Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
EC305 Microprocessor & Microcontroller
Загружено:
plbonifus0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
59 просмотров2 страницыThis document outlines the course objectives, syllabus, and course plan for the Microprocessor & Microcontroller course (EC305). The course aims to teach students about microprocessor and microcontroller architectures like 8085 and 8051, interfacing with peripheral devices, and assembly language programming. The syllabus is divided into six modules covering topics like 8085/8086 architecture, addressing modes, interfacing IC's, 8051 features, interrupts, serial communication, and interfacing devices like switches and displays. Students will be assessed through internal exams, an end semester exam, and are expected to learn to distinguish processor architectures, describe the 8085 and 8051, and develop programming skills for interfacing devices with 8051.
Исходное описание:
ktu syllabus
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документThis document outlines the course objectives, syllabus, and course plan for the Microprocessor & Microcontroller course (EC305). The course aims to teach students about microprocessor and microcontroller architectures like 8085 and 8051, interfacing with peripheral devices, and assembly language programming. The syllabus is divided into six modules covering topics like 8085/8086 architecture, addressing modes, interfacing IC's, 8051 features, interrupts, serial communication, and interfacing devices like switches and displays. Students will be assessed through internal exams, an end semester exam, and are expected to learn to distinguish processor architectures, describe the 8085 and 8051, and develop programming skills for interfacing devices with 8051.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
59 просмотров2 страницыEC305 Microprocessor & Microcontroller
Загружено:
plbonifusThis document outlines the course objectives, syllabus, and course plan for the Microprocessor & Microcontroller course (EC305). The course aims to teach students about microprocessor and microcontroller architectures like 8085 and 8051, interfacing with peripheral devices, and assembly language programming. The syllabus is divided into six modules covering topics like 8085/8086 architecture, addressing modes, interfacing IC's, 8051 features, interrupts, serial communication, and interfacing devices like switches and displays. Students will be assessed through internal exams, an end semester exam, and are expected to learn to distinguish processor architectures, describe the 8085 and 8051, and develop programming skills for interfacing devices with 8051.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
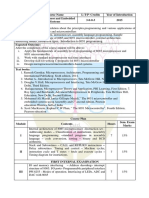
COURSE YEAR OF
CODE COURSE NAME L-T-P-C INTRODUCTION
EC305 Microprocessor & Microcontroller 3-0-0-3 2016
Prerequisite: EC207 Logic Circuit Design
Course objectives:
1. To understand fundamental operating concepts of microprocessors and microcontrollers.
2. To communicate with various devices using controller.
3. To design a microcontroller based system with the help of the interfacing devices.
4. To program the controller to make various peripherals work for specified application.
Syllabus:
Microprocessors: 8085 architecture and its operation, microprocessor initiated operations
and bus organization, pin configuration and functions, generation of control signals for
external operations- fetch, IO/M, read/write, machine cycles and bus timings. Addressing
modes, instruction set, instruction classification. Overview/concept of peripheral IC
interfacing with 8085 microprocessor (8251, 8253, 8255, 8279). Simple examples in
assembly language programming for 8085 (only for internal examination). Introduction to
development tools: IDE, cross assembler, builder, linker and debugger.( not required for
exam). Introduction to 8086 and comparison between 8086, 80286, 80386, 80486 and
Pentium.
Microcontrollers: 8051- features, architecture, memory organization, registers, I/O ports, pin
configuration and functions. Addressing modes, instruction set, instruction classification.
Assembly language programming. Interrupts in 8051. Timer/Counter programming:
Operating modes, time delay generation, Waveform generation. Serial communication: RS
232 interface, registers in UART, modes of operation, programming examples for serial data
transmission and reception. Interfacing of DIP switch, stepper motor, ADC, DAC, LEDs and
seven segment displays, alphanumeric LCD module with 8051.
Expected outcome:
The students will be able to:
1. Distinguish various types of processor architectures.
2. Describe architectures, memory organization of 8085 microprocessor and 8051.
3. Develop programming skills in assembly for interfacing peripheral devices with 8051
Text Books:
1. Kenneth J. Ayala, The 8051 Microcontroller, Cengage learning, 3/e.
2. Lyla B.Das : Microprocessors and Microcontrollers, Pearson Education, India, 2011
3. Ramesh S. Goankar. 8085 Microprocessors Archiecture Application and
Programming. Penram International, 5/e.
References:
1. Aditya P Mathur, Introduction to Microprocessor. Tata Mc Graw – Hill
2. Han Way Hung, “PIC Microcontroller, An introduction to software and hardware
interfacing “, Cenage learning.
3. I.Scott Mackenzie, Raphel C.-W Phan, The 8051 microcontroller, 4th edition.
4. Muhammed Ali Mazidi, The 8051 Microcontroller and Embedded Systems, Pearson
Education, 2nd edition
5. Nagoorkani, Microprocessors and Microcontrollers 2e, McGraw Hill Education India,
2012.
6. Soumitra Kumar Mandal. Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Architecture,
Programming & Interfacing Using 8085, 8086 and 8051, McGraw Hill Education
(2011).
7.
Course Plan
Module Course content End
Sem.
Hours
Exam
Marks
Microprocessors: Introduction, organization of a
microprocessor based system, evolution of microprocessors,
8085 architecture and its operation, microprocessor initiated
5 15
I operations and bus organization, pin configuration and
functions, generation of control signals for external operations-
fetch, IO/M, read/write.
Machine cycles and bus timings, Addressing modes, instruction
4
set instruction classification.
15
Overview/concept of peripheral IC interfacing with 8085
3
microprocessor (8251, 8253, 8255, 8279).
II
Simple examples in assembly language programming for 8085
2
(only for internal examination)
0
Introduction to development tools: IDE, cross assembler,
3
builder, linker and debugger.( not required for exam)
FIRST INTERNAL EXAM
Introduction to 8086 and comparison between
2
8086,80286,80386,80486 and Pentium
Microcontrollers: Introduction, comparison between
III 15
microprocessors and microcontrollers, microcontroller families,
6
8051- features, architecture, memory organization, registers,
I/O ports, pin configuration and functions.
Addressing modes, instruction set, instruction classification. 2
IV 15
Assembly language programming examples for 8051. 3
SECOND INTERNAL EXAM
Interrupts in 8051: Types, interrupt source, interrupt handling
2
and programming
Timer/Counter programming: Operating modes, time delay
2
V generation, Waveform generation. 20
Serial communication: RS 232 interface, registers in UART,
modes of operation, programming examples for serial data 2
transmission and reception
Interfacing: Interfacing (block schematic and assembly
language programming) of DIP switch, stepper motor, ADC,
VI 6 20
DAC, LEDs and seven segment displays, alphanumeric LCD
module with 8051.
END SEMESTER EXAM
Question Paper Pattern (End semester exam)
Max. Marks: 100 Time: 3 hours
The question paper shall consist of three parts. Part A covers modules I and II, Part B covers
modules III and IV, and Part C covers modules V and VI. Each part has three questions
uniformly covering the two modules and each question can have maximum four subdivisions.
In each part, any two questions are to be answered. Mark patterns are as per the syllabus with
80 % for theory and 20% for logical/numerical problems and programming.
Вам также может понравиться
- Microprocessors & their Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide to 8, 16 & 32 Bit Hardware, Assembly Language & Computer ArchitectureОт EverandMicroprocessors & their Operating Systems: A Comprehensive Guide to 8, 16 & 32 Bit Hardware, Assembly Language & Computer ArchitectureРейтинг: 1 из 5 звезд1/5 (1)
- EC305 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersS5-EC-Syllabus PDFДокумент3 страницыEC305 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersS5-EC-Syllabus PDFHKОценок пока нет
- EC305 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersS5-EC-SyllabusДокумент3 страницыEC305 Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersS5-EC-SyllabusshafinshamsudheenОценок пока нет
- CS305 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers PDFДокумент2 страницыCS305 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers PDFlaraОценок пока нет
- EE309 Microprocessors and Embedded SystemsДокумент2 страницыEE309 Microprocessors and Embedded SystemsSarin C. R EeeОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University Electronics (10), Electronics & Communication (11), Electronics & Telecommunication EngineeringДокумент3 страницыGujarat Technological University Electronics (10), Electronics & Communication (11), Electronics & Telecommunication Engineeringhiren456789Оценок пока нет
- Ae305 Microprocessors Microcontrollers PDFДокумент2 страницыAe305 Microprocessors Microcontrollers PDFCharlotte DunkenОценок пока нет
- 8086 CourseoutlineДокумент3 страницы8086 CourseoutlineBiruk DawitОценок пока нет
- Microcontrollers 8051-Notes For IV Sem StudentsДокумент60 страницMicrocontrollers 8051-Notes For IV Sem StudentsDr Ravi Kumar A.VОценок пока нет
- EMPДокумент2 страницыEMPAvinash SamuelОценок пока нет
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersДокумент3 страницыMicroprocessors and MicrocontrollersNathanОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 5Документ5 страницGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 5Keval PatelОценок пока нет
- 3 CS305 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Slot CДокумент2 страницы3 CS305 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers Slot CBinesh RBОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor PDFДокумент3 страницыMicroprocessor PDFmkrajasekarОценок пока нет
- BPS Cse3aДокумент2 страницыBPS Cse3aPrasanthОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerДокумент2 страницыMicroprocessor and Microcontrollershimi rejiОценок пока нет
- M P I SllybusДокумент2 страницыM P I SllybusVipul RamolaОценок пока нет
- MPMCДокумент1 страницаMPMCSurya RОценок пока нет
- Mahendra Engineering College Syllabus: V SemesterДокумент3 страницыMahendra Engineering College Syllabus: V SemesterJ.Gowri ShankarОценок пока нет
- EE309 Microprocessors and Embedded Systems-ModifiedДокумент2 страницыEE309 Microprocessors and Embedded Systems-Modifiedanto5751Оценок пока нет
- Syllabus MicrocontrollerДокумент3 страницыSyllabus MicrocontrollerharshithaОценок пока нет
- 125 - EC8691 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusДокумент2 страницы125 - EC8691 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusAjeethОценок пока нет
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 4Документ4 страницыGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 4Er Umesh ThoriyaОценок пока нет
- Cse MP&MC SyllabusДокумент5 страницCse MP&MC SyllabusSenthilraja BОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor Applications and InterfacingДокумент4 страницыMicroprocessor Applications and InterfacingALBERTОценок пока нет
- MP&MCДокумент2 страницыMP&MCAnbalagan GОценок пока нет
- Ee6502 MM QB2Документ81 страницаEe6502 MM QB2senthilkumarОценок пока нет
- 5 - Microprocessors and InterfacingДокумент1 страница5 - Microprocessors and Interfacingsrikaanth3811Оценок пока нет
- 13A04601Документ1 страница13A04601RevanthkumarОценок пока нет
- 8051 MC 2010Документ7 страниц8051 MC 2010Vikram RaoОценок пока нет
- Government Polytechnic, Nagpur. Course Curriculum: Teaching SchemeДокумент41 страницаGovernment Polytechnic, Nagpur. Course Curriculum: Teaching SchemeAkhilesh PandeОценок пока нет
- Microprocessor PDFДокумент3 страницыMicroprocessor PDFfareedaОценок пока нет
- Ec302T Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerДокумент6 страницEc302T Microprocessor and Microcontrollergoons7777Оценок пока нет
- MP Notes 1675143848Документ80 страницMP Notes 1675143848gokul docОценок пока нет
- ECE Sem 5 SyllabusДокумент2 страницыECE Sem 5 SyllabusDaksh SharmaОценок пока нет
- MPMC Lecture ScheduleДокумент2 страницыMPMC Lecture ScheduleAmy OliverОценок пока нет
- (D) IC206 MicrocontrollersДокумент2 страницы(D) IC206 MicrocontrollersAbhilash ManjulОценок пока нет
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Course DescriptionДокумент7 страницDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering Course DescriptionDurga SravanthiОценок пока нет
- CS305 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers CSE Syllabus Semesters - 5Документ4 страницыCS305 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers CSE Syllabus Semesters - 5Sreejith KarunakaranpillaiОценок пока нет
- 2152006Документ3 страницы2152006Mohamed Ismail FiazОценок пока нет
- EC8691-MPMC SyllabusДокумент2 страницыEC8691-MPMC SyllabusBalaji SriОценок пока нет
- MPMC SyllabusДокумент2 страницыMPMC SyllabusfeminaОценок пока нет
- A/d and D/a Convertor Digital TechnicsДокумент6 страницA/d and D/a Convertor Digital Technicskaran007_m100% (1)
- CO Adv Microprocessor UMДокумент3 страницыCO Adv Microprocessor UMstella nОценок пока нет
- MPДокумент2 страницыMPNidhi MishraОценок пока нет
- 1-Ee8551-Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersДокумент2 страницы1-Ee8551-Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersKeerthana SahadevanОценок пока нет
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersДокумент2 страницыMicroprocessors and Microcontrollersmdivya569Оценок пока нет
- Ece IV Microcontrollers (10es42) NotesДокумент124 страницыEce IV Microcontrollers (10es42) NotesManojKumarОценок пока нет
- MP I SyllabusДокумент2 страницыMP I SyllabusjravieceОценок пока нет
- MicroprocessorДокумент2 страницыMicroprocessorKiran TimsinaОценок пока нет
- Ec8691 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers L T P C 3 0 0 3Документ1 страницаEc8691 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers L T P C 3 0 0 3VEL TECHОценок пока нет
- Lesson Plan MPIДокумент3 страницыLesson Plan MPIRaghava RaghuОценок пока нет
- 125 - EE8551 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabusДокумент2 страницы125 - EE8551 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers - Anna University 2017 Regulation SyllabuszakreaОценок пока нет
- MALPДокумент5 страницMALPjainamshahОценок пока нет
- MPMCДокумент2 страницыMPMCpriyaОценок пока нет
- Cat-352 MP Unit 3.1Документ23 страницыCat-352 MP Unit 3.1Ashish YadavОценок пока нет
- Course Name: Computer Engineering Group Course Code: Co/Cm/If/Cd Semester: Fourth Subject Title: Microprocessor and Programming Subject Code: 9065Документ5 страницCourse Name: Computer Engineering Group Course Code: Co/Cm/If/Cd Semester: Fourth Subject Title: Microprocessor and Programming Subject Code: 9065Aryan JaiswalОценок пока нет
- Ec8691 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers L T P CДокумент1 страницаEc8691 Microprocessors and Microcontrollers L T P CRaja SekarОценок пока нет
- Lession Plan 50Документ9 страницLession Plan 50dukeОценок пока нет
- Prerequisite: EC207 Logic Circuit DesignДокумент2 страницыPrerequisite: EC207 Logic Circuit DesignplbonifusОценок пока нет
- EC205 Electronic Circuits PDFДокумент2 страницыEC205 Electronic Circuits PDFplbonifusОценок пока нет
- EC204 Analog Integrated Circuits PDFДокумент2 страницыEC204 Analog Integrated Circuits PDFplbonifusОценок пока нет
- EC203 Solid State Devices PDFДокумент2 страницыEC203 Solid State Devices PDFplbonifus100% (1)
- ANALOG CIRCUITS 18EC42 (Module - 5)Документ27 страницANALOG CIRCUITS 18EC42 (Module - 5)mahendra naik82% (11)
- Computador Tipo 2 M75S Gen 2 Ryzen 7 4750G 11JAS0RU00Документ1 страницаComputador Tipo 2 M75S Gen 2 Ryzen 7 4750G 11JAS0RU00cesar624Оценок пока нет
- Taotronics Headphones TT-BH079 - User-ManualДокумент3 страницыTaotronics Headphones TT-BH079 - User-ManualatubellaОценок пока нет
- Service Manual: EnglishДокумент18 страницService Manual: EnglishAlberto MoralesОценок пока нет
- FortiOS 6.2.0 AWS CookbookДокумент240 страницFortiOS 6.2.0 AWS CookbookCarole ShuОценок пока нет
- Computer HardwareДокумент33 страницыComputer Hardwareahmad ryanОценок пока нет
- Ge6151 Computer Programming All Five UnitsДокумент159 страницGe6151 Computer Programming All Five UnitsMonica EstherОценок пока нет
- Asynchronous (Serial, CommunicationДокумент2 страницыAsynchronous (Serial, CommunicationS.Ramesh rajaОценок пока нет
- Elec CommsДокумент1 страницаElec Commsseia deirahОценок пока нет
- Ec PBL FinalДокумент11 страницEc PBL FinalAli Shan AhmadОценок пока нет
- Monitor LED HP E223 21.5 4AA7-0717EEEДокумент4 страницыMonitor LED HP E223 21.5 4AA7-0717EEEddmaciaseОценок пока нет
- Fuji Frn3.7e1s-2j (204-217) PDFДокумент14 страницFuji Frn3.7e1s-2j (204-217) PDFMadison MadisonОценок пока нет
- Stand-Alone Installations and Upgrades: Oracle Primavera P6 V7.0Документ19 страницStand-Alone Installations and Upgrades: Oracle Primavera P6 V7.0Muhammak SKОценок пока нет
- Ohmeda4700 PDFДокумент1 страницаOhmeda4700 PDFGiovanny CedeñoОценок пока нет
- 2G Mobile Communication SystemsДокумент66 страниц2G Mobile Communication SystemsHossein HosseinpourОценок пока нет
- Grade 11-Q1 - W4-PCO-2Документ28 страницGrade 11-Q1 - W4-PCO-2Juren Andrew NievesОценок пока нет
- Effects of The Deduplication/Compression Function in Virtual PlatformsДокумент17 страницEffects of The Deduplication/Compression Function in Virtual PlatformsHung Do MinhОценок пока нет
- Features ApplicationsДокумент13 страницFeatures ApplicationsVinicius Mastelaro RodriguesОценок пока нет
- E560 Cmu80 CSДокумент4 страницыE560 Cmu80 CSCosmic Garash 2Оценок пока нет
- KU BAND MICROWAVE POWER AMPLIFIER Using AWRДокумент81 страницаKU BAND MICROWAVE POWER AMPLIFIER Using AWRKrishna PrasadОценок пока нет
- Fabrication Techniques of A PN Junction DiodeДокумент5 страницFabrication Techniques of A PN Junction DiodeNida Amber100% (3)
- Research On Key Technology in SaaSДокумент4 страницыResearch On Key Technology in SaaSeyetea68Оценок пока нет
- EEE310 11 Performance of Digital Communcation Systems PDFДокумент35 страницEEE310 11 Performance of Digital Communcation Systems PDFSupipi HiyadmaОценок пока нет
- Microprocessors and Microsystems: Prateek Sikka, Abhijit R Asati, Chandra ShekharДокумент8 страницMicroprocessors and Microsystems: Prateek Sikka, Abhijit R Asati, Chandra ShekharBhargav BhatОценок пока нет
- BetagageДокумент2 страницыBetagageHans CohnОценок пока нет
- Torex 4 Brochure - FINALДокумент24 страницыTorex 4 Brochure - FINALslimer777Оценок пока нет
- MU Patch Cable Spec SheetДокумент2 страницыMU Patch Cable Spec SheetMohan KОценок пока нет
- Programming The PIC16F877 in PIC MPASM Assembly LanguageДокумент28 страницProgramming The PIC16F877 in PIC MPASM Assembly Languagefarhan ghafoorОценок пока нет
- Information Systems For ManagersДокумент2 страницыInformation Systems For ManagersMbacasestudyhelpОценок пока нет
- 4th Assessment ExamДокумент3 страницы4th Assessment ExamDhealine JusayanОценок пока нет