Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Distillation Rectification English PDF
Загружено:
Rohit PrakashОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Distillation Rectification English PDF
Загружено:
Rohit PrakashАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
THERMAL PROCESS ENGINEERING DISTILLATION/RECTIFICATION
BASIC KNOWLEDGE BASIC KNOWLEDGE
DISTILLATION RECTIFICATION
Distillation is a unit operation that can be used to fractionate liquid Distillation does not result in complete Rectification is an application of
mixtures. It utilises the different volatility of the components of separation of the liquid mixture, but distillation and its uses include
the mixture to be separated. Volatility refers to the tendency of a rather its division into two mixtures fractionation of crude oil.
substance to pass from the liquid phase into the gas phase. Examples with different contents of volatile and
of volatile liquids include acetone, alcohol and petrol. less volatile components. The sepa- If the distillate obtained during
rating principle is based on the fact distillation is distilled again, a
To achieve separation, the liquid mixture is brought to boiling point. that the content of volatile compo- new distillate is obtained with
The resulting vapour phase is made up of several components, mainly nents is greater in the vapour phase an even higher concentration
the more volatile components of the mixture. The vapour phase is than in the liquid phase. of volatile components. As the
separated from the liquid phase and condensed (distillate). The less procedure is repeated, the
volatile components predominantly remain in the liquid phase. concentration of volatile compo-
nents in the distillate increases
on each occasion.
In practice, this multi-stage
distillation process is carried
out in the form of countercur-
rent distillation (rectification) in
a column. The liquid mixture to
be separated (feed) is fed to the
bottom of the column, where
it is brought to boiling point.
The vapour produced moves
upwards inside the column, exits
it at the top and is condensed.
Part of the condensate is
carried away as top product.
The remainder flows back into
the column and moves down-
wards as liquid opposite phase.
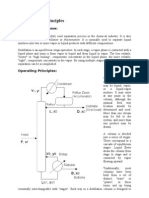
Simplified illustration of a rectification column:
1 feed, 2 bottom heating, 3 bottom product, 4 bottom of column, 5 top product,
Principle of distillation: 6 reflux, 7 condenser, 8 top of column, 9 tray (here: bubble tray);
1 vapour phase, 2 boiling liquid mixture, 3 distillate, 4 condenser x liquid phase, y vapour phase
On its way to the top of the column, the liquid phase. At the same time, the liquid phase concentration of less
mixed vapour created at the bottom is condensation heat released evapo- volatile components increases in
subjected to an intensive exchange of rates the more volatile components the opposite direction, from the top
heat and material with the liquid phase of the liquid phase. These proc- of the column to the bottom.
as it passes through the tray or packing esses in the column increase the
in the column. The less volatile compo- vapour phase concentration of vola-
nents of the vapour phase condense tile components moving from the
and increase in concentration in the bottom to the top of the column. The
15
Вам также может понравиться
- Distillation Rectification English PDFДокумент1 страницаDistillation Rectification English PDFQian Jun AngОценок пока нет
- Instrumentation and Control of Distillation TowersДокумент20 страницInstrumentation and Control of Distillation TowersHenry OkoyeОценок пока нет
- Industrial Process Control: Control of Distillation TowersДокумент20 страницIndustrial Process Control: Control of Distillation TowersAmeya DalviОценок пока нет
- Distil at Ion MaterialДокумент17 страницDistil at Ion MaterialUmang V ShahОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 DistillationДокумент77 страницChapter 2 DistillationAhmad DanialОценок пока нет
- DistillationДокумент2 страницыDistillationarun kumarОценок пока нет
- SyedmujahedalirizwanДокумент6 страницSyedmujahedalirizwanVictor VazquezОценок пока нет
- 3) Pertemuan 3 (Distilasi)Документ15 страниц3) Pertemuan 3 (Distilasi)ILHAM KIKI SHAHILAОценок пока нет
- Lab Report 4 Group 4Документ19 страницLab Report 4 Group 42023389329Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 7.1 DistillationДокумент63 страницыChapter 7.1 Distillationamira nabillaОценок пока нет
- Distillation: Definition & Purpose Operating Principles Ideal StagesДокумент5 страницDistillation: Definition & Purpose Operating Principles Ideal StagesIffatОценок пока нет
- Distillation ColumnsДокумент6 страницDistillation ColumnsSK ChuaОценок пока нет
- Seperation MethodsДокумент7 страницSeperation MethodsjjknarutotokyoОценок пока нет
- Mto-2 Oep (30,31,32)Документ1 страницаMto-2 Oep (30,31,32)Nayan ParmarОценок пока нет
- Distillation Is Defined As:: How Does Distillation Work?Документ35 страницDistillation Is Defined As:: How Does Distillation Work?sankalpnambiarОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 DistillationДокумент73 страницыChapter 1 DistillationNUR HIDAYAHОценок пока нет
- Distillation Rectification: Basic Knowledge Basic KnowledgeДокумент1 страницаDistillation Rectification: Basic Knowledge Basic KnowledgeRohan lallОценок пока нет
- Figure 1.1: Basic Operation of Distillation ProcessДокумент2 страницыFigure 1.1: Basic Operation of Distillation ProcessianharОценок пока нет
- Absorption Refrigeration SystemДокумент32 страницыAbsorption Refrigeration SystemEngr ModestoОценок пока нет
- CHE 319 Module 1 LatestДокумент79 страницCHE 319 Module 1 Latestpeter-albert.danielОценок пока нет
- Technological Institute of The Philippines - Manila (CHEP 510L1, 2 Semester, SY 2015-2016)Документ4 страницыTechnological Institute of The Philippines - Manila (CHEP 510L1, 2 Semester, SY 2015-2016)Sharmaine RoseОценок пока нет
- Lesson 8 Distillation ProcessesДокумент27 страницLesson 8 Distillation ProcesseskhumisoОценок пока нет
- WLP Science q1 w7 LandscapeДокумент17 страницWLP Science q1 w7 LandscapeJayral PradesОценок пока нет
- Technip Separations PDFДокумент60 страницTechnip Separations PDFProcess EngineerОценок пока нет
- An Introduction: Factors Affecting Distillation Column OperationДокумент3 страницыAn Introduction: Factors Affecting Distillation Column OperationEngr Ghulam SarwarОценок пока нет
- Separation Process Principles PDFDrive 1Документ6 страницSeparation Process Principles PDFDrive 1pascualmandyrogielynОценок пока нет
- Process Calculation: DistillationДокумент15 страницProcess Calculation: DistillationJohn RajОценок пока нет
- Article 1652173631Документ7 страницArticle 1652173631Shiena AscueОценок пока нет
- WLP Science q1 w7w8 LandscapeДокумент13 страницWLP Science q1 w7w8 LandscapeJayral PradesОценок пока нет
- Sections & RefluxДокумент50 страницSections & RefluxOmar JrОценок пока нет
- Equilibrium Separation ColumnsДокумент18 страницEquilibrium Separation ColumnsBenjamin Angel Flores ZavalaОценок пока нет
- Distillation Assignment PDFДокумент13 страницDistillation Assignment PDFcalliemozartОценок пока нет
- Entrainment Issues in Vacuum Column Flash ZonesДокумент10 страницEntrainment Issues in Vacuum Column Flash ZonesZangОценок пока нет
- Design of A Continuous Distillation Column For A Multi Component MixtureДокумент45 страницDesign of A Continuous Distillation Column For A Multi Component MixtureSerkan73% (11)
- Distllation PrintДокумент29 страницDistllation Printsanjay YadavОценок пока нет
- The Essentials of Continuous Evaporation: Back To BasicsДокумент5 страницThe Essentials of Continuous Evaporation: Back To BasicsJohn AnthoniОценок пока нет
- The Essentials of Continuous EvaporationДокумент5 страницThe Essentials of Continuous EvaporationRajendraОценок пока нет
- DistillationДокумент72 страницыDistillationYashfa YasinОценок пока нет
- TEACHING PP 411 (Autosaved)Документ135 страницTEACHING PP 411 (Autosaved)Osan ThorpeОценок пока нет
- Distillation: by Assistant Professor Jntua-Otpri AnantapurДокумент39 страницDistillation: by Assistant Professor Jntua-Otpri AnantapurRAJESHPAVANОценок пока нет
- Batch DistillationДокумент29 страницBatch Distillationytconstance50% (4)
- Aspen Hysys Week 6Документ7 страницAspen Hysys Week 6Saroo BastkyОценок пока нет
- Chemical Engineering and Physical and Chemical Principles QuestionsДокумент84 страницыChemical Engineering and Physical and Chemical Principles QuestionsMark Vincent EspinosaОценок пока нет
- Basic Distillation: Process Modeling Using Aspen Plus (Radfrac Models)Документ21 страницаBasic Distillation: Process Modeling Using Aspen Plus (Radfrac Models)ashraf-84Оценок пока нет
- IFPEXOLДокумент10 страницIFPEXOLMicaela Flores LanzaОценок пока нет
- CE620e - V1.1 23 41Документ19 страницCE620e - V1.1 23 41Carlos CortesОценок пока нет
- Chem ENgg Board Exam QuestionsДокумент42 страницыChem ENgg Board Exam QuestionsAllyana Marie TiemsimОценок пока нет
- ChE ReviewerДокумент82 страницыChE ReviewerKristineОценок пока нет
- Ayat PDFДокумент13 страницAyat PDFMariam AliОценок пока нет
- 2.2 Air Release and Cavitation: Saturation Pressure Induces Aeration. This Is The Process Where TheДокумент2 страницы2.2 Air Release and Cavitation: Saturation Pressure Induces Aeration. This Is The Process Where TheRichard De Medeiros CastroОценок пока нет
- Pressure-Temperature-Concentration Phase DiagramДокумент8 страницPressure-Temperature-Concentration Phase DiagrammadhujayarajОценок пока нет
- QuizBowl QuestionsДокумент84 страницыQuizBowl QuestionsJowel MercadoОценок пока нет
- Lab Report Experiment 6 (g13)Документ13 страницLab Report Experiment 6 (g13)Ahmad Mu'azОценок пока нет
- Le Chatelier's Principle NotesДокумент2 страницыLe Chatelier's Principle NotesChitraОценок пока нет
- Solvent Evaporations:: Step 1Документ5 страницSolvent Evaporations:: Step 1Hide AnomousОценок пока нет
- UNIT Proses IN Chemical EngineeringДокумент21 страницаUNIT Proses IN Chemical EngineeringZakiyah Kamto IrfinОценок пока нет
- Kettle Type Reboiler WorkingДокумент7 страницKettle Type Reboiler WorkingCepi Sindang KamulanОценок пока нет
- DISTILLATION UNIT 1 28.2.22 - WatermarkДокумент26 страницDISTILLATION UNIT 1 28.2.22 - WatermarkHardik ChauhanОценок пока нет
- Pectin Production and Global Market PDFДокумент5 страницPectin Production and Global Market PDFRohit PrakashОценок пока нет
- Department of Chemical Engineering Government Polytechninc College, Kalamassery NoticeДокумент3 страницыDepartment of Chemical Engineering Government Polytechninc College, Kalamassery NoticeRohit PrakashОценок пока нет
- Phosphoric Acid PlantДокумент56 страницPhosphoric Acid PlantRohit PrakashОценок пока нет
- 57633686815341466119814dAJVL PDFДокумент13 страниц57633686815341466119814dAJVL PDFRohit PrakashОценок пока нет
- Simple Machines (p288) : Velocity Ratio VR S / SДокумент8 страницSimple Machines (p288) : Velocity Ratio VR S / SParamaet TamОценок пока нет
- HW5 PDFДокумент7 страницHW5 PDFKamineni JagathОценок пока нет
- Gunaan CONTENT 2011-2012Документ42 страницыGunaan CONTENT 2011-2012Khay OngОценок пока нет
- Microsoft Word - Conceptual Questions For ForceДокумент3 страницыMicrosoft Word - Conceptual Questions For ForceSarveshrau MagentharauОценок пока нет
- Finite Element Analysis of The Orthogonal Metal Cutting Process 2000 Journal of Materials Processing TechnologyДокумент15 страницFinite Element Analysis of The Orthogonal Metal Cutting Process 2000 Journal of Materials Processing TechnologyEdo DestradaОценок пока нет
- Performance Cycle Analysis of TurbofanДокумент14 страницPerformance Cycle Analysis of TurbofanLilis TrianiОценок пока нет
- ASHRAE Psychrometric ChartДокумент1 страницаASHRAE Psychrometric ChartKenneth Dale San JuanОценок пока нет
- Teleportation - Dream or RealityДокумент13 страницTeleportation - Dream or Realityjamafisica7981Оценок пока нет
- Electromagnetic Waves (Report)Документ22 страницыElectromagnetic Waves (Report)astria alos100% (1)
- The Granulation Methods of Double Base PropellantДокумент5 страницThe Granulation Methods of Double Base PropellantSimbarashe NyotaОценок пока нет
- 15 - CHAPTER 2 Thesis - 2Документ22 страницы15 - CHAPTER 2 Thesis - 2afinde100% (1)
- ARE Module 3 NotesДокумент47 страницARE Module 3 NotesSamyak DhutaleОценок пока нет
- (DEsign Manual) Hollow Section Structural StabilityДокумент58 страниц(DEsign Manual) Hollow Section Structural StabilityShaileshRastogi100% (1)
- Lab 2 Endo-Exo ReactionsДокумент2 страницыLab 2 Endo-Exo Reactionsapi-213645632Оценок пока нет
- Measuring and Compensating For Emissivity Using Infrared Imaging RadiometersДокумент3 страницыMeasuring and Compensating For Emissivity Using Infrared Imaging RadiometersSammoonОценок пока нет
- Pei Et Al 2014 Dynamical Wear Prediction Along Meshing Path in Mixed Lubrication of Spiral Bevel GearsДокумент16 страницPei Et Al 2014 Dynamical Wear Prediction Along Meshing Path in Mixed Lubrication of Spiral Bevel GearsMing MaОценок пока нет
- JRA-CST-22 Construction Well Connection With Dredging & Pipe Laying Activity (Rev 03)Документ136 страницJRA-CST-22 Construction Well Connection With Dredging & Pipe Laying Activity (Rev 03)Andy SintyaОценок пока нет
- Vapor Liquid Equilibrium GraphsДокумент7 страницVapor Liquid Equilibrium Graphsmahbub1332Оценок пока нет
- 2.01-Motion in A Straight Line-HWДокумент2 страницы2.01-Motion in A Straight Line-HWNirmal gkОценок пока нет
- Paper - Ceotto, Tavares - Design of A Liquid Nitrous Oxide and Ethanol Rocket Engine InjectorДокумент10 страницPaper - Ceotto, Tavares - Design of A Liquid Nitrous Oxide and Ethanol Rocket Engine Injectortony pinkОценок пока нет
- FEA Buckling AnalysisДокумент7 страницFEA Buckling AnalysisThuy Giang LeОценок пока нет
- Practice Problems For Advanced Vibrations: April 2019Документ36 страницPractice Problems For Advanced Vibrations: April 2019Animesh ChandraОценок пока нет
- March 2017 (v2) MS - Paper 4 CIE Physics IGCSEДокумент12 страницMarch 2017 (v2) MS - Paper 4 CIE Physics IGCSEMohamed LabibОценок пока нет
- CH2254 Unit 4 Solution PS4Документ14 страницCH2254 Unit 4 Solution PS4Vignesh KОценок пока нет
- MRI Protocol Knee Epioscopy - Philips V01Документ6 страницMRI Protocol Knee Epioscopy - Philips V01ManuCastroОценок пока нет
- A Class of Exact Solutions To Navier-Stokes Equations For The Given VorticityДокумент9 страницA Class of Exact Solutions To Navier-Stokes Equations For The Given VorticityMarco Picchi ScardaoniОценок пока нет
- Mechanical and Microstructural Characterization of Ductile Iron Produced From Fuel - Fired Rotary FurnaceДокумент12 страницMechanical and Microstructural Characterization of Ductile Iron Produced From Fuel - Fired Rotary FurnacemaorealesОценок пока нет
- CE 420 CEM 402 Study Guide - Structural TheoryДокумент5 страницCE 420 CEM 402 Study Guide - Structural TheoryKaryl Briant FloresОценок пока нет
- 6mm Hole DeagssingДокумент10 страниц6mm Hole DeagssingAkintoye AsaoluОценок пока нет
- CHEM F111: General Chemistry: PilaniДокумент25 страницCHEM F111: General Chemistry: Pilanicukdbjsisns shsusbsbvzОценок пока нет