Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
QP Strategic Management 2020 IA-2 With Eavluation Scheme
Загружено:
Purnajit CИсходное описание:
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
QP Strategic Management 2020 IA-2 With Eavluation Scheme
Загружено:
Purnajit CАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
USN
INTERNAL ASSESSMENT TEST
Subject: Strategic Management Subject code:19MBA25
Sem: II Date: 09-05-2020 Max marks: 50
Faculty: Prof. Purnajit Chatterjee & Dr. Praveenasri Time: 90 minutes
Instructions: Answer any 2 full sets out of 1, 2 & 3 and 4th & 5th are compulsory.
Bloom’s
Marks COs
level
a) What is meant by competitive advantage?
Competitive advantage is the leverage a business has over its
competitors. This can be gained by offering clients better and greater
value. Advertising products or services with lower prices or higher
quality piques the interest of consumers. Target markets recognize
these unique products or services. This is the reason behind brand
loyalty, or why customers prefer one particular product or service
over another.
Value proposition is important when understanding competitive
advantage. If the value proposition is effective, that is, if the value
3 2 1
proposition offers clients better and greater value, it can produce a
competitive advantage in either the product or service. The value
Q1 proposition can increase customer expectations and choices.
Michael Porter defined the two ways in which an organization can
achieve competitive advantage over its rivals: cost advantage and
differentiation advantage. Cost advantage is when a business provides
the same products and services as its competitors, albeit at a lesser
cost. Differentiation advantage is when a business provides better
products and services as its competitors. In Porter's view, strategic
management should be concerned with building and sustaining
competitive advantage
b) Discuss the various strategic factors necessary for a company Macro
7 3 1
Environment?
c) Explain elaborately about Michael Porter‘s Five Force Model?
10 2 2
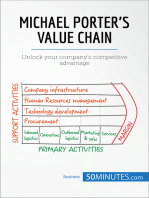
Q2 a) What do you mean by the term Value Chain in an organization? 3 1 2
A company’s business consists of all activities undertaken in
designing, producing, marketing, delivering, and supporting its
product or service
All these activities that a company performs internally combine
to form a value chain—so-called because the underlying intent
of a company’s activities is to do things that ultimately create
value for buyers
The value chain contains two types of activities
Primary activities (where most of
the value for customers is created)
Support activities that facilitate
performance of the primary activities
b) Why do companies form strategic alliances and partnerships?
Several firms think that the most effective way to get ahead is to
expand business boundaries through mergers and acquisitions (M&A).
Mergers produce synergies and economies of scale, increasing
operations and cutting prices. Investors will take comfort within the
idea that a merger can deliver increased market power.
To collaborate on technology development or new product
development
To fill gaps in technical or manufacturing expertise
Master new technologies and build new expertise faster than
would be possible internally
Access valuable skills and competencies concentrated in
particular geographic locations
To improve supply chain efficiency 7 3 2
To gain economies of scale in
production and/or marketing
To acquire or improve market access
via joint marketing agreements
Get into critical country markets quickly to accelerate process
of building a global presence
Gain inside knowledge about unfamiliar markets and cultures
Establish a beachhead to participate in target industry
Open up expanded opportunities in target industry by
combining firm’s capabilities with resources of partners
c) What are the Five Generic competitive strategies, explain with an 10 3 1
industry example?
Porter's generic strategies describe how a company pursues
competitive advantage across its chosen market scope. There are
three/four generic strategies, either lower cost, differentiated, or focus.
A company chooses to pursue one of two types of competitive
advantage, either via lower costs than its competition or by
differentiating itself along dimensions valued by customers to
command a higher price. A company also chooses one of two types of
scope, either focus (offering its products to selected segments of the
market) or industry-wide, offering its product across many market
segments. The generic strategy reflects the choices made regarding
both the type of competitive advantage and the scope. The concept was
described by Michael Porter in 1980
Three potentially successful strategic approaches to
outperforming rivals
o Overall cost leadership
o Differentiation
o Focus
Could follow more than one or a combination
Structure, Value chain, market positioning and approach etc
are all different in each case
Cost Leadership strategy involves the firm winning market share by
appealing to cost-conscious or price-sensitive customers. This is
achieved by having the lowest prices in the target market segment, or at
least the lowest price to value ratio (price compared to what customers
receive). To succeed at offering the lowest price while still achieving
profitability and a high return on investment, the firm must be able to
operate at a lower cost than its rivals. There are three main ways to
achieve this.
Differentiation Strategy: Differentiate the products/services in some
way in order to compete successfully. Examples of the successful use
of a differentiation strategy are Hero, Asian Paints, HUL, Nike
athletic shoes (image and brand mark), BMW Group Automobiles,
Perstorp BioProducts, Apple Computer (product's design), Mercedes-
Benz automobiles.
A differentiation strategy is appropriate where the target customer
segment is not price-sensitive, the market is competitive or saturated,
customers have very specific needs which are possibly under-served,
and the firm has unique resources and capabilities which enable it to
satisfy these needs in ways that are difficult to copy.
Focus Strategy: This dimension is not a separate strategy for big
companies due to small market conditions. Big companies which chose
applying differentiation strategies may also choose to apply in
conjunction with focus strategies (either cost or differentiation). On
the other hand, this is definitely an appropriate strategy for small
companies especially for those wanting to avoid competition with big
one.
In adopting a narrow focus, the company ideally focuses on a few
target markets (also called a segmentation strategy or niche strategy).
These should be distinct groups with specialised needs. The choice of
offering low prices or differentiated products/services should depend
on the needs of the selected segment and the resources and
capabilities of the firm. It is hoped that by focusing your marketing
efforts on one or two narrow market segments and tailoring your
marketing mix to these specialized markets, you can better meet the
needs of that target market.
Q 3 a) What is benchmarking and how does it help build competitive
advantage?
Benchmarking is the practice of comparing business processes and
performance metrics to industry bests and best practices from other
companies. Dimensions typically measured are quality, time and cost.
Benchmarking is used to measure performance using a specific
indicator (cost per unit of measure, productivity per unit of measure,
cycle time of x per unit of measure or defects per unit of measure)
resulting in a metric of performance that is then compared to others.
[1]
Also referred to as "best practice benchmarking" or "process
benchmarking", this process is used in management in which
organizations evaluate various aspects of their processes in relation to
best-practice companies' processes, usually within a peer group
defined for the purposes of comparison. This then allows organizations
to develop plans on how to make improvements or adapt specific best 3 1 2
practices, usually with the aim of increasing some aspect of
performance. Benchmarking may be a one-off event, but is often
treated as a continuous process in which organizations continually
seek to improve their practices.
Identify best and most efficient means of performing various
value chain activities
Learn what is the “best” way to perform a particular activity
from those companies who have demonstrated that they are
“best-in-industry” or “best-in-world” at performing the
activity
Learn what other firms do to perform
an activity at lower cost
Figure out what actions to take to improve a company’s
own cost competitiveness
b) Explain the role of SWOT in crafting a better strategy? Do a brief 7 3 1
SWOT analysis of Samsung Mobiles in India
SWOT analysis (or SWOT matrix) is a strategic planning technique
used to help a person or organization identify strengths, weaknesses,
opportunities, and threats related to business competition or project
planning. It is designed for use in the preliminary stages of decision-
making processes and can be used as a tool for evaluation of the
strategic position of a city or organization. It is intended to specify the
objectives of the business venture or project and identify the internal
and external factors that are favorable and unfavorable to achieving
those objectives. Users of a SWOT analysis often ask and answer
questions to generate meaningful information for each category to
make the tool useful and identify their competitive advantage. SWOT
has been described as the tried-and-true tool of strategic analysis, but
it has also been criticized for its limitations
S W O T analysis involves more than just developing the 4
lists of strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats
The most important part of S W O T analysis is
o Using the 4 lists to draw conclusions
about a company’s overall situation
o Acting on the conclusions to
Better match a company’s strategy to its
resource strengths and market opportunities
Correct the important weaknesses
Defend against external threats
c) Evaluate the Strategic Implications of Five Competitive forces with
special emphasis on Strategic Mapping? 10 2
Case Study
JetBlue Airlines' Success Story
The case describes the reasons for the success of JetBlue, a three-year-old, low-cost airline, operating in the
USA. JetBlue was set up by David Neeleman, who earlier founded a very successful discount airline called
Morris Air in Utah. He also helped found West Jet, another discount airline in Canada. Neeleman set up
JetBlue in 2000 and modelled it on the lines of the most well-known of discounters- Southwest Airlines.
JetBlue adopted a strategy for effective cost control by identifying and eliminating all unnecessary expenses
and concentrating on providing high quality services to its passengers. Towards this end, it adopted a
number of innovative measures on the planes such as: not serving food, point-to-point flights, and quick
turnarounds. It also made effective use of advertising to position itself as a fun airline. JetBlue's innovative
operational model helped it succeed at a time when the major players of the airline industry were crumbling.
What is the generic competitive strategy that Jet Blue is following,
please justify your answer?
Q4 5 4 4
Best Cost Provider since the company focuses on providing good
quality services without the additional frills at a low price
Analyse the measures adopted by a firm effectively cutting costs and at
the same time maintaining a high standard of service
Q5 5 4 4
Вам также может понравиться
- Strategy Formulation Integrating The CorporationДокумент8 страницStrategy Formulation Integrating The CorporationRLDОценок пока нет
- Michael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageОт EverandMichael Porter's Value Chain: Unlock your company's competitive advantageРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- Convert 2.0 - Frank Kern Official Full Download + FREEДокумент127 страницConvert 2.0 - Frank Kern Official Full Download + FREETwo Comma Club100% (1)
- Strategic Options Approaches To Sustainable Competitive AdvantageДокумент9 страницStrategic Options Approaches To Sustainable Competitive AdvantageMukhtar Hussain100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Performance Objectives of Operations ManagementДокумент17 страницChapter 6 Performance Objectives of Operations ManagementJimmy Ong Ah Huat100% (2)
- POWEV2434234Документ461 страницаPOWEV2434234John M. HemsworthОценок пока нет
- (154 Marks) : (1 Mark)Документ40 страниц(154 Marks) : (1 Mark)Manav NairОценок пока нет
- Chairperson 2012 Bar Examinations Committee: Bar Exam Question 2012 Martin S. Villarama, JRДокумент73 страницыChairperson 2012 Bar Examinations Committee: Bar Exam Question 2012 Martin S. Villarama, JRsejinma0% (1)
- Module 002 - Operations Strategy, Productivity and CompetitivenessДокумент15 страницModule 002 - Operations Strategy, Productivity and CompetitivenessAubrey CastilloОценок пока нет
- Madali V PeopleДокумент2 страницыMadali V PeopleNico NuñezОценок пока нет
- The Utopia of The Zero-OptionДокумент25 страницThe Utopia of The Zero-Optiontamarapro50% (2)
- Heirs of Candelaria V RomeroДокумент2 страницыHeirs of Candelaria V Romeromoniquehadjirul100% (1)
- Strategic Management Ass1Документ8 страницStrategic Management Ass1Milford Kudakwashe MoyanaОценок пока нет
- SU190264W Strategic Management Ass1Документ8 страницSU190264W Strategic Management Ass1Milford Kudakwashe MoyanaОценок пока нет
- Module III Strategy Formulation UpdatedДокумент19 страницModule III Strategy Formulation Updatedmacs emsОценок пока нет
- SBM Study Manual-Chapter-2 Strategic Choice-Theory & Model PDFДокумент35 страницSBM Study Manual-Chapter-2 Strategic Choice-Theory & Model PDFSafaiwat Eraq100% (1)
- Achieving Competitive Advantage Through ICT Strategy: A Study On Shimanto BankДокумент14 страницAchieving Competitive Advantage Through ICT Strategy: A Study On Shimanto BankRafee FaizeОценок пока нет
- Improve Business PracticeДокумент45 страницImprove Business PracticeSatenaw Gojame Satenaw Gojame100% (7)
- Essay - Management of Process & Competitive AdvantageДокумент8 страницEssay - Management of Process & Competitive AdvantageMohammedОценок пока нет
- Competitive Advantage Through Business Intelligence.Документ15 страницCompetitive Advantage Through Business Intelligence.Umar Mukhtar BandayОценок пока нет
- Management Information SystemДокумент13 страницManagement Information SystemVinay SainiОценок пока нет
- Strategy Formulation - Integrating The Corporation (04-30-2008) - (AIM-2-07-0012-RDNG)Документ8 страницStrategy Formulation - Integrating The Corporation (04-30-2008) - (AIM-2-07-0012-RDNG)Alexis Louisse GonzalesОценок пока нет
- Poters GenricДокумент4 страницыPoters Genricpriyank1256Оценок пока нет
- StuDY-GUIDe FiveДокумент11 страницStuDY-GUIDe Fiveambitchous19Оценок пока нет
- Competitive Advantage Vs Core Competence: TrendingДокумент8 страницCompetitive Advantage Vs Core Competence: TrendingChetna MahaurОценок пока нет
- CH 6 Business StrategyДокумент5 страницCH 6 Business StrategyfirasОценок пока нет
- Bussiness Strategy v1.0Документ3 страницыBussiness Strategy v1.0Annu BabuОценок пока нет
- STM Concepts AnsersДокумент8 страницSTM Concepts AnsersKarthick Nathan ShanmuganathanОценок пока нет
- Strategic Management Chapter1Документ30 страницStrategic Management Chapter1Arshad BashirОценок пока нет
- Chapter-Two: Competitiveness, Strategies, and Productivity in OperationsДокумент63 страницыChapter-Two: Competitiveness, Strategies, and Productivity in OperationsChernet AyenewОценок пока нет
- MDI HRD Compendium 2018Документ15 страницMDI HRD Compendium 2018Subhendu PradhanОценок пока нет
- MDI Strategy Compendium PDFДокумент15 страницMDI Strategy Compendium PDFutkarsh chaudharyОценок пока нет
- Core CompetencyДокумент3 страницыCore CompetencyAli M. AtallahОценок пока нет
- Marketing ManagementДокумент24 страницыMarketing ManagementLOHO MatembaОценок пока нет
- Business Level Strategies: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToДокумент30 страницBusiness Level Strategies: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able Tovaibhav sharmaОценок пока нет
- Strategy Formulation & ExecutionДокумент38 страницStrategy Formulation & ExecutionEduardo LleveОценок пока нет
- Lesson Number: 17 Topic: What Is A Competitive Strategy?: Course Code and Title: CBME2 - Strategic ManagementДокумент7 страницLesson Number: 17 Topic: What Is A Competitive Strategy?: Course Code and Title: CBME2 - Strategic ManagementDeriada ChristopherОценок пока нет
- SM CH 5 Business Level StrategiesДокумент42 страницыSM CH 5 Business Level StrategiesVijeshОценок пока нет
- Business Level Strategies: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToДокумент32 страницыBusiness Level Strategies: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Able ToBhai LangurОценок пока нет
- Priciples of Marketing by Philip Kotler and Gary Armstrong: Creating Competitive AdvantageДокумент30 страницPriciples of Marketing by Philip Kotler and Gary Armstrong: Creating Competitive AdvantageGeovanna VillaverdeОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2Документ4 страницыChapter 2Mixx MineОценок пока нет
- Business Policy and Strategy (BBA 6 Sem) Unit 2 Organizational CapabilitiesДокумент9 страницBusiness Policy and Strategy (BBA 6 Sem) Unit 2 Organizational CapabilitiesAyushОценок пока нет
- Competitive StrategyДокумент9 страницCompetitive StrategyTalha SiddiquiОценок пока нет
- 9 Creating Competitive AdvantageДокумент11 страниц9 Creating Competitive AdvantageJay LopezОценок пока нет
- CS Chapter3Документ4 страницыCS Chapter3Sumanth KatagouniОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 - Strategic Cost Management: MidtermДокумент19 страницChapter 1 - Strategic Cost Management: MidtermAndrea Nicole De LeonОценок пока нет
- Reporting ManagmentДокумент12 страницReporting ManagmentTuseef AhmedОценок пока нет
- Value Chain Models Version 2.1 (Last Updated - July 2010)Документ24 страницыValue Chain Models Version 2.1 (Last Updated - July 2010)kashalisahОценок пока нет
- Unit 8: Business Level StrategiesДокумент35 страницUnit 8: Business Level StrategiesFlo IglesiaОценок пока нет
- MBL 514 Assignment 3 Group 4Документ6 страницMBL 514 Assignment 3 Group 4Tendai Alfred KunakaОценок пока нет
- Assignment: Strategic ManagementДокумент17 страницAssignment: Strategic ManagementajoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5Документ7 страницChapter 5ERICKA MAE NATOОценок пока нет
- Hitt Inst Manual 13e ch04 FinalДокумент36 страницHitt Inst Manual 13e ch04 FinalMonica CruzОценок пока нет
- Rowshon Tabassom - 18133023Документ11 страницRowshon Tabassom - 18133023Rowshon TabassomОценок пока нет
- Module 5 - Strategic ManagementДокумент28 страницModule 5 - Strategic ManagementPrime Johnson FelicianoОценок пока нет
- 20ODMBT721 - SM DoneДокумент13 страниц20ODMBT721 - SM DonekushОценок пока нет
- Fundamentals of Industrial Management ExamДокумент13 страницFundamentals of Industrial Management ExamKawsar AhmedОценок пока нет
- 1714, Khitab, STM 2Документ8 страниц1714, Khitab, STM 2Ahmad KhitabОценок пока нет
- Strategy of IB-Charles Hill PDFДокумент6 страницStrategy of IB-Charles Hill PDFNikita PrasadОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 - Business Level StrategiesДокумент31 страницаUnit 4 - Business Level StrategiesDecaОценок пока нет
- Stratman ReviewДокумент9 страницStratman Reviewleiqiao saturneОценок пока нет
- IntroductionДокумент8 страницIntroductionmelvinngugi669Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 1 SCMPE Theory Keyword NotesДокумент6 страницChapter 1 SCMPE Theory Keyword NotesCA Mohit SharmaОценок пока нет
- Competitiveness, Strategy, and Productivity: Mcgraw-Hill/IrwinДокумент38 страницCompetitiveness, Strategy, and Productivity: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwintanmoy8554Оценок пока нет
- Block 4 MS 91 Unit 5Документ11 страницBlock 4 MS 91 Unit 5Anonymous P1xUTHstHTОценок пока нет
- Ciljni Trosak, Ljilja Bojana, EngДокумент15 страницCiljni Trosak, Ljilja Bojana, EngdrbaneОценок пока нет
- Final StrategicДокумент6 страницFinal StrategicStark WayneОценок пока нет
- N Advocates Act 1961 Ankita218074 Nujsedu 20221008 230429 1 107Документ107 страницN Advocates Act 1961 Ankita218074 Nujsedu 20221008 230429 1 107ANKITA BISWASОценок пока нет
- Xenophanes' ScepticismДокумент22 страницыXenophanes' Scepticismvince34Оценок пока нет
- (2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiДокумент11 страниц(2016) The Role of Requirements in The Success or Failure of Software Projects-DikonversiFajar HatmalОценок пока нет
- Muzakarah Jawatankuasa Fatwa Majlis Kebangsaan Bagi Hal Ehwal Ugama Islam Malaysia Kali KeДокумент7 страницMuzakarah Jawatankuasa Fatwa Majlis Kebangsaan Bagi Hal Ehwal Ugama Islam Malaysia Kali KeSiti Zubaidah ZulkhairieОценок пока нет
- A Clinico-Microbiological Study of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in An Indian Tertiary Care HospitalДокумент6 страницA Clinico-Microbiological Study of Diabetic Foot Ulcers in An Indian Tertiary Care HospitalJoko Cahyo BaskoroОценок пока нет
- A Vagabond SongДокумент4 страницыA Vagabond SongLiLiana DewiОценок пока нет
- Isc Class 11 Maths Sample Paper Model 1Документ2 страницыIsc Class 11 Maths Sample Paper Model 1Gaurav ShuklaОценок пока нет
- 10 1108 - JKM 01 2020 0064Документ23 страницы10 1108 - JKM 01 2020 0064BBA THESISОценок пока нет
- EikonTouch 710 ReaderДокумент2 страницыEikonTouch 710 ReaderShayan ButtОценок пока нет
- March 2009 Caro-Kann B12 by Sasa Velickovic Informant83Документ6 страницMarch 2009 Caro-Kann B12 by Sasa Velickovic Informant83kiprijanovОценок пока нет
- Code of Conduct of Dabur Company - 1Документ5 страницCode of Conduct of Dabur Company - 1Disha KothariОценок пока нет
- Skills For Developing Yourself As A LeaderДокумент26 страницSkills For Developing Yourself As A LeaderhIgh QuaLIty SVTОценок пока нет
- ShakespeareДокумент12 страницShakespeareapi-510189551Оценок пока нет
- High-Frequency Injection-Based SensorlessДокумент12 страницHigh-Frequency Injection-Based SensorlessRiad BOUZIDIОценок пока нет
- New-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies GENERAL CONTENT: Multiple-Choice QuestionsДокумент21 страницаNew-Product Development and Product Life-Cycle Strategies GENERAL CONTENT: Multiple-Choice Questionslisa voОценок пока нет
- Sanskrit LessonsДокумент195 страницSanskrit LessonsSuganya100% (1)
- Coursera Qs-Ans For Financial AidДокумент2 страницыCoursera Qs-Ans For Financial AidMarno03Оценок пока нет
- Leadership PaperДокумент6 страницLeadership PaperSTANCIU VALENTINОценок пока нет
- b8c2 PDFДокумент193 страницыb8c2 PDFRhIdho POetraОценок пока нет
- Study On SantalsДокумент18 страницStudy On SantalsJayita BitОценок пока нет
- Vip90 2021 Deso10Документ6 страницVip90 2021 Deso10Đỗ KhangОценок пока нет
- Birth and Growth of Semiotics: November 2020Документ9 страницBirth and Growth of Semiotics: November 2020Maria del Carmen Alvarado AcevedoОценок пока нет
- "Article Critique" Walden University Methods For Evidence-Based Practice, Nursing 8200 January 28, 2019Документ5 страниц"Article Critique" Walden University Methods For Evidence-Based Practice, Nursing 8200 January 28, 2019Elonna AnneОценок пока нет