Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
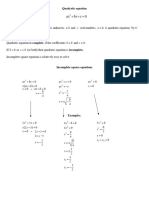
3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The Square
Загружено:
Aanya RalhanОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
3.5 Solving Quadratic Equations by Factorization and Completing The Square
Загружено:
Aanya RalhanАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Additional exercise
3.5 Solving quadratic equations by
factorization and completing the square
1 Solve the quadratic equation using the factorization method.
a x 2 + 7 x + 12 =
0 b x 2 + 3x − 10 =
0 c x 2 − 64 =
0
d 3x 2 − 5x + 2 =
0 e 4 x 2 − 8 x − 21 =
0 f 25x 2 − 9 =
0
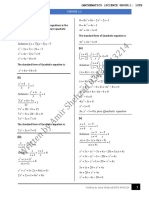
2 Rewrite the quadratic equation in standard form and then solve using the factorization method.
a x 2 − 4 x − 4 = 2 x + 12 b x ( x − 1) =
20 c 2 ( x + 3) ( x − 3) + 9 x =
0
d x 2 + 12 x =2 x − 25 e 6 x ( x + 1) = 5x + 2 f x ( x + 7= (
) 4 x2 + 1 )
3 Find the exact solutions to the quadratic equation by factoring the perfect square on the left-
hand side of the equation. Then check your work by using a GDC to approximate the solutions
graphically.
a x2 − 6x + 9 =
7 b x 2 + 8 x + 16 =
18
4 Find the exact solutions to the quadratic equation by completing the square. You may check
your work by using a GDC to approximate the solutions graphically.
a x 2 − 8x =
−12 b x 2 + 6 x − 12 =
0 c x 2 + 3x − 1 =0
d 2 x 2 − 10 x − 4 =
0 e 4 x 2 − 20 x − 5 =0 f 3x 2 + 6 x =
−2
5 The market for a product is said to be in equilibrium when supply equals demand. For a certain
product with unit price p dollars, the supply and demand functions are given below.
supply function: s ( p
= ) 2p + 4p2 demand function: d
= ( p ) 1536 − 30p
a Write down an equation that can be solved to give the equilibrium unit price.
b Use completing the square to find the equilibrium unit price.
c Use a GDC to graphically check your solution to part b.
d Find the equilibrium quantity for the product.
© Oxford University Press 2019 Additional exercise 1
Additional exercise
Answers
1 a x 2 + 7 x + 12 = 0 ⇒ ( x + 3) ( x + 4 ) = 0 ⇒ x + 3 = 0 or x + 4 = 0 ⇒ x = −3, −4
b x 2 + 3x − 10 = 0 ⇒ ( x − 2 ) ( x + 5) = 0 ⇒ x − 2 = 0 or x + 5 = 0 ⇒ x = 2, −5
c x 2 − 64 = 0 ⇒ ( x − 8 ) ( x + 8 ) = 0 ⇒ x − 8 = 0 or x + 8 = 0 ⇒ x = 8, −8
2
d 3x 2 − 5x + 2 = 0 ⇒ (3x − 2 ) ( x − 1) = 0 ⇒ 3x − 2 = 0 or x − 1 = 0 ⇒ x = ,1
3
7 3
e 4 x 2 − 8 x − 21 = 0 ⇒ (2 x − 7 ) (2 x + 3) = 0 ⇒ 2 x − 7 = 0 or 2 x + 3 = 0 ⇒ x = ,−
2 2
3 3
f 25x 2 − 9 = 0 ⇒ (5x − 3) (5x + 3) = 0 ⇒ 5x − 3 = 0 or 5x + 3 = 0 ⇒ x = ,−
5 5
2 a x 2 − 4 x − 4 = 2 x + 12 ⇒ x 2 − 6 x − 16 = 0 ⇒ ( x − 8 ) ( x + 2 ) = 0 ⇒ x = 8, −2
b x ( x − 1) = 20 ⇒ x 2 − x − 20 = 0 ⇒ ( x − 5) ( x + 4 ) = 0 ⇒ x = 5, −4
3
c 2 ( x + 3) ( x − 3) + 9 x = 0 ⇒ 2 x 2 + 9 x − 18 = 0 ⇒ (2 x − 3) ( x + 6 ) = 0 ⇒ x = , −6
2
d x 2 + 12 x = 2 x − 25 ⇒ x 2 + 10 x + 25 = 0 ⇒ ( x + 5) ( x + 5) = 0 ⇒ x = −5
2 1
e 6 x ( x + 1) = 5x + 2 ⇒ 6 x 2 + x − 2 = 0 ⇒ (3x + 2 ) (2 x − 1) = 0 ⇒ x = − ,
3 2
4
f ( )
x ( x + 7 ) = 4 x 2 + 1 ⇒ 3x 2 − 7 x + 4 = 0 ⇒ (3x − 4 ) ( x − 1) = 0 ⇒ x =
3
,1
x 2 − 6 x + 9 = 7 ⇒ ( x − 3) = 7 ⇒ x − 3 = ± 7 ⇒ x = 3 ± 7
2
3 a
x = 0.354 x = 5.65
3 − 7 ≈ 0.354 3 + 7 ≈ 5.65
18 ⇒ ( x + 4 ) =
2
b x 2 + 8 x + 16 = 18 ⇒ x + 4 =± 18 ⇒ x + 4 =±3 2 ⇒ x =−4 ± 3 2
x = −8.24 x = 0.243
−4 − 3 2 ≈ −8.24 −4 + 3 2 ≈ 0.243
© Oxford University Press 2019 2
Additional exercise
2 2
−8 −8
4a x 2 − 8x =−12 ⇒ x 2 − 8 x + =−12 + =x 2 − 8 x + 16 =−12 + 16 ⇒
2 2
( x − 4)
2
=4⇒ x−4=± 4 ⇒ x−4=±2 ⇒ x =4±2⇒ x =6,2
2 2
6 6
b x 2 + 6 x − 12 =0 ⇒ x 2 + 6 x =12 ⇒ x 2 + 6 x + =12 + ⇒ x 2 + 6 x + 9 =12 + 9 ⇒
2
2
( x + 3)
2
=21 ⇒ x + 3 =± 21 ⇒ x =−3 ± 21
2 2
−3 −3 9 9
c x 2 + 3x − 1 =0 ⇒ x 2 + 3x =1 ⇒ x 2 + 3x + =1 +
2
⇒ x + 3x + =1 + ⇒
2 2 4 4
2
3 13 3 13 3 13 3 13 −3 ± 13
x + = ⇒ x + =± ⇒ x =− ± =− ± =
2 4 2 4 2 4 2 2 2
2 2
−5 −5 25 25
d 2 x 2 − 10 x − 4 =0 ⇒ x 2 − 5x =2 ⇒ x 2 − 5x + =2 +
2
⇒ x − 5x + =2 + ⇒
2 2 4 4
2
5 33 5 33 5 33 5 33 5 ± 33
x − = ⇒ x − =± ⇒ x =± =± =
2 4 2 4 2 4 2 2 2
2 2
5 −5 5 −5 25 5 25
e 4 x 2 − 20 x − 5 =0 ⇒ x 2 − 5x = ⇒ x 2 − 5x + = +
2
⇒ x − 5x + = + ⇒
4 2 4 2 4 4 4
2
5 30 15 5 15 5 15 5 ± 30
x − = = ⇒ x − =± ⇒x = ± or
2 4 2 2 2 2 2 2
2 2
2 2 2 2 2
f 3x 2 + 6 x =
−2 ⇒ x 2 + 2 x =
− ⇒ x 2 + 2x + =
− + ⇒ x 2 + 2x + 1 =
− +1 ⇒
3 2 3 2 3
1 1 1 −3 ± 3
( x + 1)
2
= ⇒ x + 1 =± ⇒ x =−1 ± or
3 3 3 3
5 a 2 p + 4 p2 = 1536 − 30 p
b 2 p + 4 p2 = 1536 − 30 p ⇒
2 2
8 8
4 p2 + 32 p = 1536 ⇒ p2 + 8 p = 384 ⇒ p2 + 8 p + = 384 + ⇒
2
2
( p + 4)
2
=400 ⇒ p + 4 =± 400 ⇒ p =−4 ± 20 ⇒ p =−24,16
Since the price cannot be a negative value, the equilibrium price is $16.
c
d From the calculator check in part c, you can see that the equilibrium quantity is 1056.
Alternately, you can find that either s (16 ) or d (16 ) equals 1056 units.
© Oxford University Press 2019 3
Вам также может понравиться
- Ecuaciones Algebraicas 4ºesoДокумент3 страницыEcuaciones Algebraicas 4ºesokkkkkОценок пока нет
- 1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic EquationДокумент8 страниц1.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Quadratic Equationkhrr7brbpcОценок пока нет
- 5.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Square InequalitiesДокумент9 страниц5.HIGH School VIII QUADRATIC EQUATIONS AND QUADRATIC FUNCTIONS-Square Inequalitieskhrr7brbpcОценок пока нет
- Math Module 3Документ4 страницыMath Module 3Cristina AmantiadОценок пока нет
- 1 Quadratic Equations in One Unknown (I) : Review Exercise 1 (P. 1.5)Документ34 страницы1 Quadratic Equations in One Unknown (I) : Review Exercise 1 (P. 1.5)HarryОценок пока нет
- Ecuaciones Cuadráticas Incompletas - Gurpo 6Документ7 страницEcuaciones Cuadráticas Incompletas - Gurpo 6daviany pomar zabalaОценок пока нет
- Basic Technical Mathematics With Calculus Si Version Canadian 10Th Edition Washington Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент68 страницBasic Technical Mathematics With Calculus Si Version Canadian 10Th Edition Washington Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFlifemateesculentopj100% (13)
- 2 - Quadratic Functions and Equations ExtensionДокумент4 страницы2 - Quadratic Functions and Equations Extensionapi-369430795Оценок пока нет
- Ass ITMДокумент13 страницAss ITMAbdul WajidОценок пока нет
- Mathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerДокумент3 страницыMathematics 9 - Quadratic Equation ReviewerJames Russel MariОценок пока нет
- 3. GIẢI PHƯƠNG TRÌNH CHỨA ẨN TRONG DẤU CĂNДокумент2 страницы3. GIẢI PHƯƠNG TRÌNH CHỨA ẨN TRONG DẤU CĂNDần ĐoànОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 SolutionsДокумент10 страницChapter 4 SolutionsBryceОценок пока нет
- F4 Textbook Answer C2 (ENG)Документ45 страницF4 Textbook Answer C2 (ENG)Hui Ern SeeОценок пока нет
- Quadratics: Skills Check Exercise 1.1Документ16 страницQuadratics: Skills Check Exercise 1.1muhammad awaisОценок пока нет
- Malabang National High School First Periodical Examination Mathematics 9Документ4 страницыMalabang National High School First Periodical Examination Mathematics 9Allyza S. MarohomОценок пока нет
- 6.7 Solve by Factoring PDFДокумент6 страниц6.7 Solve by Factoring PDFIrish Serdeña - SigueОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 4 Solving Quadratic Equation by Quadratic FormulaДокумент9 страницLesson 2 4 Solving Quadratic Equation by Quadratic FormulaflyleafОценок пока нет
- 10th Science Ex 1 1 Amir Shehzad PDFДокумент8 страниц10th Science Ex 1 1 Amir Shehzad PDFAsiaОценок пока нет
- Important Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 1.1Документ8 страницImportant Notes of 10th Class Math Exercise 1.1Tayyabah ShahОценок пока нет
- 10th Science Ex 1 1 Amir ShehzadДокумент8 страниц10th Science Ex 1 1 Amir ShehzadShoaib ChОценок пока нет
- Mock 2021 Compulsory Part Paper 2 SolutionsДокумент7 страницMock 2021 Compulsory Part Paper 2 Solutionskiuspy72Оценок пока нет
- Algebra - Ecuaciones 2do GradoДокумент3 страницыAlgebra - Ecuaciones 2do GradoDennis Yholver Palacios BautistaОценок пока нет
- Mathematics - Grade 9 Week 1 Topic: Quadratic Equations Sub Topic: Illustrating Quadratic EquationsДокумент13 страницMathematics - Grade 9 Week 1 Topic: Quadratic Equations Sub Topic: Illustrating Quadratic EquationsCleo VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- DindaДокумент8 страницDindaSisca DamayantiОценок пока нет
- DindaДокумент8 страницDindaSisca DamayantiОценок пока нет
- A Level Preparation - Equations and Inequalities (Answers)Документ7 страницA Level Preparation - Equations and Inequalities (Answers)mhacunaОценок пока нет
- Guà - A à - LgebraДокумент4 страницыGuà - A à - LgebraSofia OgaldeОценок пока нет
- Maths Holliday ProjectДокумент29 страницMaths Holliday ProjectBellezzaОценок пока нет
- EmutДокумент8 страницEmutSisca DamayantiОценок пока нет
- Fundamentos de MatematicasДокумент12 страницFundamentos de MatematicasAlejandra EspitiaОценок пока нет
- KOLOKVIJUMДокумент19 страницKOLOKVIJUMalminamahovkic1Оценок пока нет
- Algebra 1esoДокумент3 страницыAlgebra 1esoalberto580AОценок пока нет
- SET B Values Activity Lesson 2 With Answer LongДокумент5 страницSET B Values Activity Lesson 2 With Answer LongAnonymous L7XrzMEОценок пока нет
- Quadratic Inequalities: + BX + C 0, Ax Ax AxДокумент5 страницQuadratic Inequalities: + BX + C 0, Ax Ax AxDominic Dalton CalingОценок пока нет
- QuadEquations PPT Alg2Документ25 страницQuadEquations PPT Alg2Joyce JuarezОценок пока нет
- Exam-Style Paper 3A - Pure 3: y X Yx y X y X Yx y XДокумент3 страницыExam-Style Paper 3A - Pure 3: y X Yx y X y X Yx y XThomas NgangaОценок пока нет
- Mohammed Saeed Al-Ammari - MT101 - TMA - Answer BookletДокумент6 страницMohammed Saeed Al-Ammari - MT101 - TMA - Answer BookletMoh'd Al AmmariОценок пока нет
- Dwi Pramesti WulandariДокумент6 страницDwi Pramesti WulandariDidik WidjanarkoОценок пока нет
- Ebook College Algebra in Context 5Th Edition Harshbarger Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFДокумент68 страницEbook College Algebra in Context 5Th Edition Harshbarger Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFsorrancemaneuverpmvll100% (11)
- 9 Lesson 1Документ2 страницы9 Lesson 1Sarah SaraelОценок пока нет
- C2 Differentialtion - AnswersДокумент9 страницC2 Differentialtion - AnswersfavourfjlawaniОценок пока нет
- Quadratic EquationДокумент2 страницыQuadratic EquationLynmar EnorasaОценок пока нет
- Count JuanДокумент2 страницыCount JuanJulia Arabela SantosОценок пока нет
- Worksheet A: Artial RactionsДокумент13 страницWorksheet A: Artial RactionsBryan YeohОценок пока нет
- Chapter 8 - Quadratic Equations: Solutions To Pre-TestДокумент79 страницChapter 8 - Quadratic Equations: Solutions To Pre-TestemmascirihaОценок пока нет
- Quadratic Equation Worksheet 1Документ3 страницыQuadratic Equation Worksheet 1sismemer2Оценок пока нет
- 5 17 44 418Документ17 страниц5 17 44 418kesharОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5 HW 4.4 The Quadratic FormulaДокумент2 страницыLesson 5 HW 4.4 The Quadratic FormulaJoshua RicardoОценок пока нет
- Beginning Algebra 9th Edition Tobey Solutions Manual DownloadДокумент58 страницBeginning Algebra 9th Edition Tobey Solutions Manual DownloadMary Bumgarner100% (27)
- 4b. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and Stationary Points - AnswersДокумент4 страницы4b. Increasing and Decreasing Functions and Stationary Points - Answerswaleedkhan567799Оценок пока нет
- Soal Matematika Persamaan Kuadrat KelasДокумент18 страницSoal Matematika Persamaan Kuadrat KelasNeta ApriyaniОценок пока нет
- Ejercicios para PracticarДокумент5 страницEjercicios para PracticarIsrael LópezОценок пока нет
- Algebra by Vikas Gupta SolutionsДокумент263 страницыAlgebra by Vikas Gupta Solutionspqgfd4qjv4Оценок пока нет
- 42Документ4 страницы42Vince Bagsit PolicarpioОценок пока нет
- HIGH School IV REAL NUMBERS-LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLEДокумент7 страницHIGH School IV REAL NUMBERS-LINEAR EQUATIONS IN ONE VARIABLENenad JanicijevicОценок пока нет
- Math SummДокумент11 страницMath SummRomario TambunanОценок пока нет
- Math C4 PracticeДокумент53 страницыMath C4 PracticeMoustafa SohdyОценок пока нет
- 32 DerivativeRulesДокумент8 страниц32 DerivativeRulesapi-3738981Оценок пока нет
- Eco IBdeconomics NotesДокумент3 страницыEco IBdeconomics NotesAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Answers - Worksheet C: X 9 + 2y Swap X 5Документ6 страницAnswers - Worksheet C: X 9 + 2y Swap X 5Aanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Ib Economics 1 PDFДокумент3 страницыIb Economics 1 PDFAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Eco Notes Perfect CompДокумент13 страницEco Notes Perfect CompAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Important Diagrams To Remember: Chapter 2 Competitive Markets: Demand and SupplyДокумент43 страницыImportant Diagrams To Remember: Chapter 2 Competitive Markets: Demand and SupplyAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- HL 1.4 BINOMIAL THEOREM - Solutions PDFДокумент4 страницыHL 1.4 BINOMIAL THEOREM - Solutions PDFAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Magazine Article-Saif Ali KhanДокумент2 страницыMagazine Article-Saif Ali KhanAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- 1.15 Production and Costs - Student Activity PDFДокумент6 страниц1.15 Production and Costs - Student Activity PDFAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- HL 2.8-2.10 EXPONENTS AND LOGARITHMS - SolutionsДокумент6 страницHL 2.8-2.10 EXPONENTS AND LOGARITHMS - SolutionsAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Answers - Worksheet B: X X X X X XДокумент3 страницыAnswers - Worksheet B: X X X X X XAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Worksheet B: UnctionsДокумент2 страницыWorksheet B: UnctionsAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Bks MaaSL 1104 ws00 XxaannДокумент2 страницыBks MaaSL 1104 ws00 XxaannAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- 11.5 Applications of Right-And Non-Right-Angled TrigonometryДокумент2 страницы11.5 Applications of Right-And Non-Right-Angled TrigonometryAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- 12.2 Trigonometric Ratios in The Unit CircleДокумент2 страницы12.2 Trigonometric Ratios in The Unit CircleAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Mark Zuckerberg: - The CEO and Founder of FacebookДокумент9 страницMark Zuckerberg: - The CEO and Founder of FacebookAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- 11.2 Right-angled triangle trigonometry: 1 Find the angle θ in each triangleДокумент3 страницы11.2 Right-angled triangle trigonometry: 1 Find the angle θ in each triangleAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- 11 Relationships in Space: Geometry and Trigonometry in 2D and 3DДокумент5 страниц11 Relationships in Space: Geometry and Trigonometry in 2D and 3DAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Dp1 Maths Aa SL Trigonometry Revision Questions (With GDC) Time Required: 45 MinutesДокумент2 страницыDp1 Maths Aa SL Trigonometry Revision Questions (With GDC) Time Required: 45 MinutesAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Bks MaaSL 0306 ws00 XxaannДокумент3 страницыBks MaaSL 0306 ws00 XxaannAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- 11 Relationships in Space: Geometry and Trigonometry in 2D and 3DДокумент4 страницы11 Relationships in Space: Geometry and Trigonometry in 2D and 3DAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Importance of Social EntrepreneurshipДокумент2 страницыImportance of Social EntrepreneurshipAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Word Online Training: Session 1: INTRODUCTION - 21 AugustДокумент3 страницыMicrosoft Word Online Training: Session 1: INTRODUCTION - 21 AugustAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Dp1 Maths Aa SL Trigonometry Revision Questions (Without GDC) Time Required: 50 MinutesДокумент2 страницыDp1 Maths Aa SL Trigonometry Revision Questions (Without GDC) Time Required: 50 MinutesAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Dp1 Maths Aa SL Trigonometry Revision Questions (With GDC) Time Required: 45 Minutes 1. (No Calculator)Документ2 страницыDp1 Maths Aa SL Trigonometry Revision Questions (With GDC) Time Required: 45 Minutes 1. (No Calculator)Aanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Dp1 Maths Aa SL Trigonometry Revision Questions (With GDC) Time Required: 45 Minutes 1. (No Calculator)Документ2 страницыDp1 Maths Aa SL Trigonometry Revision Questions (With GDC) Time Required: 45 Minutes 1. (No Calculator)Aanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- Ib Economics 1 PDFДокумент5 страницIb Economics 1 PDFAanya RalhanОценок пока нет
- I I Formularies Laundry Commercial Liquid Detergents 110-12-020 USДокумент6 страницI I Formularies Laundry Commercial Liquid Detergents 110-12-020 USfaissalОценок пока нет
- Santu BabaДокумент2 страницыSantu Babaamveryhot0950% (2)
- Aditya Birla GroupДокумент21 страницаAditya Birla GroupNarendra ThummarОценок пока нет
- Iphone and Ipad Development TU GrazДокумент2 страницыIphone and Ipad Development TU GrazMartinОценок пока нет
- PE MELCs Grade 3Документ4 страницыPE MELCs Grade 3MARISSA BERNALDOОценок пока нет
- Axera D06Документ2 страницыAxera D06Cristián Fernando Cristóbal RoblesОценок пока нет
- Multimodal Essay FinalДокумент8 страницMultimodal Essay Finalapi-548929971Оценок пока нет
- Mozal Finance EXCEL Group 15dec2013Документ15 страницMozal Finance EXCEL Group 15dec2013Abhijit TailangОценок пока нет
- CS-6777 Liu AbsДокумент103 страницыCS-6777 Liu AbsILLA PAVAN KUMAR (PA2013003013042)Оценок пока нет
- Famous Little Red Book SummaryДокумент6 страницFamous Little Red Book SummaryMatt MurdockОценок пока нет
- Arduino Uno CNC ShieldДокумент11 страницArduino Uno CNC ShieldMărian IoanОценок пока нет
- Union Test Prep Nclex Study GuideДокумент115 страницUnion Test Prep Nclex Study GuideBradburn Nursing100% (2)
- (Campus of Open Learning) University of Delhi Delhi-110007Документ1 страница(Campus of Open Learning) University of Delhi Delhi-110007Sahil Singh RanaОценок пока нет
- Aakriti 1Документ92 страницыAakriti 1raghav bansalОценок пока нет
- The Kicker TranscriptionДокумент4 страницыThe Kicker TranscriptionmilesОценок пока нет
- Disclosure To Promote The Right To InformationДокумент11 страницDisclosure To Promote The Right To InformationnmclaughОценок пока нет
- The Privatization PolicyДокумент14 страницThe Privatization PolicyRIBLEN EDORINAОценок пока нет
- E-Versuri Ro - Rihana - UmbrelaДокумент2 страницыE-Versuri Ro - Rihana - Umbrelaanon-821253100% (1)
- TFGДокумент46 страницTFGAlex Gigena50% (2)
- Chinese Paper Cutting Work SheetДокумент4 страницыChinese Paper Cutting Work Sheet黃梓Оценок пока нет
- Organization Culture Impacts On Employee Motivation: A Case Study On An Apparel Company in Sri LankaДокумент4 страницыOrganization Culture Impacts On Employee Motivation: A Case Study On An Apparel Company in Sri LankaSupreet PurohitОценок пока нет
- Computers in Industry: Hugh Boyes, Bil Hallaq, Joe Cunningham, Tim Watson TДокумент12 страницComputers in Industry: Hugh Boyes, Bil Hallaq, Joe Cunningham, Tim Watson TNawabMasidОценок пока нет
- CSE 202.04 Inspection of Concrete StructuresДокумент67 страницCSE 202.04 Inspection of Concrete StructuresJellyn BaseОценок пока нет
- User Manual PM3250Документ80 страницUser Manual PM3250otavioalcaldeОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Investigatory Project (R)Документ23 страницыChemistry Investigatory Project (R)BhagyashreeОценок пока нет
- Syllabus PDFДокумент3 страницыSyllabus PDFBibin Raj B SОценок пока нет
- 2 To 20 Years - Girls Stature-For-Age and Weight-For-Age PercentilesДокумент1 страница2 To 20 Years - Girls Stature-For-Age and Weight-For-Age PercentilesRajalakshmi Vengadasamy0% (1)
- Experiment - 1: Batch (Differential) Distillation: 1. ObjectiveДокумент30 страницExperiment - 1: Batch (Differential) Distillation: 1. ObjectiveNaren ParasharОценок пока нет
- Design and Analysis of Modified Front Double Wishbone Suspension For A Three Wheel Hybrid VehicleДокумент4 страницыDesign and Analysis of Modified Front Double Wishbone Suspension For A Three Wheel Hybrid VehicleRima AroraОценок пока нет
- 1995 Biology Paper I Marking SchemeДокумент13 страниц1995 Biology Paper I Marking Schemetramysss100% (2)