Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Ph.D-Syll Geog
Загружено:
irc_avtar0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
67 просмотров2 страницыSubject - GEOGRAPHY Syllabus of Ph.D. Eligibility Entrance Test Examination Total No. Of marks - 100 Unit(s) Geographic Thought : General character of Geographic knowledge during the ancient and medieval period. (ii) geomorphology : Fundamental concepts, Endogenetic and Exogenetic process. (iv) Oceonography : Composition and structure of atmosphere, insolation, green house effect, concept of Air mass, Temperature and tropical cuclones.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Ph.D-Syll_Geog
Авторское право
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документSubject - GEOGRAPHY Syllabus of Ph.D. Eligibility Entrance Test Examination Total No. Of marks - 100 Unit(s) Geographic Thought : General character of Geographic knowledge during the ancient and medieval period. (ii) geomorphology : Fundamental concepts, Endogenetic and Exogenetic process. (iv) Oceonography : Composition and structure of atmosphere, insolation, green house effect, concept of Air mass, Temperature and tropical cuclones.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
67 просмотров2 страницыPh.D-Syll Geog
Загружено:
irc_avtarSubject - GEOGRAPHY Syllabus of Ph.D. Eligibility Entrance Test Examination Total No. Of marks - 100 Unit(s) Geographic Thought : General character of Geographic knowledge during the ancient and medieval period. (ii) geomorphology : Fundamental concepts, Endogenetic and Exogenetic process. (iv) Oceonography : Composition and structure of atmosphere, insolation, green house effect, concept of Air mass, Temperature and tropical cuclones.
Авторское право:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 2
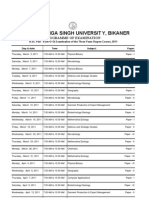
Subject – GEOGRAPHY
Syllabus of Ph.D. Eligibility Entrance Test Examination
Total No. of marks - 100
Unit-
(I) Geographic Thought : General character of Geographic knowledge during the
ancient and medieval period; Foundation of Modern Geography, Determinism
and possibilism; qualitative revolution; Areal differentiation and Spatial orga
- nization, Modern geography.
(II) Geomorphology : Fundamental concepts, Endogenetic and Exogenetic process.
Dedudation and weathering, isotasy, plate tectonics, seismicity, vulcancity, moun
tain building, landforms associated with fluvial, glacial, Aeolian, Karst cycles con
cept of geomorphic cycle, applied geomorphology.
(III) Oceonography : Compostion and structure of atmosphere, insolation, green
house effect, concept of Air mass, Temperature and tropical Cuclones, Monsoon
and jet streams; Theory of climate changes, climate classification of koppen and
Thornthwaite, Stability and instability of the atmosphere. Global warming.
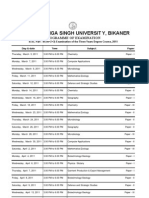
(IV) Ocean deposits, coral-reefs, Temperature and salinety of oceans. Tides and cur
rents, floor of the ocean basins, marine resources and environment.
(V) Economic Geography : Location of economics activities, sectors of economy-
Primary, secondary and tertiary. Concepts and techniques of delimitation of ag
riculture region. Crop combination and diversification, Von-thunen’s model and
its modification, Classification of industries, Resource based and footloose indus
tries, Theories of Industrial location by weber and losch, case studies of selected
industries; Textile of bombay and iron and steel, industry of Jamshedpur, Role of
market in the development of trade and commerce.
(VI) Population Geography : Patterns of world distribution of population
Growth and density of population, policy issues, patterns and process of
migration; Demograhic transition, Population resource regions.
Population Composition :_ Age and sex, Literacy.
Population dynamics :- Measurements of fertility and mortality.
(VII) Indian Geography : Physiographic divisions; climate, Its regional variations
Vegetation types and vegetation regions; Major soil types; Coastal andmarine
resources; water resources; Irrigation agriculture; agroclimatic regions, Minerals and
power resources, major industries and industrial regions, population distribution and
grwoth, settlement patterns; Regional disparities in social and economic development,
Minerals resources of Jharkhand, problems of planning and development in
Jharkhand.
(VIII) Settlement Geography : Site, Situation and internal Morphology of rural and urbans
settlement; city-regions; Primate city, Rank-size rule; Christaller’s central place theory;
rural-urban frinage, issues, Perspective and policies of population and Human
settlements.
(IX) Regional Planning : Regional Concept in Geographic; its application to planning,
concept of planning region, Type of regions and methods of regional delineation,
conceptual and theoretical framework of regional plan ning; Regional planning in
India; Concept of development; indicators of development; regional imbalances.
(X) Cartoraphy : Cartography and statistical methods, Maps a tool in geographical
studies; types of maps; Techniques for the study of spetial patterns of distribution;
choropleth and isopleth and chrochromatic maps and pie diagrams;
Remote sensing; Geographic information system (GIS):Thematic maps.
Data sources and types of data; statistical diagrams study of frequency
distribution and cumulative frequency; Lorenz curve; Scaling techniques; Sampling
techniques for Geographical analysis. Types of map Projection; Use and
characteristics of Mercator’s Projection.
Вам также может понравиться
- Preliminary Examination of Civil Services Exam: (Syllabus)Документ3 страницыPreliminary Examination of Civil Services Exam: (Syllabus)Somu TiwariОценок пока нет
- HPSC Geography Assistant ProfessorДокумент3 страницыHPSC Geography Assistant Professorvivek sОценок пока нет
- Faculty of Science M. Sc. (Geography)Документ2 страницыFaculty of Science M. Sc. (Geography)FërØz AhmädОценок пока нет
- Part-B: Aprcet Andhra University VisakhapatnamДокумент2 страницыPart-B: Aprcet Andhra University VisakhapatnamKali PrasadОценок пока нет
- Rajasthan Public Service Commission, Ajmer: Rajasthan State and Subordinate Services Combined Competitive ExaminationДокумент3 страницыRajasthan Public Service Commission, Ajmer: Rajasthan State and Subordinate Services Combined Competitive ExaminationAgarwal AakashОценок пока нет
- Auxiliary Material For Lecture No 2Документ6 страницAuxiliary Material For Lecture No 2Zunaira MajeedОценок пока нет
- Net SyllabusДокумент6 страницNet Syllabusanon_20637111Оценок пока нет
- Geography Optional SyllabusДокумент3 страницыGeography Optional Syllabussangu1434Оценок пока нет
- (UPSC Syllabus) : Main Examination Syllabus - Subject: GeographyДокумент4 страницы(UPSC Syllabus) : Main Examination Syllabus - Subject: GeographyVivek MishraОценок пока нет
- Geography SyllabusДокумент3 страницыGeography SyllabusNaveen ThummaОценок пока нет
- Geography English SET 2019Документ5 страницGeography English SET 2019Rakib HasanОценок пока нет
- Geography SET SyllabusДокумент6 страницGeography SET SyllabusArahant LabhaneОценок пока нет
- 04 Geography - PDF UsetДокумент8 страниц04 Geography - PDF UsetVijay Singh SultanОценок пока нет
- Geography PDFДокумент2 страницыGeography PDFPulakesh PradhanОценок пока нет
- Geo HecДокумент2 страницыGeo HecNeeraj TiwariОценок пока нет
- Syllabus Geography 2Документ2 страницыSyllabus Geography 2Sailen GopeОценок пока нет
- Orientation Program DR - Krishnanand Ugc NetДокумент11 страницOrientation Program DR - Krishnanand Ugc Netvarun singhОценок пока нет
- GEOGRAPHYH Syllabus of WBДокумент2 страницыGEOGRAPHYH Syllabus of WBDeep GhoshОценок пока нет
- Geography Detailed SyllabusДокумент4 страницыGeography Detailed SyllabusdavidjecОценок пока нет
- Geography - MainsДокумент4 страницыGeography - MainssunnybhanotОценок пока нет
- Geogrophy OptioalДокумент4 страницыGeogrophy OptioalKiran KondeОценок пока нет
- Optional Paper - GeographyДокумент3 страницыOptional Paper - GeographyShîvåmPrîýädårshïОценок пока нет
- UpscДокумент29 страницUpscabhinav_samaiya9497Оценок пока нет
- UPSC Slabus For GeographyДокумент2 страницыUPSC Slabus For GeographyAjit MishraОценок пока нет
- Climate ClassificationДокумент4 страницыClimate ClassificationAbdo WudadОценок пока нет
- WBCS Main GEOGRAPHY Optional Syllabus NewДокумент6 страницWBCS Main GEOGRAPHY Optional Syllabus NewCHANDRANI SAHAОценок пока нет
- Geography Syllabus For Main Examination: Principles of Geography Physical GeographyДокумент6 страницGeography Syllabus For Main Examination: Principles of Geography Physical GeographyWajid MohammadОценок пока нет
- Civil Service Main Examination Syllabus Geography - OptionalДокумент3 страницыCivil Service Main Examination Syllabus Geography - OptionalSumit Kumar RaiОценок пока нет
- Geography Optional SyllabusДокумент6 страницGeography Optional SyllabusEvolve IASОценок пока нет
- Main Examination of Civil Services ExamДокумент5 страницMain Examination of Civil Services ExamrupasmОценок пока нет
- WBCS Syllabus For GeographyДокумент3 страницыWBCS Syllabus For Geographymotherindia1947bengaliОценок пока нет
- Geography Optional SyallbusДокумент3 страницыGeography Optional SyallbusSurya VashishthaОценок пока нет
- UPSC IAS Civil Services Mains Optional Subject Geography Exam Syllabus in English - WWW - Dhyeyaias.comДокумент4 страницыUPSC IAS Civil Services Mains Optional Subject Geography Exam Syllabus in English - WWW - Dhyeyaias.comsarwat fatmaОценок пока нет
- Wildlife Protection ActДокумент5 страницWildlife Protection ActShivangi AgrawalОценок пока нет
- UPSC Geography Syllabus - IAS Mains Optional Subjects PDFДокумент5 страницUPSC Geography Syllabus - IAS Mains Optional Subjects PDFMAHESH RAMОценок пока нет
- Geography Book List For IASДокумент6 страницGeography Book List For IASNeetu SinghОценок пока нет
- ISC GeographyДокумент15 страницISC GeographyAkshit BindhaniОценок пока нет
- Geography SyllabusДокумент4 страницыGeography SyllabusmvrthedocОценок пока нет
- Origin and Evolution of The Earth's Crusts Fundamentals of Geomagnetism Physical Conditions of The Earth'sДокумент3 страницыOrigin and Evolution of The Earth's Crusts Fundamentals of Geomagnetism Physical Conditions of The Earth'sronitraj157Оценок пока нет
- Geo Syllabus NotesДокумент2 страницыGeo Syllabus NotesmaharshiОценок пока нет
- GeographyДокумент2 страницыGeographyshunmuveniОценок пока нет
- B.A. (Geography) Ambedkar UniversityДокумент25 страницB.A. (Geography) Ambedkar UniversityAbhi Jayakumar0% (1)
- UPSC CSE Mains Geography SyllabusДокумент2 страницыUPSC CSE Mains Geography SyllabusGowtham NayakОценок пока нет
- Optional Geo Paper 1 PDFДокумент2 страницыOptional Geo Paper 1 PDFHarpreet KourОценок пока нет
- Geography Optional Paper - I Principles of Geography: WWW - Gradeup.coДокумент2 страницыGeography Optional Paper - I Principles of Geography: WWW - Gradeup.coab bcОценок пока нет
- Cuet PG SyllabusДокумент6 страницCuet PG SyllabusMuskan GhargeОценок пока нет
- Geography Optionals SyllabusДокумент4 страницыGeography Optionals SyllabusAbhay ChilkotiОценок пока нет
- Principles of GeographyДокумент13 страницPrinciples of GeographybharathimmkОценок пока нет
- ANNUAL SyllabusДокумент12 страницANNUAL SyllabusKumar SiddhantОценок пока нет
- Geography Syllabus - UPSC Civil Services Mains ExamДокумент6 страницGeography Syllabus - UPSC Civil Services Mains ExamcyberhygieneprojectcicОценок пока нет
- Geography Paper I Principles of Geography Physical GeographyДокумент3 страницыGeography Paper I Principles of Geography Physical GeographyAdithya DasОценок пока нет
- Cuet 2024 Geo SyllabusДокумент6 страницCuet 2024 Geo SyllabusRidha mubarackОценок пока нет
- Geography PDFДокумент3 страницыGeography PDFDibyasingh MajhiОценок пока нет
- BA BSC GeographyДокумент14 страницBA BSC GeographyPratham NishadОценок пока нет
- ICSE SYLLABUS GeographyДокумент8 страницICSE SYLLABUS GeographyDskОценок пока нет
- Geography Optional SyllabusДокумент6 страницGeography Optional SyllabusDCASОценок пока нет
- Qualitative Change in Human GeographyОт EverandQualitative Change in Human GeographyS. S. DuncanРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- JU AcaCalScncДокумент2 страницыJU AcaCalScncirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- JU PhyReunionДокумент1 страницаJU PhyReunionirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- VIdu-DE ProposdSchdulPGДокумент1 страницаVIdu-DE ProposdSchdulPGirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- DU ThreeYrDegriCoursPrt3Документ2 страницыDU ThreeYrDegriCoursPrt3irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- JU AcaCalArtsДокумент2 страницыJU AcaCalArtsirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- UOB-B ScPart2Документ1 страницаUOB-B ScPart2irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- UOB BAPart2Документ2 страницыUOB BAPart2irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- UOB-B ScHmScPart1Документ1 страницаUOB-B ScHmScPart1irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- UOB-B ScPart1Документ2 страницыUOB-B ScPart1irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- UOL VivaVocenPraДокумент2 страницыUOL VivaVocenPrairc_avtarОценок пока нет
- UOB-B ScPart3Документ1 страницаUOB-B ScPart3irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- UOB-B ScHmScPart3Документ1 страницаUOB-B ScHmScPart3irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- Ohj CGKNQJ Flag Iwokzupy Fo'Ofo - Ky ) Tksuiqj Okf"Kzd Ijh (KK DK Zøe& 2011Документ6 страницOhj CGKNQJ Flag Iwokzupy Fo'Ofo - Ky ) Tksuiqj Okf"Kzd Ijh (KK DK Zøe& 2011irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- Nhus de PgprofdipspeduДокумент1 страницаNhus de Pgprofdipspeduirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- UOB BFAPart1Документ1 страницаUOB BFAPart1irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- Part 3Документ1 страницаPart 3irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- Mgkvu-Llb Bca Bbasem1& 3xmttДокумент1 страницаMgkvu-Llb Bca Bbasem1& 3xmttirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- NG BachelorsDegriXmCntrsДокумент4 страницыNG BachelorsDegriXmCntrsirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- CSJM AcaCalendarДокумент1 страницаCSJM AcaCalendarirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- Jain Vishva Bharati University, Ladnun (Rajasthan) : ACADEMIC CALENDAR: 2010-2011Документ4 страницыJain Vishva Bharati University, Ladnun (Rajasthan) : ACADEMIC CALENDAR: 2010-2011irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- North - Eastern Hill University Permanent Campus:: Shillong - 7930022 NotificationДокумент5 страницNorth - Eastern Hill University Permanent Campus:: Shillong - 7930022 Notificationirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- H P Board of School Education Dharmasala (Kangra) 176700Документ7 страницH P Board of School Education Dharmasala (Kangra) 176700irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- Engexampostpond13 02 11Документ1 страницаEngexampostpond13 02 11irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- MHCETExam DateДокумент1 страницаMHCETExam Dateirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- UUni MngmntPCPSchdulДокумент1 страницаUUni MngmntPCPSchdulirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- VBPU UGExmДокумент3 страницыVBPU UGExmirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- VBPU M.ScAgriДокумент1 страницаVBPU M.ScAgriirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- Admsn DE - MBAProjctReportSbmisnDeadlin16 3 11Документ1 страницаAdmsn DE - MBAProjctReportSbmisnDeadlin16 3 11irc_avtarОценок пока нет
- MH PGD CET11 - NotificatnДокумент2 страницыMH PGD CET11 - Notificatnirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- MH PGM CET11 - NotificatnДокумент2 страницыMH PGM CET11 - Notificatnirc_avtarОценок пока нет
- Mercator's Atlas of 1595Документ6 страницMercator's Atlas of 1595Florea Mihai StefanОценок пока нет
- Map - UNIFILДокумент1 страницаMap - UNIFILcartographica100% (2)
- Topographic Map of Star MountainДокумент1 страницаTopographic Map of Star MountainHistoricalMaps100% (1)
- GE 155 - Lecture1 - Introduction To Geodetic Control NetworkДокумент60 страницGE 155 - Lecture1 - Introduction To Geodetic Control NetworkRonnie Oliva MalalisОценок пока нет
- 103 257 1 PBДокумент9 страниц103 257 1 PBJohana KetinОценок пока нет
- Debre Birhan University: PR .By: Tewodros ZegeyeДокумент62 страницыDebre Birhan University: PR .By: Tewodros ZegeyeZeleke TaimuОценок пока нет
- Mary Midgley.Документ26 страницMary Midgley.GeeKinqestОценок пока нет
- Chapter 1Документ29 страницChapter 1Kit Meng LimОценок пока нет
- Geological Mapping in ExplorationДокумент17 страницGeological Mapping in ExplorationDebbie Novalina100% (1)
- Kornati - Simicic FaricicДокумент20 страницKornati - Simicic FaricicgunarОценок пока нет
- Topographic SurveyingДокумент90 страницTopographic SurveyingRobert Jhon Boa AgojoОценок пока нет
- Topographic Map of Diamond Y Spring NWДокумент1 страницаTopographic Map of Diamond Y Spring NWHistoricalMapsОценок пока нет
- Gebco World Map 2014Документ1 страницаGebco World Map 2014Romel PozoОценок пока нет
- The Top GIS Masters Programs in The US-Ranked! - Spatial PostДокумент3 страницыThe Top GIS Masters Programs in The US-Ranked! - Spatial PostNammratha PalliОценок пока нет
- Los Survey Report Customer Site: Wireless PTMP Phase 1Документ5 страницLos Survey Report Customer Site: Wireless PTMP Phase 1Mujahed AhmedОценок пока нет
- Basemap PythonДокумент24 страницыBasemap PythonSankirna JogeОценок пока нет
- DatumsДокумент13 страницDatumsMiguel Gallego GarcíaОценок пока нет
- Map Projection QuestionsДокумент3 страницыMap Projection QuestionsP SCRIBD D scribdОценок пока нет
- FC 11319 Basics in CartographyДокумент1 страницаFC 11319 Basics in CartographyAbi ebayОценок пока нет
- M.sc. Geography MU and DeanДокумент42 страницыM.sc. Geography MU and DeanTop 10 telugu 10Оценок пока нет
- Geography: By: Ms. May-Ann S. CahiligДокумент10 страницGeography: By: Ms. May-Ann S. CahiligMay-Ann S. CahiligОценок пока нет
- Majeed Bathos Architecture ForsterДокумент16 страницMajeed Bathos Architecture ForsterlaboetieОценок пока нет
- Appendix I - VicinityДокумент1 страницаAppendix I - VicinityMark_GecoОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 LevellingДокумент122 страницыChapter 2 Levellingthe bitchОценок пока нет
- Science 7 Quarter 4 Module 1 Week 1: Locating Places On EarthДокумент5 страницScience 7 Quarter 4 Module 1 Week 1: Locating Places On Earthrailyn bolonos100% (1)
- Cartography TermsДокумент7 страницCartography TermsJeziel AtaОценок пока нет
- Sunyani WestДокумент93 страницыSunyani WestEricBoamahОценок пока нет
- Introduction To GISДокумент78 страницIntroduction To GISKim Young ShElfОценок пока нет
- X Project Proposal - Slide - Advanced&Innovative Carto Project - 2022Документ7 страницX Project Proposal - Slide - Advanced&Innovative Carto Project - 2022Eva Nazeha01Оценок пока нет
- Royal Cartographer - Solo - SpreadsДокумент7 страницRoyal Cartographer - Solo - SpreadsŞan ImuetinyanОценок пока нет