Академический Документы
Профессиональный Документы
Культура Документы
#3.1 - How Rocks Differ From Minerals
Загружено:
Knshn BrllntsИсходное описание:
Оригинальное название
Авторское право
Доступные форматы
Поделиться этим документом
Поделиться или встроить документ
Этот документ был вам полезен?
Это неприемлемый материал?
Пожаловаться на этот документАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
#3.1 - How Rocks Differ From Minerals
Загружено:
Knshn BrllntsАвторское право:
Доступные форматы
🌎
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from
Minerals
Rocks and Minerals
Rocks - are naturally occurring aggregates of minerals, rock fragments, or
organic matter that have been cohesively brought together by a rock-forming
process.
Minerals - naturally occurring, inorganic, solid with a definite chemical
composition and an ordered internal structure. Every mineral is unique, but they
exhibit general characteristics.
We have 118 elements
Atom = element
Compound = minerals
No elements, no minerals. No minerals, no rocks.
Which of the following is a mineral? Why and why not?
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 1
Steel - not a mineral because it is artificial and already processed.
Charcoal - not a mineral because charcoal can be man-made. Also, it is
organic. It comes from living organisms (from the remains of plants).
Iodized salt - not a mineral because it went through a process (combination
of iodine and salt). However, table salt is a mineral.
Petroleum - not a mineral because it is liquid, and a type of fossil fuel (from
the remains of aquatic organisms, which is organic).
Pyrite/Fool' gold - a mineral because it is solid.
Pearl - not a mineral because it is naturally occurring, solid, and came from
clamps and shells.
Characteristics of Minerals
Naturally occurring - minerals should exist naturally. If its created artificially,
therefore, are not a mineral.
Gold
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 2
Iron
Jade
Inorganic - minerals are limited to substances formed through inorganic
processes, and exclude materials derived from living organisms which
involved organic processes; should not be coming and should not be a living
organism.
Not consisting of or deriving from living matter.
Inorganic compound any substance in which two or more chemical
elements (usually other than carbon) are combined, nearly always in
definite proportions.
Substances that fulfill all the requirements but do not have an ordered
internal structure are called mineraloids examples: obsidian, pearl
Solid - all liquids and gases- even those are naturally formed are not
considered minerals.
Essential minerals - needed by our bodies
Ores - needed by the society
Ordered internal structure/Orderly crystalline structure - the atoms in
mineral are organized in a regular, repetitive geometric patterns or crystal
structure (because minerals are made of 2 or more elements).
The atoms are arranged in an orderly, repetitive manner.
The orderly packing of atoms is reflected in the regularly shaped objects
called crystals.
See picture
Molecular geometry (ordered internal structure)
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 3
Well defined chemical composition - the chemical composition of minerals
should express the exact chemical formula with the elements and compounds
in specific ratios.
Rock-forming Minerals
Quartz - can be found in fiber glass.
Feldspar - porcelains; makes the object appear to be white; also contained in
white glue.
Mica - resistors, capacitors. Mica has very high conductivity.
Calcite - chalk contains calcite.
Composition of Minerals
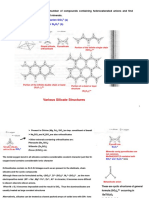
Silicates - contains silicon and oxygen.
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 4
Oxides - oxygen + other elements except silicon; metal cations bonded to
oxygen anions.
Used in magnets
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 5
Sulfides - contains sulfur + other elements; metal cation bonded to sulfide.
mirrors
Carbonates - carbon + other elements.
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 6
chalk
Native metals - consists of a single metal.
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 7
Properties of Minerals
Color
Most easily observed
Usually the least useful
Can be changed by the impurities that are found in the mineral.
Luster
The way light is reflected from a newly exposed surface.
Metallic or non-metallic
Non-metallic - vitreous (glassy), adamantine (brilliant/diamond-like),
resinous, silky, pearly, dull (earthy), greasy, etc.
Minerals with non-metallic luster are calcite, quartz and feldspar.
Types of Luster
Streak
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 8
Color of the mineral in powder form.
The test is done by rubbing the mineral across a white streak
plane/unglazed porcelain streak plate.
May differ from the color of the mineral.
Crystal Structure
Depends on the chemical composition of the mineral.
The crystal pattern of a mineral is controlled by the internal arrangement
of the atoms that make up the mineral.
Crystal Form
The shape of the mineral
Basis: will be the bond between the elements
Crystal Habit
More detailed feature
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 9
Habit
Outward appearance of the mineral's crystal form.
Hardness
This is a measurement of the strength of the chemical bonds.
Can be measures by scratching it with another mineral or a reference
material with known hardness.
Cleavage and Fracture
Cleavage
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 10
Fracture
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 11
The manner in which a mineral breaks is dependent on its molecular
bonding and structure.
Cleavage - when a mineral breaks along a flat, smooth surface.
Fracture - when a mineral breaks along an irregular surface.
Other properties that are exhibited by a limited number of minerals
include magnetism, taste, smell, double refraction, and chemical reaction
to hydrochloric acid.
Picture examples
fluorite
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 12
quartz
Others
Texture
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 13
Density
Taste
Color
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 14
All are fluorites
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 15
Common Rock-forming Minerals
The 8 elements make up the rock-forming minerals (Oxygen, Silicon,
Aluminum, Iron, Calcium, Sodium, Potassium, and Magnesium).
Silicon and Oxygen are the most common element in Earth’s crust.
Silicates – common mineral group 800 silicate minerals).
Nonsilicates – less abundant (iron and aluminum to build automobiles; copper
for electrical wiring, carbonates, sulfates and halides)
#3.1 - How Rocks differ from Minerals 16
Вам также может понравиться
- Geologyx 1Документ101 страницаGeologyx 1dummy accoutОценок пока нет
- Geology InventoryДокумент85 страницGeology Inventorywalaa yasserОценок пока нет
- Reviewer: MineralsДокумент8 страницReviewer: MineralsMyla Joy EstrellaОценок пока нет
- What Are Minerals - Types, Properties & Examples - Geology inДокумент3 страницыWhat Are Minerals - Types, Properties & Examples - Geology inÁngelОценок пока нет
- 02 Minerals STD CopyДокумент30 страниц02 Minerals STD CopyZeeОценок пока нет
- ASSIGNMENT RocksssДокумент6 страницASSIGNMENT RocksssDarwin SawalОценок пока нет
- What Are Minerals? - Types, Properties & ExamplesДокумент3 страницыWhat Are Minerals? - Types, Properties & ExamplesÁngelОценок пока нет
- Properties of MineralsДокумент18 страницProperties of MineralsKaylee Geraldine BuenaobraОценок пока нет
- MINERALOGYДокумент38 страницMINERALOGYMark BalinsayoОценок пока нет
- A Worksheet On Minerals and RocksДокумент14 страницA Worksheet On Minerals and RocksRuth May-osОценок пока нет
- Lesson 2 Minerals Building Blocks of RocksДокумент6 страницLesson 2 Minerals Building Blocks of RocksJiesel MayОценок пока нет
- Introduction To MinirologyДокумент36 страницIntroduction To Minirologykeltechnology2666Оценок пока нет
- Discussion 4 (Rocks and Minerals)Документ3 страницыDiscussion 4 (Rocks and Minerals)Jerica CagadasОценок пока нет
- MinerologyДокумент38 страницMinerologyGOPALОценок пока нет
- UntitledДокумент32 страницыUntitledMa’am Diana V.Оценок пока нет
- Engineering Geology Unit - IIДокумент55 страницEngineering Geology Unit - IIsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- G11 - Earth Science 2ND Sem WK4Документ9 страницG11 - Earth Science 2ND Sem WK4jovan amihanОценок пока нет
- Engineering Geology Unit - IIДокумент73 страницыEngineering Geology Unit - IIsivabharathamurthyОценок пока нет
- Lec 1 - Mineralogy - Third CalssДокумент37 страницLec 1 - Mineralogy - Third Calssfatima earribiОценок пока нет
- Jasmin Baga SLG 2 Earth and LifeДокумент12 страницJasmin Baga SLG 2 Earth and LifeJasОценок пока нет
- GLGY 471 - Lab 2: Earth Materials 1Документ14 страницGLGY 471 - Lab 2: Earth Materials 1Ayesha AОценок пока нет
- 1 MineralsДокумент24 страницы1 MineralsKristine BaguinatОценок пока нет
- Earth Science 11 - Q1 - MOD 3 - Physical and Chemical Properties of MineralsДокумент12 страницEarth Science 11 - Q1 - MOD 3 - Physical and Chemical Properties of MineralsNiña SalvatieraОценок пока нет
- Earth Materials and Processes Part 1Документ25 страницEarth Materials and Processes Part 1Glyneth Dela TorreОценок пока нет
- Igneous and Sedimentary Handout (Документ30 страницIgneous and Sedimentary Handout (Ramy HusseinОценок пока нет
- Properties of MineralsДокумент22 страницыProperties of MineralsJohn Ray PaquibotОценок пока нет
- Prentice Hall: Earth ScienceДокумент30 страницPrentice Hall: Earth ScienceAliana CabalunaОценок пока нет
- LESSON 3 AND 4 Earth ScienceДокумент14 страницLESSON 3 AND 4 Earth SciencejojoОценок пока нет
- Minerals: Lesson 3 Earth and Life ScienceДокумент23 страницыMinerals: Lesson 3 Earth and Life ScienceRegine LiscanoОценок пока нет
- 7 Minerals and RocksДокумент6 страниц7 Minerals and RocksmarkОценок пока нет
- Lesson 5: Earth Materials and ResourcesДокумент11 страницLesson 5: Earth Materials and Resources아지3Оценок пока нет
- GeologyДокумент9 страницGeologydipeshОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 Properties of MineralsДокумент38 страницLesson 3 Properties of MineralsFumika ShionОценок пока нет
- Earth Science Lesson 3Документ17 страницEarth Science Lesson 3Frances Marinnelle EstrellanОценок пока нет
- Applied Geology: Earth Igneous Metamorphic Sedimentary Rocks Mantle Peridotite Moho's Discontinuity SeismicДокумент9 страницApplied Geology: Earth Igneous Metamorphic Sedimentary Rocks Mantle Peridotite Moho's Discontinuity SeismicAbdullah SimpsonОценок пока нет
- Lesson 1 - Minerals and RocksДокумент30 страницLesson 1 - Minerals and RocksBelle SevillenoОценок пока нет
- Earth ScienceДокумент4 страницыEarth SciencenamiswanmnnОценок пока нет
- Module 3 (Physical and Chemical Properties of Minerals)Документ3 страницыModule 3 (Physical and Chemical Properties of Minerals)AkiОценок пока нет
- Lesson 3 Minerals Its Characteristics and Properties 2Документ37 страницLesson 3 Minerals Its Characteristics and Properties 2Yreal PangilinanОценок пока нет
- Rocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesДокумент47 страницRocks and Minerals For Grade 11 Earth and Life SciencesRegz CustodioОценок пока нет
- Earth and Life Science Lecture 2 STДокумент54 страницыEarth and Life Science Lecture 2 STMieОценок пока нет
- Handouts in Minerals and RocksДокумент8 страницHandouts in Minerals and RocksAlpha Jireh DegraciaОценок пока нет
- 03 MineralsДокумент33 страницы03 MineralsGio SalupanОценок пока нет
- General Characteristics of MineralsДокумент15 страницGeneral Characteristics of Mineralsritz delos santosОценок пока нет
- MineralsДокумент20 страницMineralsLem CastilloОценок пока нет
- Mineralogy and MineralsДокумент2 страницыMineralogy and MineralsMarycorОценок пока нет
- Topic 6 - Minerals and Its PropertiesДокумент1 страницаTopic 6 - Minerals and Its Propertieslesly AnneОценок пока нет
- Lithosphere: Rocks & MineralsДокумент41 страницаLithosphere: Rocks & MineralsBenedicto IluminОценок пока нет
- Rocks and MineralsДокумент20 страницRocks and MineralsAl Sakib RahmanОценок пока нет
- VERSION 2 HANDOUT Physical and Chemical Properties of Minerals On EarthДокумент8 страницVERSION 2 HANDOUT Physical and Chemical Properties of Minerals On EarthEricson CecОценок пока нет
- Activity #3 (Dalida)Документ9 страницActivity #3 (Dalida)kathleenmaerdalidaОценок пока нет
- Finalminerologyppt 150223221945 Conversion Gate01Документ22 страницыFinalminerologyppt 150223221945 Conversion Gate01Sagar DadhichОценок пока нет
- Minerals and RocksДокумент6 страницMinerals and RocksVenice MedranoОценок пока нет
- Minerals-First IATДокумент51 страницаMinerals-First IATpandieswari mОценок пока нет
- ENV:1203 Fundamentals of Earth ScienceДокумент45 страницENV:1203 Fundamentals of Earth ScienceJawad Rahman 1921324030Оценок пока нет
- Physical and Chemical PropertiesДокумент35 страницPhysical and Chemical PropertiesBien DielОценок пока нет
- Earth's Science (Minerals)Документ6 страницEarth's Science (Minerals)Prince Edrow Dela CruzОценок пока нет
- Powerpoint 2 Earth and Life ScienceДокумент66 страницPowerpoint 2 Earth and Life ScienceEms TeopeОценок пока нет
- Lesson-4-Minerals Physical ScienceДокумент46 страницLesson-4-Minerals Physical ScienceHarvey LizardoОценок пока нет
- Little Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksОт EverandLittle Rocks & Small Minerals! | Rocks And Mineral Books for Kids | Children's Rocks & Minerals BooksРейтинг: 4 из 5 звезд4/5 (1)
- 4.33. Manufacturing Paper-33Документ6 страниц4.33. Manufacturing Paper-33Rajat YadavОценок пока нет
- The Identification of Rocks: I. Classification of Igneous Rocks Textures of Igneous RocksДокумент10 страницThe Identification of Rocks: I. Classification of Igneous Rocks Textures of Igneous RocksRafeh KhanОценок пока нет
- Geology and Mineralisation of The Rocklands CopperДокумент5 страницGeology and Mineralisation of The Rocklands Copperga6ba5Оценок пока нет
- Bio LeachingДокумент4 страницыBio LeachingSmitha KollerahithluОценок пока нет
- SML 2008 04 30 More Visible Gold at SunnysideДокумент3 страницыSML 2008 04 30 More Visible Gold at SunnysidejoebaichОценок пока нет
- Gemstone - WikipediaДокумент3 страницыGemstone - WikipediaNyx Bella DarkОценок пока нет
- Asbestos Mining in Southern Africa, 1893-2002Документ6 страницAsbestos Mining in Southern Africa, 1893-2002Cebelihle MbuyisaОценок пока нет
- MSC Course Industrial MineralДокумент5 страницMSC Course Industrial MineralRaju BMОценок пока нет
- Gem Bearing Pegmatites A Review PDFДокумент14 страницGem Bearing Pegmatites A Review PDFJotagrcОценок пока нет
- Course Gem IdentificationДокумент79 страницCourse Gem IdentificationAnonymous IcptMgwZlОценок пока нет
- Simple Silicate Anion Sio (A) Pyrisilicate or Disilicate Anion Si O (B)Документ8 страницSimple Silicate Anion Sio (A) Pyrisilicate or Disilicate Anion Si O (B)Puneet KaurОценок пока нет
- Transition From Open-Pit To Underground As A New Optimization Challenge in Mining EngineeringДокумент10 страницTransition From Open-Pit To Underground As A New Optimization Challenge in Mining EngineeringSasha ElenaОценок пока нет
- 5 Mineral Id GizmoДокумент6 страниц5 Mineral Id Gizmoapi-31480410678% (49)
- Minerals India 1 95 PDFДокумент18 страницMinerals India 1 95 PDFROHIT KUMAR YADAVОценок пока нет
- Deposit ModelingДокумент14 страницDeposit ModelingPresidita Putri MileniaОценок пока нет
- Endapan Vms Endapan Sedex Dan MVT: (Major Pb-Zn-Cu Suppliers)Документ40 страницEndapan Vms Endapan Sedex Dan MVT: (Major Pb-Zn-Cu Suppliers)ilham nasrunОценок пока нет
- 109271-43134-1-PB 4 VentilasiДокумент11 страниц109271-43134-1-PB 4 VentilasiDonelОценок пока нет
- Engpedia - Ir: Dimension StoneДокумент7 страницEngpedia - Ir: Dimension StoneHossein DoudiОценок пока нет
- Heavy Minerals and Magnetic SeparationДокумент5 страницHeavy Minerals and Magnetic SeparationMaster Geologia UsalОценок пока нет
- 2016 08 31 NI 43 101 VictoriaДокумент128 страниц2016 08 31 NI 43 101 VictoriaGianfranco FernandezОценок пока нет
- Geography Key Notes CH 07 Mineral and Energy ResourcesДокумент4 страницыGeography Key Notes CH 07 Mineral and Energy ResourcesJohn WickОценок пока нет
- Earth Scie Module 3Документ23 страницыEarth Scie Module 3Katrina Ella Joy CaraangОценок пока нет
- Provenance of Heavy-MineralsДокумент4 страницыProvenance of Heavy-MineralsMuhannad RasemОценок пока нет
- ASSIGNMENT RocksssДокумент6 страницASSIGNMENT RocksssDarwin SawalОценок пока нет
- C. Low SioДокумент14 страницC. Low SioShaina Mae Degal Saraum100% (1)
- Prioritizing Sustainable Development Criteria Affecting Open Pit Mine Design A Mathematical ModelДокумент8 страницPrioritizing Sustainable Development Criteria Affecting Open Pit Mine Design A Mathematical ModelIan ToniОценок пока нет
- Emerald GuideДокумент2 страницыEmerald Guidecelia m c corriglianoОценок пока нет
- Fluoride Content of Clay Minerals and Argillaceous Earth MaterialsДокумент7 страницFluoride Content of Clay Minerals and Argillaceous Earth MaterialsLaura TartauОценок пока нет
- Olivine GroupДокумент3 страницыOlivine GroupBalaRajKumarОценок пока нет