15 страницProchem: Stainless Steel SpecialistsPooja ThaparОценок пока нет
- 1605 HOBAS Jacking Pipes WebДокумент16 страниц1605 HOBAS Jacking Pipes Weballouche_abdОценок пока нет
- 300-C Slotted Channel Product Data - Multi-PageДокумент8 страниц300-C Slotted Channel Product Data - Multi-PageRavi LoharОценок пока нет
- Bending StiffДокумент7 страницBending StiffShanthaОценок пока нет
- Lineas de Corte LongitudinalДокумент4 страницыLineas de Corte LongitudinalYeisonОценок пока нет
- 13 Major Differences Between Seamless and Welded PipeДокумент4 страницы13 Major Differences Between Seamless and Welded PipeAnil kumarОценок пока нет
- Difference Between Seamless and Welded PipeДокумент1 страницаDifference Between Seamless and Welded PipealokbdasОценок пока нет
- Pipeline Design For Pigging: Pipeline Dimention Pipeline Materials DivertersДокумент13 страницPipeline Design For Pigging: Pipeline Dimention Pipeline Materials DivertersSazzadОценок пока нет
- 44 46 PDFДокумент3 страницы44 46 PDFRahmat RiskiОценок пока нет
- Welded Tube PDFДокумент17 страницWelded Tube PDFhirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- SBT BakerДокумент2 страницыSBT BakerTC ShekarОценок пока нет
- Design of Prestressed Concrete Pressure PipeДокумент14 страницDesign of Prestressed Concrete Pressure Pipeunix0123Оценок пока нет
- HydroMax Weld NippleДокумент12 страницHydroMax Weld NippleAyman AlhalfawyОценок пока нет
- Tubing DataДокумент8 страницTubing DataGunawan AdeОценок пока нет
- Forming - Lec. 5 - Drawing Processes - Dr. Mohamed DahaДокумент16 страницForming - Lec. 5 - Drawing Processes - Dr. Mohamed DahaKareem MahdyОценок пока нет
- Data Sheet SS316L Seamless Tube Fluidline CustomerДокумент2 страницыData Sheet SS316L Seamless Tube Fluidline Customerinstrument.engineer.123Оценок пока нет
- Tubing DataДокумент4 страницыTubing DataEdder CortesОценок пока нет
- Mechanical Working of Materials: Wire and Tube DrawingДокумент8 страницMechanical Working of Materials: Wire and Tube DrawingSahil MaharОценок пока нет
- Butting Seamless or WeldedДокумент4 страницыButting Seamless or Weldedkhanz88_rulz1039Оценок пока нет
- Flux Cored Wires (Elga)Документ15 страницFlux Cored Wires (Elga)DarkoPerićОценок пока нет
- uPVC Waste Soil Drainage Pipes BrochurДокумент4 страницыuPVC Waste Soil Drainage Pipes Brochurhazzaa3091993 rashidОценок пока нет
- Key Catalogue PDFДокумент7 страницKey Catalogue PDFmsyan1965Оценок пока нет
- 19 DWC MДокумент6 страниц19 DWC MNikita KadamОценок пока нет
- Stainless Steal Repair 1 6Документ6 страницStainless Steal Repair 1 6Wee Bing TanОценок пока нет
- KRAH PIPES - Brochure LayoutДокумент9 страницKRAH PIPES - Brochure LayoutFELОценок пока нет
- Modelling Probe Wedge and Pipe Geometry As Critical Parameters in Pipe Girth Weld Ultrasonic Inspections Using Civa SimulationДокумент29 страницModelling Probe Wedge and Pipe Geometry As Critical Parameters in Pipe Girth Weld Ultrasonic Inspections Using Civa SimulationpjhollowОценок пока нет
- Pipeline Design and Pigging ParametersДокумент18 страницPipeline Design and Pigging ParametersSK. Sazzad HossainОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic Port DsДокумент2 страницыHydraulic Port Dsdanang_apriyantoОценок пока нет
- 15 EcodrainДокумент2 страницы15 EcodrainNikita KadamОценок пока нет
- Bonded System - Design: Water QualityДокумент22 страницыBonded System - Design: Water QualityiulianhansaОценок пока нет
- Funke Kunststoffe CONNEX Junction Brochure 10 2020.pdfДокумент8 страницFunke Kunststoffe CONNEX Junction Brochure 10 2020.pdfTranda ZaineaОценок пока нет
- Welded Connection - 3Документ18 страницWelded Connection - 3Ravi RawatОценок пока нет
- The Friction Stir Welding of Small-Diameter Pipe: An Experimental and Numerical Proof of Concept For Automation and ManufacturingДокумент16 страницThe Friction Stir Welding of Small-Diameter Pipe: An Experimental and Numerical Proof of Concept For Automation and ManufacturingShahbazAhmadОценок пока нет
- CASING DESIGNДокумент7 страницCASING DESIGNKader BakourОценок пока нет
- Dokumen - Tips - Simplified Reinforced Concrete Design 2010 NSCPДокумент200 страницDokumen - Tips - Simplified Reinforced Concrete Design 2010 NSCPmedel araoОценок пока нет
- 1.UPVC Column Casing Pipes CatalogДокумент22 страницы1.UPVC Column Casing Pipes Catalogsris802Оценок пока нет
- Solar Wärmetauscher e Geschützt 2Документ2 страницыSolar Wärmetauscher e Geschützt 2depinfor lusofabrilОценок пока нет
- Tender Boq Iwd ct49 Ceiling 773Документ8 страницTender Boq Iwd ct49 Ceiling 773Govind Ram TripathiОценок пока нет
- Tube Pullout Testing Experience - Final PaperДокумент9 страницTube Pullout Testing Experience - Final PaperRavi AbuwalaОценок пока нет
- SWCC-Water Cooled CableДокумент8 страницSWCC-Water Cooled CableElafanОценок пока нет
- Column Plant LayoutДокумент7 страницColumn Plant Layoutsteepa22Оценок пока нет
- MIG Pulse Welding: PrincipleДокумент6 страницMIG Pulse Welding: PrincipleOnder TemelОценок пока нет
- Steel Beams With Web OpeningsДокумент17 страницSteel Beams With Web OpeningspestfariaОценок пока нет
- Introduction to ASP PipesДокумент24 страницыIntroduction to ASP PipesJavan Omiti100% (1)
- Industries: The Manila'S Expert EngineersДокумент12 страницIndustries: The Manila'S Expert EngineersJohn Carlos Moralidad CriticaОценок пока нет
- Edison Welding Institute Hot Tap WeldingДокумент19 страницEdison Welding Institute Hot Tap WeldingShikhar JainОценок пока нет
- CNC Damping System Using Viscous Shear Damper and Hydro Static BearingsДокумент3 страницыCNC Damping System Using Viscous Shear Damper and Hydro Static BearingsFabrizio GrassoОценок пока нет
- 5.tube VS PipeДокумент4 страницы5.tube VS PipeJohn Larry CorpuzОценок пока нет
- ACI Concrete Beam DetailingДокумент12 страницACI Concrete Beam DetailingShaik Eliyas BashaОценок пока нет
- Ms 01 107Документ21 страницаMs 01 107Adi RaharjoОценок пока нет
- TTI Catalogue PDFДокумент1 страницаTTI Catalogue PDF24horas2Оценок пока нет
- Piping Manual For Stainless Steel Pipe For BuildingДокумент246 страницPiping Manual For Stainless Steel Pipe For Buildinghirenkumar patel100% (1)
- Piping Drawings Basics: Mr. T. N. GopinathДокумент39 страницPiping Drawings Basics: Mr. T. N. Gopinathhirenkumar patel100% (1)
- Process Plant LayoutДокумент2 страницыProcess Plant LayoutvijeyimusОценок пока нет
- Pipeline Pigging (Visit http://Piping-Info - Blogspot.com)Документ33 страницыPipeline Pigging (Visit http://Piping-Info - Blogspot.com)Antoshal100% (7)
- Whats Different in B31.1 PDFДокумент30 страницWhats Different in B31.1 PDFhirenkumar patel100% (2)
- Pipeline BendsДокумент18 страницPipeline Bendshirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Flexibility and Weight Analysis For Piping SystemsДокумент16 страницFlexibility and Weight Analysis For Piping Systemshirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Pipe Cost #Документ5 страницPipe Cost #processpipingdesignОценок пока нет
- ANSI Standard for Pipe Marker IdentificationДокумент5 страницANSI Standard for Pipe Marker Identificationhirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- EJMA Standard 9th Ed. 2008 - Standards of The Expansion JoinДокумент238 страницEJMA Standard 9th Ed. 2008 - Standards of The Expansion Joinmichski4488% (8)
- Equipmentand Piping 1Документ39 страницEquipmentand Piping 1hirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Carbon SteelДокумент15 страницCarbon Steelhirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Piping Layout PresentationДокумент56 страницPiping Layout Presentationhirenkumar patel89% (9)
- Equipmentand Piping 2Документ55 страницEquipmentand Piping 2hirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Weld Training JointsДокумент12 страницWeld Training Jointshirenkumar patel100% (1)
- Pipe Tapping ComponentsДокумент11 страницPipe Tapping Componentshirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Piping Isometric by Sateesh LeleДокумент46 страницPiping Isometric by Sateesh Lelehirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Piping FittingsДокумент21 страницаPiping Fittingshirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Equipment & Piping Layout T.N. GopinathДокумент88 страницEquipment & Piping Layout T.N. Gopinathhirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- 04 ExtrusionДокумент57 страниц04 Extrusion9811923100% (1)
- Piping Engineering-Iit Material PDFДокумент202 страницыPiping Engineering-Iit Material PDFhirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Piping Vibration & Stress by J.c.wachel PDFДокумент9 страницPiping Vibration & Stress by J.c.wachel PDFhirenkumar patel100% (1)
- Pipingflexibilityanalysis PDFДокумент762 страницыPipingflexibilityanalysis PDFhirenkumar patel100% (1)
- General Piping DesignДокумент32 страницыGeneral Piping DesignS_hassan_16Оценок пока нет
- Process Plant Layout and Piping DesignДокумент460 страницProcess Plant Layout and Piping Design~E~97% (32)
- Design Guidelines For The Selection & Use of Stainless Steel PDFДокумент55 страницDesign Guidelines For The Selection & Use of Stainless Steel PDFhirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- Welded Tube PDFДокумент17 страницWelded Tube PDFhirenkumar patelОценок пока нет
- XII Maths Chapterwise Advanced Study Material 2015 17Документ491 страницаXII Maths Chapterwise Advanced Study Material 2015 17Ashok Pradhan100% (2)
- Smartcom® Remote Diagnostics ManualДокумент89 страницSmartcom® Remote Diagnostics Manualrob vОценок пока нет
- CPA Review School Philippines Final Exam GuideДокумент14 страницCPA Review School Philippines Final Exam GuideAzureBlazeОценок пока нет
- Geotechnic Paper PublishedДокумент10 страницGeotechnic Paper PublishedWasiu OsisanyaОценок пока нет
- JEE Main 2017 Set A Question PaperДокумент45 страницJEE Main 2017 Set A Question PaperDhananjay SateeshОценок пока нет
- Maths 2b PapersДокумент12 страницMaths 2b Papersycharansai0Оценок пока нет
- WORKSHEET HydrologyДокумент3 страницыWORKSHEET Hydrologylyana1234Оценок пока нет
- Zemichael Berhe MehariДокумент99 страницZemichael Berhe Meharidhanesh kumarОценок пока нет
- CAPE Chemistry Data BookletДокумент5 страницCAPE Chemistry Data BookletAnvitha PanyamОценок пока нет
- User Guide For Auto-WEKA Version 2.2: Lars Kotthoff, Chris Thornton, Frank HutterДокумент15 страницUser Guide For Auto-WEKA Version 2.2: Lars Kotthoff, Chris Thornton, Frank HutterS M IbrahimОценок пока нет
- Stats Form 4Документ35 страницStats Form 4kirin19100% (2)
- Vacon Theoretical Harmonic Simulation ReportДокумент4 страницыVacon Theoretical Harmonic Simulation Reportbriamserna91Оценок пока нет
- LTC3108 EnergyHarvestДокумент3 страницыLTC3108 EnergyHarvestliawyssbdОценок пока нет
- Watzlawick 1967 Beavin Jackson Pragmatics of Human CommunicationДокумент288 страницWatzlawick 1967 Beavin Jackson Pragmatics of Human CommunicationPhalangchok Wanphet100% (21)
- Chapter1 Det10013Документ30 страницChapter1 Det10013che syakirОценок пока нет
- Cemented Sand B E C MIX 23-9Документ7 страницCemented Sand B E C MIX 23-9Mohammed Ghareib NasrОценок пока нет
- MCQ Iapm Double Final 1Документ48 страницMCQ Iapm Double Final 1moamen BОценок пока нет
- Methods of Separating & Purifying Substances 1 QPДокумент11 страницMethods of Separating & Purifying Substances 1 QPShahzaib AhmadОценок пока нет
- Alerting FAQ MFMonДокумент18 страницAlerting FAQ MFMonIndramani M BaraiОценок пока нет
- Design Report 10T 7m 25m R03Документ24 страницыDesign Report 10T 7m 25m R03GR CRANE &ELEVATORSОценок пока нет
- Polymer Flooding - IntechOpen - 1629669729888Документ41 страницаPolymer Flooding - IntechOpen - 1629669729888Bichara DjimetОценок пока нет
- Statistical Quality Control: by 4Th Edition © Wiley 2010 Powerpoint Presentation by R.B. Clough - Unh M. E. Henrie - UaaДокумент40 страницStatistical Quality Control: by 4Th Edition © Wiley 2010 Powerpoint Presentation by R.B. Clough - Unh M. E. Henrie - UaaInderpreet SinghОценок пока нет
- Mech4005y 5 2010 2Документ4 страницыMech4005y 5 2010 2Balgo BalgobinОценок пока нет
- Van Der Meer - Application and Stability Criteria For Rock and Artificial UnitsДокумент24 страницыVan Der Meer - Application and Stability Criteria For Rock and Artificial Unitsapi-3709579100% (1)
- EDX AnalysisДокумент18 страницEDX AnalysisjosephineОценок пока нет
- Bread and Pastry Production NC IIДокумент88 страницBread and Pastry Production NC IIjhessica ibal50% (2)
- Natural Convection Heat Transfer Coe Cients in Phase Change Material (PCM) Modules With External Vertical FinsДокумент11 страницNatural Convection Heat Transfer Coe Cients in Phase Change Material (PCM) Modules With External Vertical FinsResearcherzОценок пока нет
- Internet Technologies (IT)Документ167 страницInternet Technologies (IT)Pramod GedamОценок пока нет
- GuidelinesДокумент14 страницGuidelinesemailad_ayoОценок пока нет