Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheet
Загружено:
booty hole0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
111 просмотров1 страницаThis document provides an overview of key concepts and steps for drawing Lewis structures of molecules, including:
1. Definitions of important terms like valence electrons, octet rule, and bonding pairs.
2. A process for arranging atoms and determining the number of valence electrons before drawing the Lewis structure.
3. Guidelines for drawing single, double, and triple bonds between atoms as well as exceptions to the octet rule.
4. A method for drawing Lewis structures of ionic compounds by transferring electrons between atoms.
Исходное описание:
drawing molecules
Оригинальное название
Drawing Molecules
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document provides an overview of key concepts and steps for drawing Lewis structures of molecules, including:
1. Definitions of important terms like valence electrons, octet rule, and bonding pairs.
2. A process for arranging atoms and determining the number of valence electrons before drawing the Lewis structure.
3. Guidelines for drawing single, double, and triple bonds between atoms as well as exceptions to the octet rule.
4. A method for drawing Lewis structures of ionic compounds by transferring electrons between atoms.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
111 просмотров1 страница16: Drawing Molecules - Lewis Structures: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheet
Загружено:
booty holeThis document provides an overview of key concepts and steps for drawing Lewis structures of molecules, including:
1. Definitions of important terms like valence electrons, octet rule, and bonding pairs.
2. A process for arranging atoms and determining the number of valence electrons before drawing the Lewis structure.
3. Guidelines for drawing single, double, and triple bonds between atoms as well as exceptions to the octet rule.
4. A method for drawing Lewis structures of ionic compounds by transferring electrons between atoms.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
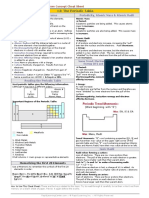
High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheet
16: Drawing Molecules – Lewis Structures
Key Lewis Structure Terms Arranging Atoms in Lewis Structures
Valence Shell: Electrons in the outermost shell that are
involved in bonding. 1. For molecules with only 2 elements, arrange the atoms
Valence Bond Theory: Overlap of atomic orbitals forming symmetrically.
the bond. 2. “COOH” is a carboxylic acid (both O’s bond to the C and
Covalent Bond: Bond formed between two nonmetals that the H goes on one of the O’s).
involves shared electrons. 3. Hydrogen and halogens cannot go in the middle.
Octet Rule: Atoms are most stable with a full valence shell 4. Write the remaining atoms in the order they appear in the
(in most cases is “8”). formula.
Lewis Structure: A 2D representation of a molecule and 5. Write the hydrogen and halogen atoms around the
its bonds. element they are written next to in the formula.
Lone Pair: Pair of electrons not being shared in a bond.
Bonding Pair: A pair of electrons is to form a bond. Both
atoms sharing the electrons can “count” them in their
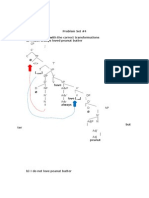
Drawing Covalent Lewis Structures
valence shell.
Single bond: One pair of shared electrons. 1. Arrange the atoms as above.
Double bond: Two pairs of shared electrons. Shorter and 2. Determine the # of valence electrons for each atom.
stronger than a single bond. 3. Draw the valence electrons—do not double up where a
Triple bond: Three pairs of shared electrons. Shorter and bond is going to form between two atoms.
stronger than a double bond. 4. Count to see if all atoms have full valences (notice the
Polyatomic Ion: Group of atoms covalently bonded exceptions).
together that have a net charge. 5. If two atoms adjacent to each other do not have full
Ionic Compound: Electrons are transferred from one valences, move in an electron from each to form a double
atom to another. Transfer of electrons results in net bond. Repeat for triple bond if necessary.
charges, which bond with electrostatic attraction. 6. If two atoms that are not adjacent to each other need to
double bond, try moving a hydrogen to one of them to
Determining # of Valence Electrons cause two atoms adjacent to each other to need the
Determining valence electrons from the periodic table: double bond.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
Single bonds:
Note: Valence electrons in transition metals are not as
Double bonds:
reliable and predictable as the ones in main group elements.
Drawing Lewis Structures for an Element
1. Use the element symbol to represent the nucleus and
core electrons.
Polyatomic anion:
2. Determine # of valence electrons.
3. Draw valence electrons—placing one on each side before
doubling up. Drawing Ionic Lewis Structures
Transfer the electrons from the metal to the nonmetals until
HONC Valence Rule Mnemonic: The electrons needed for
all have full valences and the net charge = 0
full valence shell and covalent bonds formed are H(1), O(2),
N(3) and C(4) = HONC.
Ionic compound (BaF2): Ba+2 2F-1
Exceptions to the Octet Rule
1. Hydrogen and Helium can only hold 2 electrons (they
only have a 1s orbital).
2. Boron and Beryllium can be full with 6 electrons. Another Approach to Lewis Structures
3. Any element in period 3 or below can have more than 8
electrons (they have empty d orbitals that can hold
1. Arrange the atoms as above.
them).
2. Determine the total # of valence electrons for the whole
molecule.
Octet Exception Mnemonic: H&He: 2(full valence); Be: 4;
3. Put one bonding pair between each set of atoms to be
B = 6; S&P > 8 = “2 Hawks and Hens (2-legs); 4 Bears (4-
bonded.
legs); 6 Bugs (6-legs); many SPiders (<8 legs).”
4. Place remaining electrons in lone pairs, starting with the
most electronegative element.
Note: Elements in period 3 and below have empty “d”
5. If atoms do not have full valence shells, move a lone pair
orbitals that can be used to hold more than 8 valence
from an adjacent atom in to double, or triple, bond.
electrons (18 Electrons Rule). Free radicals with one unpaired
electron clearly do not follow the Octet rule.
How to Use This Cheat Sheet: These are the keys related to this topic. Try to read through it carefully twice then write it out on a
blank sheet of paper. Review it again before the exams.
RapidLearningCenter.com Rapid Learning Inc. All Rights Reserved
Вам также может понравиться
- 15: Lewis Structures & VSEPR TheoryДокумент1 страница15: Lewis Structures & VSEPR TheoryIcathiu CardosoОценок пока нет
- Key Chemistry Terms Arranging Atoms in Lewis StructuresДокумент1 страницаKey Chemistry Terms Arranging Atoms in Lewis StructuresIcathiu CardosoОценок пока нет
- Chemistry (STM 128) : Lesson 1: Chemical BondingДокумент7 страницChemistry (STM 128) : Lesson 1: Chemical BondingBUAHIN JANNAОценок пока нет
- 2020 2.4 Chemistry GZДокумент187 страниц2020 2.4 Chemistry GZgeetub1Оценок пока нет
- Chapter - 7 Slides - General Chemistry - Open StaxДокумент96 страницChapter - 7 Slides - General Chemistry - Open Staxonline purchaseОценок пока нет
- L3 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent MoleculesДокумент33 страницыL3 Polar and Nonpolar Covalent Molecules1256- FRONDA, RHOVIC D.Оценок пока нет
- Unit 2 Chemistry RemedialДокумент69 страницUnit 2 Chemistry Remedialabdimoh7522100% (1)
- Bonding and StructureДокумент72 страницыBonding and StructureHannah Jean EstebanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding: 3.1 The Octet RuleДокумент89 страницChapter 2. Molecular Structure and Bonding: 3.1 The Octet RuleAnn BorromeoОценок пока нет
- Part 1Документ35 страницPart 1Ola100% (1)
- CHEM 10a Unit 4Документ3 страницыCHEM 10a Unit 4McHaley HalОценок пока нет
- Week 9 NotesДокумент5 страницWeek 9 Notesapi-402936737Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding 2020Документ73 страницыChemical Bonding 2020HANNAH JULIA CAPUNGCOОценок пока нет
- BondingДокумент17 страницBondingShahd ElfkiОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding Class 11Документ18 страницChemical Bonding Class 11bansarigadhvi23Оценок пока нет
- Geometry BkgdroundДокумент7 страницGeometry Bkgdroundtanique.nembhard1022Оценок пока нет
- Psfsiee ReviewДокумент10 страницPsfsiee Reviewlimichael000Оценок пока нет
- Points To Remember Class: XI Chapter Name: Chemical Bonding and Molecular StructureДокумент15 страницPoints To Remember Class: XI Chapter Name: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structureaustinfru7Оценок пока нет
- Chemical BondingДокумент2 страницыChemical Bondingapi-304350501Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding ScriptДокумент4 страницыChemical Bonding ScriptAkhil MathewОценок пока нет
- CHEM 205 Chapter 8 Section 12.3Документ30 страницCHEM 205 Chapter 8 Section 12.3phikjaeОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond ModelДокумент16 страницChemical Bonding: The Covalent Bond ModelBreana MilesОценок пока нет
- CHM 121 Chapter 8 LectureДокумент21 страницаCHM 121 Chapter 8 Lecturecd aОценок пока нет
- Lewis Atructures and ShapesДокумент38 страницLewis Atructures and ShapesPatrick AbidraОценок пока нет
- Lewis Theory Valence Electrons Are The Electrons Involved in BondingДокумент15 страницLewis Theory Valence Electrons Are The Electrons Involved in BondingmaryОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding 1Документ7 страницChemical Bonding 1rhiannemitchbОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding: Home WorkДокумент54 страницыChemical Bonding: Home WorkSam LoveОценок пока нет
- Covalent BondДокумент27 страницCovalent BondAstig GamingОценок пока нет
- General Chem 2 ReviewerДокумент5 страницGeneral Chem 2 ReviewerBeverly A PanganibanОценок пока нет
- Differentiating AtomsДокумент3 страницыDifferentiating AtomsChennille Ann Bleu GundayaoОценок пока нет
- Ch01-Introduction of Organic ChemistryДокумент47 страницCh01-Introduction of Organic ChemistrySİNEM GÜVENОценок пока нет
- Basic Concepts of Chemical BondingДокумент46 страницBasic Concepts of Chemical BondingHendri KurniawanОценок пока нет
- Organic Chemistry NotesДокумент29 страницOrganic Chemistry NotesbitangyarahОценок пока нет
- CH 6 Chemical BondingДокумент14 страницCH 6 Chemical Bondingapi-240972605Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Objectives, Notes, QuestionsДокумент26 страницChapter 6 Objectives, Notes, QuestionsPreet KaurОценок пока нет
- Examples of Chemical BondsДокумент11 страницExamples of Chemical BondsRondel ForjesОценок пока нет
- Group 6 Covalent BondsДокумент37 страницGroup 6 Covalent BondsCarl Lewis TongcuaОценок пока нет
- Chemistry Chapter 6 ReviewДокумент3 страницыChemistry Chapter 6 Reviewjuan carlos quispe mamaniОценок пока нет
- Bonding: General ConceptsДокумент41 страницаBonding: General ConceptsOlufifehanmi OsikoyaОценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding Ionic Bonding Characteristics of Ionic CompoundsДокумент2 страницыChemical Bonding Ionic Bonding Characteristics of Ionic CompoundsBittu100% (1)
- Lewis StructuresДокумент12 страницLewis StructuresLisandrea BrownОценок пока нет
- Lewis Structure Spring 2014Документ7 страницLewis Structure Spring 2014Mohamed DahmaneОценок пока нет
- Compiled Lecture in General Chemistry (Organic Chemistry) (Midterm) CcjeДокумент21 страницаCompiled Lecture in General Chemistry (Organic Chemistry) (Midterm) CcjeEmil Vince T. CumilangОценок пока нет
- Topic 4 Chemical BondingДокумент39 страницTopic 4 Chemical BondingskywalkerОценок пока нет
- Atomic Structure: Electron Proton NeutronДокумент4 страницыAtomic Structure: Electron Proton NeutronTalao, Angelie Rei S.Оценок пока нет
- Chemical Bonding: Asst. Prof. Jean Theresa O. GoДокумент51 страницаChemical Bonding: Asst. Prof. Jean Theresa O. GoOsannah Irish InsongОценок пока нет
- Covalent Bonding NotesДокумент1 страницаCovalent Bonding Noteschongkee56100% (1)
- Organic Chemistry,: Structure & BondingДокумент74 страницыOrganic Chemistry,: Structure & BondingilhamfaturachmanagusОценок пока нет
- Pptx5 Chemical BondingДокумент39 страницPptx5 Chemical BondingLumbay, Jolly MaeОценок пока нет
- Polar and Nonpolar MoleculesДокумент32 страницыPolar and Nonpolar MoleculeshensoncarlosjrОценок пока нет
- Prelim Org Chem Lecture Notes Chap 1 Intro To Organic ChemistryДокумент5 страницPrelim Org Chem Lecture Notes Chap 1 Intro To Organic ChemistryKaye Selene Raphaelle SyОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Molecular Structure and BondingДокумент31 страницаLecture 1 Molecular Structure and Bondingthuy36030Оценок пока нет
- Chemical BondingДокумент5 страницChemical BondingHillary DalitОценок пока нет
- Chap 1 Valence Bond TheoryДокумент86 страницChap 1 Valence Bond TheoryAre lipОценок пока нет
- CH 3 Covalent SubstancesДокумент53 страницыCH 3 Covalent SubstancesHeidi VagueОценок пока нет
- Lewis StructuresДокумент2 страницыLewis StructuresMajed JallouliОценок пока нет
- Bonding - Covalent N Metallic BondДокумент22 страницыBonding - Covalent N Metallic Bondwadheea.thaufeeqОценок пока нет
- Gen Chem Leson 2Документ90 страницGen Chem Leson 2Jay-mee Claire V. DioОценок пока нет
- A-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsОт EverandA-Level Chemistry Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (5)
- 19: Solutions: Key Solution Terms Concentrations of SolutionДокумент1 страница19: Solutions: Key Solution Terms Concentrations of Solutionbooty holeОценок пока нет
- 18: Gas Laws: Key Gas Law Terms Attacking Strategy For Gas LawsДокумент1 страница18: Gas Laws: Key Gas Law Terms Attacking Strategy For Gas Lawsbooty holeОценок пока нет
- Molecular GeometryДокумент1 страницаMolecular Geometrybooty holeОценок пока нет
- 15: Chemical Bonding: Key Chemistry Terms Using Bond CharacteristicsДокумент1 страница15: Chemical Bonding: Key Chemistry Terms Using Bond Characteristicsbooty holeОценок пока нет
- 14: The Periodic Table: Key Chemistry Terms Periodicity, Atomic Mass & Atomic RadiiДокумент1 страница14: The Periodic Table: Key Chemistry Terms Periodicity, Atomic Mass & Atomic Radiibooty holeОценок пока нет
- 13: Electron Configuration: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat SheetДокумент1 страница13: Electron Configuration: High School Chemistry - Core Concept Cheat Sheetbooty holeОценок пока нет
- Gregorian-Lunar Calendar Conversion Table of 1960 (Geng-Zi - Year of The Mouse)Документ1 страницаGregorian-Lunar Calendar Conversion Table of 1960 (Geng-Zi - Year of The Mouse)Anomali SahamОценок пока нет
- Play Tennis Manual PDFДокумент52 страницыPlay Tennis Manual PDFAnonymous GJuRvp9A5T100% (2)
- Siemens 6SL31622AA000AA0 CatalogДокумент20 страницSiemens 6SL31622AA000AA0 CatalogIrfan NurdiansyahОценок пока нет
- Motorola Phone Tools Test InfoДокумент98 страницMotorola Phone Tools Test InfoDouglaswestphalОценок пока нет
- Paper 19 AugustДокумент552 страницыPaper 19 AugustUma Sankar Pradhan100% (1)
- Stats 116 SUДокумент128 страницStats 116 SUCОценок пока нет
- ECS 3390 - Business and Technical CommuncationsДокумент293 страницыECS 3390 - Business and Technical CommuncationsEliseo Robles0% (3)
- 热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远Документ7 страниц热虹吸管相变传热行为CFD模拟 王啸远小黄包Оценок пока нет
- Design and Fabrication of Light Electric VehicleДокумент14 страницDesign and Fabrication of Light Electric VehicleAshish NegiОценок пока нет
- Vacuum Braking SystemДокумент20 страницVacuum Braking SystemPrashant RaiОценок пока нет
- Vivekananda'S Conception of Normative Ethics and Resolution Ethical Problems in BusinessДокумент8 страницVivekananda'S Conception of Normative Ethics and Resolution Ethical Problems in BusinessYajat BhargavОценок пока нет
- 1) About The Pandemic COVID-19Документ2 страницы1) About The Pandemic COVID-19محسين اشيكОценок пока нет
- New York LifeДокумент38 страницNew York LifeDaniel SineusОценок пока нет
- Soal Try Out Ujian NasionalДокумент9 страницSoal Try Out Ujian NasionalAgung MartaОценок пока нет
- CSMP77: en Es FRДокумент38 страницCSMP77: en Es FRGerson FelipeОценок пока нет
- Physics Cheat SheetДокумент8 страницPhysics Cheat SheetJeremiah MoussaОценок пока нет
- 100 IELTS Essay Topics For IELTS Writing - My IELTS Classroom BlogДокумент16 страниц100 IELTS Essay Topics For IELTS Writing - My IELTS Classroom BlogtestОценок пока нет
- Neoclassical CounterrevolutionДокумент1 страницаNeoclassical CounterrevolutionGraziella ValerioОценок пока нет
- AQAR-Report 2018-19 Tilak VidyapeethДокумент120 страницAQAR-Report 2018-19 Tilak VidyapeethAcross BordersОценок пока нет
- Emerging and Less Common Viral Encephalitides - Chapter 91Документ34 страницыEmerging and Less Common Viral Encephalitides - Chapter 91Victro ChongОценок пока нет
- Cot 4 Mapeh (Health)Документ15 страницCot 4 Mapeh (Health)RELYN LUCIDOОценок пока нет
- Science9 Q3 SLM1Документ15 страницScience9 Q3 SLM1Zandra Musni Delos ReyesОценок пока нет
- 06 Renr5908 08 01 All PDFДокумент108 страниц06 Renr5908 08 01 All PDFFrancisco Ospino Arrieta100% (2)
- Syntax Ps4Документ6 страницSyntax Ps4blue_child86% (7)
- 1st Quarter 2016 Lesson 5 Powerpoint With Tagalog NotesДокумент25 страниц1st Quarter 2016 Lesson 5 Powerpoint With Tagalog NotesRitchie FamarinОценок пока нет
- Part-II Poem Article and Report For College Magazine-2015-16 Dr.M.Q. KhanДокумент4 страницыPart-II Poem Article and Report For College Magazine-2015-16 Dr.M.Q. KhanTechi Son taraОценок пока нет
- Youth and Moral ValuesДокумент6 страницYouth and Moral ValuesAlka SinghОценок пока нет
- UST Corporation Law Syllabus 2020 2021Документ26 страницUST Corporation Law Syllabus 2020 2021PAMELA ALEXIA CASTILLOОценок пока нет
- Certification Programs: Service As An ExpertiseДокумент5 страницCertification Programs: Service As An ExpertiseMaria RobОценок пока нет