Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
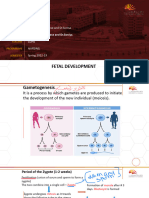
Age Fetal Development Approximate Length Approximate Weight: Sex Distinguishable
Загружено:
Chigas ManilaОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Age Fetal Development Approximate Length Approximate Weight: Sex Distinguishable
Загружено:
Chigas ManilaАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Age Fetal Development Approximate Approximate
Length Weight
By 8 Head and heart grow rapidly 2.5 2 grams
weeks Head is larger than trunk centimeters
Central hemispheres appear
Face elongates
Eyelid folds have developed by eyes are still far apart
Flat nose and recognizable mouth
External ears look similar to final appearance
Arms, legs, fingers and toes are distinct
Heart and liver are prominent
The end of the eighth week marks the end of the "embryonic period"
and the beginning of the "fetal period"
By 12 Intestinal villi form 7 centimeters 28 grams
weeks Bladder and urethra separate from rectum
Kidneys begin to secrete urine that makes up the amniotic fluid
Bronchioles branch and pleural; lungs assume definitive shape
Pericardial cavities appear
Thyroid and pancreas begin to secrete hormones
Red blood cells are produced in the liver
Sex distinguishable
Bone ossification occurs; tooth buds appear
Able to suck and swallow
Eyelids close and will not reopen until about the 28th week
By 16 Joint cavities are present 10-17 15-120 grams
weeks Bile is secreted centimeters
Intestines assume normal position; meconium is made
Kidneys in proper position
Lanugo develops on the head
Testes begin to descend into inguinal canal
Skin is almost transparent
Sucking motions are made with the mouth
By 20 Brain grossly formed 16-25 225-300
weeks Spinal cord myelinization begins centimeters grams
Lanugo hair covers entire body
Eyebrows and lashes appear
Nails appear on the fingers and toes
The mother can feel the baby moving
The fetal heartbeat can be heard with a stethoscope
By 24 External genitalia discernible 24-28 680-1000
weeks Skin red and wrinkled centimeters grams
Lungs begin to produce surfactant
Meconium present in rectum
Eyes are structurally complete
By 28 Rapid brain development occurs 35-38 1000-1200
weeks Face matures centimeters grams
Eyelids open and close
The baby has a hand and startle reflex
Immature respiratory system can support gas exchange
Viable as a neonate with intensive care
By 32 Increase in subcutaneous fat 43-48 2400-2800
weeks Hair evident centimeters grams
Still covered with vernix caseosa
Can turn head side-to-side
Skin begins to smooth out
Bones are fully developed, but soft and pliable
Chance of survival outside utero increases
By 36 Lanugo begins to disappear 43-48 2400-2800
weeks Subcutaneous fat continues to increase centimeters grams
Elongation of spinal cord almost complete
Good chance of survival
By 40 Baby is full term 48-52 2800 grams or
weeks Both testes have descended in the male centimeters more
Lanugo has disappeared
All organ systems have developed
Fetal circulation normally ceases to exist after birth:
By removing the placenta reservoir, the baby's venous resistance/blood pressure goes up
By filling the lungs with air, the blood pressure in the lung arteries does down; this
eventually leads to the closing of the two areas for shunting:
Patent foramen ovale - the circulation in the lungs increases and more blood
flows into the left atrium of the heart; this increased pressure causes the foramen ovale to close
and blood circulate normally
Patent ductus arteriosus - because the ductus arteriosus (the normal connection
between the aorta and the pulmonary artery) is no longer needed, it begins to constrict and
close off
Вам также может понравиться
- Milestones of Fetal Growth AND DevelopmentДокумент31 страницаMilestones of Fetal Growth AND DevelopmentBryan Lloyd Ballestar RayatОценок пока нет
- Maternal-Reviewer MДокумент2 страницыMaternal-Reviewer MAia RecaidoОценок пока нет
- Fetaldevelopment Powerpoint Secondary HealthДокумент30 страницFetaldevelopment Powerpoint Secondary Healthapi-277611497Оценок пока нет
- Presentation 1Документ25 страницPresentation 1vinuarunОценок пока нет
- Milestone of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentДокумент3 страницыMilestone of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentGem DasmariñasОценок пока нет
- Embryo and Fetal DevelopmentДокумент37 страницEmbryo and Fetal DevelopmentAnuchithra50% (2)
- Fertilization to Birth: A Guide to Pregnancy DevelopmentДокумент7 страницFertilization to Birth: A Guide to Pregnancy DevelopmentSamson BongsiwОценок пока нет
- Fetal Growth and DevelopmentДокумент3 страницыFetal Growth and DevelopmentAngel Shaina VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- FETAL DEVELOPMENT - CopyДокумент36 страницFETAL DEVELOPMENT - Copyalmayasa2002Оценок пока нет
- Fetal Growth and Development 20 Weeks To Birth-2Документ24 страницыFetal Growth and Development 20 Weeks To Birth-2hangoverОценок пока нет
- Fetal DevelopmentДокумент1 страницаFetal DevelopmentrenjiniОценок пока нет
- Fetal development and human sexual responseДокумент4 страницыFetal development and human sexual responsehahahahaaaaaaaОценок пока нет
- KLM Chapter 6Документ4 страницыKLM Chapter 6Ceo MedComОценок пока нет
- Milestone of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentДокумент21 страницаMilestone of Fetal Growth and DevelopmentPrecious Abueg RNОценок пока нет
- Milestones of Fetal Development PDFДокумент2 страницыMilestones of Fetal Development PDFApRil Anne BalanonОценок пока нет
- Development of FetusДокумент12 страницDevelopment of FetusmOHAN.SОценок пока нет
- End of Fourth Gestational WeekДокумент3 страницыEnd of Fourth Gestational WeekCamille De Jesus100% (1)
- Lesson 2 NCM 107aДокумент5 страницLesson 2 NCM 107aInsatiable CleeОценок пока нет
- Gender Dysphoria Breakthrough 2Документ117 страницGender Dysphoria Breakthrough 2Flourence ZafranОценок пока нет
- Embryonic Development and The ChildbirthДокумент10 страницEmbryonic Development and The Childbirthsfr yberverОценок пока нет
- Fetal Morphological and Physiological Development PDFДокумент10 страницFetal Morphological and Physiological Development PDFKim RamosОценок пока нет
- Stages of Pregnancy GuideДокумент17 страницStages of Pregnancy GuidePrachi DasОценок пока нет
- 2nd trasesnsДокумент8 страниц2nd trasesnssenecabheОценок пока нет
- Health and Lifestyle Issues On PregnancyДокумент3 страницыHealth and Lifestyle Issues On PregnancySelene BrondialОценок пока нет
- PERKEMBANGAN JANIN DAN PERUBAHAN PADA IBU HAMILДокумент43 страницыPERKEMBANGAN JANIN DAN PERUBAHAN PADA IBU HAMILAditya PrambudhiОценок пока нет
- Growing FetusДокумент4 страницыGrowing FetusMaria ThereseОценок пока нет
- Stages of Fetal Development FinalДокумент43 страницыStages of Fetal Development Finalsanthiyasandy100% (6)
- Early childhood curriculum modelsДокумент4 страницыEarly childhood curriculum modelsKatrina Mae ReyesОценок пока нет
- Nursing Care for Normal Pregnancy and Fetal DevelopmentДокумент10 страницNursing Care for Normal Pregnancy and Fetal DevelopmentShanealle Athaliah Magsalay CuaОценок пока нет
- 1-Pre-Natal PeriodДокумент61 страница1-Pre-Natal PeriodLady Mairyl N. BrigondoОценок пока нет
- What Are Some Early Signs of Pregnancy?Документ194 страницыWhat Are Some Early Signs of Pregnancy?Menard VelascoОценок пока нет
- Slide Skenario 1 Blok TumbangДокумент45 страницSlide Skenario 1 Blok TumbangTripser LockyОценок пока нет
- Dev Psych CHAPTER3Документ54 страницыDev Psych CHAPTER3Ezri Mariveles Coda Jr.Оценок пока нет
- Embryogenesis & Fetal DevelopementДокумент38 страницEmbryogenesis & Fetal DevelopementDasha Vee100% (1)
- What Happens During Weeks 1-4 of Pregnancy?Документ3 страницыWhat Happens During Weeks 1-4 of Pregnancy?ReemaОценок пока нет
- Journal: What Thought Will You Have When You or Your Wife Is Pregnant? Does It Scare You? What Will Be Your Concerns?Документ26 страницJournal: What Thought Will You Have When You or Your Wife Is Pregnant? Does It Scare You? What Will Be Your Concerns?Rhonnel DulnuanОценок пока нет
- Educ 11 Unit 2 ActivityДокумент15 страницEduc 11 Unit 2 ActivityQueen DaguroОценок пока нет
- Prof. Ed. 1 HardДокумент23 страницыProf. Ed. 1 HardJhony Pernin AlparОценок пока нет
- Fisiologi Kehamilan Dan Maternal-Fetal Exchange: Acholder SiraitДокумент61 страницаFisiologi Kehamilan Dan Maternal-Fetal Exchange: Acholder SiraitBunga sujatnikaОценок пока нет
- Prenatal StageДокумент1 страницаPrenatal StagemaraОценок пока нет
- The Fetal Period: by DR - Abdallah GreeballahДокумент55 страницThe Fetal Period: by DR - Abdallah GreeballahrawanОценок пока нет
- The Process of ConceptionДокумент62 страницыThe Process of ConceptionKaren Ivy BacsainОценок пока нет
- Assessing Newborns' Structure and DevelopmentДокумент41 страницаAssessing Newborns' Structure and DevelopmentCharm Abyss la MorenaОценок пока нет
- Prenatal Development: From Single Cell to Full-Term BabyДокумент13 страницPrenatal Development: From Single Cell to Full-Term BabyElisan MarilouОценок пока нет
- 3.embryonic & Fetal Period 1st Yr MedcДокумент34 страницы3.embryonic & Fetal Period 1st Yr MedcTofik MohammedОценок пока нет
- Maturity Cycle Fetal Growth and DeveloplmentДокумент3 страницыMaturity Cycle Fetal Growth and DeveloplmentMary Claire SodeОценок пока нет
- Stages of PregnancyДокумент14 страницStages of PregnancyRovilyn DizonОценок пока нет
- Milestones of Fetal Growth and Development Power PointДокумент24 страницыMilestones of Fetal Growth and Development Power PointCymilo100% (1)
- Prenatal StageДокумент1 страницаPrenatal StagemaraОценок пока нет
- Lecture 6.1 Prenatal Development and BirthДокумент15 страницLecture 6.1 Prenatal Development and BirthZari Sofia LevisteОценок пока нет
- One Month: Fertilization ImplantationДокумент4 страницыOne Month: Fertilization ImplantationAgui S. AugusthineОценок пока нет
- "Fetal Development Milestone": Weeks Organ To Be Developed Clinical ImplicationДокумент3 страницы"Fetal Development Milestone": Weeks Organ To Be Developed Clinical ImplicationSoniaMarieBalanayОценок пока нет
- Fetal Developmental MilestonesДокумент28 страницFetal Developmental MilestonesShahad HakimuddinОценок пока нет
- MJKHVJHV 3 PDFДокумент3 страницыMJKHVJHV 3 PDFChloe TangonanОценок пока нет
- PBL SS 2 - Fetal DevelopmentДокумент3 страницыPBL SS 2 - Fetal DevelopmentJellie MendozaОценок пока нет
- Fetal Circulation Development StagesДокумент44 страницыFetal Circulation Development StagesMarc BantilanОценок пока нет
- Fetus Developing: Teacher: Carlos Montenegro Grade: 2 º AДокумент14 страницFetus Developing: Teacher: Carlos Montenegro Grade: 2 º AMonica VillanuevaОценок пока нет
- Cranial Nerves - Functions & Deviation From NormalДокумент1 страницаCranial Nerves - Functions & Deviation From NormalChigas ManilaОценок пока нет
- Blood Studies GuideДокумент21 страницаBlood Studies GuideChigas ManilaОценок пока нет
- Guide To Obtaining A PermitДокумент10 страницGuide To Obtaining A PermitChigas ManilaОценок пока нет
- Daycare 2Документ23 страницыDaycare 2Marija Josipović100% (1)
- OSCE and Clinical Skills Handbook 2nd EditionДокумент443 страницыOSCE and Clinical Skills Handbook 2nd EditionMarc Tarcu93% (43)
- 2018-02-12 Star Magazine USA PDFДокумент76 страниц2018-02-12 Star Magazine USA PDFChigas ManilaОценок пока нет
- CANADAupdated2017s 21 PDFДокумент55 страницCANADAupdated2017s 21 PDFChigas ManilaОценок пока нет
- 2 Food Orders 2017Документ1 страница2 Food Orders 2017Chigas ManilaОценок пока нет
- ANTIBODY SCREENING - FinalДокумент4 страницыANTIBODY SCREENING - FinalHaniya KhanОценок пока нет
- Cell types and adaptations for specialized functionsДокумент24 страницыCell types and adaptations for specialized functionsJae Ann CaliñadaОценок пока нет
- Intraosseous Arteriovenous Malformations Mimicking Malignant DiseaseДокумент7 страницIntraosseous Arteriovenous Malformations Mimicking Malignant DiseaseNm SОценок пока нет
- Far Eastern University Institue of Arts and Science Department of Medical Technology Histology 2 SEMESTER AY 2020-2021Документ1 страницаFar Eastern University Institue of Arts and Science Department of Medical Technology Histology 2 SEMESTER AY 2020-2021Kaye RiofloridoОценок пока нет
- Reproductive Cell, Organ, CycleДокумент56 страницReproductive Cell, Organ, CycleAjay MeghanathiОценок пока нет
- Darah Dan Fungsi DarahДокумент14 страницDarah Dan Fungsi DarahdelisОценок пока нет
- HormonesДокумент31 страницаHormonestuvvacОценок пока нет
- Chapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneДокумент6 страницChapter 9 - Plant Organization and Function - DoneApostolos KoutsaftisОценок пока нет
- Chapter 6: Holes Anatomy and Physiology The Integumentary System (A Cutaneous Membrane)Документ5 страницChapter 6: Holes Anatomy and Physiology The Integumentary System (A Cutaneous Membrane)ccami709Оценок пока нет
- Blood (Anaphy)Документ8 страницBlood (Anaphy)CORONEL, SOPHIAОценок пока нет
- المصطلحات - الطبيه - بالعربية - مبارك - عبدالهادي - موقع المكتبة نتДокумент199 страницالمصطلحات - الطبيه - بالعربية - مبارك - عبدالهادي - موقع المكتبة نتAli AimanОценок пока нет
- Chapter 7 Student Version The Nervous System 2020 (1138)Документ21 страницаChapter 7 Student Version The Nervous System 2020 (1138)S. MartinezОценок пока нет
- ONCO 21 Desember 2020 Undiferentiated Pleomorfic Sarcoma Rev 1Документ46 страницONCO 21 Desember 2020 Undiferentiated Pleomorfic Sarcoma Rev 1ciptakarwanaОценок пока нет
- BreastДокумент49 страницBreastcryphonexyОценок пока нет
- Tetanus PathoДокумент3 страницыTetanus PathoElisha Gine AndalesОценок пока нет
- Liver Structure and FunctionДокумент16 страницLiver Structure and FunctionApolloMPОценок пока нет
- Embryonic Development of Male and Female Reproductive SystemsДокумент14 страницEmbryonic Development of Male and Female Reproductive SystemsDiana Jangmi MerhanОценок пока нет
- Modul F2 Science C2Документ14 страницModul F2 Science C2NorelyanaAli67% (3)
- Parasympathetic Nervous SystemДокумент20 страницParasympathetic Nervous SystemShahid Maqbool100% (1)
- Male Reproductive Anatomy and FunctionДокумент42 страницыMale Reproductive Anatomy and FunctionBlodin ZylfiuОценок пока нет
- Nervous System WorksheetДокумент2 страницыNervous System WorksheetHAA-BEEОценок пока нет
- 1001 MCQ S in Physiology Including Biochemistry A D Amondikar.05576 3sampleДокумент6 страниц1001 MCQ S in Physiology Including Biochemistry A D Amondikar.05576 3samplenasibdinОценок пока нет
- Repair and Regeneration of Oral Tissues - Ten Cate Chapter 15Документ3 страницыRepair and Regeneration of Oral Tissues - Ten Cate Chapter 15Chris Tay100% (2)
- 2nd Lecture On Action Potential by Dr. Roomi.Документ14 страниц2nd Lecture On Action Potential by Dr. Roomi.Mudassar Roomi100% (1)
- Sexual Reproduction: Grade 11/12Документ17 страницSexual Reproduction: Grade 11/12lyn weiОценок пока нет
- Acute Tubular NecrosisДокумент5 страницAcute Tubular NecrosiscedricОценок пока нет
- Soft Tissue Tumor Treatment and Diagnosis in the NeckДокумент15 страницSoft Tissue Tumor Treatment and Diagnosis in the NeckCynthia BarrientosОценок пока нет
- Ultrasound Measurement Cheat SheetДокумент1 страницаUltrasound Measurement Cheat SheetDr. MLKОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Excitable TissuesДокумент26 страницIntroduction To Excitable TissuesSohail KhanОценок пока нет
- Orientation Clinical HemaДокумент10 страницOrientation Clinical HemaPRECIOUS DIANNE BARDON-MEMPINОценок пока нет