Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
Introduction To Fuels: Gaseous Fuel
Загружено:
kcp1986Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
Introduction To Fuels: Gaseous Fuel
Загружено:
kcp1986Авторское право:
Доступные форматы
Workshop on Efficient Operation & Maintenance of Boilers
INTRODUCTION TO FUELS: GASEOUS FUEL
Properties of Gaseous Fuel
Gaseous fuels in common use are liquefied petroleum gases (LPG), Natural gas,
producer gas, blast furnace gas, coke oven gas etc. The calorific value of gaseous
fuel is expressed in Kilocalories per cubic meter (kcal/m 3) of the gas at normal
temperature and pressure. Liquefied petroleum gases (LPG) are stored in liquid
state under pressure and must be reduced in pressure and vaporised before they
can be safely burnt.
Calorific Value
Since most gas combustion appliances cannot utlilize the heat content of the water
vapour, gross calorific value is of little interest. Fuel should be compared based on
the net calorific value. This is especially true for natural gas, since increased
hydrogen content results in high water formation during combustion. Most natural
gas has an average heat value of 9350 kcal/m 3.
Wobbe Index
The Wobbe Index is a function of gas quality and allows matching one gas to a
replacement gas. If the two different gases have an identical Wobbe Index, they will
produce an equal amount of heat and combustion products and will require the same
amount of combustion air. If two fuels have identical Wobbe indices, then for a given
burner pressure, the energy input will also be identical.
Wobbe Index = Gross Heating Value / (Square root of Specific Gravity)
Typical physical and chemical properties of various gaseous fuels are given in Table
1.
Table 1 Typical physical and chemical properties of various gaseous fuels
Higher
Req’d Air/Gas Flame Flame
Relative Heating
Fuel Gas ratio-m3 of air Temp. Speed
Density Value O
to m3 of Fuel C m/s
kcal/m3
Manufactured
0.5 4450 5 1982 0.66
Gas
Natural Gas 0.6 9350 10 1954 0.290
Propane 1.52 22200 25 1967 0.460
Butane 1.96 28500 32 1973 0.870
National Productivity Council, Gandhinagar
Workshop on Efficient Operation & Maintenance of Boilers
Storage, Handling And Preparation of Gaseous Fuel
LPG
The two liquefied petroleum gases, which are generally available, are Commercial
Butane and Commercial Propane. The combustion of LPG produces carbon dioxide
(CO2) and water vapour. Inadequate appliance ventilation, or poor air gas mixing (for
example due to lack of servicing) can result in the production of toxic carbon
monoxide. LPG is stored under pressure in vessels designed to withstand their
vapor pressure at the maximum expected liquid temperature. Any vessel containing
propane shall have a design pressure of 17.5 kg/cm 2. Butane must be stored in a
vessel with a design pressure of 7 kg/cm 2.
LPG vapour is denser than air: butane is about twice as heavy as air and propane
about one and a half times as heavy as air. Consequently, the vapour may flow
along the ground and into drains, sinking to the lowest level of the surroundings and
be ignited at a considerable distance from the source of leakage. In still air vapour
will disperse slowly. Escape of even small quantities of the liquefied gas can give
rise to large volumes of vapour / air mixture and thus cause considerable hazard. To
aid in the detection of atmospheric leaks, all LPG’s are required to be odorized.
Natural Gas
Methane is the main constituent of Natural gas and accounting for about 95% of the
total volume. Other components are: Ethane, Propane, Butane, Pentane, Nitrogen,
Carbon Dioxide, and traces of other gases. Very small amounts of sulphur
compounds are also present. Since methane is the largest component of natural
gas, generally properties of methane are used when comparing the properties of
natural gas to other fuels
Natural gas is a high calorific value fuel requiring no storage facilities. It mixes with
air readily and does not produce smoke or soot as it has no sulphur content. It is
lighter than air and disperses into air easily in case of leak
National Productivity Council, Gandhinagar
Вам также может понравиться
- Properties and Combustion of Common Gaseous FuelsДокумент5 страницProperties and Combustion of Common Gaseous FuelsOkky Kusumo Indradi100% (1)
- Module 4. Lesson 3 Gaseous FuelsДокумент6 страницModule 4. Lesson 3 Gaseous FuelsVJ CarbonellОценок пока нет
- Properties of LPGДокумент33 страницыProperties of LPGmukund madhav100% (2)
- AP&CДокумент35 страницAP&CChethan K. ReddyОценок пока нет
- Bab 2 - LPGДокумент175 страницBab 2 - LPGSatria KenariОценок пока нет
- No. Title Page No.: IndexДокумент43 страницыNo. Title Page No.: IndexAbbas ALhasnawyОценок пока нет
- 1.5 Liquefied Petroleum Gas CombustionДокумент4 страницы1.5 Liquefied Petroleum Gas CombustionfnujoefrizalОценок пока нет
- Understanding O&G-MDSO 801 (2nd Vol)Документ156 страницUnderstanding O&G-MDSO 801 (2nd Vol)Anonymous IwqK1Nl100% (1)
- Gaseous FuelДокумент46 страницGaseous Fuelanurag8419Оценок пока нет
- Gaseous Fuels: 朱信 Hsin Chu Professor Dept. of Environmental Engineering National Cheng Kung UniversityДокумент52 страницыGaseous Fuels: 朱信 Hsin Chu Professor Dept. of Environmental Engineering National Cheng Kung UniversityvictorОценок пока нет
- Gaseous FuelsДокумент2 страницыGaseous FuelsSree MurthyОценок пока нет
- Chapter 3 explores conventional and alternative fuelsДокумент49 страницChapter 3 explores conventional and alternative fuelsmharitmsОценок пока нет
- 13_chapter3Документ49 страниц13_chapter3Abdelkrim RACHEDIОценок пока нет
- Raw Nat GasДокумент15 страницRaw Nat GasamirlngОценок пока нет
- Hiller 2011Документ20 страницHiller 2011satya.usct.900450Оценок пока нет
- ME301A: Energy Systems - I: Instructor: Santanu de NL - 302, Northern Lab PH: 6478, Email: Office HourДокумент20 страницME301A: Energy Systems - I: Instructor: Santanu de NL - 302, Northern Lab PH: 6478, Email: Office HourMukul ChandraОценок пока нет
- Incineration - Gasification - PyrolysisДокумент65 страницIncineration - Gasification - Pyrolysistatchanok1525Оценок пока нет
- Sub Topic of Biomass: BiogasДокумент17 страницSub Topic of Biomass: BiogasAidan Leonard SeminianoОценок пока нет
- لقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠٢-٢٧ في ٧.٤٨.٢٧ صДокумент55 страницلقطة شاشة ٢٠٢٤-٠٢-٢٧ في ٧.٤٨.٢٧ صahmad243809Оценок пока нет
- PETROLEUM PROPERTIES, Lecture 2Документ10 страницPETROLEUM PROPERTIES, Lecture 2Ali MahamadОценок пока нет
- 6.1 Types of Fuels - 4 MarksДокумент17 страниц6.1 Types of Fuels - 4 Marksaditya yadavОценок пока нет
- Crude Oil and Product Properties 3rd Lecture 2023-2024Документ22 страницыCrude Oil and Product Properties 3rd Lecture 2023-2024Montazer WorkОценок пока нет
- Combustion Properties GuideДокумент41 страницаCombustion Properties GuideHarshini BaskaranОценок пока нет
- Fuels and CombustionДокумент17 страницFuels and CombustionaОценок пока нет
- Ombustion AND AFE Urnace Perations: C S F OДокумент79 страницOmbustion AND AFE Urnace Perations: C S F OTruth Seeker100% (1)
- BIOMASS GASIFICATION PROCESS OVERVIEWДокумент23 страницыBIOMASS GASIFICATION PROCESS OVERVIEWbharatОценок пока нет
- Share CE-112-MODULE-4-FUELSДокумент17 страницShare CE-112-MODULE-4-FUELSAngelo GranadaОценок пока нет
- Applied Chemistry Unit-1 Fuels: Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg (C.G.)Документ20 страницApplied Chemistry Unit-1 Fuels: Bhilai Institute of Technology, Durg (C.G.)Subscribefor MEMEОценок пока нет
- Topic: Fuels & Combustion Intended Learning Outcomes:: A Fuel To Be Burne A Source of Oxygen A Source of HeatДокумент11 страницTopic: Fuels & Combustion Intended Learning Outcomes:: A Fuel To Be Burne A Source of Oxygen A Source of HeatMurvin VillarosaОценок пока нет
- 6 184623437Документ24 страницы6 184623437Dr.Srinivasa Rao K.V.NОценок пока нет
- Fuels and CombustionДокумент24 страницыFuels and Combustionmukirir47Оценок пока нет
- The Red Book MY3Документ47 страницThe Red Book MY3Syed Arsalan AfsarОценок пока нет
- m4l26 PDFДокумент8 страницm4l26 PDFvelmuruganОценок пока нет
- Report On LPG ManufacturingДокумент20 страницReport On LPG ManufacturingsuchismitapalОценок пока нет
- CHAPTER 2 Properties of Natural Gases & Condensate SystemsДокумент68 страницCHAPTER 2 Properties of Natural Gases & Condensate Systemsfaitholiks841Оценок пока нет
- Fuel PPTДокумент60 страницFuel PPTr55088299Оценок пока нет
- LPG Induction Course NewДокумент28 страницLPG Induction Course NewMha RizОценок пока нет
- Module 4 - Gaseous FuelsДокумент56 страницModule 4 - Gaseous Fuelsermias100% (1)
- Umar 2020Документ13 страницUmar 2020Stefan QuangОценок пока нет
- Fuel Gases: Primary (Natural) Secondary (Artificial)Документ5 страницFuel Gases: Primary (Natural) Secondary (Artificial)Souvik PaulОценок пока нет
- Boiler 1Документ11 страницBoiler 1Krishna KumarОценок пока нет
- Q.1.What Are Fuels .How Are They Classified?: Engineering Chemistry-Ii Unit-Ii-Fuels Sem-IiДокумент3 страницыQ.1.What Are Fuels .How Are They Classified?: Engineering Chemistry-Ii Unit-Ii-Fuels Sem-IiSahil VishwakarmaОценок пока нет
- Methane Propane: 2.1 GeneralДокумент10 страницMethane Propane: 2.1 GeneralEryn VeliquetteОценок пока нет
- CombustionДокумент35 страницCombustionm_mukbel8752Оценок пока нет
- Episode 3: Production of Synthesis Gas by Steam Methane ReformingДокумент31 страницаEpisode 3: Production of Synthesis Gas by Steam Methane ReformingSAJJAD KHUDHUR ABBASОценок пока нет
- 03gaseous FuelДокумент44 страницы03gaseous FuelSheensky V. SalasaОценок пока нет
- BioEner 4-2 Biomassa-EnДокумент140 страницBioEner 4-2 Biomassa-EnL RockОценок пока нет
- Gas Technology LECTURE 1Документ7 страницGas Technology LECTURE 1عباس محمد سيد27 A100% (1)
- Fuels and Combustion: Understanding Liquid, Solid and Gaseous FuelsДокумент24 страницыFuels and Combustion: Understanding Liquid, Solid and Gaseous FuelsGetachew TikueОценок пока нет
- An Overview of Biomass Gassification 2008Документ6 страницAn Overview of Biomass Gassification 2008Costas AggelidisОценок пока нет
- L P GДокумент11 страницL P GAwlad HossainОценок пока нет
- Basic Fundamentals of Natural GasДокумент22 страницыBasic Fundamentals of Natural GastribhuОценок пока нет
- 1st Unit LNGДокумент12 страниц1st Unit LNGShaik ShafiОценок пока нет
- LPG RefrigeratorДокумент29 страницLPG RefrigeratorSodum MaheswarreddyОценок пока нет
- PTRT2323ch1 2Документ55 страницPTRT2323ch1 2Rosie Mo' StewartОценок пока нет
- Lecture F12Документ13 страницLecture F12Shakeel AhmadОценок пока нет
- AmmoniaДокумент49 страницAmmoniaAnonymous fhKOhG6Оценок пока нет
- Thermochemical Processing of Biomass: Conversion into Fuels, Chemicals and PowerОт EverandThermochemical Processing of Biomass: Conversion into Fuels, Chemicals and PowerОценок пока нет
- Api 62Документ2 страницыApi 62saroaeroОценок пока нет
- BEARING (Recovered)Документ40 страницBEARING (Recovered)Rushikesh DandagwhalОценок пока нет
- Angular Contact Ball BearingsДокумент3 страницыAngular Contact Ball BearingsDannyschОценок пока нет
- Bearing TypesДокумент7 страницBearing TypesMaintenance Circle100% (1)
- Application of Bearings: Buyers GuideДокумент46 страницApplication of Bearings: Buyers Guidekcp1986Оценок пока нет
- Api 52Документ3 страницыApi 52Sofiane HalimiОценок пока нет
- Api 54Документ2 страницыApi 54almandhari33100% (1)
- SKF BearingДокумент28 страницSKF Bearingvasuraj002Оценок пока нет
- Centrifugal Pump Design - Rev 2Документ11 страницCentrifugal Pump Design - Rev 2jehadyam100% (1)
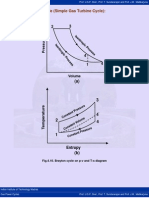
- 4.10 Brayton Cycle (Simple Gas Turbine Cycle) :: Fig.4.10. Brayton Cycle On P-V and T-S DiagramДокумент3 страницы4.10 Brayton Cycle (Simple Gas Turbine Cycle) :: Fig.4.10. Brayton Cycle On P-V and T-S DiagrammominjeelaniОценок пока нет
- Type KPD-KPDQF: Instructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar PumpДокумент49 страницType KPD-KPDQF: Instructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar Pumpkcp1986100% (1)
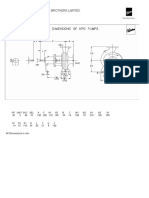
- OutlineDrawing KPD25-16QFДокумент1 страницаOutlineDrawing KPD25-16QFkcp1986Оценок пока нет
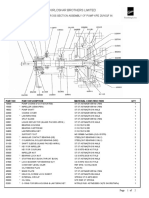
- Kirloskar Brothers Limited Cross Section Assembly of Pump KPD 25/16QFДокумент2 страницыKirloskar Brothers Limited Cross Section Assembly of Pump KPD 25/16QFkcp1986Оценок пока нет
- Type KPD-KPDQF: Instructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar PumpДокумент49 страницType KPD-KPDQF: Instructions On Installation, Operation and Maintenance For Kirloskar Pumpkcp1986100% (1)
- OutlineDrawing KPD25-16QFДокумент1 страницаOutlineDrawing KPD25-16QFkcp1986Оценок пока нет
- Kirloskar Brothers Limited Cross Section Assembly of Pump KPD 25/16QFДокумент2 страницыKirloskar Brothers Limited Cross Section Assembly of Pump KPD 25/16QFkcp1986Оценок пока нет
- 1.3 Energy Management & AuditДокумент25 страниц1.3 Energy Management & AuditEdd GithaeОценок пока нет
- Neptel - Design of Brakes-1Документ9 страницNeptel - Design of Brakes-1srideviОценок пока нет
- Pinch TechДокумент32 страницыPinch TechDaniel Puello Rodelo100% (1)
- 20 Design of Helical Springs For Variable LoadДокумент16 страниц20 Design of Helical Springs For Variable LoadPRASAD326Оценок пока нет
- 19 Introduction To Design of Helical SpringsДокумент12 страниц19 Introduction To Design of Helical SpringsPRASAD326100% (3)
- Training Reliance Industries Ltd. Jamnagar Refinery ComplexДокумент93 страницыTraining Reliance Industries Ltd. Jamnagar Refinery Complexसंजय घिल्डियालОценок пока нет
- Flywheel: Flywheels-Function Need and OperationДокумент11 страницFlywheel: Flywheels-Function Need and OperationKristian John B Rabino100% (2)
- Plate Clucht Lesson 5 NewДокумент15 страницPlate Clucht Lesson 5 Newkcp1986Оценок пока нет
- Energy considerations: II 1 2 1 2 t 1 TI I 1 2 ω − ω = +Документ5 страницEnergy considerations: II 1 2 1 2 t 1 TI I 1 2 ω − ω = +Sunny VermaОценок пока нет
- BrakesДокумент11 страницBrakesSiddartth M KumaarОценок пока нет
- Energy Consideration: Heat Generated in BrakingДокумент13 страницEnergy Consideration: Heat Generated in BrakingabcmetumОценок пока нет
- Brakes BasicsДокумент7 страницBrakes BasicsPushkin SaxenaОценок пока нет
- Shell& Tube HT DesignДокумент8 страницShell& Tube HT Designvsraochemical1979100% (1)
- MEng Presentation-M VD HovenДокумент35 страницMEng Presentation-M VD Hovenashoku2Оценок пока нет
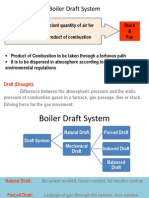
- Boiler Draft SystemДокумент56 страницBoiler Draft SystemAmit Chauhan78% (9)
- VCB Detail of PSSДокумент189 страницVCB Detail of PSSPawan Kumar RaiОценок пока нет
- High Efficiency 16 SEER Ductless Mini-Split SystemsДокумент2 страницыHigh Efficiency 16 SEER Ductless Mini-Split SystemsSergio ChupinaОценок пока нет
- Notification Order Equipment DescriptionДокумент18 страницNotification Order Equipment Descriptionઅનુરુપ સોનીОценок пока нет
- Catalogo Val MTSДокумент33 страницыCatalogo Val MTSrcuitivasОценок пока нет
- Fans Blowers and CompressorsДокумент7 страницFans Blowers and CompressorsChristina SignioОценок пока нет
- Compressor Theory: Technical TrainingДокумент55 страницCompressor Theory: Technical TrainingAlka GoyalОценок пока нет
- Industrial Training Report on Suratgarh Super Thermal Power StationДокумент39 страницIndustrial Training Report on Suratgarh Super Thermal Power StationpriyaОценок пока нет
- Series Variable Displacement Piston Pumps ...............................Документ5 страницSeries Variable Displacement Piston Pumps ...............................Daniel VuletaОценок пока нет
- LV 2000LowVolumeДокумент2 страницыLV 2000LowVolumeDian MiauОценок пока нет
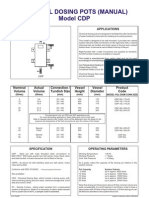
- Chemical Do Sing Pots ManualДокумент1 страницаChemical Do Sing Pots ManualPaul KwongОценок пока нет
- Piping Hydro-Static Test ComprehensionДокумент9 страницPiping Hydro-Static Test ComprehensionViệt Đặng XuânОценок пока нет
- Chapter - 6Документ10 страницChapter - 6BennyОценок пока нет
- Atmospheric Distillation GuideДокумент27 страницAtmospheric Distillation GuideAhmad Deyab100% (2)
- SAES-B-062 Editorial Revision-16 March 2023Документ22 страницыSAES-B-062 Editorial Revision-16 March 2023Faheem Khan100% (1)
- Thermodynamics 7 Steam TurbineДокумент5 страницThermodynamics 7 Steam Turbinep_nicks89Оценок пока нет
- 000000003002000049Документ2 страницы000000003002000049mhdsolehОценок пока нет
- Trouble Shooting GuideДокумент26 страницTrouble Shooting GuideArun S100% (1)
- Capacity factor explained: the ratio of actual output to potential outputДокумент5 страницCapacity factor explained: the ratio of actual output to potential outputCh Srikanth ReddyОценок пока нет
- Technical English Course For Students in Renewable EnergiesДокумент16 страницTechnical English Course For Students in Renewable Energiesdjoudi mouradОценок пока нет
- Boiler Manual Fulton IcxДокумент102 страницыBoiler Manual Fulton IcxReymundo ChanОценок пока нет
- Analysis of Power Plant Deaerator Under Transient Turbine LoadsДокумент9 страницAnalysis of Power Plant Deaerator Under Transient Turbine LoadsTanju OralОценок пока нет
- Crude CharacterizationДокумент43 страницыCrude CharacterizationHussein100% (1)
- Turn Over by Bunan MV Ariso WiperДокумент6 страницTurn Over by Bunan MV Ariso WiperJoren PalminОценок пока нет
- Lab 2 HydraulicДокумент7 страницLab 2 Hydraulicohoodalfowdaie123Оценок пока нет
- Inversor PV1800 VHM (220V) SPECSДокумент4 страницыInversor PV1800 VHM (220V) SPECSwilliam andres pena castanoОценок пока нет
- N2 Generation - Adsorption TypeДокумент2 страницыN2 Generation - Adsorption Typeashim_ju983902Оценок пока нет
- Dynamic Programming Solution Yields Minimum CostДокумент13 страницDynamic Programming Solution Yields Minimum CostSarayu GowdaОценок пока нет
- Molten Salts and Applications I: Molten Salt History, Types, Thermodynamic and Physical Properties, and CostДокумент10 страницMolten Salts and Applications I: Molten Salt History, Types, Thermodynamic and Physical Properties, and CostGoran OsmakОценок пока нет
- Aaru - SCADA Operator Console PDFДокумент3 страницыAaru - SCADA Operator Console PDFArumugam RajendranОценок пока нет