Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Carbon Compunds and The Macromolecules of Life
Загружено:
Jordan ChizickОригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Carbon Compunds and The Macromolecules of Life
Загружено:
Jordan ChizickАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
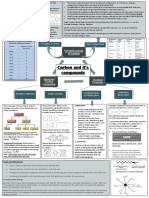
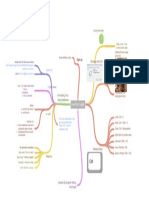
Many formed by a chemical reaction called dehydration
A large molecule formed when many smaller molecules bond Cells build biomolecules by bonding small molecules
together together to form chains called polymers Each gram of carbohydrates stores 4 calories of energy, and
Polymers form when monomers bond togther lipids store 9 calories. Lipids more compact, therefore fat
stores energy long term and carbs to store energy short term.
Carbon atoms bond with each other can form straight
chains, branched chains, and rings Made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. The monomer of carbs
are glucose molecules. Carbohydrates provide short-term energy
Carbon Chains and Rings
4 valence electrons available for bonding in its outer energy
level
To be stable carbon atoms must form four covalent bonds fill in foods.
its outer energy level
High Energy Bonds
Large organic compounds called biomolecules Made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen. The monomer of lipids
are glycerol and fatty acids. Lipids provide long term energy
storage. Unsaturated fats are fats that don't have every possible
Carbohydrate bond with hydrogen, in fact, they have a double bond instead.
Oxygen
Hydrogen
Carbon Compunds Four Basic
Six Common Elements Macromolecules Lipid
Carbon
and the
Macromolecules of
Phosphorus Life
Nitrogen Made of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, and Nitrogen. Monomer of
Protein
Sulfur
proteins are amino acids.
Nucleic Acid
A fundamental task of proteins is to act as enzymes—catalysts Role Enzymes are proteins
that increase the rate of virtually all the chemical reactions within
cells Characteristics and Role of Enzymes
Made of Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorus.
Means to add water to a molecule to break bonds The monomer of nucleic acids are nucleotides that have three
parts: a sugar, a base, and a phosphate group.
Hydrolysis
Are inhibited by inhibitors The covalent bond of a molecule breaks, a water molecule
Dehydration and Hydrolysis separates into H and OH and attaches to the exposed sites thus
separating them into smaller molecules
Are affected by pH
Means to take water out so bonds can form
Dehydration
Are required in minute amounts
Either way water is released
Speed up chemical reactions in the cell Either the hydrogen of one monomer combines with the hydroxyl
group of another monomer releasing a molecule of water, or two
Characteristics hydrogens from one monomer combine with one oxygen from the
other monomer releasing a molecule of water.
Are affected by temperature
Some catalyse reversible reactions
Build and break molecules
Вам также может понравиться
- Worksheet AnswersДокумент50 страницWorksheet Answersoliviahy.lauОценок пока нет
- Chapter 4 Carbon & It S Compounds - cb213bc1 20d4 4a89 8c1c A5f5f709c776Документ1 страницаChapter 4 Carbon & It S Compounds - cb213bc1 20d4 4a89 8c1c A5f5f709c776TOMO DACHIОценок пока нет
- 2.3 Guided Notes With AnswersДокумент3 страницы2.3 Guided Notes With Answersparam sivam100% (1)
- Bmed 105 (Lec) Lecture 2a and 2b (Notes)Документ5 страницBmed 105 (Lec) Lecture 2a and 2b (Notes)Jobelle MalihanОценок пока нет
- Glucose: C H O: Chapter 2.2: Properties of WaterДокумент1 страницаGlucose: C H O: Chapter 2.2: Properties of WaterZeena BayoudОценок пока нет
- 2.3 BiologyДокумент4 страницы2.3 Biologyminda.eslteacherОценок пока нет
- Carbon CompoundДокумент35 страницCarbon CompoundErica NatividadОценок пока нет
- 06 Handout 2Документ5 страниц06 Handout 2Ma FheОценок пока нет
- Campbell Biology Chapter 4: Terms in This SetДокумент2 страницыCampbell Biology Chapter 4: Terms in This SetAngelene PelayoОценок пока нет
- AQA GCSE Chemistry Combined U7 Organic Chemistry Knowledge OrganiserДокумент2 страницыAQA GCSE Chemistry Combined U7 Organic Chemistry Knowledge OrganiserDEVANDRAN A/L MOHAN MoeОценок пока нет
- Activity 2 Carbohydrates Preiy Julian M de GuiaДокумент3 страницыActivity 2 Carbohydrates Preiy Julian M de GuiaPreiy Julian De GuiaОценок пока нет
- 【ddl0808】试译稿 Biochemistry《生物化学》Документ4 страницы【ddl0808】试译稿 Biochemistry《生物化学》kyleОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes CHPTR 4Документ3 страницыBiology Notes CHPTR 4Wan HasliraОценок пока нет
- Chapter 2 - The Chemical Basis of LifeДокумент3 страницыChapter 2 - The Chemical Basis of Lifellena llenaОценок пока нет
- Biochem Lec Trans - Module 1 Unit 1Документ8 страницBiochem Lec Trans - Module 1 Unit 156bmkkn2rnОценок пока нет
- 10th Science Carbon and Its CompoundДокумент9 страниц10th Science Carbon and Its Compoundmathan baОценок пока нет
- Characteristics of Carbon: PhosphateДокумент7 страницCharacteristics of Carbon: Phosphate둡챙브로Оценок пока нет
- General Chemistry 1 - REVIEWERДокумент5 страницGeneral Chemistry 1 - REVIEWEREunice GarciaОценок пока нет
- Pathway 10 U2 SummaryДокумент6 страницPathway 10 U2 Summarymatiasalcivar1710Оценок пока нет
- Pre-Assessment: Determine What Is Asked. Encircle The Correct Letter of The Best AnswerДокумент20 страницPre-Assessment: Determine What Is Asked. Encircle The Correct Letter of The Best AnswerRNee AlfnsoОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates and LipidsДокумент56 страницCarbohydrates and Lipidsbrenda.mboghoОценок пока нет
- CLASS 10 - ChemistryДокумент38 страницCLASS 10 - ChemistryKavyansh GuptaОценок пока нет
- Macromolecules ReviewДокумент2 страницыMacromolecules Reviewparislash101Оценок пока нет
- Fat - Saturated FAT: Solid Form. Animals. Unhealthy For Humn HealthДокумент2 страницыFat - Saturated FAT: Solid Form. Animals. Unhealthy For Humn HealthAnthea SmeraldoОценок пока нет
- Organic ChemistryДокумент6 страницOrganic ChemistryAnn Gabrielle M. PetilosОценок пока нет
- Worksheet IGCSE Match Key Words and Definition For Revision 4Документ2 страницыWorksheet IGCSE Match Key Words and Definition For Revision 4oscarbec0% (1)
- What Is Organic Compound?Документ3 страницыWhat Is Organic Compound?Mark Joseph LatadeОценок пока нет
- Educ 202 Week 1 (Carbon-Molecules of Life)Документ52 страницыEduc 202 Week 1 (Carbon-Molecules of Life)Genel YutucОценок пока нет
- L5 Organic+Molecules+of+Living+OrganismsДокумент44 страницыL5 Organic+Molecules+of+Living+Organismsbmnyandu2003Оценок пока нет
- CH 3 Lecture NotesДокумент62 страницыCH 3 Lecture NotesSarah LewisОценок пока нет
- Final Term ReviewerДокумент27 страницFinal Term ReviewerBenna Cyril OrbinoОценок пока нет
- Carbohydrates P1 TransesBiochemistryДокумент10 страницCarbohydrates P1 TransesBiochemistryLuxi LuxiОценок пока нет
- GEN CHEM REVIEWER EulerДокумент20 страницGEN CHEM REVIEWER EulerJem PagadОценок пока нет
- Carbon CompoundsДокумент11 страницCarbon CompoundsDannia RoblesОценок пока нет
- Biochemistry Reviewer Prelims 2nd SemДокумент6 страницBiochemistry Reviewer Prelims 2nd Semorangeshibuya99Оценок пока нет
- 2.3 Carbohydrates LipidsДокумент25 страниц2.3 Carbohydrates LipidsbelenОценок пока нет
- C7 Part 1 Organic Chemistry.218563238Документ2 страницыC7 Part 1 Organic Chemistry.218563238Trudy- Ann CaineОценок пока нет
- Adv Chem Reviewer 1st QTRДокумент6 страницAdv Chem Reviewer 1st QTRValery Ken CañegaОценок пока нет
- 1 Organic ChemistryДокумент15 страниц1 Organic ChemistryKeizel Anne MananguОценок пока нет
- Part 2 AlkenesДокумент30 страницPart 2 AlkenesGerald AquinoОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 Carboxylic AcidsДокумент5 страницLesson 1 Carboxylic AcidsMARY JANE ANGELICA SEVAОценок пока нет
- II. CarbohydratesДокумент36 страницII. CarbohydratesAngel Hope Maceda0% (1)
- IB Diploma BiologyДокумент59 страницIB Diploma BiologyPatricia SoesantoОценок пока нет
- Molecules To Metabolism (2.1) : IB Diploma BiologyДокумент30 страницMolecules To Metabolism (2.1) : IB Diploma BiologyKumutha ChelliahОценок пока нет
- Nomenclature of Organic Compounds NotesДокумент42 страницыNomenclature of Organic Compounds NotesMahalaksshmi .DОценок пока нет
- Lesson 4 "Carbohydrates"Документ4 страницыLesson 4 "Carbohydrates"Therese TimbalОценок пока нет
- CA Lesson 04 The Building Blocks of LifeДокумент20 страницCA Lesson 04 The Building Blocks of LifeI Dont think you should knowОценок пока нет
- 2.1 Lipid Chemistry Part 1Документ6 страниц2.1 Lipid Chemistry Part 1Alexandra DalisayОценок пока нет
- Model Answers: Chapter 4 Chemical Composition in A CellДокумент3 страницыModel Answers: Chapter 4 Chemical Composition in A CellireneОценок пока нет
- Organic ChemДокумент15 страницOrganic ChemasjfkdОценок пока нет
- BIO122 Chapter 4Документ174 страницыBIO122 Chapter 4Miss KillerОценок пока нет
- UNIT I Gen Bio ReviewerДокумент4 страницыUNIT I Gen Bio ReviewerKym DacudaoОценок пока нет
- Biology Notes SLДокумент69 страницBiology Notes SLIker GОценок пока нет
- OutlineДокумент2 страницыOutlineRaymond ChivelОценок пока нет
- The Chemistry of MicrobiologyДокумент46 страницThe Chemistry of MicrobiologygsnptiОценок пока нет
- Q2.week 5-Activity 8-10 Classes and Uses of Organic Compounds-Zyriel Jane LibutanДокумент11 страницQ2.week 5-Activity 8-10 Classes and Uses of Organic Compounds-Zyriel Jane LibutanZyriel Jane LibutanОценок пока нет
- Topic 2 and 3 NotesДокумент15 страницTopic 2 and 3 NotesvDraqОценок пока нет
- Lipids NotesДокумент17 страницLipids Notescsdeguzman7241pamОценок пока нет
- Biologia A LevelДокумент18 страницBiologia A LevelAna ReisОценок пока нет
- Longmeadow Studio Brand Strategy WorkbookДокумент12 страницLongmeadow Studio Brand Strategy WorkbookJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Brand Discovery WorkbookДокумент8 страницBrand Discovery WorkbookJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- 62e7f1ed72b473060964becd - SC Brand Strategy Workbook 2022Документ24 страницы62e7f1ed72b473060964becd - SC Brand Strategy Workbook 2022Jordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Ignores Time Value of Money: Biased Towards LiquidityДокумент1 страницаIgnores Time Value of Money: Biased Towards LiquidityJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- WavesДокумент1 страницаWavesJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Branding Workbook Extended VersionДокумент25 страницBranding Workbook Extended VersionJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Branding WorksheetДокумент5 страницBranding WorksheetJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Light Colour in The AtmosphereДокумент1 страницаLight Colour in The AtmosphereJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Web Awareness and Digital CitizenshipДокумент1 страницаWeb Awareness and Digital CitizenshipJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Regression - Classification:: When Is CategoricalДокумент1 страницаRegression - Classification:: When Is CategoricalJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Using The Help: Learning CoggleДокумент1 страницаUsing The Help: Learning CoggleJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Specific Pricing Strategy: Marketing Mix - 4PsДокумент1 страницаSpecific Pricing Strategy: Marketing Mix - 4PsJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Passe Subjunctif: Infinitif PresentДокумент1 страницаPasse Subjunctif: Infinitif PresentJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- ManagementДокумент1 страницаManagementJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- "Why Some Firms Outperform Others" Resource Possession & Exploitation Resources & CapabilitiesДокумент1 страница"Why Some Firms Outperform Others" Resource Possession & Exploitation Resources & CapabilitiesJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- A Startup Is "A Temporary Organisation Designed To Search For A Repeatable and Scalable Business Model."Документ1 страницаA Startup Is "A Temporary Organisation Designed To Search For A Repeatable and Scalable Business Model."Jordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- ChangeДокумент1 страницаChangeJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- King TutДокумент1 страницаKing TutJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- What Is The Process of Taste Sensation and PerceptionДокумент1 страницаWhat Is The Process of Taste Sensation and PerceptionJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- 4 Major Contingency Leadership TheoriesДокумент1 страница4 Major Contingency Leadership TheoriesJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- The Skills Base™ Competency Framework v1.0 Page 1 of 14Документ14 страницThe Skills Base™ Competency Framework v1.0 Page 1 of 14Jordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- What Are The Most Important Educational PrinciplesДокумент1 страницаWhat Are The Most Important Educational PrinciplesJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- XQ Knowledge Module 04 - School Mission & CultureДокумент15 страницXQ Knowledge Module 04 - School Mission & CultureJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- What Is Creativity Ability To Adapt Change and Make New Connections Bruce 2011 P 9Документ1 страницаWhat Is Creativity Ability To Adapt Change and Make New Connections Bruce 2011 P 9Jordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Manage Conflicts Better: Do Not Afraid of ChallengesДокумент1 страницаManage Conflicts Better: Do Not Afraid of ChallengesJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Sample: Compelling and Memorable Portfolios of Creative WorkДокумент19 страницSample: Compelling and Memorable Portfolios of Creative WorkJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Zero To OneДокумент1 страницаZero To OneJordan ChizickОценок пока нет
- Product Data Sheet Anodeflex 1500 Rev. 0 04NOV20Документ2 страницыProduct Data Sheet Anodeflex 1500 Rev. 0 04NOV20tylon85Оценок пока нет
- Glossário NstperfumeДокумент2 страницыGlossário NstperfumeMarta VarekaiОценок пока нет
- Database Excel Sheet 1Документ75 страницDatabase Excel Sheet 1Sumit Kumar100% (1)
- Lett 8b04147Документ5 страницLett 8b04147Alane Priscilla AméricoОценок пока нет
- SPEC Carbopol Ultrez 20Документ1 страницаSPEC Carbopol Ultrez 20Raida SiagianОценок пока нет
- Sodium Chlorite & Chlorine Dioxide (MMS Protocols) Quick Reference GuideДокумент92 страницыSodium Chlorite & Chlorine Dioxide (MMS Protocols) Quick Reference Guide:laura-lee: Murphy U/T/AОценок пока нет
- Keeler & Long KL65487107 Product Data SheetДокумент2 страницыKeeler & Long KL65487107 Product Data SheetRussell ShacklefordОценок пока нет
- Sodium BenzoateДокумент3 страницыSodium BenzoateFred Lee Akins100% (2)
- 3-2. Assessing Production DocumentsДокумент48 страниц3-2. Assessing Production DocumentsSandeep sharmaОценок пока нет
- Understanding Adobe: Balla SidibeДокумент30 страницUnderstanding Adobe: Balla SidibeSriraamОценок пока нет
- 1.10 Partial Pressures and KP: Mole FractionДокумент3 страницы1.10 Partial Pressures and KP: Mole Fractionbazel mukuzeОценок пока нет
- Gen. Chem. 162 All SlidesДокумент558 страницGen. Chem. 162 All SlidesBASEM ABDEL-MEGEEDОценок пока нет
- MS35758DДокумент5 страницMS35758DchemtausifОценок пока нет
- Cs Se 0006 HumastarДокумент2 страницыCs Se 0006 Humastarluisoft88Оценок пока нет
- MOLYKOTE 3400A Anti-Friction Coating LF 80-3061C-01Документ2 страницыMOLYKOTE 3400A Anti-Friction Coating LF 80-3061C-01MAHESH BELEОценок пока нет
- Polymer Additives: Product Solutions From CorbionДокумент8 страницPolymer Additives: Product Solutions From CorbionXuân Giang NguyễnОценок пока нет
- Reviewer in Pee MidtermДокумент9 страницReviewer in Pee MidtermMARIEL MUTUCОценок пока нет
- Properties and Applications of Xanthan Gum: Barbara KatzbauerДокумент4 страницыProperties and Applications of Xanthan Gum: Barbara KatzbauerAsfi AniОценок пока нет
- Amravati Municipal Corporation: For Municipal Solid Waste Treatment ProjectДокумент6 страницAmravati Municipal Corporation: For Municipal Solid Waste Treatment ProjectLevi OrtizОценок пока нет
- Primary Battery Basics Cell Chemistry and Cell DesignДокумент40 страницPrimary Battery Basics Cell Chemistry and Cell DesignAliОценок пока нет
- NRZ 7 Vinyl Ester GlassflakeДокумент2 страницыNRZ 7 Vinyl Ester GlassflakecandraОценок пока нет
- Chromium Metal: Standard Specification ForДокумент2 страницыChromium Metal: Standard Specification ForJerry Bean100% (1)
- Algaesys AsrilSattar Jl30jul22Документ17 страницAlgaesys AsrilSattar Jl30jul22asril sattarОценок пока нет
- ZenTreat D 100 (TDS)Документ1 страницаZenTreat D 100 (TDS)Abhay BhoirОценок пока нет
- Water Pollution FactsДокумент1 страницаWater Pollution FactsUDjie Udjie TheeXplorerОценок пока нет
- 212labexp06 NitrationOfToluene RДокумент3 страницы212labexp06 NitrationOfToluene REngrAneelKumarAkhaniОценок пока нет
- K465 Knauf Perlfix: Bonding Gypsum For Dry LiningДокумент2 страницыK465 Knauf Perlfix: Bonding Gypsum For Dry LiningDamir PrstenkovОценок пока нет
- Comedogenic IngredientsДокумент2 страницыComedogenic IngredientsMAS, GardinОценок пока нет
- INCI NAME-convertido EXCELДокумент786 страницINCI NAME-convertido EXCELAline Silva Gomes100% (1)