Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Transformers Notes - 3 PDF
Загружено:
Eng Ogada KelvinОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Transformers Notes - 3 PDF
Загружено:
Eng Ogada KelvinАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
r
la
te
Es
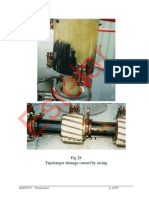
Figure 10: Practical core constructions using cold-rolled silicon steel and
mitre joints.
ELEC9712: Transformers p. 15/79
r
la
te
Es
Figure 11: Typical core loss values at 50Hz.
1 – conventional grade, 0.3mm
2 – HI-B grade, 0.23mm
3 – HI-B grade laser irradiated, 0.23mm
4 – amorphous metal compound, 0.13mm
[Ref. CIGRE Paper 12-09,1986]
ELEC9712: Transformers p. 16/79
2.3 Winding Arrangements and Insulation
In most low voltage power transformers (including 11kV
windings in large transformers) the winding turns are wound
on a base cylinder over spacers to form one or more layers,
thus giving a helical winding coil configuration.
At higher voltages the conductors are transposed to form
r
discs of perhaps ten turns each. These may be wound in pairs
and stacked at the assembly stage or wound as a continuous
la
winding (see Figure 8(a), 12, 13 and 15). Conventionally
these operations are carried out with the mandrel horizontal
but modern techniques allow vertical winding, thus avoiding
the turning through 90o on completion.
te
The Pancake Coils used in Shell Type windings are wound
separately and are of larger dimensions than the equivalent
Core-Type Discs. The Shell form is limited to a few
Es
manufacturers.
Possible winding configurations are given in Figures 12 and
13, including the insulation arrangements. The usual
configuration for delta windings, e.g. 33 and 66kV is
indicated in Figure 12 (a) (ii).
A major factor in the design of high voltage windings is to
ensure they will withstand lightning impulses as well as
power frequency over-voltages. The relevant test levels for
Um < 300kV are given in Figure 4. The design of windings to
withstand the electric stresses will be discussed with
reference to Figures 15 and 16.
ELEC9712: Transformers p. 17/79
r
la
te
Es
Figure 12: Layout of windings for core and shell types.
ELEC9712: Transformers p. 18/79
r
la
te
Es
Figure 13:
Insulating materials and typical locations as used
in power transformers
ELEC9712: Transformers p. 19/79
r
la
te
Es
Figure 14: Impulse voltage distributions.
ELEC9712: Transformers p. 20/79
r
la
te
Es
Figure 15a
Winding designs for improvement of voltage distributions
ELEC9712: Transformers p. 21/79
Вам также может понравиться
- Ee-353 Electrical Power Distribution & UtilizationДокумент60 страницEe-353 Electrical Power Distribution & Utilizationshaikpeer7Оценок пока нет
- Infinix Hot 10 Lite Emmc 2008121142 - FORESEE-FEMDNN064G-58K72 - C719492Документ9 страницInfinix Hot 10 Lite Emmc 2008121142 - FORESEE-FEMDNN064G-58K72 - C719492Eli GonzalezОценок пока нет
- Transformers Notes - 2 PDFДокумент7 страницTransformers Notes - 2 PDFEng Ogada KelvinОценок пока нет
- Transformers Notes - 6 PDFДокумент7 страницTransformers Notes - 6 PDFEng Ogada KelvinОценок пока нет
- ELEC9712 - Lec5 - Overhead Lines PDFДокумент60 страницELEC9712 - Lec5 - Overhead Lines PDFsauravkafle1Оценок пока нет
- TransДокумент17 страницTransMd sajjad AnsariОценок пока нет
- SMT by N4UAU - Part 2Документ3 страницыSMT by N4UAU - Part 2david reyesОценок пока нет
- TransformerДокумент33 страницыTransformermanjeshsingh0245Оценок пока нет
- Transformer & MotorДокумент92 страницыTransformer & MotorAshutosh RaiОценок пока нет
- Kawooya Charles 20 - U - 1298 Ele3114Документ12 страницKawooya Charles 20 - U - 1298 Ele3114Kawooya CharlesОценок пока нет
- Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electromechanical Systems LabДокумент11 страницCenter For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electromechanical Systems LabIrfan HaiderОценок пока нет
- Transformers - Three Phase TransformersДокумент25 страницTransformers - Three Phase TransformersDeepakDeep100% (1)
- 1 Phase TransformerДокумент35 страниц1 Phase Transformermendu7000Оценок пока нет
- Electrical and Instrumentation Technology: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah AlamДокумент52 страницыElectrical and Instrumentation Technology: Faculty of Chemical Engineering Universiti Teknologi MARA, Shah AlamMy EverythingОценок пока нет
- Capacitors. Description and FunctionДокумент12 страницCapacitors. Description and FunctionscufigОценок пока нет
- Transformers Notes - 1 PDFДокумент7 страницTransformers Notes - 1 PDFEng Ogada KelvinОценок пока нет
- Home Construction of A TransformerДокумент20 страницHome Construction of A TransformerNelson P. ColoОценок пока нет
- Part 2 - Module2 - Parts of DC Generator and Emf EquationДокумент35 страницPart 2 - Module2 - Parts of DC Generator and Emf EquationJohn Hennessy De CastroОценок пока нет
- DC Motor CalculationsДокумент18 страницDC Motor CalculationsHarshana RandheeraОценок пока нет
- Bahir Dar University Technology of Institute: School of Computing and Electrical EngineeringДокумент55 страницBahir Dar University Technology of Institute: School of Computing and Electrical Engineeringkrishnareddy_chintala0% (1)
- Welding TransformerДокумент20 страницWelding TransformerratbatcatОценок пока нет
- EI6402 - Electrical Machines Department of EIE&ICE 2016-2017Документ91 страницаEI6402 - Electrical Machines Department of EIE&ICE 2016-2017Dhivya SОценок пока нет
- Transformer Theory Questions and AnswersДокумент9 страницTransformer Theory Questions and AnswersVishal Sawh100% (3)
- DC MachineДокумент40 страницDC Machinedsfsdf sdfdsОценок пока нет
- ECE320 Chapter 3 PDFДокумент23 страницыECE320 Chapter 3 PDFAhsan NisarОценок пока нет
- Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Course Name:-Electrical Machines and DrivesДокумент54 страницыDepartment of Electrical and Computer Engineering Course Name:-Electrical Machines and DrivesKorsa KorsaОценок пока нет
- Polymer CapacitorДокумент19 страницPolymer CapacitorGilberto ManhattanОценок пока нет
- Expt 8,9Документ7 страницExpt 8,9HARSH RAIОценок пока нет
- 9 TransformerДокумент7 страниц9 TransformerMThana BalanОценок пока нет
- TransformerДокумент25 страницTransformerJerald SagusayОценок пока нет
- Chapter 5 - TransformerДокумент84 страницыChapter 5 - TransformerZulfikri Zulkifli50% (2)
- Unit 2 D.C. MachinesДокумент33 страницыUnit 2 D.C. MachinesnandhakumarmeОценок пока нет
- Electromagnet QuestionДокумент18 страницElectromagnet QuestionAtikah Abd RahmanОценок пока нет
- Module 4 Transformers Notes and IM Notes - TH and RMHДокумент25 страницModule 4 Transformers Notes and IM Notes - TH and RMHHarsha MayankОценок пока нет
- Transformador Básico (En Ingles)Документ4 страницыTransformador Básico (En Ingles)jona12345Оценок пока нет
- Electrical Machines IIДокумент49 страницElectrical Machines IISuram Dileep ReddyОценок пока нет
- Eme Practical PDFДокумент68 страницEme Practical PDFr kОценок пока нет
- TMT Microwave Oven PDFДокумент9 страницTMT Microwave Oven PDFDan MorettiОценок пока нет
- CapacitorsДокумент12 страницCapacitorsAndrei NicolaeОценок пока нет
- Western Electric Vacuum Tube Data 1941Документ212 страницWestern Electric Vacuum Tube Data 1941wa4gvt5044100% (1)
- A2125040331 - 14289 - 12 - 2018 - Transformer & MotorДокумент97 страницA2125040331 - 14289 - 12 - 2018 - Transformer & MotorRaj RathoreОценок пока нет
- Electric Arc Furnace Transformer Secondary Circuit CalculationsДокумент13 страницElectric Arc Furnace Transformer Secondary Circuit CalculationsikamelyaastutiОценок пока нет
- ASAT - Volume 1 - Issue A.S.A.T. CONFERENCE 14-16 May 1985 R CAIRO - Pages 1327-1334Документ8 страницASAT - Volume 1 - Issue A.S.A.T. CONFERENCE 14-16 May 1985 R CAIRO - Pages 1327-1334riccardo tarelliОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 DC GeneratorsДокумент51 страницаChapter 3 DC GeneratorsSolomon Tadesse AthlawОценок пока нет
- Basic Electrical Engineering NotesДокумент25 страницBasic Electrical Engineering NotesAnas AnsariОценок пока нет
- Kskcet Ee6352-Electrical Engg & Instrm. Year/Sem:Iv/ViiДокумент15 страницKskcet Ee6352-Electrical Engg & Instrm. Year/Sem:Iv/ViimanikandanОценок пока нет
- 1.5v Battery ChargerДокумент25 страниц1.5v Battery ChargerJOHN BRICCO A. MATACSILОценок пока нет
- ET Modue 1Документ51 страницаET Modue 1Sahal T YousephОценок пока нет
- U2 L1 Function of ConductorДокумент8 страницU2 L1 Function of ConductorChesley CarolinoОценок пока нет
- U2 L1 Function of ConductorДокумент8 страницU2 L1 Function of ConductorChesley CarolinoОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 DC Machines-Construction and Principle of OperationДокумент13 страницTopic 2 DC Machines-Construction and Principle of OperationAthul RameshОценок пока нет
- Leakage Flux TransformerДокумент5 страницLeakage Flux TransformerVishnu PillaiОценок пока нет
- Experiment No.7 Transformers: Engr. Conrado QuinalayoДокумент9 страницExperiment No.7 Transformers: Engr. Conrado QuinalayoJaloyd MacalalagОценок пока нет
- C3 Transformers S1Документ44 страницыC3 Transformers S1mhmd.akzrОценок пока нет
- Electrical Machines 1 PDFДокумент12 страницElectrical Machines 1 PDFThangam MaheshОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ14 страницChapter 1Dawit LijalemОценок пока нет
- Siddharth PhyДокумент12 страницSiddharth Physiddharthdeuri476Оценок пока нет
- Complete EDM Handbook - 9Документ8 страницComplete EDM Handbook - 9Prahlad GargОценок пока нет
- 17S2 EE3010 PPT Lecture7-TransformersДокумент25 страниц17S2 EE3010 PPT Lecture7-Transformersming yangОценок пока нет
- Lecture 5: Transformers (Continued)Документ16 страницLecture 5: Transformers (Continued)Aldiansyah dtsОценок пока нет
- Auto-Transformer Design - A Practical Handbook for Manufacturers, Contractors and WiremenОт EverandAuto-Transformer Design - A Practical Handbook for Manufacturers, Contractors and WiremenРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (2)
- Transformers Notes - 8 PDFДокумент7 страницTransformers Notes - 8 PDFEng Ogada KelvinОценок пока нет
- Transformers Notes - 7 PDFДокумент7 страницTransformers Notes - 7 PDFEng Ogada KelvinОценок пока нет
- Transformers Notes - 5 PDFДокумент7 страницTransformers Notes - 5 PDFEng Ogada KelvinОценок пока нет
- Transformers Notes - 1 PDFДокумент7 страницTransformers Notes - 1 PDFEng Ogada KelvinОценок пока нет
- Introduction To ProgrammingДокумент20 страницIntroduction To ProgrammingJohnBenedictRazОценок пока нет
- Course Allocation For First Semester 2017/2018 SessionДокумент9 страницCourse Allocation For First Semester 2017/2018 SessionlivityhotОценок пока нет
- Predatory JournalsДокумент9 страницPredatory JournalsNabeel MuhammadОценок пока нет
- Assignment On LifiДокумент19 страницAssignment On LifiMushir BakshОценок пока нет
- ERP Planning, Design and ImplementationДокумент20 страницERP Planning, Design and ImplementationKshitij LauОценок пока нет
- CS-AI 2ND YEAR Final SyllabusДокумент40 страницCS-AI 2ND YEAR Final Syllabusafgha bОценок пока нет
- The Procedure Is As Follows: Glpi InstallationДокумент3 страницыThe Procedure Is As Follows: Glpi InstallationjacksonrppОценок пока нет
- Engineering UtilitiesДокумент13 страницEngineering UtilitiesJessaLyza CordovaОценок пока нет
- Split Charge InstructionsДокумент4 страницыSplit Charge InstructionsAugusto ZanlungoОценок пока нет
- VSCode Shortcuts CheatSheetДокумент51 страницаVSCode Shortcuts CheatSheetMarko TodorovicОценок пока нет
- Selenium ToolДокумент24 страницыSelenium ToolSayali NagarkarОценок пока нет
- DM No. 438, S. 2021 GUIDELINES ON THE ISSUANCE AND RESETTING OF DEPED EMAIL ACCOUNTSДокумент2 страницыDM No. 438, S. 2021 GUIDELINES ON THE ISSUANCE AND RESETTING OF DEPED EMAIL ACCOUNTSMichael V. MagallanoОценок пока нет
- Tax Invoice: Pay ImmediatelyДокумент5 страницTax Invoice: Pay ImmediatelySMART DESIGNSОценок пока нет
- Install Flutter in WindowsДокумент10 страницInstall Flutter in WindowsazharОценок пока нет
- David Hatcher Childress Technology of The GodsДокумент2 страницыDavid Hatcher Childress Technology of The GodsLeonardoОценок пока нет
- Bts3900 v100r010c10spc255 Enodeb FDD UpgДокумент38 страницBts3900 v100r010c10spc255 Enodeb FDD UpgJennis Sherano FernandoОценок пока нет
- Digital Dice (DLD Project)Документ3 страницыDigital Dice (DLD Project)233679Оценок пока нет
- Project Report 1Документ5 страницProject Report 1abdullah bhattiОценок пока нет
- Computers & Education: Pavel Smutny, Petra SchreiberovaДокумент11 страницComputers & Education: Pavel Smutny, Petra SchreiberovaMaruan MCOОценок пока нет
- Thycotic PrivilegeManger 10.7.1 CompleteДокумент586 страницThycotic PrivilegeManger 10.7.1 CompleteDadeОценок пока нет
- Artikel Engineering 400 Kata 1Документ6 страницArtikel Engineering 400 Kata 1Ferdhy BlongorОценок пока нет
- Interface AplicadorДокумент8 страницInterface AplicadorNelson RibeiroОценок пока нет
- ReadmeДокумент26 страницReadmepaquito sempaiОценок пока нет
- ATEX ComplianceДокумент2 страницыATEX ComplianceEfari BahchevanОценок пока нет
- Itc e Choupal PPT Final 111114132618 Phpapp01Документ30 страницItc e Choupal PPT Final 111114132618 Phpapp01pks009Оценок пока нет
- Laboratory Exercise No 1Документ1 страницаLaboratory Exercise No 1GamОценок пока нет
- Grp03 Blinking MiniprojectДокумент3 страницыGrp03 Blinking MiniprojectYasin OmaryОценок пока нет
- Satyam Eye Hospital - Google SearchДокумент1 страницаSatyam Eye Hospital - Google SearchRajeshwar GargeОценок пока нет
- 23 Construction Schedule Templates in Word & ExcelДокумент7 страниц23 Construction Schedule Templates in Word & ExcelnebiyuОценок пока нет