Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ferry Loading Ramp: TP501 Festo Didactic
Загружено:
nanekОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Ferry Loading Ramp: TP501 Festo Didactic
Загружено:
nanekАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
A-63
Exercise 15
Hydraulics Subject
Ferry loading ramp Title
To familiarise the student with a speed control circuit with a tractive Training aim
load
To compare circuits with flow control valves in the inlet line and outlet
line respectively
Drawing the hydraulic circuit diagram Problem definition
Practical assembly of the circuit
Measuring the cylinder advance time and travel and back pressures
with flow control valves in the inlet line and outlet line respectively
Comparison and assessment of results
TP501 • Festo Didactic
A-64
Exercise 15
Exercise The loading ramp of a car ferry must be capable of being set to different
heights. The ramp is raised and lowered by a hydraulic cylinder. This
motion must be carried out smoothly and at a constant speed. A flow
control valve is to be used to adjust the speed. This must be installed in
such a way as to prevent excessive pressures from developing within
the system.
Positional sketch
TP501 • Festo Didactic
A-65
Exercise 15
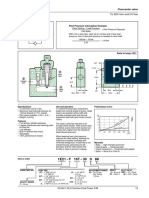
EXERCISE SHEET
Circuit diagram, hydraulic
TP501 • Festo Didactic
A-66
Exercise 15
Evaluation Measure the following:
t→ = Cylinder advance-stroke time
p1Z1 = Cylinder travel pressure
p1Z2 = Cylinder back pressure
p0Z2 = System pressure
Vary the following:
Applied load
Counter-holding
Flow control in inlet and outlet lines
Settings:
First, without an applied load or counter-holding and with a flow con-
trol valve in the inlet line, make settings to obtain an advance-stroke
time of t –> = 5 s with a system pressure of p0Z2 = 50 bar.
Then set a counter pressure of p1Z2 = 10 bar.
Then use a flow control valve in the outlet line to provide counter-
holding.
When dismantling the circuit, ensure that no pressurised fluid is trapped
(p1Z2 = 0 bar).
TP501 • Festo Didactic
A-67
Exercise 15
EXERCISE SHEET
Load and counter-holding p0Z2 p1Z1 p1Z2 t→ Flow control valve
in inlet line
Without load or counter-holding 50 bar 5s
With load without counter-holding
With load and counter-holding 10 bar
Without load with counter-holding 10 bar
Load p0Z2 p1Z1 p1Z2 t→ Flow control valve
in outlet line
Without load 50 bar 5s
With load
How does the travel time change as the load is varied? Conclusion
Which circuit is more suitable?
TP501 • Festo Didactic
C-69
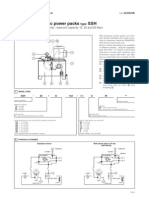
Solution 15
Ferry loading ramp
Circuit diagram, hydraulic,
with counter-holding
and flow control valve
in inlet line
In Inlet line
p = 10 bar
(1 MPa)
System
pressure
p = 50 bar
(5 MPa)
Pump
safety valve
pmax = 60 bar
(6 MPa)
TP501 • Festo Didactic
C-70
Solution 15
Practical assembly,
hydraulic,
with flow control valve
in outlet line
System
pressure
p = 50 bar
(5 MPa)
Pump
safety valve
pmax = 60 bar
(6 MPa)
TP501 • Festo Didactic
C-71
Solution 15
Item no. Qty. Description Components list
0Z1 1 Hydraulic power pack
0Z2, 1Z1, 1Z2 3 Pressure gauge
0V1, 1V4 2 Pressure relief valve
0V2 1 Shut-off valve
1V1 1 4/3-way valve
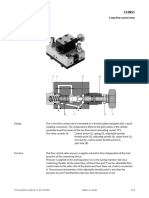
1V3 1 Flow control valve
1V2, 1V5 2 Non-return valve
1A 1 Cylinder, double-acting
1Z3 1 Loading weight
13 Hose line
4 Branch tee
1 Stop-watch
Assemble and check the circuit. Mount the cylinder 1A on the profile Solution description
plate in such a way that it can advance downwards. First close the shut-
off valve 0V2. Switch on the hydraulic power pack and then use the
pressure relief valve 0V1 to set a system pressure of 50 bar. Open the
shut-off valve and adjust the pressure relief valve 1V3 in such a way that
the piston rod advances in approx. 5 sec. The flow control valve setting
should be retained throughout the series of measurements. Only the
circuit should be modified. Dismantle the circuit only when the pressure
has fallen to zero, as shown by the pressure gauge 1Z2.
TP501 • Festo Didactic
C-72
Solution 15
Evaluation Measure the following:
t→ = Cylinder advance-stroke time
p1Z1 = Cylinder travel pressure
p1Z2 = Cylinder back pressure
p0Z2 = System pressure
Flow control valve With load and counter-holding p0Z2 p1Z1 p1Z2 t→
in inlet line
Without load without counter-holding 50 bar 0 bar 0 bar 5s
With load without counter-holding 50 bar 0 bar 0 bar 0.6 s
With load and counter-holding 50 bar 3 bar 10 bar 5s
Without load with counter-holding 50 bar 8 bar 10 bar 5s
Flow control valve Load p0Z2 p1Z1 p1Z2 t→
in outlet line
Without load 50 bar 48 bar 77 bar 5s
With load 50 bar 48 bar 84 bar 3.1 s
Conclusions Without counter-holding, the piston rod is pulled out by the load. It ad-
vances jerkily. With counter-holding, the same speed is achieved with
and without a load. If, however, the flow control valve is installed in the
outlet line to provide counter-holding, very high pressures will occur on
the outlet side. This is often unacceptable in practice.
A suitable circuit is thus one with a flow control valve in the inlet line and
counter-holding by means of a pressure relief valve in the outlet line.
TP501 • Festo Didactic
Вам также может понравиться
- Parker Re15196 - 2013-12Документ16 страницParker Re15196 - 2013-12Ashley Dean100% (1)
- User Manual NovДокумент578 страницUser Manual Novgennaro100% (1)
- A05 PDFДокумент8 страницA05 PDFElmeysОценок пока нет
- Conveyor Tensioning Device: TP501 Festo DidacticДокумент9 страницConveyor Tensioning Device: TP501 Festo DidacticGiang TônОценок пока нет
- Skip Handling: TP501 Festo DidacticДокумент7 страницSkip Handling: TP501 Festo DidacticHossam AbdelhameedОценок пока нет
- FileДокумент6 страницFileGiang TônОценок пока нет
- Exercise 20Документ7 страницExercise 20islamОценок пока нет
- Valve Technology: - by Fabian C. GonzalezДокумент106 страницValve Technology: - by Fabian C. GonzalezNyoman RakaОценок пока нет
- Hardening FurnanceДокумент8 страницHardening FurnanceFerariF.ArdiansyahОценок пока нет
- AT Nissan EnglishДокумент20 страницAT Nissan EnglishjoseОценок пока нет
- Denison Hydraulics Pressure Controls - Flanged Type: Series R5with 3 PortsДокумент17 страницDenison Hydraulics Pressure Controls - Flanged Type: Series R5with 3 PortsYuriPasenkoОценок пока нет
- Fluid Power SystemДокумент14 страницFluid Power SystemVBlazeeОценок пока нет
- Lcbca/Lcbcg/Lcbch: 工作 OperationДокумент2 страницыLcbca/Lcbcg/Lcbch: 工作 Operationதமிழன் இராமசாமிОценок пока нет
- Beaker Installation.: Hydraulic Circuit For BreakerДокумент7 страницBeaker Installation.: Hydraulic Circuit For BreakerMasterrОценок пока нет
- TROUBLESHOOT 50000811-MAN-001 BX ElevatorДокумент8 страницTROUBLESHOOT 50000811-MAN-001 BX ElevatorpabloОценок пока нет
- Denison Hydraulics Proportional Directional Valves Cetop 07: Series 4DP03-E/HДокумент19 страницDenison Hydraulics Proportional Directional Valves Cetop 07: Series 4DP03-E/Hpostolache mariusОценок пока нет
- Formacion Valvulas PVG32 (Bobcat)Документ25 страницFormacion Valvulas PVG32 (Bobcat)HANSELL MIRANDA ALVAОценок пока нет
- RN RN: Itj:SjДокумент1 страницаRN RN: Itj:SjAryaman MahajanОценок пока нет
- Valve Hyva PTДокумент2 страницыValve Hyva PTAnangtri WahyudiОценок пока нет
- Kip KIPДокумент28 страницKip KIPAndrijana MajoОценок пока нет
- Testing & Adjusting PW200/ 220-7Документ13 страницTesting & Adjusting PW200/ 220-7Teknik Makina100% (2)
- Pump Control PW200 220-7Документ21 страницаPump Control PW200 220-7Teknik Makina100% (1)
- Solenoid Valve SelectДокумент3 страницыSolenoid Valve Selecttoddski1Оценок пока нет
- Info On DRS, MRS, SRДокумент23 страницыInfo On DRS, MRS, SRsushant shirsatОценок пока нет
- 1ZUA549200-505 VRLTC Technical Guide Rev2Документ20 страниц1ZUA549200-505 VRLTC Technical Guide Rev2Mạnh Nguyễn VănОценок пока нет
- A4VG40Документ60 страницA4VG40gastonreyОценок пока нет
- Hydraulic SystemДокумент29 страницHydraulic SystemCaliche Guerra100% (1)
- 3.9S Excavator - HydДокумент85 страниц3.9S Excavator - HydJorge Rojas100% (1)
- Breaker Piping InstallationДокумент11 страницBreaker Piping InstallationZawminhtunОценок пока нет
- HYD0003 Solar Main Pump K3V, K5VДокумент31 страницаHYD0003 Solar Main Pump K3V, K5VSergey100% (2)
- Group 4 Mechatronics System: 1. All Actuators Speed Are SlowДокумент10 страницGroup 4 Mechatronics System: 1. All Actuators Speed Are SlownajafaliОценок пока нет
- Operation and TheoryДокумент13 страницOperation and TheoryŞansal DikmenerОценок пока нет
- Group 3 Mechatronics System: 1. All Speed Are SlowДокумент25 страницGroup 3 Mechatronics System: 1. All Speed Are SlowDavidОценок пока нет
- 6-4. Mechatronics SystemДокумент10 страниц6-4. Mechatronics Systemdima65Оценок пока нет
- Input Station For Laser Cutter: TP101 Festo DidacticДокумент13 страницInput Station For Laser Cutter: TP101 Festo Didacticsudesh_bhugaloo0% (1)
- Cocon QTZ PN 16 Pressure Independent Control Valve: ApplicationДокумент6 страницCocon QTZ PN 16 Pressure Independent Control Valve: ApplicationBeshoyОценок пока нет
- Control Chapter 5 - RemoteДокумент87 страницControl Chapter 5 - RemoteJhonny PerezОценок пока нет
- 14.صمام تخفيض الضغط الاتناسبي الكهربائيДокумент5 страниц14.صمام تخفيض الضغط الاتناسبي الكهربائيالمهندسوليدالطويلОценок пока нет
- Hyva Valvula Volvo Volcadora PDFДокумент2 страницыHyva Valvula Volvo Volcadora PDFricardo bueraОценок пока нет
- Lec10 Hydr CircuitsДокумент27 страницLec10 Hydr Circuitsas2899142Оценок пока нет
- Accumulateurs GBДокумент2 страницыAccumulateurs GBVânio CoelhoОценок пока нет
- V. Other-Excitation Idle-Loaded Pressure Build-Up Test in The GeneratorДокумент51 страницаV. Other-Excitation Idle-Loaded Pressure Build-Up Test in The GeneratorClip nhungcaunoihayОценок пока нет
- DX80R Control Valve 9SX14Документ34 страницыDX80R Control Valve 9SX14ZawminhtunОценок пока нет
- © Festo Didactic GMBH & Co. KG, 02/2003 Subject To ChangeДокумент2 страницы© Festo Didactic GMBH & Co. KG, 02/2003 Subject To ChangecioranescuОценок пока нет
- Fluid Power ControlДокумент40 страницFluid Power ControlSonali DeyОценок пока нет
- Group 4 Mechatronics System: 1. All Actuators Speed Are SlowДокумент17 страницGroup 4 Mechatronics System: 1. All Actuators Speed Are SlowTaha RdmanОценок пока нет
- Part 4 Hydraulic Control Principle and ParametersДокумент22 страницыPart 4 Hydraulic Control Principle and ParametersrohanОценок пока нет
- Preliminary - MITTEN HPU Only Rev DДокумент120 страницPreliminary - MITTEN HPU Only Rev DFabyano BrittoОценок пока нет
- Group 4 Mechatronics System: 1. All Actuators Speed Are SlowДокумент28 страницGroup 4 Mechatronics System: 1. All Actuators Speed Are Slowhamdi galipОценок пока нет
- OLSS & EOLSS Valves - S&F - A3 SizeДокумент4 страницыOLSS & EOLSS Valves - S&F - A3 Sizeprem sagar100% (3)
- Present ValvesДокумент27 страницPresent ValvesAbhishek ChoudharyОценок пока нет
- Motion Control ValvesДокумент1 страницаMotion Control ValvesSLK Amg55Оценок пока нет
- Carlyle IOM 5H-F CompressorДокумент40 страницCarlyle IOM 5H-F CompressorBenito Antonio Formoso LouroОценок пока нет
- Technical Training Presentations - 564-574 ForwardersДокумент152 страницыTechnical Training Presentations - 564-574 ForwardersSantos Condori MurilloОценок пока нет
- Chapt 6 AntijamДокумент6 страницChapt 6 AntijamManuelОценок пока нет
- FloSet 80 ABVДокумент1 страницаFloSet 80 ABVHector TosarОценок пока нет
- A4VGДокумент68 страницA4VGИгорь ИгорьОценок пока нет
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGОт EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGОценок пока нет
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2От EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2Оценок пока нет
- ReadingДокумент98 страницReadingIvory MojicaОценок пока нет
- Notes-Ch 10. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis PDFДокумент39 страницNotes-Ch 10. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis PDFnanekОценок пока нет
- The Power of Reading A Presentation by Dr. Charles CabellДокумент33 страницыThe Power of Reading A Presentation by Dr. Charles CabellWalben SijabatОценок пока нет
- M1 Automation PDFДокумент169 страницM1 Automation PDFnanekОценок пока нет
- Circuit ApplicationsДокумент65 страницCircuit ApplicationsAman Baviskar100% (1)
- Lesson1 170207031218Документ22 страницыLesson1 170207031218Janine B. JavierОценок пока нет
- Thermo1 Chapter 04Документ110 страницThermo1 Chapter 04Yasser Hijji80% (15)
- 3 - 0 - Support Your Child With Reading Parent Event 010316Документ19 страниц3 - 0 - Support Your Child With Reading Parent Event 010316nanekОценок пока нет
- Batangas State University Assessment of Fees: This Form Is Printed Online Using Student Registration SystemДокумент1 страницаBatangas State University Assessment of Fees: This Form Is Printed Online Using Student Registration SystemnanekОценок пока нет
- Reading Is Fun Presentatie DefinitiefДокумент19 страницReading Is Fun Presentatie DefinitiefnanekОценок пока нет
- Blended Learning in The ClassroomДокумент16 страницBlended Learning in The ClassroomnanekОценок пока нет
- Ferry Loading Ramp: TP501 Festo DidacticДокумент9 страницFerry Loading Ramp: TP501 Festo Didacticnanek100% (1)
- HPVM Series: Hydraulic Pilot ControlsДокумент4 страницыHPVM Series: Hydraulic Pilot ControlsMichael AkhramovichОценок пока нет
- Systems: Chapter B-6Документ22 страницыSystems: Chapter B-6stolehaОценок пока нет
- Rexroth - MCR-10 - Radial Piston - Size 780 To 1340Документ10 страницRexroth - MCR-10 - Radial Piston - Size 780 To 1340Chali AndresОценок пока нет
- VOLVO EXCAVATOR - Volvo Construction EquipmentДокумент8 страницVOLVO EXCAVATOR - Volvo Construction Equipmentabduallah muhammad100% (1)
- Excavadora Hyundai 340 SL EN 1Документ18 страницExcavadora Hyundai 340 SL EN 1cesar agusto quispe vilcaОценок пока нет
- 1.backhoe HydДокумент47 страниц1.backhoe HydJorge RojasОценок пока нет
- Section - 11356 - Dewatered Sludge Storage SilosДокумент24 страницыSection - 11356 - Dewatered Sludge Storage SilosjufrejjОценок пока нет
- Presentasi Coiled Tubing - Virnando Batu AraДокумент20 страницPresentasi Coiled Tubing - Virnando Batu AraVirnando NainggolanОценок пока нет
- SL030 PDFДокумент2 страницыSL030 PDFchidambaram kasiОценок пока нет
- Shop Manual Allis-Chalmers: IviodelsДокумент78 страницShop Manual Allis-Chalmers: IviodelsDmitryОценок пока нет
- Komatsu AcronymsДокумент7 страницKomatsu Acronymsالمهندسوليدالطويل100% (4)
- Automotive CBCДокумент75 страницAutomotive CBCEdgardo RicaldeОценок пока нет
- Lifts & Escalators: (Transportation System in Buildings)Документ43 страницыLifts & Escalators: (Transportation System in Buildings)Vamsi Prasad100% (2)
- WD Cross ReferenceДокумент12 страницWD Cross ReferenceCentral HydraulicsОценок пока нет
- Bench Test Procedure For Hydraulic Piston PumpsДокумент20 страницBench Test Procedure For Hydraulic Piston PumpscarlosОценок пока нет
- Integrated Recycling Systems: Harris Complete PackageДокумент4 страницыIntegrated Recycling Systems: Harris Complete PackageNicolás Toro ValenzuelaОценок пока нет
- JLG Service 340AJ DocДокумент348 страницJLG Service 340AJ DocArgopartsОценок пока нет
- ME080 Section 6 - Hydraulic MotorsДокумент56 страницME080 Section 6 - Hydraulic MotorsAhmed FaragОценок пока нет
- Bosch Rexroth HaggludsДокумент20 страницBosch Rexroth HaggludsLubricants ServerОценок пока нет
- Paver: SD2550CSДокумент959 страницPaver: SD2550CSNguyen AlmiraОценок пока нет
- Plano Hidraulico 140K CatДокумент21 страницаPlano Hidraulico 140K CatMatiasf797100% (1)
- P-28 Cargo Pumping System (1-4)Документ281 страницаP-28 Cargo Pumping System (1-4)Raúl Oscar Ledesma100% (7)
- Basic Blueprint Reading 110Документ110 страницBasic Blueprint Reading 110Vidjeane Mourthy100% (2)
- Volvo Excavator: BE Backhoe EquipmentДокумент6 страницVolvo Excavator: BE Backhoe EquipmentAbduОценок пока нет
- Technical Manual VVH40C-DSK - G14-0048Документ28 страницTechnical Manual VVH40C-DSK - G14-0048mantenimientokmdОценок пока нет
- Material-KOSB (Part2) NEWДокумент48 страницMaterial-KOSB (Part2) NEWSyalokОценок пока нет
- T40000 LD Transmission ManualДокумент166 страницT40000 LD Transmission Manualyeya1963tito100% (4)
- Oil Coolers: Mobile Air CooledДокумент5 страницOil Coolers: Mobile Air CooledErdincОценок пока нет