Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
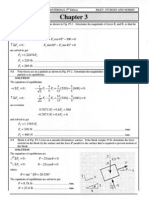
If A Body Is in Equilibrium It Will Never Accelerate
Загружено:
Hannah MijaresОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
If A Body Is in Equilibrium It Will Never Accelerate
Загружено:
Hannah MijaresАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
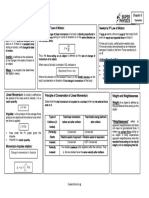
Translational Equilibrium – is in translational Center of Mass – is the point at which all the
equilibrium if the net force is zero mass is considered to be concentrated
Rotational Equilibrium – if the net - also the point at which the system can
torque/moment is zero be balanced.
- For simple symmetrical objects with
*If a body is in equilibrium it will never
uniform density, the center of mass is
accelerate
located at the centroid.
Static Translation Equilibrium – for motionless - If an object has rotational symmetry
objects that is in equilibrium about a single point, then that is the
center of mass
Dynamic Translational Equilibrium – for objects - Sometimes the center of mass does not
in motion that is still in equilibrium fall on the object itself
Clockwise – Positive (+) - The center of gravity will be at the same
C.Clockwise – Negative (-) point as the center of mass IF the
gravitational field is uniform
Lami’s Theorem – alternate solution for a 3-
Force Equilibrium system Kinematics – study of motion of objects without
references to forces
- When three forces acting at a point are
in equilibrium, each force is
proportional to the sine of the angle
between the two other forces
Beam – a structural element that is capable of
withstanding loads as it simply transfers the
loads to the supports
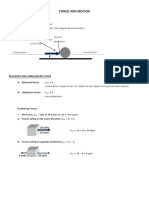
Friction – is a force that resists motion
- It is a reaction to motion
Static Friction – acting on a stationary object
Kinetic Friction – acting on a moving object
- Always less than the maximum static
friction
- Maximum or limiting static friction
occurs when the object is about to
move.
- Friction is independent of the area of
contact.
Belt Friction – friction present between the
cable and the cylinder of the pulley
- the lesser the friction, the pulling force
needed approaches the holding force
Вам также может понравиться
- Phys 100 SERIES Physics GuideДокумент12 страницPhys 100 SERIES Physics GuideimagemaniaОценок пока нет
- Physics Reviewer PDFДокумент6 страницPhysics Reviewer PDFJam Uly Gasty100% (1)
- Powerpoint On GravityДокумент10 страницPowerpoint On Gravitylucille anne umosoОценок пока нет
- CH 03Документ20 страницCH 03Ng Heng Lim100% (7)
- f4 Phy Part 2 - MergedДокумент43 страницыf4 Phy Part 2 - Merged苏恩恩Оценок пока нет
- Why Symmetry Runs The Positive Circular Economy: Underpinned by the deep, symmetric wisdom of Rav Yehuda Ashlag, Albert Einstein, Benjamin Graham & Emmy NoetherОт EverandWhy Symmetry Runs The Positive Circular Economy: Underpinned by the deep, symmetric wisdom of Rav Yehuda Ashlag, Albert Einstein, Benjamin Graham & Emmy NoetherОценок пока нет
- 4th Grading PHYSICSДокумент4 страницы4th Grading PHYSICSgabongabonОценок пока нет
- Objects and Systems at RestДокумент2 страницыObjects and Systems at RestMarian Margarette PegaridoОценок пока нет
- P6 Reviewer DefДокумент5 страницP6 Reviewer DefLexter AlteradoОценок пока нет
- Phy and Eapp Semis ReviewerДокумент6 страницPhy and Eapp Semis ReviewerJOYОценок пока нет
- Center of Mass and EquilibriumДокумент3 страницыCenter of Mass and EquilibriumZane VelasquezОценок пока нет
- Physics QuantityДокумент4 страницыPhysics QuantityYONGRENYIEОценок пока нет
- Test 1 Review: Topic DetailsДокумент4 страницыTest 1 Review: Topic Detailsdavidtrump3440Оценок пока нет
- Chapter9 Linear MomentumДокумент5 страницChapter9 Linear Momentumjacknorp1Оценок пока нет
- General Physics 1Документ2 страницыGeneral Physics 1Aifah HernandezОценок пока нет
- DRB-TERMSДокумент3 страницыDRB-TERMSvia.butalОценок пока нет
- What Is PhysicsДокумент5 страницWhat Is PhysicswatermelonОценок пока нет
- Law of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5Документ13 страницLaw of Motion Class 11 Notes Physics Chapter 5pujal dabasОценок пока нет
- 1stQA ScienceДокумент3 страницы1stQA ScienceAriana Kayree DavidОценок пока нет
- 2 Simple Harmonic MotionДокумент2 страницы2 Simple Harmonic MotionInfo -Baseline TechnologiesОценок пока нет
- Statics of Rigid Bodies IntorductionДокумент4 страницыStatics of Rigid Bodies IntorductionMaria TheresaОценок пока нет
- Laws of Motion-1Документ4 страницыLaws of Motion-1prachi98601Оценок пока нет
- Physics for Engineers Lecture on Dynamics of MotionДокумент5 страницPhysics for Engineers Lecture on Dynamics of MotionErianne ReyesОценок пока нет
- CE 1101 - Introduction and Equilibrium SystemДокумент31 страницаCE 1101 - Introduction and Equilibrium SystemnayeemislammeghОценок пока нет
- Waves and Optics - ReviewerДокумент15 страницWaves and Optics - ReviewerJoshua QuimsonОценок пока нет
- Physics Fundamentals: Motion, Forces, Energy & MoreДокумент10 страницPhysics Fundamentals: Motion, Forces, Energy & MoreKatrina Anne Layson YeenОценок пока нет
- Science 8 1Документ18 страницScience 8 1Hannah Leigh CoronelОценок пока нет
- Basics and Statics of ParticlesДокумент25 страницBasics and Statics of ParticlesparthibankОценок пока нет
- CH-5 Laws of MotionДокумент12 страницCH-5 Laws of MotionSaransh KumarОценок пока нет
- Force and Motion - Energy, Work and Power PDFДокумент7 страницForce and Motion - Energy, Work and Power PDFAnonymous ee5dOjОценок пока нет
- Physics Quantities and Forces ReviewДокумент2 страницыPhysics Quantities and Forces ReviewLei StarosaОценок пока нет
- SCIENCEДокумент3 страницыSCIENCEdzveaОценок пока нет
- Introduction To Engineering MechanicsДокумент13 страницIntroduction To Engineering MechanicsMaria RiveraОценок пока нет
- UNIT4Документ47 страницUNIT4Vijay KrishnaОценок пока нет
- Propulsion - I NotesДокумент28 страницPropulsion - I NotesVIGNESH BОценок пока нет
- CH-7 System of Particles and Rotaional MotionДокумент9 страницCH-7 System of Particles and Rotaional MotionMithul VPОценок пока нет
- Elements of Mechanical EngineeringДокумент14 страницElements of Mechanical EngineeringVivekОценок пока нет
- Physics Vector Addition and ForcesДокумент5 страницPhysics Vector Addition and ForcesV KimОценок пока нет
- Unit 2: Force, Motion, and Energy: Chapter 4: Balance and StabilityДокумент18 страницUnit 2: Force, Motion, and Energy: Chapter 4: Balance and StabilityRosemarie Cabanilla50% (2)
- Physics 101 Chapter 2Документ39 страницPhysics 101 Chapter 2Andrew GoolsbyОценок пока нет
- Stem 305 Final Exam ReviewerДокумент6 страницStem 305 Final Exam ReviewerBeyoncé GalvezОценок пока нет
- CH-7 Rotational MotionДокумент7 страницCH-7 Rotational Motionnegishreshth1985Оценок пока нет
- Lecture Note 1 8Документ15 страницLecture Note 1 8swatiishekhawat28Оценок пока нет
- COE 2001 Statics - Lecture 1 - IntroductionДокумент22 страницыCOE 2001 Statics - Lecture 1 - Introductionremino1Оценок пока нет
- Phy10 Wk07 Newtons Laws 2Документ12 страницPhy10 Wk07 Newtons Laws 2Jed Efraim EspanilloОценок пока нет
- OscillationsДокумент47 страницOscillationsrohilsingh01Оценок пока нет
- Physical Quantities and Units DefinitionsДокумент9 страницPhysical Quantities and Units DefinitionsKoushiki MukherjeeОценок пока нет
- Physics-Notes 02Документ7 страницPhysics-Notes 02JanusОценок пока нет
- Chapter 13: Harmonic Motion Part 1: Harmonic MotionДокумент6 страницChapter 13: Harmonic Motion Part 1: Harmonic MotionvectralivesОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4.2 First Condition of EquilibriumДокумент8 страницLesson 4.2 First Condition of EquilibriumJulius Matthew MarananОценок пока нет
- ScienceДокумент2 страницыScienceGAGARIN XYRAH C.Оценок пока нет
- Chapter 3-DynamicsДокумент1 страницаChapter 3-DynamicsantonstefanbiehlerОценок пока нет
- Grade 12 Physics Note 1.Документ6 страницGrade 12 Physics Note 1.babaОценок пока нет
- E=mc2: Mass-Energy Equivalence in Special RelativityДокумент4 страницыE=mc2: Mass-Energy Equivalence in Special RelativityAnkita RajputОценок пока нет
- Bio MechДокумент7 страницBio MechmarcusОценок пока нет
- 4309 Topper 21 101 3 4 122 Motion in A Straight Line Up201611021148 1478067495 4997Документ9 страниц4309 Topper 21 101 3 4 122 Motion in A Straight Line Up201611021148 1478067495 4997sadhu associatesОценок пока нет
- Lec 01-27-02-2019 - Introductory MechanicsДокумент79 страницLec 01-27-02-2019 - Introductory MechanicsLiviu LucaОценок пока нет
- Newton-Euler equations for planar and spatial mechanismsДокумент2 страницыNewton-Euler equations for planar and spatial mechanismsSomen BagОценок пока нет
- Physics Oscillations GuideДокумент9 страницPhysics Oscillations GuideMordecai ChimedzaОценок пока нет
- Forces: Force Can Cause An Object To Change Its Velocity or ShapeДокумент8 страницForces: Force Can Cause An Object To Change Its Velocity or ShapeLabeenaОценок пока нет
- Untitled Document 1Документ6 страницUntitled Document 1JEROME MICHAEL LAZAROОценок пока нет
- Statics of Rigid BodiesДокумент7 страницStatics of Rigid BodiesMarc BuenaflorОценок пока нет
- Lecture 1 Statics. Basic Concepts and AxiomsДокумент38 страницLecture 1 Statics. Basic Concepts and AxiomsДана Қарасайқызы100% (1)
- Engineering Mechanics NotesДокумент44 страницыEngineering Mechanics NotesLawrence LubangaОценок пока нет
- 4 PhyДокумент42 страницы4 PhyRacoОценок пока нет
- Jacobians and Manipulator SingularitiesДокумент35 страницJacobians and Manipulator SingularitiessivaeeinfoОценок пока нет
- PHYSICSG5Документ21 страницаPHYSICSG5Eric TiempoОценок пока нет
- HSH Footing V4 SecureДокумент12 страницHSH Footing V4 Secure3cesОценок пока нет
- Lecture 9 IlyДокумент39 страницLecture 9 IlyLauKingWeiОценок пока нет
- Newton'sLaws Inertia LectДокумент30 страницNewton'sLaws Inertia LectYomiko Danise P. EloresОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanics Unit-1Документ35 страницEngineering Mechanics Unit-1M.suresh SureshОценок пока нет
- Bab 2 Force & Motion Trial 2020Документ49 страницBab 2 Force & Motion Trial 2020Karen LactovaОценок пока нет
- Understanding GravitationДокумент13 страницUnderstanding GravitationPL NLОценок пока нет
- Kepler's laws of planetary motionДокумент17 страницKepler's laws of planetary motionCyril Marie Alfonso100% (1)
- ENSC 2113 Statics Syllabus and Chapter 1 OverviewДокумент25 страницENSC 2113 Statics Syllabus and Chapter 1 OverviewSafiurrehmanОценок пока нет
- Equilibrium: This Module Aims That The Students Will Be Able ToДокумент12 страницEquilibrium: This Module Aims That The Students Will Be Able ToMonique UnicoОценок пока нет
- Biomechanics and Sports (Lecture Notes)Документ6 страницBiomechanics and Sports (Lecture Notes)Corteza, Ricardo Danilo E. UnknownОценок пока нет
- Problem Set No. 1 Tekiner, Aldrien CE1Документ23 страницыProblem Set No. 1 Tekiner, Aldrien CE1Aldrien TekinerОценок пока нет
- Fixed Beam S RamamruthamДокумент11 страницFixed Beam S RamamruthamasdadОценок пока нет
- Circular MotionДокумент17 страницCircular Motionapi-3755159100% (3)
- 2013 Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. Vol.12-Springer (2013)Документ445 страниц2013 Cable-Driven Parallel Robots. Vol.12-Springer (2013)Thanh Hai NguyenОценок пока нет
- Engineering Mechanic - Chapter 1Документ22 страницыEngineering Mechanic - Chapter 1NurzanM.JefryОценок пока нет
- TD statics particle and rigid bodyДокумент5 страницTD statics particle and rigid bodyUng ChannoutdomОценок пока нет
- Hydrostatic Force on Inclined Plane SurfacesДокумент14 страницHydrostatic Force on Inclined Plane SurfacesanxaanОценок пока нет
- EP 222: Classical Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 3Документ12 страницEP 222: Classical Mechanics Tutorial Sheet 3haroldoОценок пока нет
- Week 4: Resultant of Parallel Force SystemДокумент4 страницыWeek 4: Resultant of Parallel Force SystemMarc PacaoОценок пока нет
- STATICS OF RIGID BODIES Chapter IДокумент23 страницыSTATICS OF RIGID BODIES Chapter IViron LucerianoОценок пока нет
- ENGINEERING MECHANICS FORCE SYSTEM RESULTANTSДокумент18 страницENGINEERING MECHANICS FORCE SYSTEM RESULTANTSVivek VaibhavОценок пока нет
- Statics of Rigid Bodies The Overview: ReferencesДокумент21 страницаStatics of Rigid Bodies The Overview: ReferencesNazareth Rick Otom ArcinoОценок пока нет
- Homework #2Документ3 страницыHomework #2Deniz GüneşОценок пока нет