Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
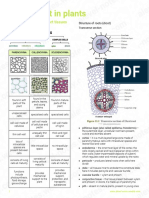
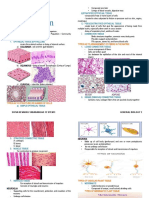
Highly-Branched: General Biology 1 Basic Plant Cell and Tissue Types 1. Parenchyma
Загружено:
Alfonso PlantillaИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Highly-Branched: General Biology 1 Basic Plant Cell and Tissue Types 1. Parenchyma
Загружено:
Alfonso PlantillaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
Long Test #2 Reviewer
BASIC PLANT CELL AND TISSUE TYPES - Stellate Parenchyma: highly-branched,
adjacent cells connected to each other
1. Parenchyma
- most common type (all soft parts)
- thin-walled, evenly thickened
- alive at maturity
- photosynthesis, storage, respiration,
division, protection, secretion, excretion
- resume meristematic activity (protection,
healing, regeneration)
2. Collenchyma
- elongated, unevenly thickened,
non-lignified cell walls
- complete protoplasts capable of
meristematic activity and photosynthesis
- alive at maturity
- functions for support and growth
- sides of young stems, stalk and midrib of
leaves
- Storage Parenchyma: contain lots of
amyloplasts 3. Sclerenchyma
- Aerenchyma: large air spaces - evely thickened secondary walls (with
lignin)
- dead at maturity (no protoplast, seems to
be empty)
- Fibers: long, spindle-shaped, occur in
- Chlorenchyma: contains plastids, strands (cortex, phloem, xylem) or in
photosynthesis sheaths/bundle caps (vascular bundles)
- Sclereids: short cells, strongly lignified
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
Long Test #2 Reviewer
- Types of Sclereids: Brachysclereids - Adventitious System: primary root from
(isodiametric, elongated), radicle dies early (no taproot), grows in
Macrosclereids (elongated, columnar), unusual places
Osteosclereids (columnar w/ enlarged - Unique Features: Root Hair (increase
ends), Astrosclereids (with lobes/arm SA) and Root Cap (protect root apical
diverging from central body) meristem)
PRIMARY AND SECONDARY GROWTH
OF THE ROOT
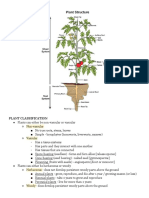
Overview of the Plant Basic Morphology
● Modified Roots
1. Storage Roots - store food and water
2. Pneumatophores - obtain oxygen
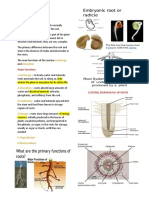
The Root
- anchorage, absorption, storage
- primary (first root at center) and lateral
(spread out)
- Taproot System: absorption restricted to 3. Buttress - distribution of shallow roots,
tip of lateral roots, structural support for architectural support
tall plants 4. Prop - growing from stem, additional
- Fibrous System: thick mat of slender support
roots, absorption and prevention of soil 5. Contractile - pull plants to desirable
erosion depth
No shortcuts. Work for it.Nothing worth having ever comes easy.
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
Long Test #2 Reviewer
6. Epiphytic - silvery velamen (can be
photosynthetic), support, prevent water Epidermis: outer protective covering
loss, absorption Ground Tissue: parenchyma, stores starch
- Cortex: between epidermis and vascular
cambium
- Pith: innermost part for eudicots
Vascular Tissue: for vascular transport
- Xylem: conducts water/minerals
- Phloem: conducts dissolved sugar
Endodermis: innermost part of cortex, prevents
water/materials from entering xylem
Pericycle: layer of cells inside endodermis, gives
7. Symbiotic - Mychorizza (fungus root),
rise to lateral roots
Nodule (Rhizobium in leguminous
Casparian Strip: waterproof material (composed
plants)
of suberin)
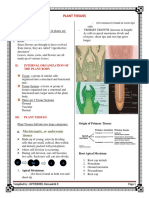
● Root Anatomy
SECONDARY GROWTH
Anatomy of Woody Dicot Root
THE LEAF
- main photosynthetic structure
- collects solar energy and carbon dioxide
No shortcuts. Work for it.Nothing worth having ever comes easy.
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
Long Test #2 Reviewer
- flattened blade/lamina and petiole Mesophyll:ground meristematic tissue between
● Leaf Anatomy epidermal layers, specialized parenchyma
(photosynthetic)
→ Isobilateral: both sides are of the same color,
mesophyll is not divided, mostly monocot
→ Dorsiventral: palisade mesophyll (elongated
parenchyma) and spongy mesophyll
(loosely-arranged for air circulation)
Veins: bring xylem/phloem near photosynthetic
tissue
Bundle Sheath: encloses vein, regulates
substance movement
Leaf Primordia: projections alongside shoot
apical meristem (where leaves develop from)
Stomata: exchange of O2 and
CO2 (pore)
Guard Cells: opening/closing of pore, with
chloroplast to maximize photosynthesis
Bulliform Cells: responsible for rolling/unrolling
● Leaf Type
Simple - undivided blade, single axillary bud at
end of petiole
Compound - leaflets with no axillary bud,single
bud at the end of petiole
Pinnately Compound - pairs attached to rachis
Palmately Compound - same point at the base of
petiole
Peltate - petiole attached to the middle of the blade
Perfoliate -
sessile(no petiole),
pierced by the
stem
No shortcuts. Work for it.Nothing worth having ever comes easy.
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
Long Test #2 Reviewer
● Leaf Venation ● Leaf Base
● Modified Leaves
1. Cotyledons/Seed Leaves
- first leaves, store food from endosperm,
● Leaf Phyllotaxy dicots (phanero cotylar), monocots (krypto
cotylar)
2. Colored Bracts
- petal-like, to attract pollinators
3. Insect-Trapping Leaves
- digest insect bodies to get nitrogen and
nutrients (venus flytrap, pitcher plant)
● Leaf Forms 4. Tendrils
- extension of the midrib, cling to other object
5. Spines
- prevent desiccation, protect from predation
6. Storage Leaves
- retain water in large vacuoles
7. Absorptive Leaves
- no xylem,water can pass through diffusion
- foliar fertilization (apply directly on leaves)
● Leaf Margins - Hydrilla verticillata
8. Others
- reproductive (Kalanchoe plantlets)
- window leaves (transparent, light
penetration)
- flower pot leaves (catch water, nutrients)
- pulvinus leaves (swollen, receptive to K+)
● Leaf Tips
No shortcuts. Work for it.Nothing worth having ever comes easy.
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
Long Test #2 Reviewer
Node: point where leaves are attached
Internode: segment between nodes
Apical Bud: concentration of young shoot growth
Axillary Bud: in the axis between leaf and stem, may
form lateral branch, thorn, or flower
PRIMARY AND SECONDARY GROWTH
OF THE STEM
The Stem
- bears leaves and buds
- maximizes photosynthesis
- elevates reproductive organs
- Main function: support and conduction
Stem Morphology
Stem Anatomy
No shortcuts. Work for it.Nothing worth having ever comes easy.
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
Long Test #2 Reviewer
Lacuna: cavity caused by
collapse of cells during
elongation
Phloem: Sieve Tube
Elements (cell-to-cell
fluid flow), Companion
Cell (nucleus,ribosomes)
Xylem: Tracheids (H2O
through pit), Vessel
Element (H2O through
perforation)
Secondary
Growth
Vascular Bundle = Bundle Cap Fiber (sclerenchyma)
No shortcuts. Work for it.Nothing worth having ever comes easy.
GENERAL BIOLOGY 1
Long Test #2 Reviewer
Heartwood: no longer conducting H2O, good for
building ships
Sapwood: transports xylem sap
Modified Stems
→ Above Ground
1.Thorn - no terminal bud
2.Tendril - cling, sunlight
3.Cladophyll - photosynthetic, storage
4.Stolon - asexual reproduction
5.Sucker - young plants at base of mother plant
6.Tiller - one plant from another
7.Offset - water hyacinth
→ Underground
1.Tuber - enlarged end of rhizomes, stolons
2. Bulb - short stem enclosed by leaves
3. Rhizome - horizontal root (ginger)
4.Corm - swollen stem base + scale leaves
No shortcuts. Work for it.Nothing worth having ever comes easy.
Вам также может понравиться
- Plant TissuesДокумент32 страницыPlant TissuesVikneswaran Gunahlan Nesh100% (2)
- Tissues, Roots, Stems, LeavesДокумент128 страницTissues, Roots, Stems, LeavesAlfonso PlantillaОценок пока нет
- Anatomy Class NotesДокумент57 страницAnatomy Class NotesClinical Psychology0% (1)
- Flowers:: Sexual Reproductive Organs of AngiospermsДокумент106 страницFlowers:: Sexual Reproductive Organs of AngiospermsAlfonso PlantillaОценок пока нет
- Botany 5 Root System PDFДокумент31 страницаBotany 5 Root System PDFZyreeneNicoleОценок пока нет
- Cinchoneae), A New Species From The Sira Mountains, Eastern Andes of Central Peru, and The Identity of Ladenbergia AcutifoliaДокумент8 страницCinchoneae), A New Species From The Sira Mountains, Eastern Andes of Central Peru, and The Identity of Ladenbergia AcutifoliaEdersin TorresОценок пока нет
- Test Bank For Stress Management For Life A Research Based Experiential Approach 5th Edition Michael Olpin Margie HessonДокумент24 страницыTest Bank For Stress Management For Life A Research Based Experiential Approach 5th Edition Michael Olpin Margie HessonJamesNewmanazpy100% (32)
- Angiosperm Life Cycle For BotanyДокумент11 страницAngiosperm Life Cycle For BotanyCyrose Silvosa MilladoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Points To RememberДокумент7 страницChapter 6 Points To RememberNANDA KISHORE S X A AD : 1 0 6 4 4Оценок пока нет
- Botany Notes PDFДокумент21 страницаBotany Notes PDFKrizel LagundiОценок пока нет
- Theories of The Origin of Solar SystemДокумент18 страницTheories of The Origin of Solar SystemGWYNETH REIN CARI�OОценок пока нет
- 7 Transport in PlantsДокумент7 страниц7 Transport in PlantsTina EtoileОценок пока нет
- 02 - Plant TissuesДокумент23 страницы02 - Plant Tissuestri hastutiОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of PlantsДокумент4 страницыAnatomy of PlantsSreekutty SudhiОценок пока нет
- Morphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsДокумент3 страницыMorphology and Anatomy of Flowering PlantsAyako HayashidaОценок пока нет
- Science BotanyДокумент6 страницScience BotanybalagbaganjoymargaretОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsДокумент33 страницыAnatomy of Flowering PlantsRaichal P Biju100% (1)
- Plant Tissue For Class 9 - 1Документ60 страницPlant Tissue For Class 9 - 1DHARSHAN BOOPALANОценок пока нет
- Topic-5-Bio-1130 Plant TissueДокумент3 страницыTopic-5-Bio-1130 Plant TissueMohamidin MamalapatОценок пока нет
- 02 PlantAnatomyДокумент50 страниц02 PlantAnatomyPoonam RanieОценок пока нет
- Module 4 - Cell Specialization and ModificationДокумент12 страницModule 4 - Cell Specialization and ModificationRein Margaret RogelОценок пока нет
- Ch35 PlantStructure&GrowthДокумент5 страницCh35 PlantStructure&GrowthCristie SumbillaОценок пока нет
- 1 Botlec ReviewerДокумент7 страниц1 Botlec ReviewerKamille PobleteОценок пока нет
- Mauseth Chapter 05 PDFДокумент2 страницыMauseth Chapter 05 PDFCharlotte AmanteОценок пока нет
- Lecture 3 - Plant TissuesДокумент60 страницLecture 3 - Plant TissuesdmdlouiseОценок пока нет
- Pha611 (Lab)Документ24 страницыPha611 (Lab)RHODAОценок пока нет
- Tissue 9th BiologyДокумент8 страницTissue 9th BiologyNestor Bong Bordaje NemeñoОценок пока нет
- ePSYCH1B Exercise7 CAMBELMДокумент3 страницыePSYCH1B Exercise7 CAMBELMKdrama SweetieОценок пока нет
- Plant Body: Dorothy D. Silva School of Teacher Education Saint Louis UniversityДокумент54 страницыPlant Body: Dorothy D. Silva School of Teacher Education Saint Louis UniversityMario RectoОценок пока нет
- Parts and Functiond of PlantsДокумент5 страницParts and Functiond of PlantsCjoy MañiboОценок пока нет
- II ME NRP B SS 05. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsДокумент5 страницII ME NRP B SS 05. Anatomy of Flowering PlantsAmit RavindhraОценок пока нет
- EPITHELIUMДокумент2 страницыEPITHELIUMALEXIS MOIRAH CALIGAGANОценок пока нет
- Exercise No. 17Документ9 страницExercise No. 17Francis Jay MerencilloОценок пока нет
- Evolution and Diversiy: Nutrients)Документ12 страницEvolution and Diversiy: Nutrients)Jeanette RiosОценок пока нет
- Bio ActivitiesДокумент10 страницBio ActivitiesErrol Chester Salvador CabadingОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsДокумент7 страницAnatomy of Flowering PlantsArthav KumarОценок пока нет
- Anatomy of Flowering PlantsДокумент13 страницAnatomy of Flowering Plantsaravind kishanОценок пока нет
- Bio 11.1 LE 2 NotesДокумент7 страницBio 11.1 LE 2 NotesCode BlueОценок пока нет
- Simple Permanent Tissues Three Major Types of Root SystemДокумент4 страницыSimple Permanent Tissues Three Major Types of Root SystemAleczandra QuesadaОценок пока нет
- Ground TissuesДокумент17 страницGround TissuesHelen Gail EmbudoОценок пока нет
- CH 6Документ6 страницCH 6Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956Оценок пока нет
- General Biology 1 - Plants Form and FuctionДокумент2 страницыGeneral Biology 1 - Plants Form and FuctionAlly OcbianОценок пока нет
- Plant TissueДокумент5 страницPlant TissueClarenz100% (1)
- Lecture 7Документ4 страницыLecture 7김j.kОценок пока нет
- Integumentary System NoteДокумент5 страницIntegumentary System Noteleighzy lalaОценок пока нет
- Sa Nka LP: Sankalp EducationДокумент3 страницыSa Nka LP: Sankalp Educationshalini priyaОценок пока нет
- GS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsДокумент9 страницGS BIO 206. Functional Organization in PlantsChary Johanne MenesesОценок пока нет
- Core CH 19 BiodiversityДокумент8 страницCore CH 19 Biodiversitystudy.stkgОценок пока нет
- Cnidaria SummaryДокумент12 страницCnidaria SummaryJose ArroyoОценок пока нет
- ZooLec Reviewer February 27Документ6 страницZooLec Reviewer February 27Charles GuillermoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plant CompressedДокумент7 страницChapter 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plant Compressed65vxdx9ddgОценок пока нет
- Plant Form and FunctionsДокумент2 страницыPlant Form and FunctionsJason TaburnalОценок пока нет
- Biology Lesson 4Документ4 страницыBiology Lesson 4Medija FamilyОценок пока нет
- ROOTS ReviewerДокумент5 страницROOTS ReviewerMANALANG JULIA ALEXISОценок пока нет
- Plant Tissue FinalДокумент18 страницPlant Tissue FinalEunice AcunaОценок пока нет
- Observations of Cells and TissuesДокумент13 страницObservations of Cells and TissuesIrish MercadoОценок пока нет
- Anatomy in Flowering PlantsДокумент5 страницAnatomy in Flowering PlantsDanish UllahОценок пока нет
- Chemical Components of CellsДокумент5 страницChemical Components of CellsDannika LouiseОценок пока нет
- Plant Form, Eco, Aqua, BiologicalДокумент17 страницPlant Form, Eco, Aqua, BiologicalPolee SheaОценок пока нет
- Tissue 9 PDFДокумент5 страницTissue 9 PDFNilesh NagarОценок пока нет
- Plant Organs: Roots: Xylem Does Not Form The Central Tissue in Some Monocot RootsДокумент2 страницыPlant Organs: Roots: Xylem Does Not Form The Central Tissue in Some Monocot RootsLara GreyjoyОценок пока нет
- NMAT Review 2018 Module - BiologyДокумент34 страницыNMAT Review 2018 Module - BiologyRaf Lin DrawsОценок пока нет
- Botany Module 2.1Документ11 страницBotany Module 2.1Yaz VergaraОценок пока нет
- Biological Organization: B) Stratified Epithelial TissueДокумент8 страницBiological Organization: B) Stratified Epithelial TissueShane V. TabalbaОценок пока нет
- Plant CellДокумент112 страницPlant CellAlfonso PlantillaОценок пока нет
- Psych Journal ReflectionДокумент2 страницыPsych Journal ReflectionAlfonso PlantillaОценок пока нет
- Psychiatric HistoryДокумент6 страницPsychiatric HistoryAlfonso PlantillaОценок пока нет
- Monroy Christian CCMH OpdДокумент5 страницMonroy Christian CCMH OpdAlfonso PlantillaОценок пока нет
- Bioethics PaperДокумент1 страницаBioethics PaperAlfonso PlantillaОценок пока нет
- Pteridophytes: General Characters of Pteridophytes: OccurrenceДокумент11 страницPteridophytes: General Characters of Pteridophytes: Occurrencearissa noorОценок пока нет
- Bramwell - 1969 PDFДокумент8 страницBramwell - 1969 PDFrockfestОценок пока нет
- SMM2 For Site ClaranceДокумент4 страницыSMM2 For Site ClaranceShukri AzhariОценок пока нет
- Notes-Morphology of Flowering PlantsДокумент37 страницNotes-Morphology of Flowering PlantsKisna guptaОценок пока нет
- Orquídeas Del PerúДокумент308 страницOrquídeas Del PerúAndres CabanillasОценок пока нет
- Bentham and Hooker Classification System - OecДокумент22 страницыBentham and Hooker Classification System - OecDAVALDARIYA WALIKARОценок пока нет
- Transport in PlantsДокумент4 страницыTransport in PlantsGianina Shakila EdwardОценок пока нет
- Identifikasi Kerusakan Daun Pada Tanaman Balangeran (KHDTK) Tumbang NusaДокумент8 страницIdentifikasi Kerusakan Daun Pada Tanaman Balangeran (KHDTK) Tumbang NusaBustami HidayatullahОценок пока нет
- Autecology Is The Ecology of A Single SpeciesДокумент23 страницыAutecology Is The Ecology of A Single SpeciesmaygracedigolОценок пока нет
- L4-Stem MorphologyДокумент57 страницL4-Stem MorphologySleeping BeautyОценок пока нет
- O Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsДокумент45 страницO Level Biology 17 Reproduction in PlantsHamzu GamingОценок пока нет
- Biology The RootДокумент11 страницBiology The RootTanaka ChirawuОценок пока нет
- Practical Analysis 2023Документ32 страницыPractical Analysis 2023Queen BettyОценок пока нет
- Morphology ProjectДокумент13 страницMorphology ProjectFizaОценок пока нет
- Let's Do This!: General Biology 2: Performance Task 1Документ2 страницыLet's Do This!: General Biology 2: Performance Task 1Jeric CantillanaОценок пока нет
- EpigynyДокумент5 страницEpigynyNirmala BhatОценок пока нет
- Understanding Flower Anatomy: FlowersДокумент4 страницыUnderstanding Flower Anatomy: FlowersLara ZainОценок пока нет
- CaesalpiniaceaeДокумент6 страницCaesalpiniaceaePrerna JindalОценок пока нет
- Angiosperms: An Overview: January 2015Документ24 страницыAngiosperms: An Overview: January 2015aniruskОценок пока нет
- Plant StudyДокумент209 страницPlant StudyScot RobertsОценок пока нет
- Week 8 - Leaves and StemsДокумент77 страницWeek 8 - Leaves and StemsPrincess De LeonОценок пока нет
- Usnh 0032.01Документ176 страницUsnh 0032.01Nilson Esmar TorresОценок пока нет
- Biology 3rd QTR Activities 1Документ7 страницBiology 3rd QTR Activities 1Mark Laurence MasellonesОценок пока нет
- Structure of LeavesДокумент7 страницStructure of Leaves门门Оценок пока нет
- Turcz 2011 15-100Документ87 страницTurcz 2011 15-100love gisОценок пока нет
- Transport 2Документ2 страницыTransport 2Lyra Ane IlaganОценок пока нет
- InflorescenceДокумент2 страницыInflorescenceelcivilengОценок пока нет