Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
System Security: 8.1 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
Загружено:
Do Xuan Huu0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров1 страницаDevices connected to an IP network have both a MAC address and IP address. The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) allows devices to map IP addresses to MAC addresses by maintaining an ARP table. This table stores IP/MAC address mappings to allow quick lookup and transmission of packets. Network administrators can also statically configure ARP entries to map specific IP/MAC address pairs.
Исходное описание:
Оригинальное название
V801 sec
Авторское право
© © All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документDevices connected to an IP network have both a MAC address and IP address. The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) allows devices to map IP addresses to MAC addresses by maintaining an ARP table. This table stores IP/MAC address mappings to allow quick lookup and transmission of packets. Network administrators can also statically configure ARP entries to map specific IP/MAC address pairs.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
0 оценок0% нашли этот документ полезным (0 голосов)
14 просмотров1 страницаSystem Security: 8.1 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
Загружено:
Do Xuan HuuDevices connected to an IP network have both a MAC address and IP address. The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) allows devices to map IP addresses to MAC addresses by maintaining an ARP table. This table stores IP/MAC address mappings to allow quick lookup and transmission of packets. Network administrators can also statically configure ARP entries to map specific IP/MAC address pairs.
Авторское право:
© All Rights Reserved
Доступные форматы
Скачайте в формате DOCX, PDF, TXT или читайте онлайн в Scribd
Вы находитесь на странице: 1из 1
System Security
8.1 Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
Devices connected to IP network have two addresses, LAN address and network address.
LAN address is sometimes called as a data link address because it is used in Layer 2
level, but more commonly the address is known as a MAC address. A switch on Ethernet
needs a 48-bit-MAC address to transmit packets. In this case, the process of finding a
proper MAC address from the IP address is called an address resolution.
On the other hand, the progress of finding the proper IP address from the MAC address is
called reverse address resolution. Our switches and DSLAMs find their MAC addresses
from the IP addresses through Address Resolution Protocol (ARP). ARP saves these addresses in ARP table for
quick search. Referring to the IP addresses in ARP table, the
packets containing the IP address are transmitted to network. When configuring the ARP
table, it is possible to do it only in some specific interfaces.
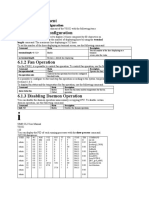
8.1.1 ARP Table
Hosts typically have an ARP table, which is a cache of IP/MAC address mappings. The
ARP Table automatically maps the IP address to the MAC address of a switch. In addition
to address information, the table shows the age of the entry in the table, the encapsulation method, and the switch
interface (VLAN ID) where packets are forwarded.
The V8102 ARP saves IP/MAC addresses mappings in ARP table for quick search. Referring to the information in
ARP table, packets attached IP address is transmitted to network.
When configuring ARP table, it is possible to do it only in some specific interfaces.
8.1.1.1 Registering ARP Table
The contents of ARP table are automatically registered when MAC address corresponds
to IP address. The network administrator could use MAC address of specific IP address in
network by registering on ARP table.
To specify a static ARP entry, use the following command.
Command Mode Description
arp A.B.C.D MACADDR [vlan Specifies a static ARP entry.
Global
VLANID] MAC-ADDR: MAC address.
Specifies a static ARP entry with an interface
arp A.B.C.D MACADDR INTER name.
FACE INTERFACE: interface name
MAC-ADDR: MAC address
no arp [A.B.C.D] Deletes static ARP entries.
no arp A.B.C.D INTERFACE
User Manual UMN:CLI
V8102
269
To delete ARP entries, use the following command.
Command Mode Description
Deletes all ARP entries.
clear arp Global A.B.C.D: IP address (e.g. 10.1.1.20)
A.B.C.D/M: IP prefix (e.g. 10.1.1.20/24)
clear arp A.B.C.D
clear arp A.B.C.D/M
Deletes the ARP entries on a specified interface.
bitethernet } IFPORT IFPORT: interface port number
VLANID: VLAN ID
clear arp interface vlan
VLANID
clear arp interface {channelgroup | gpon | tengiga
Вам также может понравиться
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamОт EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamОценок пока нет
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkОт EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkОценок пока нет
- 5.2.1.8 Lab - Observing ARP With The Windows CLI, IOS CLI, and WiresharkДокумент11 страниц5.2.1.8 Lab - Observing ARP With The Windows CLI, IOS CLI, and WiresharkNitika. SoodОценок пока нет
- Observing ARP With The Windows CLI, IOS CLI, and Wireshark - ILMДокумент16 страницObserving ARP With The Windows CLI, IOS CLI, and Wireshark - ILMEmy HazlindaОценок пока нет
- Lab 5 - Observing ARP: TopologyДокумент12 страницLab 5 - Observing ARP: Topologyjramisch44Оценок пока нет
- Sergio David Valdes Torres A01365520: Lab - Observing ARP With The Windows CLI, IOS CLI, and WiresharkДокумент21 страницаSergio David Valdes Torres A01365520: Lab - Observing ARP With The Windows CLI, IOS CLI, and Wiresharka01365520Оценок пока нет
- DynarpДокумент22 страницыDynarpPA2 ksplОценок пока нет
- 16 ARP CommandДокумент14 страниц16 ARP Commandlucian1961Оценок пока нет
- 5.2.1.8 Lab - Observing ARP With The Windows CLI, IOS CLI, and Wireshark PDFДокумент11 страниц5.2.1.8 Lab - Observing ARP With The Windows CLI, IOS CLI, and Wireshark PDFa01365520Оценок пока нет
- Configuring Dynamic ARP Inspection: Understanding DAIДокумент22 страницыConfiguring Dynamic ARP Inspection: Understanding DAInggianglx100% (2)
- Cisco CCNA Lab 9.8.1 Address Resolution Protocol ARPДокумент8 страницCisco CCNA Lab 9.8.1 Address Resolution Protocol ARPBms AgОценок пока нет
- IP Addressing CommandsДокумент102 страницыIP Addressing Commandssathya2314Оценок пока нет
- IP Addressing Commands (IOS 12)Документ96 страницIP Addressing Commands (IOS 12)SergeyОценок пока нет
- CISCo - P ARPДокумент4 страницыCISCo - P ARPpantelimon11Оценок пока нет
- What Is An ARP Entry ?: KarishmaДокумент2 страницыWhat Is An ARP Entry ?: Karishmavijay6996Оценок пока нет
- Dynamic Arp InspectionДокумент22 страницыDynamic Arp InspectionFUCKBALLZОценок пока нет
- ARP InspectionДокумент3 страницыARP InspectionObi A AgusioboОценок пока нет
- Configuring Dynamic ARP InspectionДокумент20 страницConfiguring Dynamic ARP InspectionKhoa Huynh DangОценок пока нет
- Understanding Dynamic ARP InspectionДокумент16 страницUnderstanding Dynamic ARP InspectionBlue PitОценок пока нет
- Marantz FY21 AVR Control Protocol: Application Terminal: Ethernet/RS-232CДокумент17 страницMarantz FY21 AVR Control Protocol: Application Terminal: Ethernet/RS-232CjimmymacbootОценок пока нет
- CST 3607 ARP LabДокумент7 страницCST 3607 ARP Labericherrera09Оценок пока нет
- Manual Interface - Bridge - MikroTik Wiki - OtraversionДокумент19 страницManual Interface - Bridge - MikroTik Wiki - OtraversionElio MIlanoОценок пока нет
- Ex ArpДокумент3 страницыEx ArpFAIZ AHMED H 17CSОценок пока нет
- 5.1.2.8 Lab - Viewing Network Device MAC AddressesДокумент5 страниц5.1.2.8 Lab - Viewing Network Device MAC Addresseschristian hallОценок пока нет
- Tracert:: Computer NetworkДокумент12 страницTracert:: Computer NetworkUmesh BhosaleОценок пока нет
- 07-BCMSN-Layer 3 Switching PDFДокумент7 страниц07-BCMSN-Layer 3 Switching PDFChoubane LamineОценок пока нет
- Network CommandsДокумент67 страницNetwork CommandsPriya KansalОценок пока нет
- Analog Comparator: PE2 PE3Документ16 страницAnalog Comparator: PE2 PE3Arup NayakОценок пока нет
- Can IP Addresses Be Determined From MACДокумент2 страницыCan IP Addresses Be Determined From MACFereidoun SadrОценок пока нет
- Arp, Its Challenges & Solutions: Study: Mohit JaniДокумент6 страницArp, Its Challenges & Solutions: Study: Mohit JaniIJRAERОценок пока нет
- Dynamic ARP Inspection: DAI in A DHCP EnvironmentДокумент2 страницыDynamic ARP Inspection: DAI in A DHCP Environmentziad Al-showaiterОценок пока нет
- Digital-to-Analog Conversion: Microchip MCP4921 Features General Overview Serial SPI InterfaceДокумент8 страницDigital-to-Analog Conversion: Microchip MCP4921 Features General Overview Serial SPI InterfaceRi Cha RdОценок пока нет
- NWC204 Lab4 SE162147Документ14 страницNWC204 Lab4 SE162147Tran Xuan Hai Duong (K16 HCM)Оценок пока нет
- Lab6c Using Wireshark To Study ARP and ICMP PDFДокумент6 страницLab6c Using Wireshark To Study ARP and ICMP PDFJohn Lloyd A. CortezОценок пока нет
- Unit 4 ARP PoisoningДокумент8 страницUnit 4 ARP PoisoningJovelyn Dela RosaОценок пока нет
- Static Routing: Routing Protocols and ConceptsДокумент41 страницаStatic Routing: Routing Protocols and ConceptsAtmanОценок пока нет
- Linux Ip Command ExamplesДокумент8 страницLinux Ip Command ExamplesMai TeОценок пока нет
- Module06 Arpv2Документ12 страницModule06 Arpv2omarkhanfar2Оценок пока нет
- BC AppNote 005Документ6 страницBC AppNote 005David CheОценок пока нет
- Area 0 Is Required For OSPF To Function, and Is Considered The "Backbone"Документ8 страницArea 0 Is Required For OSPF To Function, and Is Considered The "Backbone"clubmanОценок пока нет
- 1 - Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717Документ2 страницы1 - Created by Ahmad Ali E-Mail:, Mobile: 056 430 3717alokОценок пока нет
- MC C3. ADC Rv01 - HC v19.1Документ49 страницMC C3. ADC Rv01 - HC v19.1BodeaGabrielaОценок пока нет
- Embedded SystemДокумент15 страницEmbedded Systembrahma2deen2chaudharОценок пока нет
- 06.100 CCNA Exam Gotchas!Документ12 страниц06.100 CCNA Exam Gotchas!asegunloluОценок пока нет
- Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) : Relates To Lab 2Документ12 страницAddress Resolution Protocol (ARP) : Relates To Lab 2switi patelОценок пока нет
- Ags - 20Документ52 страницыAgs - 20Ivan100% (1)
- Edgar Paul Valdez Velazquez 18030566 Packet Tracer - Examine The ARP TableДокумент3 страницыEdgar Paul Valdez Velazquez 18030566 Packet Tracer - Examine The ARP Tablessf 2018Оценок пока нет
- CP7112-Network Design Lab Manual DownloadДокумент166 страницCP7112-Network Design Lab Manual DownloadSaravanan Nallusamy100% (2)
- Chapter 5: Network Security I: CIS3360: Security in ComputingДокумент27 страницChapter 5: Network Security I: CIS3360: Security in ComputingTeshome MulugetaОценок пока нет
- Module 2 Exam - CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks (Version 5.0)Документ7 страницModule 2 Exam - CCNP: Building Scalable Internetworks (Version 5.0)phreneticsОценок пока нет
- Lab No. 9-UpdatedДокумент4 страницыLab No. 9-Updatedmayashamaim72002Оценок пока нет
- Adc Atmega128Документ4 страницыAdc Atmega128M70AB2Оценок пока нет
- A Comparison of Virtual Ip CommandsДокумент6 страницA Comparison of Virtual Ip Commandsdeep kОценок пока нет
- 7.2.7 Lab - View Network Device Mac AddressesДокумент6 страниц7.2.7 Lab - View Network Device Mac AddressesJoshua BuenaventuraОценок пока нет
- CCNA ICND2 CheatsheetДокумент10 страницCCNA ICND2 CheatsheetLulzim BruçajОценок пока нет
- AVR ATMEGA16/32: Your Best Friend in Autonomous Robotics !!!Документ25 страницAVR ATMEGA16/32: Your Best Friend in Autonomous Robotics !!!sidraiz26Оценок пока нет
- Router CommandsДокумент9 страницRouter Commandsanon-640566100% (2)
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingОт EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingОценок пока нет
- ARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsОт EverandARM Microcontrollers Programming for Embedded SystemsРейтинг: 5 из 5 звезд5/5 (1)
- AP3370A Booster Amplifier ModulesДокумент1 страницаAP3370A Booster Amplifier ModulesDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Bandwidth and RateДокумент2 страницыBandwidth and RateDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Transmitting Data-Like Delivering ParcelsДокумент1 страницаTransmitting Data-Like Delivering ParcelsDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Increasing Bit Rate With Denser Modulation SchemesДокумент2 страницыIncreasing Bit Rate With Denser Modulation SchemesDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- V801 OLT SysoverviewДокумент2 страницыV801 OLT SysoverviewDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Coherent DWDM, From Then To Now: 400G-ZR & ZR+: The Latest in Pluggable Coherent DWDMДокумент2 страницыCoherent DWDM, From Then To Now: 400G-ZR & ZR+: The Latest in Pluggable Coherent DWDMDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Shared Line Card Grooming (Ring Mode) : Figure 3-18Документ1 страницаShared Line Card Grooming (Ring Mode) : Figure 3-18Do Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- ROADM Networks Enable Adding New Services Without Redesign or Major Changes To NetworkДокумент3 страницыROADM Networks Enable Adding New Services Without Redesign or Major Changes To NetworkDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- System Environment 6.1.1 Terminal ConfigurationДокумент2 страницыSystem Environment 6.1.1 Terminal ConfigurationDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- What Is An SFP Transceiver?: SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable)Документ2 страницыWhat Is An SFP Transceiver?: SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable)Do Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- V801 OLT IntroductionДокумент2 страницыV801 OLT IntroductionDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Tip Create Command Line: V.laurieДокумент3 страницыTip Create Command Line: V.laurieDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- The Road To 600GДокумент3 страницыThe Road To 600GDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- There Is A Kind of Network Tap To Capture East-West Traffic That Is Called Virtual TapДокумент1 страницаThere Is A Kind of Network Tap To Capture East-West Traffic That Is Called Virtual TapDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Roadm Optical Line SystemДокумент8 страницRoadm Optical Line SystemDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Table 11.1 Summary of The Main Parameters of The Atm Pons, Ethernet PonДокумент6 страницTable 11.1 Summary of The Main Parameters of The Atm Pons, Ethernet PonDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- WDM Passive NetworkДокумент6 страницWDM Passive NetworkDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Applications QoS CharacteristicsДокумент1 страницаApplications QoS CharacteristicsDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- OTN Line Structure BreakdownДокумент5 страницOTN Line Structure BreakdownDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Secure Optical Transport: Not All Solutions Are EqualДокумент4 страницыSecure Optical Transport: Not All Solutions Are EqualDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- The One and Only Email Security Solution Just Doesn't Exist. However, We Found The Best Solution For Us and That Is Why We Are 100% Satisfied.Документ1 страницаThe One and Only Email Security Solution Just Doesn't Exist. However, We Found The Best Solution For Us and That Is Why We Are 100% Satisfied.Do Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- The One and Only Email Security Solution Just Doesn't Exist. However, We Found The Best Solution For Us and That Is Why We Are 100% Satisfied.Документ1 страницаThe One and Only Email Security Solution Just Doesn't Exist. However, We Found The Best Solution For Us and That Is Why We Are 100% Satisfied.Do Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- Coriant WP The Case For Open Line SystemsДокумент15 страницCoriant WP The Case For Open Line SystemsAndrea ValleОценок пока нет
- Weighing Exclusive Vs Non Exclusive PartnerДокумент4 страницыWeighing Exclusive Vs Non Exclusive PartnerDo Xuan HuuОценок пока нет
- 5G Nework Architecture A High Level View HuaweiДокумент21 страница5G Nework Architecture A High Level View HuaweiRudyno100% (2)
- OTN TutorialДокумент62 страницыOTN TutorialIvan CuadrosОценок пока нет
- Collins Ks3 Science Homework Book 3Документ5 страницCollins Ks3 Science Homework Book 3g3pz0n5h100% (1)
- Zillah P. Curato: ObjectiveДокумент1 страницаZillah P. Curato: ObjectiveZillah CuratoОценок пока нет
- ENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014Документ12 страницENSC1001 Unit Outline 2014TheColonel999Оценок пока нет
- VERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperДокумент2 страницыVERGARA - RPH Reflection PaperNezer Byl P. VergaraОценок пока нет
- Review Course 2 (Review On Professional Education Courses)Документ8 страницReview Course 2 (Review On Professional Education Courses)Regie MarcosОценок пока нет
- Swiss Army Triplet 1Документ2 страницыSwiss Army Triplet 1johnpwayОценок пока нет
- Citrus Information Kit-Update: Reprint - Information Current in 1998Документ53 страницыCitrus Information Kit-Update: Reprint - Information Current in 1998hamsa sewakОценок пока нет
- Panera Bread Case StudyДокумент28 страницPanera Bread Case Studyapi-459978037Оценок пока нет
- The Limits of The Sectarian Narrative in YemenДокумент19 страницThe Limits of The Sectarian Narrative in Yemenهادي قبيسيОценок пока нет
- AIP 2020 FINAL JuneДокумент5 страницAIP 2020 FINAL JuneVINA ARIETAОценок пока нет
- Simple Enzymes Kinetics and Kinetics ModelДокумент14 страницSimple Enzymes Kinetics and Kinetics ModelSidra-tul MuntahaОценок пока нет
- P6 - TT2 - Revision Test 2021-2022 Page 1 of 11Документ11 страницP6 - TT2 - Revision Test 2021-2022 Page 1 of 11Nilkanth DesaiОценок пока нет
- ANTINEOPLASTICSДокумент21 страницаANTINEOPLASTICSGunjan KalyaniОценок пока нет
- The Handmaid's TaleДокумент40 страницThe Handmaid's Taleleher shahОценок пока нет
- Solid Waste Management in The World's Cities, UN-HABITAT: January 2010Документ17 страницSolid Waste Management in The World's Cities, UN-HABITAT: January 2010Rajasri SОценок пока нет
- Writing About Graphs, Tables and DiagramsДокумент68 страницWriting About Graphs, Tables and DiagramsLangers BastasaОценок пока нет
- Cornish BoilerДокумент3 страницыCornish BoilerDeepak KV ReddyОценок пока нет
- (Ebook - Antroposofia - EnG) - Rudolf Steiner - Fundamentals of TheraphyДокумент58 страниц(Ebook - Antroposofia - EnG) - Rudolf Steiner - Fundamentals of Theraphyblueyes247Оценок пока нет
- Arc Hydro - Identifying and Managing SinksДокумент35 страницArc Hydro - Identifying and Managing SinkskbalОценок пока нет
- Ass AsДокумент23 страницыAss AsMukesh BishtОценок пока нет
- NamalДокумент5 страницNamalAyusnab KarkiОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 Extension - Game Theory-StДокумент25 страницChapter 3 Extension - Game Theory-StQuynh Chau TranОценок пока нет
- Lahore Waste Management CompanyДокумент45 страницLahore Waste Management CompanyHadia NasirОценок пока нет
- C103 - General Checklist - ISO-IEC 17025:2017 Accreditation of Field Testing and Field Calibration LaboratoriesДокумент19 страницC103 - General Checklist - ISO-IEC 17025:2017 Accreditation of Field Testing and Field Calibration LaboratorieshuidhyiuodghОценок пока нет
- Prometric Questions-1 AnswersДокумент45 страницPrometric Questions-1 AnswersNina Grace Joy Marayag-Alvarez100% (1)
- Rare Watches (Christie's) 16. 05. 2016.Документ236 страницRare Watches (Christie's) 16. 05. 2016.Simon LászlóОценок пока нет
- Installation of Submarine PE PipesДокумент84 страницыInstallation of Submarine PE Pipeswaseemiqbal133100% (2)
- Nascsa - Sponsor Solicitation List: January 06, 2021Документ35 страницNascsa - Sponsor Solicitation List: January 06, 2021Prasoon SimsonОценок пока нет
- Essay On Stem CellsДокумент4 страницыEssay On Stem CellsAdrien G. S. WaldОценок пока нет
- Final LUS EvaluationДокумент36 страницFinal LUS EvaluationNextgenОценок пока нет