Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Content Server
Загружено:
PauloОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Content Server
Загружено:
PauloАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
TEM Journal. Volume 8, Issue 2, Pages 516-524, ISSN 2217-8309, DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27, May 2019.
Reputation Risk Management Companies
Based on Competence Approach
Andriushchenko Kateryna 1, Lavruk Vitalii 2, Uliganets Sergey 3 ,
Kovtun Vita 1, Matviienko Halyna 4
1
SHEE «Kyiv National Economic University named after Vadym Hetman», Department of Economics and
Entrepreneurship, Peremogy ave., 54/1, Kyiv, 03057, Ukraine
2
State Agrarian and Engineering University in Podilia, Head of the Department of Geodesy and Land
Management, street Shevchenko, 13, city of Kamyanets-Podilsky, Khmelnytsky region, 32300, Ukraine
3
Taras Shevchenko National University of Kyiv, Ukrainian Geography Department of Geography Faculty,
Vladimirskaya street, 60, Kyiv, 01033,Ukraine
4
Taurida National V.I. Vernadsky University, Department of «Finance and accounting», St. Ivana Kudri, 33
Kiyiv, 02000, Ukraine
Abstract –The article substantiates the need to focus reputational risk of an enterprise is relevant for
on the use of the competence-based approach in all enterprises competing in a market
managing the reputational risks of an enterprise. The economy. Skilled labor is the basis for sustainable
purpose of the article is to identify risk-forming factors growth of the labor market, affecting the productivity
affecting the reputation of the enterprise. The article
and high productivity of the enterprise. Today, we
displays a modern approach to managing the
reputational risk of an enterprise, which is focused on
almost completely switched to information and
the use of appropriate methodology and tools for communication technologies and devices that we did
competency-based approach. A scheme for assessing not even know about 30 years ago. The set of skills
the reputational risks of an enterprise is proposed, that we need to fully apply ourselves in society has
which is based on a combination of five system changed a lot. The use of personnel skills of
components. Based on the study, reputational risk- cognitive (literacy, ability to analytics) and
forming factors are identified and specified. “communicative” (influencing the negotiation)
Keywords – knowledge, skills, enterprise reputation character in the work is associated with advanced
matrix. training throughout life, which, in turn, is possible
with the economic and social well-being of the
1. Introduction enterprise.
The use of a competence-based approach in the
Today, competence is one of the main advantages
management of an enterprise by identifying risk-
of employees in the labor market. Today, the use of
forming factors will make it possible to apply
the competence approach in managing the
knowledge and skills that affect the reputational risks
of an enterprise, regardless of nationality or
DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27 geographical location of the business. This decision
https://dx.doi.org/10.18421/TEM82-27 involves, above all, the construction of appropriate
methodologies and tools for assessing the
Corresponding author: Andriushchenko Kateryna, competencies obtained during vocational education
SHEE «Kyiv National Economic University named after and training, as well as the competencies required in
Vadym Hetman», Kyiv, Ukraine the workplace, namely:
Email: katya373@i.ua
system thinking. Today, for success in work,
Received: 26 January 2019. it is not enough to own knowledge or to understand
Accepted: 09 April 2019. well your own “segment” of work. It is necessary to
Published: 27 May 2019. move to thinking that is able to understand the work
© 2019 Andriushchenko Kateryna et al;
of the enterprise as a whole, to be able to shape the
published by UIKTEN. This work is licensed under the work of the system from individual elements, to
Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs predict how specific changes affect the work process
3.0 License. of the company;
interdisciplinary communication. More and
The article is published with Open Access more professions and projects arise at the junction of
at www.temjournal.com several disciplines (areas). To solve many problems,
516 TEM Journal – Volume 8 / Number 2 / 2019
TEM Journal. Volume 8, Issue 2, Pages 516-524, ISSN 2217-8309, DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27, May 2019.
we need people versed in several areas of knowledge direction will remain among the “leaders” of
simultaneously. They can create unexpected, unique, corporate training;
breakthrough solutions. This skill also allows you to work in conditions of uncertainty. And what
learn faster, to take the best from different areas, to else to expect from the VUCA (Volatility,
ensure development within your area at the expense Uncertainty, Complexity, Ambiguity) - the
of such a “meta-transfer”. Big Data Specialist ( world? Ability to work in a situation where only
Big Data ) in personnel management is one of the changes are constant. Fortunately, representatives of
professions of the future. It will require both generation Y have already developed this
knowledge of mathematics, IT systems, and an skill. Uncertainty for them is comfortable, and they
understanding of key aspects of working with easily cope with it. Well, we — X — will learn to
staff. By the way, brand management specialists of love uncertainty and its “black swans” (a theory that
the company also work at the junction of two areas - considers hard-to-predict and rare events that have
communications and personnel management. In the significant consequences);
future, the need for interdisciplinary approaches and multiculturalism and openness. Diversity is
solutions will only grow; the main trend in the world of big international
project and process management. Project business. It turned out that if you look at the problem
management is becoming an increasingly common from different positions, then the probability of
approach in business, so you need to have finding a non-trivial solution is several times
competencies that allow you to answer not only for higher. But this requires openness of mind, ability to
their work, but also the performance of certain listen and hear alternative ideas, to perceive them, to
tasks. A specialist at any level today may be in the be flexible. Since the best ideas can be born in
role of a person who should be responsible for the different parts of the world, the team should be from
project (and this project may not only be in the field different countries and cultures. You will need the
of its professional specialization). It is unlikely that ability to find a language with other people, accept
certification will be required, but an understanding of them and use their capabilities to solve business
the principles, approaches and skills to put them into problems;
practice is needed by an ever wider range of mindfulness. As Pavel Luksha, the head of
employees; the Atlas of New Professions project, said at the
work with IT systems. If you go to work in a EdEx conference: “Awareness is the key competence
large company, then the skill of working in SAP will of the 21st century” [1] (Luksha P., Shamenkov D.,
be your advantage. And this is not the only 2018). It allows you to develop the skill of reflection,
example. In the future, we need to master various IT to make a conscious choice, to understand the
systems that systematize our work and features of yourself and others. It helps to focus on
processes. Possession of IT systems will become the present and see the future. This competence,
mandatory as a skill to work in MS Office today; which makes us more efficient and, at the same time,
customer focus. An increasing number of happier, allows us to listen to ourselves and ensure
companies are developing in employees the ability to balance and harmony in our own lives;
listen and hear each other. Loyalty Indexes ( communication. The Internet has removed
Net Promoter Score, NPS ), measuring the work of the boundaries and made the economy truly
various units (primarily serving), have become quite global. Therefore, we will communicate with a large
common practice. A modern system administrator number of people from different parts of the
should be able to explain the basics of work to a globe. Modern business requires the creation of new
“teapot” and do it correctly and efficiently. The contacts to move forward through the exchange of
personnel officer must quickly arrange all ideas. At the same time, we must learn to
documents, and the accountant must provide the communicate our thoughts and achieve our goals at a
necessary calculations and payments. And for all distance, to be able to appreciate each contact and
this, you will need to be able not only to do it, but such an important “currency” of our time as
also to conduct negotiations at a high professional attention. This competence is needed by every person
level with your internal or external client. So the in business today, and more importantly it will be in
emphasis on emotional intelligence is still relevant; the near future [2] (Anan'eva).
working with people and
teamwork. Processes become so complex that 2. Literature review and problem statement
without working in a team it will be impossible to
complete most tasks. Some companies have already For more than 30 years, business and the state
embarked on the development of empathy and have used the competence approach separately for
teamwork (which can include both those who “want staff selection. Recently, there has been a tendency to
to embrace” and much less comrades in spirit), this use the competence approach in education, training,
TEM Journal – Volume 8 / Number 2 / 2019. 517
TEM Journal. Volume 8, Issue 2, Pages 516-524, ISSN 2217-8309, DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27, May 2019.
assessment and development of personnel. In the development of competencies and skills of
early 1970s, in his works [3] (McClelland, 1973), he staff. Each country used comparative data and
discussed and conducted competency assessments analyzed the policies of the OECD (Organization for
based on individual characteristics that were Economic Cooperation and Development), which
recognized as significant predictors (means of promoted cooperation within the country between
prediction) of employee performance and success, relevant ministries and all interested parties -
where the emphasis was on testing [4] (Lucia, A. D., employers, trade unions, academics, and society.
& Lepsinger, R. , 1999), as well as the academic It is also necessary to take into account the
knowledge of a man. possibility of holding interactive seminars that help
Competence-based approach is the basis for the promote a common understanding among
application or use of knowledge, skills, abilities and stakeholders, providing a solid basis for the transition
personal characteristics for the successful from general diagnostics to the development and
performance of functional duties, solving implementation of specific actions to develop a
problematic tasks [5] (Dubois, 1993). Maintained a competence-based approach in personnel
competency-based approach, where personal management that affects the reputational risks of an
qualities can be mental [4] (Lucia, A. D., & enterprise.
Lepsinger, R. , 1999) / intellectual [6] (Boyatzis, The key element of using the competence
1982) / cognitive, social / emotional / relative, and approach in managing the reputational risk of an
physical [7] (Fogg, 1999) necessary to perform the enterprise is a common understanding of the
work. problems facing the company. It is necessary to fully
Motivation and attitude to work are considered as study the problem, connecting all interested parties to
the main elements of the successful implementation this dialogue; this in turn will provide an opportunity
of their functional tasks [8] (Fulmer, R. M., & to implement the main stages, namely:
Conger, J. A., 2004), [9] (Gangani, N., McLean, G.
N., & Braden, R. A., 2009). • clarify whether the problems with detailed
Competences are specific personal qualities that consideration are real;
“are primarily related to efficiency and / or • identify obstacles, difficulties and work out
productivity” [10] (Sandberg, 2000) of the solutions to eliminate them;
enterprise’s work, are common to many situations, • create a basis for successful implementation of
are used during the period of work on a specific the model, involving in this process a business-state-
enterprise [11] ( Delamare Le Deist, F. & Winterton, science [16] (Andriushchenko, 2016).
J., 2005). The first stage (action phase), as a rule, includes
In the literature one can find a large number of several diagnostic workshops, in which all interested
authors who offer their own vision of using the parties will participate. Seminars are based on
competence approach in managing the reputational methods based on the specifics of the business and
risks of an enterprise [12] (Beer, M. et al. , 1989), taking into account the relevant markers.
[13] (Moreno, 2014), [14] (Chiavenato, 2011). The next stage includes several workshops for
stakeholders, which focus on solving the problems in
3. Research the field of skills identified during the diagnostic
phase, and forming an agreement on what actions
3.1. General features of the use of competence- need to be taken and by whom. The activity is aimed
based approach in managing reputation risks of an at supporting and assisting in the promotion of the
enterprise development strategy of each enterprise, taking into
The use of the competence-based approach in account their peculiarities of doing business and
managing the reputational risks of an enterprise positioning themselves in the market.
provides for a strategic approach in the area of
developing skills aimed at improving the skills and 3.2. Methodical approaches to the use of
working places of employees. It aims to develop staff competence-based approach in managing
skills by consistently enhancing and effectively using reputation risks of an enterprise
skills to promote economic prosperity and social
In the study, the level of reputational risk is an
cohesion of the enterprise, which is reflected in the
indicator, the value of which characterizes the level
“lifelong employment” of staff [15] (Cartaya, 2006).
of threat of loss for a given subject when performing
Based on the experience of countries such as
a certain type of activity. In a comprehensive
Austria, Italy, Korea, the Netherlands, Norway, Peru,
assessment of the level of reputational risk, it would
Portugal, Slovenia and Spain, led us to innovative
be advisable to express it as an integral indicator. The
ways to develop and solve complex problems in the
determination of the integral indicator of the
518 TEM Journal – Volume 8 / Number 2 / 2019
TEM Journal. Volume 8, Issue 2, Pages 516-524, ISSN 2217-8309, DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27, May 2019.
reputational risk level of an enterprise activity is product’s danger from the
based on an assessment of the degree of risks target audience
generated by the output parameters of the variables 3. Reputation of top С3
included in it and their possible fluctuations under managers
the influence of internal and external factors, taking Reputation 3.1. The deterioration of the SС 3.1
into account the competence approach. The proposed of top reputation of the head
technology for assessing the reputational risks of an managers 3.2. Negative attitude of the SС 3.2
leader to ethics, corporate
enterprise allows for a comprehensive assessment of
culture, social responsibility
the reputational risks of an enterprise and is the basis of business
for using the competence approach in personnel 3.3. Inappropriate manager SС 3.3
management affecting the company's operations. actions to improve the
We regard the competence-based approach that company's reputation
influences the company's reputation as a combination 4. Corporate governance С4
of its five system components: ethics in relations Corporate 4.1. Low corporate culture SС 4.1
with external partners, corporate governance, the Governance 4.2. Lack of awareness of SС 4.2
reputation of top managers, the quality of products staff about possible
and services, and the effectiveness of management. reputational risks
On the basis of the study, reputational risk-forming 4.3. Staff incompetence SС 4.3
factors (RFIs) are identified and specified, which are 5. Ethics in relations with С5
systematized and the interrelationships with key external partners
elements of reputation are defined, which allows Ethics in 5.1. Uncompetitive and SС 5.1
relations unethical behavior of the
considering reputational risks.
with enterprise in the market
The proposed classification of reputational risk- external 5.2. Failure to comply with SС 5.2
forming factors is based on the competences of the partners contractual obligations
enterprise staff (Table 1.). This systematization of 5.3. Non-transparency of SС 5.3
risk factors makes it possible to justify the use of a business, providing
competence-based approach in personnel inaccurate information
management affecting the company's reputational 5.4. Non-compliance with SС 5.4
risks, which will ensure positive reputational the requirements of general
transformations. business etiquette, legal
norms, partnerships
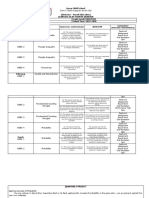
Table 1. Competence of staff as a factor affecting risk 5.5. Dubious legality of SС 5.5
forming elements of an enterprise's reputation methods of lobbying the
interests of the enterprise
Key Symbols
Risk forming reputation Developed by the authors
components in the
factors
of reputation matrix
Identification of reputational risk-forming factors
1. Effectiveness of С1
is based on the analysis of research on information
management
needs and the perception of stakeholders, practical
Management 1.1. Non-productive high- SС 1.1
Effectiveness risk alliances and cases, the strengthening of the reputational risk of
partnerships enterprises [17] (Andriushchenko K., Stefanyshyn
1.2. Indecision of top SС 1.2 D., Sahaidak М.,Tepliuk М.,Buchynska O.,
managers, makes the target Rozmetova E., Marusei T., Levchenko Ia., Smyrnova
audience feel a sense of I., Zhytomyrska T., 2018). In order to form a positive
their incompetence opinion about the company among the target
1.3. Lack of reputation risk SС 1.3 audiences, an impact assessment tool is needed,
management strategy taking into account the specific conditions of the
1.4. Inconsistency of SС 1.4 enterprise’s work for each target audience. Therefore,
enterprise management the next step should be to use the mechanisms of the
processes
competence approach to determine the boundaries of
1.5. The financial condition SС 1.5
influence on priority target audiences in order to
of the company
achieve the tactical and strategic goals of the
2. Quality of services С2
enterprise to shape its reputation. We believe that the
Quality of 2.1. Uncompetitive product SС 2.1
service quality complex components of the reputation effectively
2.2. Lack of response to SС 2.2 deal with certain cognitive frameworks (contours).
criticism in the media and Then you can select from any whole its most
the Internet significant components and manage them only within
2.3. Accusation of the SС 2.3 certain limits (synergistic influence contours - SIC),
TEM Journal – Volume 8 / Number 2 / 2019. 519
TEM Journal. Volume 8, Issue 2, Pages 516-524, ISSN 2217-8309, DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27, May 2019.
which have a strategic influence on the components reputation by various stakeholder groups. The
of reputation. To the synergistic impact contours reputation matrix is proposed for filling in to focus
(SIC), we assign the main reputational risk-forming groups, representatives of various target groups of
factors of the internal and external environment, stakeholders (consumers, investors, employees,
systematized in conjunction with the reputation of government, society, media) in order to determine
the enterprise (Table 1.). the significance of each SIC for each group of
The proposed model for identifying synergistic stakeholders.
contours of interrelation with target audiences
(stakeholders) allows establishing a relationship Table 2. Enterprise Reputation Matrix
between a specific target audience and a synergistic Synergistic Target groups (stakeholders)
influence contour to determine the significance and, contours of MG 1 MG 2 ....... MG n
therefore, non-consistent formation of a positive influence
opinion in this target audience and within the process C1 C 1 C 1 ....... C j
that is displayed in the control loop. MG 1 MG 2 MG n
By the target audience we will understand the SC 1.1 SC 1.1 SC 1.1 ....... SC 1.k
most important of audiences for the enterprise group MG 1 MG 2 MG n
to which the efforts of top management are directed ……… …… .. …… .. …… .. …… ..
SC 1.k SC 1.k SC 1.k ....... SC 1.k
through the relevant reputational risk management
MG 1 MG 2 MG n
processes. By the synergetic contour of influence, we
C2 C 2 C 2 ....... C j
will mean the totality of the processes controlled by MG 1 MG 2 MG n
the top managers of the company, whose efforts are SC 2.1 SC 2.1 SC 2.1 ....... SC 2.k
directed at the impact of the most important MG 1 MG 2 MG n
reputational risk factors. In the proposed model, the ……… …… .. …… .. …… .. …… ..
following 5 contours are highlighted: SC 2.k SC 2.k SC 2.k ....... SC 2.k
MG 1 MG 2 MG n
C1 - management efficiency (strategy of the ……… …… .. …… .. …… .. …… ..
enterprise, non-productive high-risk alliances and Ci C C ....... C
J J j
partnerships, financial condition of the enterprise, MG 1 MG 2 MG n
dynamics of financial indicators, cost management SC ik SC jk SC jk ....... SC 1.k
policies, etc.) MG 1 MG 2 MG n
C2 - the quality of products and services Developed by the authors
(inconsistency of the production process with certain
conditions, accusations against the company about In Tab. 3., Ci - synergistic influence contours;
dangerous products from interested audiences SCi.k - risk forming factors of reputation,
(customers, regulatory bodies, etc.), reaction to systematized into synergistic influence contours; M
complaints and remarks, customer perception, Gn - target groups (stakeholders).
organization behavior in the market) ; Evaluation (SC 1 .kMGn) occurs for each
C3 - the reputation of top managers (lack of component of the contour Ci. And the value of Ci is
actions by the head to enhance the reputation of the calculated as the arithmetic average of the
enterprise, the negative attitude of the head to ethics, components of this circuit.
corporate culture, social responsibility of business, When filling the reputation matrix, it is proposed
etc.); to use the Delphi method, which is most appropriate
C4 - corporate governance (low level of corporate under the given conditions, since the information
culture, social responsibility, incompetence of staff, needs of the target groups of stakeholders are
etc.); interconnected, and take into account the estimates of
C5 - ethics in relations with external partners other groups.
(position and policy of informational openness and This method allows you to take into account the
accessibility, value of an organization in a independent opinion of all members of the expert
partnership, non-compliance with the requirements of group on the subject under discussion by consistently
common business etiquette, legal norms, combining ideas, conclusions and proposals and
partnerships, etc.). agree. The method is based on multiple anonymous
group interviews. The Delphi method allows you to
According to surveys of interested audiences
adjust the opinions of experts after the announcement
(target groups, stakeholders), a reputation matrix was
of the results of the responses of other groups.
compiled in which a list of risk factors was compiled,
grouped into synergistic influence contours (Table
2.), which reflects the perception of the company's
520 TEM Journal – Volume 8 / Number 2 / 2019
TEM Journal. Volume 8, Issue 2, Pages 516-524, ISSN 2217-8309, DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27, May 2019.
3.3. The results of studies of indicators of the use RR = а + C1x1j + C2x2j + ... + кixij, (1)
of a competence-based approach in personnel
management that affect the reputational risks where Ci is the assessment of the significance of
of an enterprise this indicator in the contour (reputation matrix of the
enterprise);
In our study, using the competence approach, we xi is the value of reputational risk in the i -th
define six target audiences that can reach most circuit (determined by an expert way);
stakeholders in order to manage the reputational risk a is the free coefficient.
of an enterprise: consumers, investors, employees, An expert assessment is also used to determine
government, society, the media. The higher the the indicator X i, for which a matrix of assessment of
degree of mutual involvement in a business partner, reputational risk values has been developed.
the higher the level of reputational correlation, hence In determining the value of reputational risk,
the need to assess the reputational risks that arise in experts should be representatives of the enterprise
relations between an enterprise and its stakeholders. itself, on whose data reputation risk is assessed. To
For the purpose of objective interpretation of the this end, it is proposed to form focus groups and
results obtained during surveys, it is considered conduct a study of expert opinions through
necessary to conduct in-depth interviews and focus questionnaires. The list of questions and criteria for
groups with respondents to determine their scoring proposed in the questionnaire was developed
motivation and avoid errors. on the basis of studying and comparative analysis of
The reputation of the matrix forms the basis for the international practice of implementing
calculating the integral indicator of the level of reputational risks of corporate structures, as well as
reputational risk, which makes it possible to assess additional motivational factors of cooperation.
the level of significance of each SIC. Building a The use of terms in the matrix "some
reputation matrix will reveal the strengths and compliance", "compliance in general", "full
weaknesses in the formation of reputation for each compliance" is due to the processes, methods and
group of stakeholders. The strength of the risks is in description of the procedures. These terms are used
harming the reputation of the enterprise, which is in the matrix of risk values and within this
determined according to the expert survey of framework we categorize all the available
interested audiences, using the method of rating information about the enterprise.
assessments. The expert group, according to the Some compliance - risk assessment is high and
proposed assessment scale (0 points - does not associated with various factors, for example, very
generate risks, 10 - can generate very significant little information about the company to draw
reputational risks) fills the reputational matrix, conclusions about the processes, methods and
putting the corresponding points. The expert assigns procedures for risk management are not supported by
a specific score to each component of hard currency positive developments, a high degree of damage to
depending on the strength of the impact. The result of the reputation of the enterprise is manifested.
the study is a formed reputational matrix. Compliance in general - a clear description of the
The next step is to calculate the sum of points for processes that are controlled in the circuit. There are
all components of each hard currency for each group some examples of using processes in practice. There
of stakeholders and to determine the average is little quantitative information on the effectiveness
arithmetic point for each hard currency for each of the processes within the framework of the contour
group of stakeholders. under study, for example, how regular is the
Thus, using the data of the enterprise's reputation management of the processes of forming a positive
matrix, built on the basis of the method of expert opinion about the enterprise in the contour.
assessments, weighting characteristics of risk- Enterprise managers receive timely and reliable risk
forming reputation factors for each synergistic reports, in the amounts needed to make effective
impact contour ( Ci ) are determined through a priori decisions and review risk management practices.
ranking of options. Full compliance - there is not only the risk
The calculation of the integral indicator of the management business processes, but also specific
level of reputational risks is carried out using examples of the effectiveness of these processes.
regression analysis. Regression analysis is a method Risk assessment of this value can be expressed as
of establishing an analytical expression of a follows. Risks are identified and evaluated on an
stochastic relationship between the studied ongoing basis. Risk management procedures are
characteristics. The regression equation shows how, described, developed and implemented.
on average, j changes as one of xi changes . There is an assessment of the effectiveness and
The calculated value of the effective factor is the existence of procedures for the interrelation of the
presented in formula (1). needs of interested parties. Risk management is
TEM Journal – Volume 8 / Number 2 / 2019. 521
TEM Journal. Volume 8, Issue 2, Pages 516-524, ISSN 2217-8309, DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27, May 2019.
based on developing a strategy to prevent their or are absent. Low product
occurrence. Constant monitoring of the reputation quality due to the use of
strategy is carried out. This model allows you to outdated technology. Lack
visually identify strong positions aimed at improving of quality control.
in each circuit Ci. Invalid is always The company does not
understand the
At the next stage, the values of the integral
expectations of customers /
indicator of the level of reputational risk are partners, as a result of
interpreted according to the developed scale. On the which it does not fulfill its
basis of which the assessment and formation of a obligations. Top-
conclusion on the conduct of the company's management of the
reputational strategy with the development of company forms a negative
specific measures aimed at adjusting the level of attitude towards ethics and
reputational risk will be made. Thus, for further corporate culture, social
effective personnel management on the basis of the responsibility of business;
competence-based approach affecting the unethical and fraudulent
actions of middle and
reputational risks of an enterprise, the formation of a
lower level employees.
rating scale for reputational risks, Table 5., should
Developed by the authors
become an important step.
It should be noted that the choice of the size scale, Table 3. provides an interpretation of the values
provided it is correctly applied, does not affect the of the reputational risk scale. For example, it is very
subjectivity of the assessment of reputational risks. difficult to choose a probability value between “from
Rationing component "probability". Choosing a time to time” and “possible” without analyzing the
probability value is one of the most difficult tasks in available facts and knowledge about the nature of the
assessing risks in general, and reputational risks in variability of the object of risk assessment.
particular. It is at this stage that discussions arise, Moreover, in order to preserve the probability value
disputes and false conclusions. after the assessment, it is necessary to ensure the
effectiveness of the system for managing deviations
Table 3. Characteristics of reputation risk compoters by 6- and changes, and to establish a statistical process
point scale based on competency-based approach
control. It is very important to have clear criteria and
Risk Probability Level characteristic a clear interpretation for each value of the probability
level of scale. So the formation of clear boundaries (criteria)
occurrence for assigning the value of the integral indicator of the
Minor practically The company has a high level of reputational risk to unacceptable, marginal,
impossible reputation, no doubt in the critical, moderate, moderate and insignificant is
target audiences based on a study based on expert assessments (Table
Moderate occasionally The company controls the 4.).
situation and the
perception of its target Table 4. Interpretation of the values of the integral
audiences. indicator of the enterprise's reputational risk based on the
Average are possible When building a strategy, competence approach
reputation risks are not
taken into account. The The value of Risk Level characteristic
company has some the integral level
difficulties in managing indicator of
reputation risks reputational
Critical periodically The company responds to risk
negative consequences for Up to 0.1 Minor The company has a high
reputation after the fact. reputation, no doubt in the
The reputation risk target audiences
management activity of the From 0.1 to Moderate The company controls the
enterprise is inefficient, 0.3 situation and the perception of
because it is carried out its target audiences.
only when problems arise. From 0.3 to Average When building a strategy,
Boundary almost In the framework of 0.5 reputation risks are not taken
inevitable reputational risk into account. The company
management, there are has some difficulties in
poorly developed managing reputation risks
procedures for dealing From 0.5 to Critical The company responds to
with unforeseen situations 0.7 negative consequences for
522 TEM Journal – Volume 8 / Number 2 / 2019
TEM Journal. Volume 8, Issue 2, Pages 516-524, ISSN 2217-8309, DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27, May 2019.
reputation after the fact. The 4. Conclusion
reputation risk management
activity of the enterprise is The main scientific and practical results of the
low effective because it is study led to the following conclusions:
carried out only when 1. On the basis of the conducted research, the
problems arise.
influence of the competence-based approach on the
From 0.7 to Boundary In the framework of
0.8 reputational risk management,
management of reputational risks of an enterprise is
there are poorly developed definite. Identified are the risk factors that enable the
procedures for dealing with use of knowledge and skills affecting the reputational
unforeseen situations or are risks of the enterprise. These conclusions are based
absent. Low quality products primarily on the use of appropriate methodology and
due to the use of outdated tools for assessing the competencies gained during
technology. Lack of quality vocational education and training. The competencies
control. necessary in the workplace were defined, namely:
From 0.8 to Invalid The company does not systems thinking, interdisciplinary communication
1 understand the expectations of ability, project and process management, work with
customers / partners as a
IT systems, customer focus, team focus, ability to
result of which it does not
fulfill its obligations. Top work in conditions of uncertainty, multiculturalism
management pidpriem c Twa and openness.
creates a negative attitude to 2. Developed is a structural-logical scheme for
ethics and corporate culture, assessing the reputational risks of an enterprise,
corporate social responsibility which is based on a combination of its five system
unethical and fraudulent components: ethics in relations with external
actions of the middle and partners, corporate governance, the reputation of top
lower-level managers. managers, the quality of products and services, and
Developed by the authors management efficiency. Based on the study,
reputational risk-forming factors that are
The data sources are annual quality reviews in the
systematized are identified and specified. The
business development model conducted by the
relationship between key elements of reputation is
European Foundation for Quality Management (
defined, which allows considering reputational risks
EFQM ) and annual reputation and reputation risk
for each management process separately.
studies conducted by the international consulting
3. Based on the results of surveys of interested
company Reputation Institute. The analysis of the
audiences (stakeholders), it was proposed to compile
conducted research allowed to accumulate the
a reputation matrix — a list of risk factors was
obtained results and determine the threshold values
compiled grouped into synergistic influence
of the critical value of the integral indicator of
contours, which reflects the perception of the
reputational risk (Table 4.).
company's reputation by various stakeholder groups.
The program of the enterprise should be aimed at
The reputation matrix is proposed for filling in to
the formation, implementation and monitoring of
focus groups, representatives of various target groups
measures that help reduce risks in those contours
of stakeholders (consumers, investors, employees,
where the target value is exceeded and the level of
state authorities, society, media). The main purpose
risk maintenance and actual reputational risks are
of using the reputation matrix is to determine the
within target values. Despite the variety of stages in
significance of each synergistic impact contour for
the construction of risk management systems, the
each group of stakeholders. Using data from the
main ones can be identified: identifying the sources
enterprise's reputation matrix, built on the basis of a
and causes of risks, identifying risks, assessing risks,
method of expert assessments through a priori
choosing methods to influence risks, applying
ranking of options, the weight characteristics of risk-
selected methods, monitoring and adjusting
forming reputation factors for each synergetic impact
management results.
contour are determined. When determining the value
of reputational risk, experts should be representatives
of the enterprise itself, where the reputation risk is
assessed.
TEM Journal – Volume 8 / Number 2 / 2019. 523
TEM Journal. Volume 8, Issue 2, Pages 516-524, ISSN 2217-8309, DOI: 10.18421/TEM82-27, May 2019.
References [9]. Gangani, N., McLean, G. N., & Braden, R. A.
(2006). A competency-based human resources
[1]. Luksha P., Shamenkov D. (2018). Dialogi o development strategy. Performance Improvement
budushhem na «Ostrove 10-21» [Dialogue about the Quarterly, 19(1), 127-139.
future on the "Island 10-21"]. Retrieved [10]. Sandberg, J. (2000). Understanding human
from: https://shamenkov.ru/pavel-luksha-i-dmitriy- competence at work: an interpretative approach. Academy
shamenkov-dialogi-o-budushhem-na-ostrove-10-21/ of management journal, 43(1), 9-25.
[accessed: 07 November 2018]. [in Russian]. [11]. Le Deist, F. D., & Winterton, J. (2005). What is
[2]. Anan'eva T. (2018) 10 kljuchevyh kompetencij XXI competence?. Human resource development
veka: chemu uchit' i chemu uchit'sja? [10 key competences international, 8(1), 27-46.
of the XXI century: what to learn and what to learn?]. [12]. Beer, M. et al. (1989). Gestión de recursos humanos.
Retrieved from: http://hr-portal.ru/article/10-klyuchevyh- Editorial Ministerio de Trabajo. Madrid.
kompetenciy-xxi-veka-chemu-uchit-i-chemu-uchitsya [13]. Puchol Moreno, L. (2014). Dirección y gestión de
[accessed: 15 October 2018]. [in Russian]. recursos humanos. Séptima edición. Editorial Díaz de
[3]. McClelland, D. C. (1973). Testing for competence Santos. Madrid. 446.
rather than for "intelligence." American [14]. Chiavenato, I., Mascaro Sacristan, P., & Roa, H.
psychologist, 28(1), 1-14. (2007). Administracion de recursos humanos: El capital
[4]. Lucia, A. D., & Lepsinger, R. (1999). Art & science humano de las organizaciones. McGraw-Hill
of competency models. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass. Interamericana.
[5]. Dubois, D. D. (1993). Competency-Based [15]. Morales Cartaya, A. (2006). Contribución para un
Performance Improvement: A Strategy for Organizational modelo cubano de gestión integrada de los recursos
Change. HRD Press, Inc., 22 Amherst Road, Amherst, humanos. Unpublished PhD Thesis. CUJAE. La Habana.
MA 01002. 99.
[6]. Boyatzis, R. E. (1982). The competent manager: A [16]. Andriushchenko, K. (2016). Formation of conceptual
model for effective performance. John Wiley & Sons. approaches to management of intellectual capital of
[7]. Fogg, C. D. (1999). Implementing your strategic knowledge considering hierarchical levels at the
plan: How to turn" intent" into effective action for enterprise. International Journal of Critical
sustainable change. Amacom Books. Accounting, 8(5-6), 379-395.
[8]. Fulmer, R. M., & Conger, J. A. (2004). Identifying [17]. Andriushchenko K., Stefanyshyn D., Sahaidak
talent. Executive Excellence, 21(4), 11. М.,Tepliuk М.,Buchynska O., Rozmetova E., Marusei T.,
Levchenko Ia., Smyrnova I., Zhytomyrska T. (2018)
Process of resources provision management of the
enterprise's activity with consideration of gender factor.
Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies,
6(3), (96). 6-19.
524 TEM Journal – Volume 8 / Number 2 / 2019
Copyright of TEM Journal is the property of UIKTEN-Association for Information
Communication Technology Education & Science and its content may not be copied or
emailed to multiple sites or posted to a listserv without the copyright holder's express written
permission. However, users may print, download, or email articles for individual use.
Вам также может понравиться
- Mapping Content Management System Features With Knowledge Sharing Elements For Creating Online Knowledge Sharing ModelДокумент9 страницMapping Content Management System Features With Knowledge Sharing Elements For Creating Online Knowledge Sharing ModelFazli MuhdОценок пока нет
- Brochure Business-Analytics-Konclave 2021Документ5 страницBrochure Business-Analytics-Konclave 2021suryamishraОценок пока нет
- The Management of Knowledge Workers - Key Factor of SuccesДокумент7 страницThe Management of Knowledge Workers - Key Factor of SuccesMarian GrajdanОценок пока нет
- How To Leverage Technology For Business Education: Sean Stein SmithДокумент3 страницыHow To Leverage Technology For Business Education: Sean Stein SmithBusiness Expert PressОценок пока нет
- Knowledge Management: Competent Employees Are The Only Change Agents of Imperative Organizational ExcellenceДокумент8 страницKnowledge Management: Competent Employees Are The Only Change Agents of Imperative Organizational ExcellenceInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementОценок пока нет
- Soft Skills Development Needs and Methods in Micro-Companies of ICT SectorДокумент10 страницSoft Skills Development Needs and Methods in Micro-Companies of ICT SectorBC IОценок пока нет
- MEI Notes ATME, MysoreДокумент110 страницMEI Notes ATME, Mysorestudy materialОценок пока нет
- An Engineering Entrepreneurship Course For Che Seniors: 2002 Asee Proceedings Paper Session No: - 2213Документ5 страницAn Engineering Entrepreneurship Course For Che Seniors: 2002 Asee Proceedings Paper Session No: - 2213MOSES EDWINОценок пока нет
- Knowledge Management Techniques Improve B-School Entry and ExitДокумент6 страницKnowledge Management Techniques Improve B-School Entry and ExitTyrone RiddleОценок пока нет
- Banking Management Online ModelДокумент5 страницBanking Management Online ModelNIET Journal of Engineering & Technology(NIETJET)Оценок пока нет
- Nas and TJДокумент19 страницNas and TJTijjani ZubairuОценок пока нет
- Arousal Comes of Age: Professor Peter LansleyДокумент11 страницArousal Comes of Age: Professor Peter LansleyGabriela CamachoОценок пока нет
- Article Review Ent530Документ11 страницArticle Review Ent530imaahfatimah11Оценок пока нет
- Agile and Scrum Technological Practices Among Millennial GenerationДокумент6 страницAgile and Scrum Technological Practices Among Millennial GenerationTJPRC PublicationsОценок пока нет
- Future of Work Conference Call for PapersДокумент5 страницFuture of Work Conference Call for PapersBharat ChogaleОценок пока нет
- Ai Mod 2Документ8 страницAi Mod 2ABOOBAKKERОценок пока нет
- TECHNOPRENUERSHIP Module 2Документ21 страницаTECHNOPRENUERSHIP Module 2Dryx LetranОценок пока нет
- Research Paper Knowledge ManagementДокумент7 страницResearch Paper Knowledge Managementafmctmvem100% (1)
- INSEAD DP Brochure 2019 - MIM FINAL 26 June 2019 PDFДокумент12 страницINSEAD DP Brochure 2019 - MIM FINAL 26 June 2019 PDFRickyОценок пока нет
- A Study of E-Learning Marketing Stratagies Adopted by ExtramarksДокумент14 страницA Study of E-Learning Marketing Stratagies Adopted by ExtramarksNeha Shukla100% (1)
- Professional Mit EduДокумент6 страницProfessional Mit EduAmarendra Kumar AvinashОценок пока нет
- Knowledge ManagementДокумент4 страницыKnowledge ManagementSurendaran SathiyanarayananОценок пока нет
- The Analytics Academy Bridging The Gap Between Human and Artificial Intelligence VFДокумент9 страницThe Analytics Academy Bridging The Gap Between Human and Artificial Intelligence VFSaunak DeОценок пока нет
- Lotus Framework in Knowledge ManagementДокумент7 страницLotus Framework in Knowledge ManagementpktunОценок пока нет
- KM NotesДокумент102 страницыKM NotesChauhan PrinceОценок пока нет
- Department of Management Sciences, National University of Modern LanguagesДокумент15 страницDepartment of Management Sciences, National University of Modern LanguagesSheiryОценок пока нет
- PPM 2016 01 BencsikДокумент10 страницPPM 2016 01 BencsikItiel MoraesОценок пока нет
- How Artificial Intelligence and Digital Tools Help Companies in Strategic Recruitment To Enhance Their CompetitivenessДокумент104 страницыHow Artificial Intelligence and Digital Tools Help Companies in Strategic Recruitment To Enhance Their CompetitivenessJames KalangОценок пока нет
- Managing Organizational Knowledge Through Knowledge CreationДокумент67 страницManaging Organizational Knowledge Through Knowledge CreationSharma ShikhaОценок пока нет
- Managing Organizational Knowledge: Thi Xuan Thanh NguyenДокумент67 страницManaging Organizational Knowledge: Thi Xuan Thanh NguyenHosalya Devi DoraisamyОценок пока нет
- 816 Pdfsam ICEA FAA 2009Документ8 страниц816 Pdfsam ICEA FAA 2009bharath_100929Оценок пока нет
- Enterprise Development ThesisДокумент4 страницыEnterprise Development Thesissdeaqoikd100% (2)
- Es Tech 01Документ8 страницEs Tech 01surnam63Оценок пока нет
- ICTs' Effects on Knowledge Management and Innovation: A Case Study of ZaraДокумент9 страницICTs' Effects on Knowledge Management and Innovation: A Case Study of ZaraKripa RajbhandariОценок пока нет
- The Influence of Problem Solving, Self-Management and Technology Development On Entrepreneurship With Intervening Variables of TeamworkДокумент8 страницThe Influence of Problem Solving, Self-Management and Technology Development On Entrepreneurship With Intervening Variables of TeamworkMonika GuptaОценок пока нет
- WEF CNES Putting Skills First 2023Документ30 страницWEF CNES Putting Skills First 2023osvaldo belizОценок пока нет
- Ibm Case StudyДокумент7 страницIbm Case StudyAK SEEAMОценок пока нет
- Seci ModelДокумент10 страницSeci Modelakh2101100% (1)
- KM - MBA 3rd Sem MaterialДокумент101 страницаKM - MBA 3rd Sem MaterialkunnisamiraОценок пока нет
- Role and Importance of Knowledge Management in Indian Business EnterprisesДокумент4 страницыRole and Importance of Knowledge Management in Indian Business EnterprisesMadhu DayanandaОценок пока нет
- Paper 6: Management Information System Module 13: Enterprise Communication and CollaborationДокумент15 страницPaper 6: Management Information System Module 13: Enterprise Communication and CollaborationkundankumarsharmaОценок пока нет
- Macedonia HRM Challenges of The Modern EraДокумент7 страницMacedonia HRM Challenges of The Modern EraAdrahОценок пока нет
- Business IntelligenceДокумент12 страницBusiness IntelligenceMichieru5Оценок пока нет
- City of Malabon University Graduate Studies and Applied ResearchДокумент7 страницCity of Malabon University Graduate Studies and Applied ResearchPrince Dkalm PolishedОценок пока нет
- Social Media Technologies A Waste of Time or A Good WayДокумент30 страницSocial Media Technologies A Waste of Time or A Good WayVcore MusicОценок пока нет
- WEF Jobs of Tomorrow Large Language Models and Jobs 2023Документ17 страницWEF Jobs of Tomorrow Large Language Models and Jobs 2023tgascoyneОценок пока нет
- Artificial Intelligence and Marketing, Pitfalls and OpportunitiesДокумент16 страницArtificial Intelligence and Marketing, Pitfalls and OpportunitiesLaciОценок пока нет
- Innovating Personal Knowledge Creation and Exploitation: July 2013Документ12 страницInnovating Personal Knowledge Creation and Exploitation: July 2013dffОценок пока нет
- Literature Review of Knowledge Management SystemДокумент7 страницLiterature Review of Knowledge Management SystemaflsmperkОценок пока нет
- Dystechnia - A Model of Technology Deficiency and Implications For Entrepreneurial Opportunity by Dr. Elias CarayannisДокумент36 страницDystechnia - A Model of Technology Deficiency and Implications For Entrepreneurial Opportunity by Dr. Elias CarayannisVETSIОценок пока нет
- Education 11 00356Документ13 страницEducation 11 00356T SupeekitОценок пока нет
- Pertamina PDFДокумент20 страницPertamina PDFM Dito SaputraОценок пока нет
- Linard - 2000-ICSTM - Systems Thinking Competencies & Learning OrganisationДокумент7 страницLinard - 2000-ICSTM - Systems Thinking Competencies & Learning OrganisationKeith LinardОценок пока нет
- Improving Talent Performances by Using IntegratedДокумент7 страницImproving Talent Performances by Using Integratedwisnu fitraddyОценок пока нет
- Lakshmi S. Iyer: Knowledge Management: Practices and ChallengesДокумент8 страницLakshmi S. Iyer: Knowledge Management: Practices and Challengesnesus freeОценок пока нет
- 1 s2.0 S1877042813055511 MainДокумент9 страниц1 s2.0 S1877042813055511 MainjhzooizОценок пока нет
- Week 1 CoursewareДокумент9 страницWeek 1 CoursewareMariaEzzaSyUyОценок пока нет
- Digital Business Strategy:: Harnessing Our Digital FutureДокумент9 страницDigital Business Strategy:: Harnessing Our Digital FutureAndyBarredaMoscosoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 11Документ22 страницыChapter 11PauloОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9Документ25 страницChapter 9PauloОценок пока нет
- Man-In-The-Middle Attack On BB84 Protocol and Its Defence: WANG Yong WANG Huadeng LI Zhaohong HUANG JinxiangДокумент2 страницыMan-In-The-Middle Attack On BB84 Protocol and Its Defence: WANG Yong WANG Huadeng LI Zhaohong HUANG JinxiangPauloОценок пока нет
- The World After Covid-19 - Jennifer Doudna On How Covid-19 Is Spurring Science To Accelerate - by Invitation - The Economist PDFДокумент4 страницыThe World After Covid-19 - Jennifer Doudna On How Covid-19 Is Spurring Science To Accelerate - by Invitation - The Economist PDFPauloОценок пока нет
- The World After Covid-19 - Jennifer Doudna On How Covid-19 Is Spurring Science To Accelerate - by Invitation - The Economist PDFДокумент4 страницыThe World After Covid-19 - Jennifer Doudna On How Covid-19 Is Spurring Science To Accelerate - by Invitation - The Economist PDFPauloОценок пока нет
- Formalization of Firms' Evaluation Processes in Cross-Sector Partnerships For SustainabilityДокумент43 страницыFormalization of Firms' Evaluation Processes in Cross-Sector Partnerships For SustainabilityPauloОценок пока нет
- Impact Investing Policy - FULL REPORT - FINALДокумент104 страницыImpact Investing Policy - FULL REPORT - FINALpcouto002Оценок пока нет
- Calculating The Value of Impact Investing PDFДокумент9 страницCalculating The Value of Impact Investing PDFPauloОценок пока нет
- Calculating The Value of Impact Investing PDFДокумент9 страницCalculating The Value of Impact Investing PDFPauloОценок пока нет
- Toffel 2016 POM PDFДокумент14 страницToffel 2016 POM PDFPauloОценок пока нет
- 16 082 PDFДокумент34 страницы16 082 PDFPauloОценок пока нет
- Toffel 2016 POM PDFДокумент14 страницToffel 2016 POM PDFPauloОценок пока нет
- 16 082 PDFДокумент34 страницы16 082 PDFPauloОценок пока нет
- Understanding probabilities in everyday lifeДокумент3 страницыUnderstanding probabilities in everyday lifeKhim ChiОценок пока нет
- Applied Probability Homework 3Документ3 страницыApplied Probability Homework 3ILMI USTAADОценок пока нет
- MS-INTROДокумент42 страницыMS-INTRODarylle Ann MateroОценок пока нет
- Computing Means and VariancesДокумент3 страницыComputing Means and VariancesChristian KochОценок пока нет
- Hw5sol PDFДокумент4 страницыHw5sol PDFPei JingОценок пока нет
- The Five Stages of Collapse - Dmitry Orlov PDFДокумент289 страницThe Five Stages of Collapse - Dmitry Orlov PDFgodoroja23100% (7)
- Probability and Statistics Assignment ProblemsДокумент3 страницыProbability and Statistics Assignment ProblemsDivyanshu BoseОценок пока нет
- ProbabilityДокумент10 страницProbabilityAwrangzeb AwrangОценок пока нет
- 05 PDFДокумент70 страниц05 PDFRahul RahulОценок пока нет
- 02 Signal Detection Theory PDFДокумент30 страниц02 Signal Detection Theory PDFMuhammad Atif100% (1)
- Midterm ExamДокумент2 страницыMidterm ExamMelissa Nazar0% (1)
- Probability and Probability Distributions (Chapter 5)Документ49 страницProbability and Probability Distributions (Chapter 5)ryannnchongОценок пока нет
- 1 Problems in Oksendal's BookДокумент22 страницы1 Problems in Oksendal's Booktesttest10% (1)
- Principles of Risk Management and Insurance 12th Edition Rejda Test BankДокумент25 страницPrinciples of Risk Management and Insurance 12th Edition Rejda Test BankRobertBlankenshipbrwez100% (32)
- Statistics for Applications Problem Set 4Документ3 страницыStatistics for Applications Problem Set 4yilvasОценок пока нет
- Simple Random Sampling HomeworkДокумент8 страницSimple Random Sampling Homeworkh3ya7wp9100% (1)
- Listings and Diagrams of Outcomes: Learner's Module in Mathematics 6Документ12 страницListings and Diagrams of Outcomes: Learner's Module in Mathematics 6Sab Gumilao Ganotice100% (1)
- Chapter 6 17Документ6 страницChapter 6 17Ameer ElatmaОценок пока нет
- Zone 7, Bulua Cagayan de Oro City: Merry Child SchoolДокумент3 страницыZone 7, Bulua Cagayan de Oro City: Merry Child SchoolJessa Mae Neri SardanОценок пока нет
- CS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2019 Alistair Sinclair and Yun S. SongДокумент3 страницыCS 70 Discrete Mathematics and Probability Theory Fall 2019 Alistair Sinclair and Yun S. SongbobHopeОценок пока нет
- Values of The T-Distribution (Two-Tailed)Документ2 страницыValues of The T-Distribution (Two-Tailed)eric_joeОценок пока нет
- University Physics Solution ManualДокумент5 страницUniversity Physics Solution ManualRidho Manix0% (1)
- Dist Normal FullДокумент2 страницыDist Normal FullSalsha Anggia PutriОценок пока нет
- BBA Syllabus with Suggested ReadingsДокумент12 страницBBA Syllabus with Suggested ReadingsAASTHA SHARMAОценок пока нет
- John P. Nolan - Stable DistributionsДокумент34 страницыJohn P. Nolan - Stable DistributionsDániel KincsesОценок пока нет
- Carnival ProjectДокумент7 страницCarnival Projectapi-596108176Оценок пока нет
- 3 - Discrete Random Variables & Probability DistributionsДокумент80 страниц3 - Discrete Random Variables & Probability DistributionsMohammed AbushammalaОценок пока нет
- A Novel Data Leakage Detection: Priyanka Barge, Pratibha Dhawale, Namrata KolashettiДокумент3 страницыA Novel Data Leakage Detection: Priyanka Barge, Pratibha Dhawale, Namrata KolashettiIJMERОценок пока нет
- How To Use CasioДокумент3 страницыHow To Use CasioFadhel AtrasОценок пока нет
- Bayes Classifier PDFДокумент18 страницBayes Classifier PDFMohammad Jawad Jahed100% (1)