Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Press Tool Theory One Marks Q & A
Загружено:
Santosh PapleИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Press Tool Theory One Marks Q & A
Загружено:
Santosh PapleАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
GOVT.
TOOL ROOM & TRAINING CENTRE
HARIHAR
PRESS TOOL THEORY – II
2019
(ONE MARKS QUESTIONS )
COMPILED BY :
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR (GTTC HARIHAR)
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
Fill in the blanks:
1) Press tools are generally ---------- working process.
Ans : COLD.
2) Shaving & trimming are ---------- operations.
Ans : SECONDARY.
3) Two or three side cutting and one side bending is called as --------.
Ans : LANCING.
4) The size of a standard cut-band is --------.
Ans : 1/3RD OF SHEET THICKNESS.
5) The space per side between the punch and die is called --------.
Ans : CLEARANCE
6) Press tools are suitable for -------- components.
Ans : SHEET METAL
7) In optimum cutting condition the cut band will be -------- of sheet thickness.
Ans : 1/3RD OF SHEET THICKNESS
8) Broaching is an --------- cutting operation.
Ans : GRADUAL
9) Cutting clearance is expressed as ---------.
Ans : MM PER SIDE
10) The male part of a tool is called --------.
Ans : PUNCH.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 2
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
11) The operation of cutting desired shape of component with the help of die
is called --------
Ans : BLANKING .
12) The space per side between the punch and die is called ---------...
Ans : CLEARANCE.
13) The plate which holds the punches is called --------..
Ans : PUNCH PLATE.
14) For sheet thickness less than 1mm we use --------- type of stripper.
Ans : FLOATING OR SPRING LOADED .
15) Cutting clearance can be calculated by the formula --------..
Ans : C/2=0.01 X √ fs XT .
16) Shear strength of material is expressed in -----------..
Ans : KG/MM²
17) Punches that performs both cutting and non cutting are known as -------
punches.
Ans : HYBRID
18) IS codification for HcHcr material is given by --------..
Ans : T215 CR12 W90
19) For sheet thickness less than 1mm we use --------- type of stripper.
Ans : FLOATING OR SPRING LOADED
20) Slender punches are supported with -------- for performing efficient action.
Ans : QUILLS
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 3
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
21) During bending, --------- direction is to be observed carefully.
Ans : GRAIN
22) --------- are used to remove components from compound dies.
Ans : SHEDDERS .
23) The curved neutral plane of the bend area is called ----------..
Ans : BEND ALLOWANCE .
24) CRGO stands for…...
Ans : COLD ROLLED GRAIN ORIENTED .
25) The outer layer of a bent component is subjected to -------- stress..
Ans : TENSION.
26) Shear strength of material is expressed in -----------..
Ans : KG/MM².
27) Spring-loaded strippers are also called---------- strippers ..
Ans : PRESSURE PAD .
28) Wrinkles are formed when the blank holding force is ---------...
Ans : LESS
29) The most favourable condition for a bend exists when the axis of the bend is ---
------ to the grain direction .
.Ans : PERPENDICULAR
30) ------- are used to control the metal flow in draw dies.
Ans : DRAW BEADS
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 4
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
31) Corner setting is a method to prevent ---------..
Ans : SPRING BACK
32) During bending operation, ---------- remains unaffected.
Ans : NEUTRAL AXIS OR PLANE
33) Full form of OBI is-------.
Ans : OPEN BACK INCLINABLE
34) The components produced from ---------- will have burrs on only one side of the
component.
Ans : COMPOUND TOOL.
35) Cutting force can be reduced by ---------- on the face of the punch.
Ans : PROVIDING SHEAR ANGLE .
36) During bending, the inner layers are subjected to-----------..
Ans : COMPRESSION .
37) During bending operation, ---------- remains unaffected
Ans : NEUTRAL AXIS OR PLANE .
38) The full form of CRCA is ----------.
Ans : COLD ROLLED CLOSED ANNEALED .
39) The reciprocating member of the press is called--------------...
Ans : PRESS RAM .
40) ----------operation cuts out various shapes from the edge of work piece material
Ans : NOTCHING
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 5
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
41) Punch back is also called as----------
Ans : THRUST PLATE
42) Bottom plate is also called as-----------..
Ans : BASE PLATE OR DIE SHOE OR BOLSTER PLATE
43) Dowels are used for----------.
Ans : LOCATION
44) . Screw are used for---------.
Ans : CLAMPING
45) Fine blanking tools must be loaded on------------
Ans : TRIPPLE ACTION HYDRAULIC PRESS
46) In fine blanking tool “V” project ring is called-----------.
Ans : IMPINGERS.
47) Normally the clearance between punch and die in a fine blanking tool is a----.
Ans : 0.007 MICRONS (INSUFFICIENT) .
48) To prevent the punches from penetration into the top plate ------------is used
Ans : PUNCH BACK PLATE .
49) Direct pilots are sometimes called as---------.
Ans : PUNCH PILOTS .
50) The power source of fly press is-------------.
Ans : FLY WHEEL
51) To remove components from a compound die----------is used.
Ans : SHEDDERS
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 6
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
52) All partial cutting punches (notching etc) will have----------.
Ans : HEEL
53) Lancing is the best example for ---------- type of punch.
Ans : HYBRID
54) The curved neutral plane of the bend area is called----------.
Ans : BEND ALLOWANCE
55) In drawing ------------ is used to prevent wrinkles in drawing operation.
Ans : DRAW BEADS
56) Process of purposely reduction in wall thickness is called as----------.
Ans : IRONING
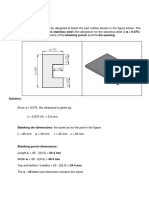
57) Formula of calculating blank diameter in drawing is------------.
Ans : D=√d²+4dh
58) ----------- is used for supporting slender punches.
Ans : QUILL
59) Heel should be provided on all --------------- punches.
Ans : PARTIAL CUTTING PUNCHES
60) Insufficient clearance results in -----------type of burr.
Ans : COMPRESSIVE BURRS
61) ----------types of die blocks are ideal for complicated die profiles.
Ans : SPLIT DIES
62) ------------type of die set is best suited for compound tools.
Ans : CENTER PILLAR
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 7
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
63) ------------is provided in die to have a free fall of the components.
Ans : DRAFT OR ANGULAR CLEARANCE
64) In ----------tools components are produced without fracture.
Ans : FINE BLANKING TOOL
65) Planishing tools are used to ----------- in the sheet.
Ans : RELIEVE INTERNAL STRESS
66) Angular clearance is also called as----------.
Ans : DRAFT
67) Generally the land portion in a die will be around ----------mm.
Ans : 3-5MM
68) Tools which perform only one operation are called as-----------.
Ans : STAGE TOOLS
69) Utilization factor is expressed in term of -------------.
Ans : PERCENTAGE
70) Generally center pillar die set is used for ----------tools.
Ans : COMPOUND
71) ----------is used to position the stock as it is initially fed into the die.
Ans : PILOTS
72) If blank holder pressure is increased -----------defect occurs.
Ans : THINNING
73) If draw radius is more than the specified---------------defect occurs.
Ans : WRINKLING
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 8
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
74) If the alignment between draw punch and die is improper -----------occurs on
cup edge.
Ans : SCORE MARKS
75) When cutting and non-cutting operation is performed in the same tool, it is
called as -------------- tool.
Ans : COMBINATION TOOL
76) Uniform shaping of sheet metal along a straight axis is called ----.
Ans : BENDING
77) For fine blanking ---------- press is used.
Ans : TRIPPLE ACTION HYDRAULIC PRESS
78) Formula to determine the bend allowance is -----------.
Ans : B=A/180 π(R+KT)
79) For intricate profiles --------------- dies are easy to make.
Ans : SPLIT DIES
80) Bending is a ---------------- type of operation.
Ans : NON CUTTING OPERATION
81) Punch plate is made up of ------------ material.
Ans : MILD STEEL
82) In drawing operation the number of draws is calculated by the ratio of ------------
.Ans : h/d
83) Bending involves ------------ type of operation.
Ans : NON CUTTING OPERATION
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 9
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
84) ------------- material used for making a cutting punch.
Ans : HIGH CARBON HIGH CHROMIUM STEEL (HCHCR)
85) ----------- die used for both cutting and non-cutting operations.
Ans : COMBINATION
86) The curved neutral plane of the bend area is called ----------.
Ans : BEND ALLOWANCE
87) The outer layer of a bent component is subjected to --------- stress.
Ans : TENSIONAL
88) ------------- is used in the fine blanking tools to grip the strip before blanking.
Ans : IMPINGERS( INVERTED V PROJECTIONS)
89) The curved neutral plane of the bend is subjected to -------- stress.
Ans : COMPRESSIONAL
90) ----------- is provided on draw punch to allow entrapped air to escape.
Ans : AIR VENT( AIR HOLE)
91) The holding force on the strip is provided by ------------- in fine blanking tool.
Ans : IMPINGERS
92) The die that performs both cutting & non-cutting operations is known as ---------
Ans : COMBINATION DIES
93) ------------- is the axis in bent component, where compression & tensions are nil.
Ans : NEUTRAL AXIS
94) Edge bending is also called as ----------.
Ans : WIPPING
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 10
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
95) Full form of EDD sheets is ----------.
Ans : EXTRA DEEP DRAWING STEEL
96) Forming is shaping of sheet metal along the -----------.
Ans : CURVED
97) Press slide is also called as --------.
Ans : PRESS RAM
98) Lancing and louvering is a ------------- type of press tool operation.
Ans : HYBRID
99) In bending the metal flow is uniform along the bend axis with inner surface in
------------- and outer surface in ---------------.
Ans : COMPRESSION AND TENSION
100) Draw punch is made up of ------------------ material.
Ans : OHNS
101) During drawing metal is made to flow ------------ by applying the required force.
Ans : PLASTICALLY(PLASTIC DEFORMATION)
102) The expansion of COP is------------.
Ans : CENTRE OF PRESSURE
103) The stock strip is held firmly by ---------------- in a fine blanking tool.
Ans : IMPINGERS
104) ---------- sheds the component from the die of a compound tool.
Ans : SHEDDER
105) Heel is provided on all -------------- punches.
Ans : PARTIAL CUTTING
106) Corner setting is a method to prevent -------------.
Ans : SPRING BACK
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 11
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
107) Components produced from ----------------- dies will have burr on only one side.
Ans : COMPOUND TOOL
108) ------------------- layer of a bent component is subjected to compression.
Ans : INNER
109) The IS designation of punch and die material is ------------.
Ans : AIR VENT
110) Heel is provided to---------punches.
Ans : PARTIAL CUTTING
111) Reciprocating member of the press machine is called--------------.
Ans : RAM
112) Expanded form of C.R.G.O is----------.
Ans : COLLED ROLLED GRAIN ORIENTED
113) In blanking clearance is given to--------.
Ans : BLANKING PUNCH
114) Metal flow is observed in----------operation.
Ans : NON CUTTING
115) Component produced from ----------tool will have burrs on both sides.
Ans : PROGRESSIVE TOOL
116) In bending corner setting is done to minimize-----------.
Ans : SPRING BACK
117) Component produced from-----------will have burrs on one side only.
Ans : COMPOUND TOOL
118) Internal forming is also called as-----------.
Ans : BULGING
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 12
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
119) Bending should be done-----------to grain direction.
Ans : PERPENDICULAR
120) In draw tool-------is incorporated to relieve stress from sheet material.
Ans : DRAW BEADS
121) Impingers are used in-------------dies.
Ans : FINE BLANKING
122) Expanded form of E.D.D.is------------.
Ans : EXTRA DEEP DRAWING
123) The location of shank is determined by calculating--------.
Ans : CENTRE OF PRESSURE ( COP )
123) If draw radius is more than the specified---------------defect occurs.
Ans : WRINKLES.
124) If the alignment between draw punch and die is improper -----------occurs on
cup edge.
Ans : SCORE MARKS
125) The operation of converting a flat blank into cup or shell is called as -------.
Ans : DRAWING
126) Shaping of material in curved axis is called as -------.
Ans : FORMING
127) Before and after bending operation ------- remains unchanged.
Ans : SHEET THICKNESS
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 13
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
128) ------- is varied after forming operation is performed on a sheet material.
Ans : SHEET THICKNESS
129) The operation of producing an elevated surface on one face and a depressed
surface on the other surface of sheet material is called as -------.
Ans : EMBOSSING
130) The operation of cold working done in press tool is called as --------.
Ans : COINING
131) The operation of producing of coins , medals is called as ------.
Ans : COINING
132) -------- is an internal forming operation
Ans : BULGING
133) The bulging media used in bulging operation will flow , but not ---------
Ans : COMPRESS
134) -------- is an operation of rolling the edges of sheet material .
Ans : CURLING
135) Flanging is also called as --------.
Ans : FLARING
136) Swaging is also called as -------- .
Ans : NECKING
137) Segregated punches are also called as --------.
Ans : SELF MOUNTED
138) Plain punches are also called as -------- punches.
Ans : HEADLESS
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 14
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
139) Integtated punches are depended on ------ plate for mounting.
Ans : PUNCH PLATE OR PUNCH HOLDER
140) In combination tool ------ type of die is used.
Ans : CONVENTIONAL
141) In combination tool ----- & ------ operations are performed in single stage.
Ans : CUTTING & NON-CUTTING
142) In compound tool , ------- type of die is used.
Ans : INVERTED
143) Fine blanking is a process of producing components without --------.
Ans : FRACTURE
144) In fine blanking tool , the clearance between punch & die is --------
Ans : 0.007 µ OR MICRONS ( INSUFFICIENT CLEARANCE)
145) Inverted V- used to grip the strip in --------- tool.
Ans : IMPINGERS
146) Impingers are made up of --------------- material.
Ans : OHNS
147) In conventional blanking the component produced has a defect called as -----.
Ans : DISHING
148) In fine blanked components ------------ cut bands are observed
Ans : TWO OR DOUBLE
149) The radius of the inner arc of the bend to extreme positions of the bend is
called as ------------.
Ans : BEND RADIUS
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 15
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
150) The angle included between the originates at the bend axis is called as------.
Ans : BEND ANGLE
151) . The area included within the bend angle is called ----------.
Ans : BEND AREA
152) . The imaginary lines created by the tangency of the bend radius with the inner
flat surfaces is called as ------------.
Ans : BEND LINES
153) The theoretical plane which does not undergo tension or compression during
bending is called ------------.
Ans : NEUTRAL PLANE
154) The curved neutral plane of the bend area is called as -----------.
Ans : BEND ALLOWANCE
155) The edge bending is also called as ----------.
Ans : WIPING
156) In ------ bending, included angle of the component and the bend angle are
same.
Ans : 90° OR RIGHT ANGLE
157) During bending, ------------- has to considered.
Ans : GRAIN DIRECTION
158) For multiple bends, --------------- type of sheet are used.
Ans : ANGULAR GRAIN
159) Bending should be performed --------- to grain direction of the sheet material.
Ans : PERPENDICULAR
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 16
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
160) The method of squeezing the metal in the corners to avoid spring back is
called as -------.
Ans : COINING
161) The formula to calculate V-bending force is ----------.
Ans : VBv =1.33 X LT²/W
162) The formula to calculate U-bending force is ----------.
Ans : UBv =2.66 X LT²/W
163) The formula to calculate wiping force is ----------.
Ans : WBv =0.68 X LT²/W
164) The radius provided on a draw punch is ----------- times of its sheet thickness.
Ans : 4T – 6T
165) The radius provided on a draw die is ----------- times of its sheet thickness.
Ans : 6T – 8T
166) During drawing, less blank holding force results in ----- on the drawn cup or
shell.
Ans : WRINKLING
167) Steep reduction in the thickness of the drawn cup is called ----------.
Ans : THINNING
168) Splitting of the wall surface of the finished component in drawing is called as
-------.
Ans : CRACKING
169) Deformation of the material into ups & downs on the edges of drawn cup or
shell is called as -----.
Ans : WRINKLING
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 17
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
170) Ups and downs formed on inner walls of drawn cup or shell is called as -------.
Ans : PUCKERING
171) Marks formed on the component due to fouling or misalignment between
punch and die in drawing is called as ----------.
Ans : SCORE MARKS
172) Projections observed on a rectangular cup or shell is called as ----------.
Ans : EARRING
173) High blank holding force, during drawing results in ----------- defect.
Ans : THINNING
174) Draw beads acts as ------------ on the roads.
Ans : SPEED BREAKERS
175) Draw beads are used to control ------------ during drawing
Ans : METAL FLOW IN DIE
176) Draw beads are made up of ------------- material.
Ans : SILVER RODS OR OHNS
177) Draw beads increases ----------- property of the material.
Ans : DUCTILITY ( ELONGATION )
178) ---------- beads are used for low or medium drawing operation .
Ans : SHALLOW BEADS
179) For deep drawing operations ------------ beads are more suitable.
Ans : DEEP BEADS
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 18
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
180) For Very deep drawing operations ------------ beads are more suitable.
Ans : TANDEM BEADS
181) --------------- formula is used to calculate blank diameter when the ratio of the
d/r is less than 10 and more than 15.
Ans : D=√d²+4dh – 0.5 r
182) . --------------- formula is used to calculate blank diameter when the ratio of the
d/r, is less than 20 and more than 15.
Ans : D=√d²+4dh - r
183) --------------- formula is used to calculate blank diameter when the ratio of the
d/r is more than 20.
Ans : D=√d²+4dh
184) Reduction percentage is calculated by -----------
Ans : D – d/D X 100
185) Draw ratio is calculated by ---------------.
Ans : h/ d
186) Draw force is calculated by --------------- formula
Ans : VD = ᴨDT ( D/d – 0.6 ) fy
187) ------------ holes are provided on draw punch for escaping of air from the draw
dies.
Ans : AIR VENT
188) The diameter of the draw beads is -------------- times its sheet thickness
Ans : 6T
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 19
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
I. Multiple choice questions:
1. Tools which perform only one operation are called ---------
a) Single stage tool c) double stage tool
b) Progressive tool d) none of these.
Ans : FINE BLANKING
2. Angular clearance is also called ----------.
a) Draft c) pilot
b) Punch d) pitch.
Ans : DRAFT
3. Pitch punch is a kind of ---------.
a) Non cutting punch c) notching punch
b) Pilot -punch d) hybrid punch.
Ans : NOTCHING
4. C.O.P. is essential for mounting the ---------.
a) Pilot c) shank
b) Die block d) guide pillar.
Ans : CENTRE OF PRESSURE
5. Knockout is used in ----------.
a) Progressive tool c) simple tool
b) Compound tool d) rubber tool.
Ans : COMPOUND TOOL
6. It is the process of making hole in a component with the help of die
is known as ---------.
a) Piercing c) notching
b) Blanking d) none.
Ans : PIERCING
7. A set consisting of a lower shoe, upper shoe, guide pillars and
bushes is called ---------.
a) Die set c) die stop
b) Punch set d) none.
Ans : DIESET
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 20
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
8. The minimum angle of angular clearance is ---------.
0
a) 2 c) 60
0
b) 6 d) 80
Ans : 2°
9. Knockout is used in---------.
a) progressive tool c) stage tool
b) compound tool d) rubber tool.
Ans : COMPOUND TOOL
10. It is as operation of removing the workpiece or material from
around the punch ---------.
a) Bending c) forming
b) Stripping d) registering.
Ans : STRIPPING
11. In piercing , clearance is given to the --------- .
a) Die c) punch
b) Stripper d) guide plate.
Ans : DIE
12. IS codification for the material of the die is ---------.
a) st-42 c) HcHcr
b) cast iron d) MS
Ans : HCHCR
13. --------- is used to register the stock while feeding.
a) Pilot c) pitch punch
b) Guide pillar d) none of the above.
Ans : PILOT
14. Washers are accurately produced from --------- tool.
a) Blanking tool c) notching tool
b) Piercing tool d) compound tool
Ans : COMPOUND TOOL
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 21
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
15. The distance between the top face of the top plate and bottom
face of the bottom plate is called ---------.
a) Shut height c) total height
b) Day light d) all of the above.
Ans : SHUT HIEGHT
16. In piercing operation, clearance should be --------- to the piercing
die opening size.
a) Added c) constant
b) Subtracted d) divided.
Ans : ADDED
17. Length of the pilot must be --------- than the length of the punch.
a) Shorter c) longer
b) Equal d) half.
Ans : LONGER
18. Deep drawing can be achieved by--------- press.
a) Pneumatic c) hydraulic
b) Mechanical d) knuckle joint.
Ans : HYDRAULIC
19. Half hardened material can be bent upto ---------.
a) 450 c) 900
0
b) 180 d) 3600.
Ans : 45°
20. Draw ratio is ---------.
a) d/h c) h/d
b) h/t d) h/d2 .
Ans : h/d
21. -------- Type of tool is used to produce cups or shell type of
components.
a) Drawing tool c) bending tool
b) Blanking tool d) swaging tool.
Ans : DRAWING TOOL
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 22
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
22. The curved neutral plane of the bend area is called ---- allowance.
a) Bend c) neutral
b) Draw d) none of these.
Ans : BEND
23. The blank holder pressure must be used to prevent ---------.
a) Wrinkling c) thinning
b) Tearing d) fracture.
Ans : WRINKLING
24. Draw die is made up of ---------.
a) Cast iron c) mild steel
b) HcHcr d) none of these.
Ans : HCHCR
25. --------- Type of tool is used to produce cups or shell type of
components.
a) Drawing tool c) bending tool
b) Blanking tool d) swaging tool
Ans : DRAWING TOOL
26. Bending operation is performed as an ---------.
a) Cutting operation c) non-cutting operation
b) Piercing operation d) none of the above.
Ans : NON CUTTING OPERATION
27. Punch plate is made up of ---------.
a) Mild steel c) cast iron
b) High speed steel d) none of the above.
Ans : MILD STEEL
28. Grain direction can be considered in ---------.
a) Blanking operation c) curling operation
b) Notching operation d) bending operation.
Ans : BENDING OPERATION
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 23
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
29. In drawing operation the number of draws is calculated by the
ratio of ---------.
a) D/d c) d/D
b) D-d/2 d) none of the above.
Ans : NONE OF THE ABOVE
30. In bending corner setting is done to minimize ---------.
a) Spring back effect c) thinning effect
b) Wrinkling effect d) none of the above.
Ans : SPRING BACK EFFECT
31. The usage of V-ring comes in --------- tool.
a) Blanking tool c) stage tool
b) Fine blanking tool d) compound tool.
Ans : FINE BLANKING TOOL
32. --------- type of material are suitable for intricate profiles.
a) T215Cr12W90 c) T2.15Cr12W90
b) St -42 d) T21.5Cr12W90
Ans : T215 Cr12 W90
33. The full form of EDD is ---------.
a) Extra developed drawing c) elaborated deep drawing
b) Extra deep drawing d) extra deep draw.
Ans : EXTRA DEEP DRAWING STEEL
34. Fit between bottom plate and pillar ---------.
a) H7/g6 c) H7/n6
b) H6/f7 d) H7/p6.
Ans : H7/P6
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 24
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
35. Bending operation on a press is performed---------.
a)Parallel to direction of grains c) perpendicular to direction of
grains
a) At any angle to the grains d) none of these.
Ans : PERPENDICULAR TO DIRECTION OF GRAINS
36. The curved neutral plane of the bend area is called---- allowance.
a) Bend c) draw
b) Neutral d) none of these.
Ans : BEND
37. Stripping force ranges between ---------.
a) 30 to 40% c) 5 to 20%
b) 50 to 60% d) nil
Ans : 5 to 20%
38. Draw die is made up of ---------.
a) Cast iron c) HcHcr
b) Mild steel d) none of these.
Ans : HCHCR
39. In drawing operation the blank holder force (F) is given by ---------.
a) F=P c) F=2P
b) F=p/3 d) none of these.
Ans : F = P/3
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 25
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
This set of Manufacturing Engineering Multiple Choice Questions &
Answers (MCQs) focuses on “Shearing Operations”.
1. Punching a number of holes in a sheet is known as?
a) Perforating
b) Parting
c) Notching
d) Lancing
Answer: a
2. Shearing the sheet into two or more pieces is known as?
a) Perforating
b) Parting
c) Notching
d) Lancing
Answer: b
3. Removing the pieces from the edge in shearing operation is known as?
a) Perforating
b) Parting
c) Notching
d) Lancing
Answer: c
4. Leaving a tab without removing any material is known as?
a) Perforating
b) Parting
c) Notching
d) Lancing
Answer: d
5. Moving a small straight punch up and down rapidly into a die is done by a
process known as?
a) Perforating
b) Parting
c) Nibbling
d) Lancing
Answer: c
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 26
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
6. As the thickness of sheet is increased the clearance needed will also?
a) Increase
b) Decrease
c) No effect
d) First decrease then increase
Answer: a
7. Beveling is particularly suitable for shearing of?
a) Thin blanks
b) Thick blanks
c) Very thin blanks
d) None of the Mentioned
Answer: b
Explanation: Beveling is particularly suitable for shearing of thick blanks.
8. Which of the following is a type of die?
a) Simple dies
b) Progressive dies
c) Compound die
d) All of the Mentioned
Answer: d
9. Which of the following die can perform multiple operations such as blanking,
punching, notching etc.?
a) Simple dies
b) Progressive dies
c) Compound die
d) None of the Mentioned
Answer: b
10. As the clearance increases, the punch force required?
a) Decreases
b) Increases
c) Remains same
d) First increases then decrease
Answer: a
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 27
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
II) Match the following:
A B
1. Land a) reduce cutting force
2. Angular clearance b) 1/3rd of sheet thickness
3. Finger stopper c) bottom plate
4. Large radius on the d) centre of pressure
Component
5. Cut band e) 2 times the sheet thickness
6. Single fracture f) stage stopper
7. Penetration g) excessive cutting clearance
8. Shear on the die h) prevents stacking of components
9. C.O.P. i) shearing action
10. Die shoe j) optimum clearance
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
e h f g b j i a d c
II) Match the following:
A B
1. Stripping force a) shank position
2. Hybrid punch b) flattening sheet
3. Peening punch c) more clearance
4. C.O.P. d) 20% of shear force
5. Curling tool e) to reduce press overloading
6. Shear angle f) less clearance
7. Case hardened steel g) to produces hinges
8. Multiple burnished land h) both cutting & non cutting
9. More edge radius i) mounting method of punch
10. Planishing j) pillars & bush
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
d h i a g e j f c b
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 28
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
II) Match the following:
A B
1. Embossing a) absolute flatness
2. Shaving b) angular clearance
3. Curling c) T215Cr12W90
4. flanging d) strengthen raw edges
5. planishing e) made from OHNS
6. HcHcr f) secondary cutting operation
7. Draft g) A draw defect
8. Non-cutting punches h) shallow forming operation
9. Wrinkles i) used in progressive dies
10. Stage stopper j) threaded holes
k) none of the above
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
h f d j a c b e g i
II) Match the following:
A B
1. Centre of pressure a) secondary operation
2. HcHcr b) damper
3. Over bending c) T110W2Cr1
4. Shaving tool d) blank ejection
5. Pilots e) T215Cr12W90
6. Bending f) avoid spring-back
7. Embossing g) precision sliding fit
8. Ball cage h) compound tool
9. Spring i) shank position
10. Knockout j) stiffening the sheet metal
k) grain direction
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
i e f a c k j g d h
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 29
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS:
1. What is a tool ?
· Anything which is necessary to make a product is called tools.
2. What are the classification of tools ?
· Press tools, Moulds, Jigs and fixtures, Cutting and assembly tools
,gauges and measuring instruments.
3. What is a press tool ?
· Press tool is a custom built tool in which we make sheet
components that not readily available in the market.
4. What do you mean by stampings?
· The sheet metal which makes with the help of press tool is called
stampings.
5. Name the different types of rolling ?
· Hot rolling, cold rolling.
6. What is Stock materials ?
· Sheet metal from which stampings made is called stock material.
7. What are the press tool operations ?
· Cutting, non cutting and combination of both.
8. What is strip?
· Each piece of sheet metal called strip.
9. What do you mean Blanking ?
· In this operation, cut out material or slug will be the component.
10. What is piercing?
· Process of making opening on sheet metal is called piercing. The
cut out material will be waste.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 30
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
11. What is called cutting off ?
· Material is going to cut in a single line, there won’t be any waste.
12. What is parting off ?
· Double line cutting material in between the line will be waste.
13. Describe about a side cam tool?
· Transforms vertical motion of the press ram into horizontal motion
of the tool. It is used for side piercing.
14. What is perforating ?
· Making no. of holes at a time.
15. What is dinking ?
· Press tool cutting operation for soft materials like paper, leather,
wood etc.
16. What is trimming ?
· Removing large amount of material from the edge of the piece part.
17. What do you understand shaving ?
· Removing small amount of material from the previously blanked
part.
18. What is broaching ?
· Series of teeth profile removes metal from blanked part.
19. Describe bending?
· Bending can be explained as shaping of material around straight
line axis. Result is a new plane which is at an angle to the mother
plane.
20. What is lancing ?
· Combination of cutting and bending.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 31
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
21. What is forming ?
· Press tool non cutting operations in which material is formed into
different shapes.
22. What do you mean drawing ?
· Process of making cup or vessel is called drawing.
23. What is curling ?
· Rolling the edge of sheet metals.
24.Define bulging?
· Internal forming operation to expand portions.
25.Name the common medias of bulging ?
· rubber, urethane, oil etc.
26. What is swaging?
· Opposite of bulge. External forming operation also called as
necking.
27. What is extrusion ?
· Operation to produce collapsible tubes, shell etc.
28. Define coining?
· Making depression and corresponding projection won’t be there.
29. What is an assembly tool ?
· Assembling of two or more parts by riveting, press fitting etc.
30.Describe flaring, lugging, collar drawing ?
· Making collar so that no. of threads can be provided.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 32
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
31. What is Planishing ?
· Flattening of material is called Planishing.
32. What is progressive tool ?
· Multi stage tool in which perform work at number of stations.
33. What is compound tool ?
· All cutting features of the component perform at one stroke of the
ram.
34. What do you meant by combination tool?
· Small press operated in large one. Blank and form very small parts.
35. What is notching ?
· Small amount of material cuts from the edge of the component.
36. What do you understand by sub press tool ?
· Small press operated in large one, blank and form very small parts.
37. What is louvering ?
· Combination of cutting and forming.
38. What is shearing?
· Method of cutting sheets without forming chips.
39. What are the stages of shearing ?
· Plastic deformation, penetration, fracture.
40. Result of plastic penetration stages is ?
· Cut band
41. Result of plastic deformation stage is ?
· Edge radius or roll over.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 33
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
42. Result of fracture stages is ?
· Break edge.
43. Name the types of shear load ?
· Internal and external loads.
44. What are the types of external shear load ?
· Compressive load and tensile load.
45. Define tensile load ?
· Force acting on opposite direction in same axis.
46. What is shear load ?
· Load which is acting on same direction but not in same axis.
47. What is compressive load ?
· Forces acting on same direction in same axis.
48. Name the types of force based on speed ?
· Impact force (quick force)
· magnetic force
49. Describe about stress ?
· Load acting on a material per unit area.
50. Formula of stress ?
· load /area
51. What is cutting force?
· The force which acts on sheet metal to cut the blank.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 34
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
52. Formula of cutting force ?
· Fc = LSTmax
· L : Length of periphery to cut in mm.
· S : sheet thickness in mm
· TM ax : shear strength in n/mm²
53. Shear strength is …. % of tensile strength.
· 80%
54. Equation to calculate press force ?
· Press force = cutting force + stripping force
55. Normal stripping force is ?
· 10 to 20 % of cutting force .
56. What are the methods to reduce cutting force ?
· Using stepped punch.
· Grind the face of the punch or die to a small sheared angle.
57. For blanking shear angle will be on ?
· Die.
58. For piercing shear angle will be on ?
· Punch
59. Briefly explain the capacity of the press ?
· Maximum amount of force can be given on the press . It is
determined by KN or TONS.
60. What is the shear strength ?
· Ability of material to resist shear stress.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 35
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
61. 1 TON =……. Kgf
· 1kgf.
62. What is reason of drill breakage ?
· Due to torsion and compression
63. U channel and angle iron made by ….. process
· Extrusion
64. 1N =... kgf
· 9.8 kgf
65. What do you meant by cutting clearance ?
· Gap between the side of the punch and corresponding side of the
die in single side.
66. Cutting clearance is expressed as ... ?
· Mm /side
67. Result of optimum cutting clearance will be....?
· Maximum cut band.
68. Result of excessive cutting clearance will be ...?
· Maximum edge radius.
69. Result of insufficient cutting clearance will be...?
· Maximum break edge.
70. Punch determines....?
· Piercing size
71. Die determines ...?
· Blanking
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 36
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
72. Calculation of cutting clearance ?
· Sheet metal up to 3mm = CXSX root of (TMAX/10)
· Sheet metal more than 3 mm=(1.5Xs) X(s-0.015)Xroot of (TM ax /10)
73. What is called land ?
· To avoid jamming of material inside the die ,we give straight portion
of certain amount from the cutting edge. That is called land.
74. For sheet metal S up to 3 mm = land will be....?
· 3mm
75. For sheet metal more than 3 mm = land will be...?
· Sheet thickness.
76. Usually ,angular clearance is provided in ... Degree ?
· 1.5 degree /side.
77. Generally, soft material require... Angular clearance ?
· more.
78.What are the types of guide plate tool ?
· Open guide plate tool
· Stripper guide plate tool
79. Name the basic elements of tool ?
· Punch and Die.
80. Punch and die materials ?
· Good quality alloy steel(HcHcr ,D2).
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 37
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
81. Hardness of punch ?
· 58-60 HRC.
82. Hardness of die ?
· 60-62 HRC.
83. Stripper plate material ?
· MS or medium carbon steel
84. Thrust plate material ?
· OHNS.
85. Hardness of thrust plate ?
· 45-48 HRC
86. Top plate and bottom plate material ?
· MS or Cast iron.
87. Screws are to ……… the parts ?
· hold
88. Dowels are to ………. the parts ?
· align
89. Name the types of cold rolled stock materials used ?
· Hard, Three quarter hard, Half hard, Quarter hard, Soft, Dead soft.
90. What is the specialty of hard sheet metal ?
· Can not bend.
91. What is the specialty of 3 quarter hard material ?
· Can bend 60 degree across the grain.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 38
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
92. Specialty of half hard material ?
· Can bend 90 degree across the grain.
93. Quarter hard material ?
· Can bend 180 degree across and 90 degree along the grain
direction.
94. Soft material ?
· Can bend 180 degree across and along.
95. Dead soft material ?
· Can be formed into different shapes.
96. What is strip lay out ?
· A layout which gives sequence of works and operations.
97. What are the factors effecting a strip layout ?
· Shape of the blank, production requirement, grain direction, burr
side, stock material.
98. Formula of economic factor ?
· (area of the blankXno. of rows )/(pitchXscrap width )
99. What is pitch ?
· Distance between two consecutive operations.
100. What is scrap bridge ?
· Portion of the material remaining between two adjacent openings.
101. Scrap bridge nearer to the operator called .... scrap ?
· Front scrap
102. Scrap bridge away from the operator called .... scrap?
· Back scrap
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 39
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
103. What are the types of strip layout ?
· Single row layout, double row, gang dies and angular.
104. Name the types of single raw layout ?
· Narrow run, wide run
105. List about the types of punches ?
· Cutting punch, non cutting punch and hybrid punch.
106. What are the groups of punches ?
· Segregated punches and integrated punches.
107. What is segregated punch ?
· Self mounted by screwing etc.
108. What are the integrated punches ?
· Mounting with the help of punch plate etc.
109. For beveled head punch bevel angle is .........?
· 30 to 45 degree
110. What is perforator?
· Punch of diameter 2mm and below.
111. What is bucking force ?
· Maximum force a punch can withstand without bucking.
112. Formula for buckling force ?
· Fb =(ii2EI)/LP2
113. Modulus of elasticity of Steel ?
· 200 to 220 GN/M2
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 40
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
114. Unit of moment of Inertia ?
· Mm4
115. The ultimate condition of buckling force is ……..?
· Buckling force =cutting force require for the operation =shear force
on the punch
116. Material of solid die ?
· Non shrinking tool steel.
117. Die bushes are inserted in …..?
· mid steel retainer plate.
118. Dies having more than one section called ....?
· Split dies
119. Material of carbide dies ?
· Tungsten carbide
120. What is the function of stopper ?
· Arrest the movement of the strip for one pitch length after each
stroke.
121. Fundamental principles of stopper ?
· Stop position and registry position.
122. What is stop position ?
· Actual position of the stopper.
123. Describe registry position ?
· Exact position where strip has to be established.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 41
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
124. Types of strippers?
· Fixed and traveling
125. Function of stripper ?
· Strip the stock material off the punches after each stroke.
126. Tunnel width formula ?
· X=w+f
· w = stock strip width at maximum tolerance
· f = desired horizontal feeding clearance
127. Hook pins are made from ……….?
· Cold drawn steel rod
128. Gauge thickness for the material up to 1.5 mm is .... ?
· 3mm
129. Gauge thickness for the material more than 1.5 mm is ... ?
· Sheet thickness +1.5 mm
130. Prevention of wrong loading can be done by... ?
· Fool proofing
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 42
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS:
1.What is recommended inside bending radius in sheet metal
fabrication?
For hard materials (CRCA and stainless steel), Minimum inside radius is 0.7
times of sheet thickness. For softer materials (for example Aluminium)
minimum inside radius is equal to sheet thickness.
2.What is the minimum required Flange Length in Sheetmetal
Bending?
Minimum flange length shall be equal to 4 times of sheet thickness plus inside
radius.
Minimum Flange length = 4 X T (sheet thickness) + R (Inside Bend
Radius)
3.What is the minimum recommended Hole/Slot distance from
Edge?
Minimum Distance = 3 X Sheet Thickness + R (Inside Bend Radius)
4.What is bending allowance?
After bending total length (Length + Height) of sheetmetal part is not equal to
Flat Length. This increase in overall length is known as bending allowance.
Flat Length = Length + Height – Bend Deduction
5.What is K-factor in sheet metal fabrication?
K-Factor is a constant, used to calculate the Sheetmetal flat length. Value of k-
factor depends on material, Bend radius, sheet thickness and machines used.
Mathematically K-Factor is a ratio of position of neutral axis and sheet
thickness. Value of K-factor is always less than 0.5
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 43
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
6.What is Y-Factor in Sheet metal?
Y-factor is similar to K factor. It is used to calculate sheet metal parts flat
length.
7.What are various surface finish operations done on sheetmetal
parts ?
Following are commonly used sheet metal surface finish operations:
· Pre-Treatment : Phosphate Conversion Coating, Chromate Conversion
Coating, Derusting, Descaling
· Powder Coating
· Anodising
· Plating: Zn Plating/Galvanising, Tin plating, Silver plating
8.What Factors affect selection of sheet metal materials?
· Product IP-Rating
· Working Temperature
· Corrosion Resistance
· Required Part Strength
· Part Weight constraints
· Final Finish operation
· Part joining Methods (Riveting/Welding/Screw)
9.What are the reinforcement techniques used to improve
sheetmetal parts strength?
Reinforcement techniques improves part strength in localized section.
· Bending: Bending in direction 90 degree to load applied, hem bend
· Forming tools: sheet-metal rib, louver, lance & Tab
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 44
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
10.What is the application of press tool in sheetmetal ?
Press tools are used in hydraulic, pneumatic & mechanical presses to produce
stamped sheet-metal parts. Press tools can be classified based on operation:
blanking, piercing, bending and forming.
11.What is stamping operation?
Stamping is a process of shaping sheet-metal parts using press tool. Blanking,
punching, pressing, piercing, bending and forming operations are done with
stamping dies.
12.What are various sheet metal manufacturing operations?
Various types of sheetmetal operation includes cutting, forming, joining and
final finish operations:
· Sheet metal Cutting operations: Punching, Piercing,Perforation, Cutting
off, Parting off, Dinking, Trimming, Shaving, Shearing, Notching etc
· Material Removal Operations: Deburring, Grinding
· Sheetmetal Forming: Straight bend, Angle bend, Hem bend
· Material Joining Operations: Welding (Tig, MIG, GAS Welding), Riveting,
Folding, Screws
· Final Finish Operations: Passivation, Chromate Conversion Coating,
Plating, powder Coating
13.What are various sheet metal assembly operations?
Following techniques can be used to join sheetmetal parts.
· Screws: self tapping screws, machine screws
· Welding : arc welding, TIG welding, MIG Welding
· Folding Techniques: Lap Joint, Hem Joint
· Riveting
· Press Fitting: PEM Inserts
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 45
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
14.What is the application of dowel pins ?
Dowel Pins are used to align two or more sheet metal parts during assembly.
15.What are the effects of grain direction in sheet metal during
bending?
Grain structure of sheet metal is aligned in rolling direction during cold rolling
process. Bending in rolling direction in softer materials result in cracks.
Therefore bending in the direction perpendicular to rolling direction is always
preferred.
16.What is the difference between sheet metal blanking, punching
& piercing operation?
Blanking is a process in which the punch operation removes a final product
from a larger piece of sheet metal.
Punching is a material removal process in which the punch operation removes
material from a final piece of sheet metal.
Piercing is process in which punch operation cuts a hole / material by tearing
operation from a final piece of sheet metal. Piercing is a blanking operation
17.What are the various steps to manufacture sheetmetal parts?
Following operations are performed during sheet metal part manufacturing:
Step-1 : Flat pattern calculations.
Step-2 : CNC Punching Process Programming
Step-3 : Cutting operations. It includes CNC Punching, laser or water cutting
Step-4: Deburring
Step-5: Hardware assembly ( PEM Hardware, Weld Nut, Rivet hardware)
Step-6 : Press Bending
Step-7 : Joining operations (welding/riveting)
Step-8 : Grinding
Step-9 ; Finish operations such as anodizing, plating, powder coating
Step-10 : Packing
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 46
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
18.What are various sheet metal materials ?
· CRCA
· HRCA
· Aluminium
· Galvanised Iron (GI)
· Stainless Steel
19.What is the difference between hot rolled & cold rolled steel
sheets?
Hot rolling process involves steel rolling above re-crystallisation temp. During
the cooling process steel will shrink. Therefore the size and shape of the steel
will be less predictable.
Whereas cold rolling involves steel rolling below re-crystallisation temp (at
room temp).
20.What are Sheet Metal Joining Operations ?
Sheet metal Joining Operations can be classified in two categories.
A) Permanent Joints:
1. Welding
2. Adhesive Bonding
3. Riveting
4. Clinching
B) Reusable Joints:
1. Metric Screws
2. Self Cutting Screws
3. Sheet metal tabs
4. Hemming
21.What are various sheetmetal cutting operations?
1. Shearing
2. Punching
3. Blanking
4. Nibbling
5. Perforation
6. Trimming
7. Deburring
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 47
PRESS TOOL THEORY- II
22.Why punching is preferred over laser cutting process?
Sheet metal forming operations such as extruded hole, lancing, cut and bend
are not feasible with laser cutting.
23.What is minimum possible hole diameter using sheet metal
turret punching press?
Minimum diameter of hole that can be punched in sheet metal should be equal
to sheet thickness.
24.What are various press bending operations on sheet metal
parts?
· 90 degree bend
· Z bend
· Hem bend
· Tab Bend
25. What are various welding operations done on sheet metal
parts ?
· TIG welding
· MIG Welding
· Gas Welding
· Spot welding
· Seam welding
26.What is Sheet metal gauge thickness?
Sheet Metal gauge represents standard sheet thickness for specified material.
Different material with same gauge number has different sheet thickness.
Gauges are defined based on material weight and rolling mills.
27.What is neutral axis in sheet metal?
When metal is bent the top section is going to undergo compression and the
bottom section will be stretched. The line where the transition from
compression to stretching occurs is called the neutral axis.
SHARAD S JAMKHANDIKAR GTTC HARIHAR Page 48
Вам также может понравиться
- Press Tool - I Notes - Documents-1Документ145 страницPress Tool - I Notes - Documents-1Sourav Vashisth98% (41)
- Strip LayoutДокумент29 страницStrip LayoutAnishMendis100% (3)
- Press Tool MCQДокумент6 страницPress Tool MCQMahesh Dalavi90% (10)
- Press Tool Theory - 1Документ144 страницыPress Tool Theory - 1Abhishek AbhiОценок пока нет
- Question Bank MCQ MouldsДокумент72 страницыQuestion Bank MCQ MouldsThilak P Gowda100% (2)
- Press Tool DesignДокумент36 страницPress Tool DesignAmar Bhopi100% (2)
- Tool and Die QuestionsДокумент8 страницTool and Die QuestionsKishan SahuОценок пока нет
- MCQ's On Jigs & FixturesДокумент20 страницMCQ's On Jigs & FixturesSahil Gauhar70% (30)
- Mould Short Question & AnswerДокумент16 страницMould Short Question & AnswerRupesh Kamat100% (3)
- Jigs and Fixtures - Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) and Answers 1-Jigs and Fixtures Are Used ForДокумент5 страницJigs and Fixtures - Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) and Answers 1-Jigs and Fixtures Are Used For312817116012 Ganesh RamОценок пока нет
- Formulas For Designing Press ToolsДокумент21 страницаFormulas For Designing Press ToolsKarthik Gopal86% (35)
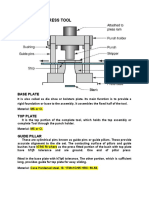
- Elements of Press Tool: Base PlateДокумент3 страницыElements of Press Tool: Base PlateSujay AvatiОценок пока нет
- Press Tool Design PPT Module 1Документ48 страницPress Tool Design PPT Module 1janak100% (1)
- Blanking and Piercing Die DesignДокумент12 страницBlanking and Piercing Die DesignChinmay Das100% (12)
- Presentation On Press Tool Design 01Документ55 страницPresentation On Press Tool Design 01Anonymous pMVR77x185% (34)
- Jigs and Fixtures - Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) and AnswersДокумент42 страницыJigs and Fixtures - Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) and AnswersAbhimannu RathoreОценок пока нет
- Metal Forming Processes - Mechanical Engineering (MCQ) Questions and AnswersДокумент5 страницMetal Forming Processes - Mechanical Engineering (MCQ) Questions and AnswersrahmaОценок пока нет
- Cutting ClearanceДокумент50 страницCutting ClearanceVinayak Aryan100% (16)
- MCQ-Metal Forming ProcessДокумент16 страницMCQ-Metal Forming ProcessKunal Wagh67% (9)
- Strip LayoutДокумент35 страницStrip LayoutJay PatelОценок пока нет
- Press Tool-IgtrДокумент176 страницPress Tool-IgtrVedang Kulkarni100% (4)
- Tool Design Data Book PDFДокумент124 страницыTool Design Data Book PDFbmvinay74% (19)
- Tool and Die Design Test Sept 2017 - 1Документ2 страницыTool and Die Design Test Sept 2017 - 1Farah Izzati FeeОценок пока нет
- MCQ On CNC MachineДокумент3 страницыMCQ On CNC Machinecbeprabhugmail100% (1)
- Press Tool Master FileДокумент196 страницPress Tool Master FileIrwan Rony86% (80)
- Press ToolДокумент12 страницPress ToolJitendra Bhole100% (1)
- Press Tool Operation and FunctionsДокумент25 страницPress Tool Operation and Functionsjagan89% (9)
- Jigs QuestionДокумент13 страницJigs QuestionShanmugavel MallaiahОценок пока нет
- MCQ Plastics WordДокумент9 страницMCQ Plastics Wordsrujankala100% (4)
- Press Tool ReportДокумент40 страницPress Tool ReportIshu Bassan100% (2)
- Machining Time CalculationДокумент7 страницMachining Time Calculationdellibabu50986% (7)
- Press Tool: Calculation For Die & Punch SizeДокумент4 страницыPress Tool: Calculation For Die & Punch Sizemayank12380% (20)
- 03 Cutting ForceДокумент3 страницы03 Cutting ForceAhmad Mustaghfiri Asrar100% (1)
- MCQ On Injection MouldДокумент14 страницMCQ On Injection MouldSahil Gauhar100% (12)
- Presses & Press WorkДокумент43 страницыPresses & Press WorkSahil Sheth100% (1)
- Milling Machine MCQДокумент4 страницыMilling Machine MCQRohit Ghulanavar50% (2)
- Metal Forming Processes Questions and Answers - SanfoundryДокумент2 страницыMetal Forming Processes Questions and Answers - Sanfoundryrahma100% (3)
- Chapter 5 Die DesignДокумент129 страницChapter 5 Die Designkb89% (9)
- Sheet Metal FormingДокумент25 страницSheet Metal Formingankushkapoor2003Оценок пока нет
- Mould QuestionsДокумент6 страницMould QuestionsRupesh KamatОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Die DesignДокумент102 страницыChapter 4 Die DesignTamirat Nemomsa100% (3)
- Press Tool-1 PDFДокумент71 страницаPress Tool-1 PDFajay100% (1)
- Formula For Press Tool DesignДокумент2 страницыFormula For Press Tool DesignJimmy Clavel100% (2)
- Stoppers: Stop PositionДокумент44 страницыStoppers: Stop PositionSubodh KumarОценок пока нет
- Design and Calculations of Piercing & Blanking DieДокумент89 страницDesign and Calculations of Piercing & Blanking DieVipul MetaОценок пока нет
- Types of Press Tools - Wikipedia PDFДокумент24 страницыTypes of Press Tools - Wikipedia PDFAvula VinayОценок пока нет
- Press ToolДокумент71 страницаPress Toolamolnjainajgmail.com 7507254906Оценок пока нет
- Objective Questions - CAD/CAM Unit - 3Документ5 страницObjective Questions - CAD/CAM Unit - 3Anonymous YkDJkSqОценок пока нет
- Recognition of Drawing Types: Detail Assembly DrawingsДокумент26 страницRecognition of Drawing Types: Detail Assembly DrawingsRamkrishna SonavaneОценок пока нет
- Vibration Engineering 003Документ9 страницVibration Engineering 003Niño Gerard JabagatОценок пока нет
- QB Jig & Fixture AnswersДокумент11 страницQB Jig & Fixture AnswersRupesh KamatОценок пока нет
- Aircraft Component Drawing Lab ManualДокумент41 страницаAircraft Component Drawing Lab ManualShanmuganathan100% (1)
- Mech311 Midterm 2009, 2011 and 2012Документ9 страницMech311 Midterm 2009, 2011 and 2012Parvinder SinghОценок пока нет
- Isro Sample Paper June 2005Документ10 страницIsro Sample Paper June 2005Dayakar RanaОценок пока нет
- Manual Operatico Guillotina Hidraulica QC11Y (4X16)Документ59 страницManual Operatico Guillotina Hidraulica QC11Y (4X16)orchidpunk0% (3)
- M1916 37mm CatalogДокумент14 страницM1916 37mm Catalogtyrant88Оценок пока нет
- Msme Technology Centre, Durg Assesment Test: Press Tool: Name: Total Marks: Course: Total Duration: BatchДокумент7 страницMsme Technology Centre, Durg Assesment Test: Press Tool: Name: Total Marks: Course: Total Duration: Batcharyan banchhorОценок пока нет
- Riveted Joints ASME IДокумент7 страницRiveted Joints ASME ICastoriadisОценок пока нет
- CNC Part A PDFДокумент25 страницCNC Part A PDFAKSHAY NambiarОценок пока нет
- Process Engg and ProductivityДокумент124 страницыProcess Engg and ProductivitySantosh PapleОценок пока нет
- Chain Renold ConveyorДокумент80 страницChain Renold ConveyorSantosh PapleОценок пока нет
- Workshop Project SupportДокумент69 страницWorkshop Project SupportSantosh PapleОценок пока нет
- 2FC DatasheetДокумент8 страниц2FC DatasheetSantosh PapleОценок пока нет
- PGCDR18Документ68 страницPGCDR18Santosh PapleОценок пока нет
- 02 Theory of ShearingДокумент6 страниц02 Theory of ShearingSantosh PapleОценок пока нет
- Aspects Mechanical DesignДокумент4 страницыAspects Mechanical DesignSantosh PapleОценок пока нет
- Wind Turbine Blade Production - New Products Keep Pace As Scale IncreasesДокумент8 страницWind Turbine Blade Production - New Products Keep Pace As Scale IncreasesSandeep BandyopadhyayОценок пока нет
- Structural Integrity Report PDFДокумент9 страницStructural Integrity Report PDFJoseph Mwangi WambuguОценок пока нет
- 1 Arc Welding 1Документ40 страниц1 Arc Welding 1ali100% (1)
- Boq of BarasДокумент6 страницBoq of BarasAILA TABRILLAОценок пока нет
- Surkhet Rate 2072 073Документ88 страницSurkhet Rate 2072 073Mishal Limbu100% (1)
- PVC W Water Sto Pper - Ins Stallation GuideДокумент4 страницыPVC W Water Sto Pper - Ins Stallation GuideZankar R ParikhОценок пока нет
- Bollhoff Quicksert Expansion InsertsДокумент4 страницыBollhoff Quicksert Expansion InsertsAce Industrial SuppliesОценок пока нет
- Material Data Sheet - Cable Gland & Fire StopДокумент5 страницMaterial Data Sheet - Cable Gland & Fire StopRizki FadillahОценок пока нет
- Wire DrawingДокумент4 страницыWire DrawingVenkat KrishnaОценок пока нет
- TDS 10566050 EN EN Easy-Mix-RK-7100 PDFДокумент1 страницаTDS 10566050 EN EN Easy-Mix-RK-7100 PDFKJ SupplyОценок пока нет
- Tool Steel ClassificationsДокумент6 страницTool Steel ClassificationsTalha MahmoodОценок пока нет
- Investigation Study On Geo-Polymer ConcreteДокумент6 страницInvestigation Study On Geo-Polymer ConcreteVishal SinghОценок пока нет
- Materials Properties Handbook Titanium Alloys CompressДокумент788 страницMaterials Properties Handbook Titanium Alloys CompressJordan Powell0% (1)
- Civil Work Specification Part 04Документ10 страницCivil Work Specification Part 04mr.xinbombayОценок пока нет
- AbsДокумент14 страницAbscak sobikОценок пока нет
- BeamsДокумент33 страницыBeamsGintokiОценок пока нет
- CERNetDev MisLink JctAbbagPackage5Документ44 страницыCERNetDev MisLink JctAbbagPackage5David CastilloОценок пока нет
- National Cancer Institute Egypt Resources Calculation SheetДокумент3 страницыNational Cancer Institute Egypt Resources Calculation SheetShady Cookies MonsterОценок пока нет
- An924 Rev. 14Документ8 страницAn924 Rev. 14David WongОценок пока нет
- Chapter OneДокумент17 страницChapter OneAlemayehu MitekuОценок пока нет
- MIL-F-5509D - Fittings, Flared Tube, Fluid ConnectionДокумент18 страницMIL-F-5509D - Fittings, Flared Tube, Fluid ConnectionthomasОценок пока нет
- Of Steel: Design Latticed StructuresДокумент13 страницOf Steel: Design Latticed StructuresCTBОценок пока нет
- Astm A29 2011 PDFДокумент16 страницAstm A29 2011 PDFJavier Ricardo Romero Bohorquez100% (2)
- SN200-8 - 2016-05 - Calculo de Cantidad Gel SilicaДокумент25 страницSN200-8 - 2016-05 - Calculo de Cantidad Gel SilicaUnidos Con PuerresОценок пока нет
- Topic-8 Ceiling EstimatesДокумент8 страницTopic-8 Ceiling EstimatesMyla Riza Sintones NepomucenoОценок пока нет
- Eei Corporation: Construction DivisionДокумент1 страницаEei Corporation: Construction DivisionEdward TamayoОценок пока нет
- c68700 Aluminum BrassДокумент1 страницаc68700 Aluminum Brassm_f_deathОценок пока нет
- Ielts WringДокумент3 страницыIelts WringVương ThànhОценок пока нет
- Aluminium Alloy - Commercial Alloy - 6063 - T6 ExtrusionsДокумент4 страницыAluminium Alloy - Commercial Alloy - 6063 - T6 ExtrusionsOgulcan CafОценок пока нет
- 2011 05 30 Document and Drawing RegisterДокумент2 страницы2011 05 30 Document and Drawing RegisterVo Kien CuongОценок пока нет